A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Murine Echocardiography and Ultrasound Imaging
In This Article
Summary
This video demonstrates use of a rail-mounted high-frequency ultrasound probe to perform echocardiography on an anesthetized mouse. The methods describe both conventional two-dimensional and M-mode measurements of cardiac function in addition to newer, more powerful tools such as color Doppler, strain analysis, as well as general and targeted contrast imaging.
Abstract
Rodent models of cardiac pathophysiology represent a valuable research tool to investigate mechanism of disease as well as test new therapeutics.1 Echocardiography provides a powerful, non-invasive tool to serially assess cardiac morphometry and function in a living animal.2 However, using this technique on mice poses unique challenges owing to the small size and rapid heart rate of these animals.3 Until recently, few ultrasound systems were capable of performing quality echocardiography on mice, and those generally lacked the image resolution and frame rate necessary to obtain truly quantitative measurements. Newly released systems such as the VisualSonics Vevo2100 provide new tools for researchers to carefully and non-invasively investigate cardiac function in mice. This system generates high resolution images and provides analysis capabilities similar to those used with human patients. Although color Doppler has been available for over 30 years in humans, this valuable technology has only recently been possible in rodent ultrasound.4,5 Color Doppler has broad applications for echocardiography, including the ability to quickly assess flow directionality in vessels and through valves, and to rapidly identify valve regurgitation. Strain analysis is a critical advance that is utilized to quantitatively measure regional myocardial function.6 This technique has the potential to detect changes in pathology, or resolution of pathology, earlier than conventional techniques. Coupled with the addition of three-dimensional image reconstruction, volumetric assessment of whole-organs is possible, including visualization and assessment of cardiac and vascular structures. Murine-compatible contrast imaging can also allow for volumetric measurements and tissue perfusion assessment.
Protocol
1. Preparation for imaging
- Begin by securing an isoflurane anesthetized mouse to an animal-handling platform in the supine position. Place a nose cone over the animal's nose and mouth to deliver 0.5-1% isoflurane to maintain the anesthesia.
- Secure the paws of the mouse to the electrode pads with conducting gel. Ensure appropriate ECG, body temperature at 37 °C and check respiratory rate for physiological assessment during imaging.
- Apply depilatory cream to the chest and upper abdomen of the mouse.
- After 2 minutes, use wet gauze remove to the cream.
2. Left parasternal long axis view
- Once the mouse has been prepared for imaging, tilt the left side of the platform to rotate the animal handling platform 30 degrees about the anterioposterior axis.
- Orient the transducer in the vertical position and rotate 10 degrees counterclockwise with the notch pointed toward the posterior of the mouse.
- Next, while in the two-dimensional viewing/video "B-mode", lower the transducer over the left parasternal line until the heart comes into view. Once the pulmonary artery comes into view, collect images and store them.
- Still in B-mode, move the transducer left or right until the aortic outflow and apex come into view. Some rotation of the probe may be necessary to ensure proper alignment with the long axis of the heart.
- Use video capture to obtain data for subsequent analysis. Minimize the field of view to ensure the highest frame rate possible for downstream regional strain analyses. Each time a video is captured, the prior 100 frames are saved.
- Switch to the Color Doppler mode by selecting "Color Doppler." Although Color Doppler has been available for over 30 years in humans, this technology has only recently been possible in rodent ultrasound.
- To quickly monitor the direction and velocity of blood flow, the Doppler window overlay digitizes the flow from red, indicating flow toward the probe, to blue, indicating flow away from the probe. Acquire necessary images by image capture.
- Once all Color Doppler data has been obtained, switch the instrument to Pulse-Wave Doppler Mode, the one-dimensional view used to digitally assess blood flow direction and velocity over time.
- Move the probe slightly toward the head of the mouse until the pulmonary artery comes into view. In the context of heart failure, PW/Color Doppler measurements of the pulmonary artery can be used as a surrogate for right heart function. Capture images as desired.
3. Left mid-papillary short axis
- Short-axis echocardiography provides a view of the entire left ventricle contracting in a concentric fashion, and allows for accurate B- and M-mode based assessment of cardiac function and morphometry.
- In B-mode, from the parasternal long axis view, rotate the transducer orthogonal to the left parasternal long axis view at the level of the papillary muscle.
- Ensure proper location along the length of the left ventricle. Both papillary muscles should be clearly visible and separated, giving a horizontal cross-sectional view.
- With the M-mode, place the sample volume through the center of the ventricle and acquire data.
- If desired, attach, initiate and utilize the 3-dimensional motor to obtain the images necessary for complete 3-dimensional reconstruction.
- Physiology settings, including respiratory rate and ECG, are set for gating 3D image capture in end-diastole
- The 3D imaging motor is initiated for image capture in end-diastole.
- Once the end-diastole 3D capture is complete, physiology settings for respiratory rate and ECG are set for gating the 3D image capture in end-systole
- The 3D imaging motor is initiated for image capture in end-systole.
4. Subcostal (four chamber) view
- The subcostal view is the best approach for measuring competency and pressure gradients across the mitral valve.
- Tilt the upper left corner of the platform all the way down. Orient the transducer toward the right shoulder of the mouse, maintaining the short axis rotation of the probe.
- In B-mode, lower the transducer over the upper abdomen so that it rests below the diaphragm. Visualize the mitral valve using color Doppler as described before.
5. Aortic view
- Rotate the animal-handling platform into the left lateral decubitus position. The left side of the platform should be tilted as far as possible. Next, orient the transducer, tilted as far up as possible, along the length of the mouse at the level of the scapula.
- Lower the transducer inferior to the right shoulder along the anterior axillary line. Visualize the aortic arch, and acquire images.
- Raise the head of the mouse, and lower the transducer into the suprasternal notch of the mouse. Visualize blood flow using color Doppler, and acquire images.
6. Representative Results
- This is a long-axis view of the heart in B-mode showing both the left ventricle and a small portion of the right ventricle.
- Here, a left short axis view of another heart was taken in M-mode. The upper image shows the position of the sample volume line in yellow through the center of the chamber. The bottom image is a one dimensional trace of the above line over time as well as calculations of morphometry in cyan
- This is a view of the aortic arch in B-mode. The closed aortic valve can be seen on the left and the blood vessels supplying the head and upper limbs of the mouse can be seen on the right.
- Radial Strain analysis was performed on a mouse prior to developing heart dysfunction, shown in the top image, and a mouse with global hypokinesis and regional dyssynchrony, shown in the bottom image. Both phenotypes were induced through transverse aortic constriction, a mouse model of increased afterload.
- In the figure, the time is displayed on the x-axis and the radial strain, as a percentage, is shown on the y-axis. Strain analysis allows for regional assessment of cardiac function that may otherwise go unnoticed in conventional techniques such as M-mode, which only directly measures function of the anterior free wall and the posterior wall.
- The anterior free wall is shown in green. The pink line shows the lateral wall is shown in pink. The posterior wall is shown in cyan. The inferior free wall is shown in blue. The posterior septal wall is shown in yellow. The anterior septum is shown in magenta, and the average is shown in black.

Figure 1. Left parasternal long axis view in B-mode.
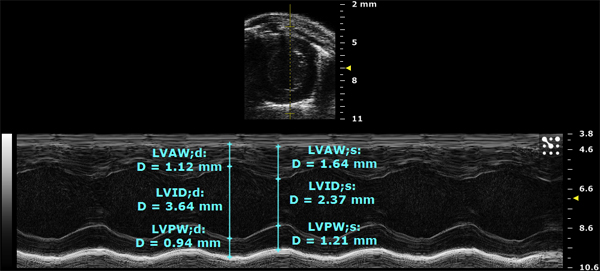
Figure 2. Left short axis view in M-mode.

Figure 3. View of the aortic arch in B-mode.
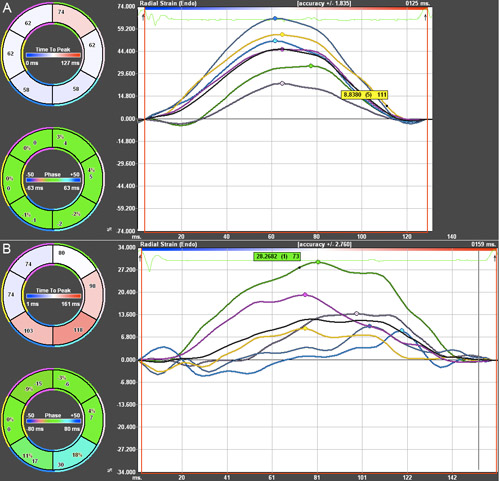
Figure 4. Radial Strain Analysis of two mice 12 weeks post-TAC. Green = ant. free wall. Pink = lateral wall. Cyan = posterior wall. Blue = inf. free wall. Yellow = post. septal wall. Magenta = anterior septum. Black = average A) Mouse with preserved function. B) Mouse with global hypokinesis and regional dyssynchrony.
Discussion
Serial high frequency echocardiography has emerged as a powerful tool for non-invasive, high-resolution assessment of cardiac morphology and function, particularly in murine models of heart disease. Maintaining physiological body temperature as well as comparable heart rates between mice by adjusting the anesthesia level prior to acquiring images, is critical to the success of this method. All images should be obtained using the same biomarkers (e.g. parasternal long axis imaging at the papillary muscles). Lastly, ana...
Disclosures
Pistner, Belmonte, Blaxall: Nothing to disclose Coulthard is a full-time employee of Visualsonics.
Acknowledgements
Funding sources: HL084087, HL089885, HL091475, S10RR027946, T32 GM07356
Materials
| Material Name | Type | Company | Catalogue Number | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |
| Vevo 2100 Imaging System (120V) | Visual Sonics | VS-11945 | ||
| Vevo 2100 Imaging Station 1 | Visual Sonics | SA-11982 | ||
| Ultrasound Gel | Parker Laboratories | 01-08 | ||
| Isoflurane | Abbott Laboratories | 05260-05 | ||
| Vevo Compact Dual Anesthesia System | Visual Sonics | SA-12055 |
References
- Patten, R. D., Hall-Porter, M. R. Small animal models of heart failure: development of novel therapies, past and present. Circ Heart Fail. 2, 138-144 (2009).
- Li, Y. Quantification and MRI Validation of Regional Contractile Dysfunction in Mice Post Myocardial Infarction Using High Resolution Ultrasound. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. 33, 894-904 (2007).
- Gardin, J. M., Siri, F. M., Kitsis, R. N., Edwards, J. G., Leinwand, L. A. Echocardiographic Assessment of Left Ventricular Mass and Systolic Function in Mice. Circ Res. 76, 907-914 (1995).
- JG, S. t. e. v. e. n. s. o. n., Weiler, T. B. M., EA, H. o. w. a. r. d., Eyer, M. Digital multigate Doppler with color echo and Doppler display - Diagnosis of atrial and ventricular septal defects. Circulation. 60, (1979).
- Patten, R. D., Aronovitz, M. J., Bridgman, P., Pandian, N. G. Use of pulse wave and color flow Doppler echocardiography in mouse models of human disease. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 15, 708-714 (2002).
- Hoit, B. D. Echocardiographic characterization of the cardiovascular phenotype in rodent models. Toxicol Pathol. 34, 105-110 (2006).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved