Для просмотра этого контента требуется подписка на Jove Войдите в систему или начните бесплатную пробную версию.
Luciferase Assay to Study Efficacy of Antiparasitic Chemicals Against Parasites
Overview
The video demonstrates the luciferase assay used to determine the efficacy of an antiparasitic chemical inhibitor against the intracellular pathogen Toxoplasma gondii. The study involves luciferase-expressing parasites invading the host cells to replicate and survive. The chemical inhibitor binds with the cysteine proteases of the parasite and inhibits replication. The luciferase activity detected is proportional to the fold changes in parasite growth, determining the drug's efficacy against the parasite.
протокол
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Evaluation of chemical compound inhibition efficacy against Toxoplasma growth
NOTE: Here, evaluation of the inhibition of LHVS in Toxoplasma growth is presented as an example. Eight different concentrations of LHVS are tested, and three technical replicates are performed for each of the three biological replicates for both RHΔku80::NLuc and RHΔku80Δcpl::NLuc strains.
- Prior to the parasite infection, seed HFFs to 96-well microplates in the format of three rows and nine columns for one biological replicate per compound per strain. Host cells will be allowed to grow for at least 7 days before use.
- Pass RHΔku80::NLuc and RHΔku80Δcpl::NLuc parasites for 2 days prior to use.
- Pass Toxoplasma parasites into confluent HFFs 2 days prior to use by transferring ~0.3-0.4 mL of fully lysed parasites into a T25 flask. Incubate infected host cells at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 2 days.
- Syringe 5 mL of freshly lysed parasites through a 21 G safety needle 5x to liberate intracellular parasites, then pass through a 3 µm filter to remove host cell debris. Rinse residual parasites out of the flask using 7 mL of phenol red-free D10 medium, then pass through the filter again.
- Centrifuge parasites at 1000 x g for 10 min at room temperature (RT). Pour off the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 10 mL of phenol red-free D10 media.
- Count parasites using a hemocytometer to determine the concentration.
- Dilute parasites to 1 x 104 parasites/mL for the wild-type (WT) strain. For growth-deficient parasite strains, increase the concentration accordingly to observe a significant increase in luciferase signals.
- Resuspend parasites in phenol red-free media at 1 x 104 parasites/mL.
- Aspirate media from a plate containing confluent HFFs and inoculate each well with 150 µL of parasite resuspension. Incubate the microplate at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 4 h.
- Prepare LHVS at eight different concentrations in a 12-well reservoir by serial dilution. Generally, the concentrations are decreased by three-fold in a serial dilution manner.
NOTE: The lowest concentration is reduced by 6,561-fold relative to the highest concentration. The fold change of the dilution can be adjusted accordingly based on different properties of individual compounds. - At 4 h post-infection, aspirate media to remove non-invaded parasites and fill each well from columns 2-9 with 150 µL of media supplemented with LHVS at different concentrations. Leave the first column filled with regular medium to serve as a non-treated control.
- Incubate the microplate at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for an additional 96 h.
- Aspirate media carefully from the wells to remove non-invaded parasites, then fill the wells with RT phenol red-free media in each row (except for the first row).
- Mix equal volumes of PBS and 2x luciferase assay buffer and dilute the luciferase substrate to 12.5 µM.
- Add 100 µL of dilute luciferase substrate into each well of the top row. Incubate the microplates at RT for 10 min to allow the cells to fully lyse.
- Measure luciferase activity of individual wells.
- Average the luciferase activities of three technical replicates from wells of each individual LHVS concentration.
- Divide the average luciferase activity for each LHVS concentration by the average luciferase activity derived from nontreated parasites to calculate the normalized luciferase activity as a percentage.
- Plot the normalized luciferase activities against the individual LHVS concentrations using graphing software (Figure 1). Inhibition of pyrimethamine against parasite growth is also measured as a control. Pyrimethamine is a clinical antibiotic used to treat acute toxoplasmosis by inhibiting folic acid metabolism in Toxoplasma.
- Calculate the IC50 values for individual compounds using the embedded method in the graphing software, normalized response vs. [inhibitor], under the "dose-response-inhibition" regression program. The IC50 is calculated using the following formula:
Y = 100/(1 + X/IC50)
Where: Y represents normalized luciferase activities of infected cells under different concentrations of inhibitor, and X represents individual concentrations of inhibitor.
Результаты
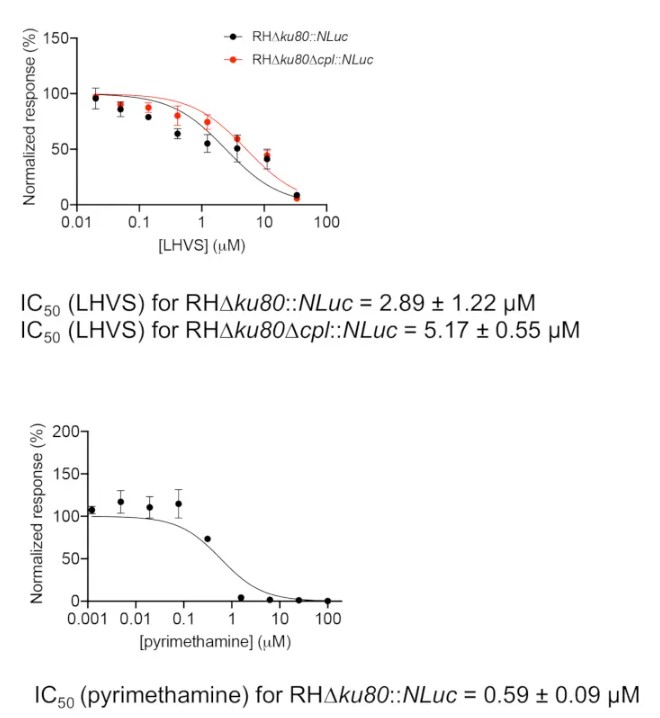
Figure 1: Inhibition efficacy assessment of LHVS and pyrimethamine using the luciferase-based growth assay. Parasites were inoculated into a 96-well microplate for 4 h to allow for invasion of host cells. Non-invaded parasites were washed away, and the plate was filled with media containing different concentrations of LHVS or pyrimethamine and incubated for an additional 96 h before determination...
Раскрытие информации
Материалы
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Biotek Synergy H1 Hybrid Multi-Mode Microplate Reader | BioTek Instuments | ||
| Coelenterazine h | Prolume | 301-10 hCTZ | |
| Software | |||
| GraphPad Prism software (8th version) |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Key, M., et al. Determination of Chemical Inhibitor Efficiency against Intracellular Toxoplasma Gondii Growth Using a Luciferase-Based Growth Assay. J. Vis. Exp. (2020).
Авторские права © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Все права защищены