33.9 : Energy Carried By Electromagnetic Waves
Anyone who has used a microwave oven knows there is energy in electromagnetic waves. Sometimes, this energy is obvious, such as in the summer sun's warmth. At other times, it is subtle, such as the unfelt energy of gamma rays, which can destroy living cells. Electromagnetic waves bring energy into a system through their electric and magnetic fields. These fields can exert forces and move charges in the system and, thus, do work on them. However, there is energy in an electromagnetic wave, whether absorbed or not. Once created, the fields carry energy away from a source. If some energy is later absorbed, the field strengths are diminished, and anything left travels on. Clearly, the greater the strength of the electric and magnetic fields, the more work they can do and the greater the energy the electromagnetic wave carries. In electromagnetic waves, the amplitude is the maximum field strength of the electric and magnetic fields. The wave energy is determined by the wave amplitude. For a traveling plane wave, its energy will be the sum of the energies of the constituent electric and magnetic fields. The energy per unit volume, or the energy density of the electromagnetic wave, is the sum of the energy density from the electric field and the energy density from the magnetic field.
Using the relationship between electric fields, magnetic fields, and the speed of light, the magnetic field energy can be written in terms of electric energy density, and they are found to be equal to each other. For an electromagnetic wave traveling along thex-axis, the expression for energy density is,
This energy density moves with the electric and magnetic fields in a similar manner to the waves themselves. The rate of transport of energy flux through a surface is defined by a vector quantity 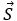 known as the Poynting vector. The expression for
known as the Poynting vector. The expression for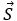 is given by
is given by
Из главы 33:

Now Playing
33.9 : Energy Carried By Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic Waves
2.9K Просмотры

33.1 : Электромагнитные волны
Electromagnetic Waves
8.5K Просмотры

33.2 : Генерация электромагнитных излучений
Electromagnetic Waves
2.6K Просмотры

33.3 : Электромагнитный спектр
Electromagnetic Waves
15.7K Просмотры

33.4 : Уравнение электромагнитной волны
Electromagnetic Waves
985 Просмотры

33.5 : Плоские электромагнитные волны I
Electromagnetic Waves
3.6K Просмотры

33.6 : Плоские электромагнитные волны II
Electromagnetic Waves
3.0K Просмотры

33.7 : Скорость распространения электромагнитных волн
Electromagnetic Waves
3.3K Просмотры

33.8 : Электромагнитные волны в веществе
Electromagnetic Waves
2.9K Просмотры

33.10 : Интенсивность электромагнитных волн
Electromagnetic Waves
4.4K Просмотры

33.11 : Импульс и давление излучения
Electromagnetic Waves
1.9K Просмотры

33.12 : Радиационное давление: решение проблемы
Electromagnetic Waves
314 Просмотры

33.13 : Стоячие электромагнитные волны
Electromagnetic Waves
1.5K Просмотры

33.14 : Стоячие волны в полости
Electromagnetic Waves
859 Просмотры
Авторские права © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Все права защищены