10.2 : Динамический модуль упругости
Динамический модуль упругости оценивает, как бетонная конструкция деформируется под воздействием ударных или динамических нагрузок. Он обычно выше статического модуля упругости, измеренного в условиях медленной и постоянной нагрузки.
Звуковой тест является распространенным методом определения динамического модуля. В этом тесте бетонная балка размером 15,24×15,24×76,20 см или 10,16×10,16×50,80 см зажимается зажимом в центре. Вибрации инициируются на одном конце балки электромагнитным возбудителем, работающим от генератора переменной частоты. Устройство приёма на другом конце обнаруживает эти вибрации, которые затем усиливаются и измеряются с помощью индикатора.
Вибрации на различных частотах передаются через образец, пока он не начнет резонировать на своей основной частоте. Динамический модуль упругости (E_d) в кг на см вычисляется математически путем подстановки основной частоты балки (n) в Герцах, длины (L) в м и плотности (⍴) в кг на кубический метр.
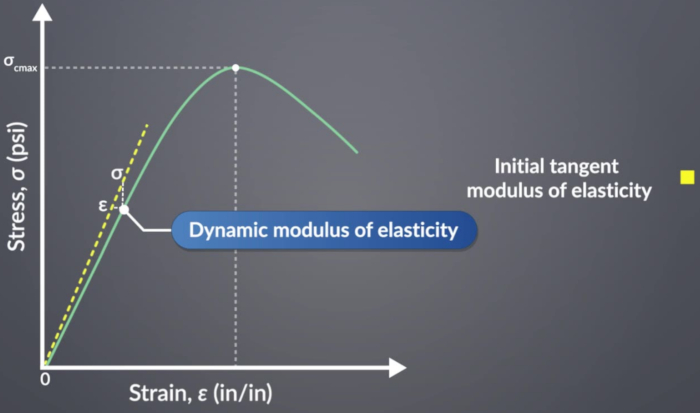
Другой метод оценки динамического модуля включает кривую напряжения-деформации бетона. Проведя касательную в начале кривой и рассчитав ее наклон, определяется начальный касательный модуль. Это значение приблизительно равно динамическому модулю упругости.
Из главы 10:

Now Playing
10.2 : Динамический модуль упругости
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
260 Просмотры

10.1 : Упругость бетона
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
82 Просмотры

10.3 : Ползучесть в бетоне
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
161 Просмотры

10.4 : Факторы, влияющие на ползучесть
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
123 Просмотры

10.5 : Эффекты слизи
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
93 Просмотры

10.6 : Усадка в бетоне
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
79 Просмотры

10.7 : Сушка Усадка
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
71 Просмотры

10.8 : Карборационная усадка
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
108 Просмотры

10.9 : Виды неструктурных трещин в бетоне
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
129 Просмотры

10.10 : Массовое бетонирование
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
59 Просмотры

10.11 : Бетонирование в жаркую погоду
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
55 Просмотры

10.12 : Бетонирование в холодную погоду
Elasticity, Creep, and Shrinkage in Concrete
57 Просмотры
Авторские права © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Все права защищены