n-Butyllithium Titration
Обзор
Source: Vy M. Dong and Diane Le, Department of Chemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA
This experiment will demonstrate a simple technique to titrate and obtain an accurate concentration of the organolithium reagent, n-butyllithium (n-BuLi). Organolithium reagents are extremely air- and moisture-sensitive and proper care must be taken to maintain the quality of the reagent so that it may be used successfully in a reaction. The n-BuLi titration experiments should be performed regularly to obtain accurate concentrations prior to use in a chemical reaction. Subsequently, we will demonstrate the addition of the titrated n-BuLi to benzaldehyde.
Принципы
Organolithium reagents are compounds containing a C−Li bond and are very strong bases. Because organolithiums are extremely air- and moisture-sensitive, proper care must be taken to handle these reagents. They are sensitive to acids, corrosive, and often pyrophoric. n-BuLi, an alkyllithium, is typically stored at low temperatures (less than 0 °C) and stored as a solution in hydrocarbons such as hexanes. N-BuLi can be used as a base or nucleophile depending on the reaction conditions. Furthermore, it can be used in halogen-lithium exchange reactions to generate aryl or vinyl lithium reagents, which can immediately react with an electrophile. In addition, n-BuLi is commonly used as an initiator in the polymerization of dienes used in elastomers.
Titration is a common quantitative analytical technique used to determine an unknown concentration of an analyte by adding a known concentration of a titrant until the reaction reaches completion, which is indicated by a color change. In this experiment, we will demonstrate the titration of n-BuLi and calculate its concentration with diphenylacetic acid as the titrant, which is a stable solid and can be easily weighed. Upon reaction of the n-BuLi with diphenylacetic acid, the solution turns a deep yellow color at the end point of the titration, and so an indicator is not needed (Figure 1). By measuring the precise volume of n-BuLi used to consume the diphenylacetic acid, we can calculate the molarity of the reaction. This experiment should be repeated three times to obtain an average measurement.
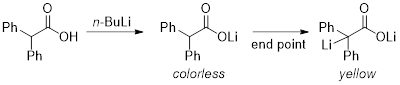
Figure 1. Reaction of n-BuLi with diphenylacetic acid.
Процедура
1. Preparation of Titrant
- To a flame-dried round bottom flask equipped with a stir bar under N2, add diphenylacetic acid (250 mg, 1.18 mmol) and anhydrous THF (5 mL).
2. Titration of n-BuLi
- Calculate the approximate amount of n-BuLi solution (in hexanes) needed to consume the diphenylacetic acid. Using a syringe, slowly adda solution of n-BuLi dropwise. The reaction mixture will turn temporarily yellow and back to a colorless solution with each drop.
- Continue adding the solution of n-BuLi dropwise until the reaction mixture continues to stay a deep yellow color. This will be the end point of the reaction.
- Repeat the titration 3x to obtain an average volume of the n-BuLi used.
3. Calculation of Molarity
- The moles of n-BuLi used in the titration are equivalent to the moles of diphenylacetic acid used in the reaction. Since the moles of diphenylacetic acid used is known, the calculation of concentration of n-BuLi is given by the following equation: mmol diphenylacetic acid/mL n-BuLi = molarity of n-BuLi solution.
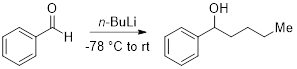
4. Addition of n-BuLi to Benzaldehyde (Figure 2)
- To a flame-dried round bottom flask equipped with a stir bar under N2, add anhydrous THF (30 mL) and benzaldehyde (3 mmol, 1 equiv.). Cool the solution to −78 °C.
- Add n-BuLi (1.1 equiv.) and let the reaction warm to room temperature.
- Add saturated NH4Cl (aq., 10 mL) to quench the reaction and extract the aqueous layer with diethyl ether (2 x 25 mL).
- Wash the combined organic layers with water (2 x 15 mL) and brine (1 x 20 mL).
- Dry with Na2SO4, filter, and concentrate the combined organic layers under reduced pressure to afford the product.
Figure 2. Addition of n -BuLi to benzaldehyde.
Результаты
Representative results for the titration of n-BuLi for Procedures 1-3
| Procedure Step | Color of reaction mixture |
| 1.1 | Colorless |
| 2.1 | Yellow, then colorless |
| 2.2 | Deep yellow |
| 3.1 | 1.18 mmol diphenylacetic acid/1 mL n-BuLi = 1.18 M n-BuLi in hexanes |
Table 1. Representative results for Procedures 1-3.
Заявка и Краткое содержание
In this experiment, we have demonstrated how to determine the concentration of an n-BuLi solution by using diphenylacetic acid. We have also performed a reaction by adding n-BuLi to benzaldehyde.
Accurate concentrations of n-BuLi are important for its successful application in a number of reactions. n-BuLi is commonly used in lithium-halogen exchange reactions to prepare aryllithium or vinyllithium reagents, which can be subsequently used in C-C bond forming reactions. Furthermore, it can be used as a base or nucleophile, depending on the reaction conditions.
Теги
Перейти к...
Видео из этой коллекции:

Now Playing
n-Butyllithium Titration
Organic Chemistry II
48.0K Просмотры

Cleaning Glassware
Organic Chemistry II
123.8K Просмотры

Nucleophilic Substitution
Organic Chemistry II
99.6K Просмотры

Reducing Agents
Organic Chemistry II
43.1K Просмотры

Grignard Reaction
Organic Chemistry II
149.1K Просмотры

Dean-Stark Trap
Organic Chemistry II
100.6K Просмотры

Ozonolysis of Alkenes
Organic Chemistry II
67.1K Просмотры

Organocatalysis
Organic Chemistry II
16.9K Просмотры

Palladium-Catalyzed Cross Coupling
Organic Chemistry II
34.6K Просмотры

Solid Phase Synthesis
Organic Chemistry II
41.1K Просмотры

Hydrogenation
Organic Chemistry II
49.6K Просмотры

Polymerization
Organic Chemistry II
94.5K Просмотры

Melting Point
Organic Chemistry II
150.0K Просмотры

Infrared Spectroscopy
Organic Chemistry II
215.4K Просмотры

Polarimeter
Organic Chemistry II
100.1K Просмотры
Авторские права © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Все права защищены