Stormwater detention basins are essential in managing runoff during heavy rainfall, particularly in urban areas where impervious surfaces increase the risk of flooding. Understanding the conservation of mass in these systems allows engineers to optimize basin performance, balancing inflow, outflow, and water storage.
In the context of a detention basin, the conservation of mass states that the total mass of water entering the basin must equal the mass leaving the basin plus any accumulation of water within it. The control volume consists of the water inside the basin, with its boundaries defined by the basin walls, inflow pipes, and outflow structures. During a rainfall event, inflow occurs through the pipes, and outflow through the designed outlets. The mass balance equation is expressed as:
Where
ṁin is the mass inflow rate,
ṁoutis the mass outflow rate and
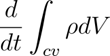 represents the change in mass inside the control volume.
represents the change in mass inside the control volume.
During heavy rainfall, the inflow rate often exceeds the outflow rate, causing water to accumulate in the basin. Engineers must design the outflow structures to control the release of water at a manageable rate, ensuring that downstream systems are not overwhelmed. As the storm subsides and the inflow decreases, the accumulated water is gradually released. The outflow rate is typically designed to increase as the water level rises, following predetermined discharge curves to maintain control over the release.
The detention basin's ability to temporarily store water is critical to flood prevention. Properly designed detention basins ensure that water is released in a controlled manner during even the most intense storm events, preventing overflow or structural failure.
From Chapter 18:

Now Playing
18.3 : Conservation of Mass in Moving, Nondeforming Control Volume
Finite Control Volume Analysis
598 Views

18.1 : Conservation of Mass in Finite Cotrol Volume
Finite Control Volume Analysis
751 Views

18.2 : Conservation of Mass in Fixed, Nondeforming Control Volume
Finite Control Volume Analysis
667 Views

18.4 : Linear Momentum in Control Volume
Finite Control Volume Analysis
577 Views

18.5 : Application of the Linear Momentum Equation
Finite Control Volume Analysis
27 Views

18.6 : Moment-of-Momentum Equation
Finite Control Volume Analysis
38 Views

18.7 : Conservation of Energy in Control Volume
Finite Control Volume Analysis
287 Views

18.8 : Application of the Energy Equation
Finite Control Volume Analysis
281 Views

18.9 : Design Example: Forces in Sluice Gate
Finite Control Volume Analysis
134 Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved