A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Periodic Acid-Schiff Staining of Cells: An In Vitro Technique to Detect Glycogen Levels in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
In This Article
Overview
This video demonstrates the periodic acid-Schiff staining technique for assessing glycogen levels of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. The stain imparts a magenta color to intracellular glycogen granules, rendering them visible under a microscope.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. PBMC Isolation from Whole Blood
NOTE: Carry out this procedure in a biosafety cabinet using sterile technique and manufacturer-sterilized equipment.
- Carefully pour 10-15 ml of whole blood from the heparinized (anti-coagulant) blood collection tubes into a 50 ml sterile conical tube. For minor blood spills, wipe with ddH2O and 70% EtOH using cleaning tissue.
- Dilute the blood in the conical tube to a 1:1 ratio with Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS 1x) pH 7.4. Ensure that the maximum total volume does not exceed 30 ml.
- Mix gently using a serological pipette gun avoiding bubbles.
NOTE: Do NOT mix by inverting the tube to avoid blood accumulation in the cap and subsequent seepage during centrifugation. - Add 13 ml of Ficoll-paque (see Materials table), to a new 50 ml capacity conical tube. Keep the tube upright in the rack.
- Using a transfer pipette, take diluted blood, touch the transfer pipette tip to the inside wall of the tube near the top. With slow and steady pressure, transfer the blood along the inside wall of the tube forming a blood layer on top of the sucrose layer. Do this step several times until all blood has been transferred.
- Cap the tube tightly and centrifuge the tube at room temperature for 30 min at 700 x g in a swing rotor with medium acceleration set to 5, and deceleration set to ZERO.
- Slowly take out the tube and without disturbing the layers, take it back to the biosafety cabinet.
- Carefully collect the buffy coat (thin cloudy white layer), where PBMCs are located, placed between the PBS/plasma and ficoll layers using a transfer pipette. Avoid collecting sucrose layer and do not disturb the red blood cell layer.
- Transfer the buffy coat into a new 50 ml sterile conical tube. It may take several times of repeating step 1.8 to collect all the PBMC.
- Add PBS pH 7.4 to the tube with the PBMC and fill up to the 45 ml mark. Shake tube thoroughly. Do not vortex.
- Wash 1: Centrifuge for 15 min at 480 x g with both maximum acceleration and deceleration set to 9. Observe formation of a pellet of PBMCs at the bottom of the conical tube.
- Discard the PBS (supernatant) into a plastic beaker with 10 ml of bleach.
- Loosen cell pellet by gently "racking" against an undulated surface (i.e., empty rack). Do not vortex.
- Add 25 ml of fresh PBS pH 7.4 to the tube. If more than one tube is being processed, pool the pellets together in this step.
- Wash 2: Centrifuge the tube for 12 min at 480 x g with both maximum acceleration and deceleration set to 9.
- Discard the PBS (supernatant) into the plastic beaker with a splash of bleach.
- Gently "rack" against an undulated surface (i.e., empty rack). Do not vortex.
- Add 25 ml of fresh PBS to the tube.
- Take out 50 µl of the cells and transfer into a microcentrifuge tube for viability count.
- Add an equal amount (50 µl) of trypan blue (a viability stain) and pipette up and down to mix gently.
- Take out 10 µl and transfer it to a hemocytometer to check the viability of cells per ml. Record the number of cells/ml.
- Take out the desired amount of cells and centrifuge the tube for 12 min at 480 x g with both maximum acceleration and deceleration set to 9.
- Discard the PBS (supernatant) into the beaker with bleach.
- Gently "rack" against an undulated surface (i.e., empty rack). Add 80 µl of PBS into the tube.
2. Making the PBMC Slide
- Place 80 µl of the cells onto a microscope slide. Smear the drop with the help of another slide or place 2 drops of 40 µl each on both ends of the slide.
- Leave slide in the biological safety cabinet to dry. Label the slide with a pencil on the frosted side.
3. Fixing the Samples on the Slides
- Prepare the fixative solution by mixing 0.5 ml of 37% formaldehyde to 4.5 ml of 99% ethanol.
- After the slides are dried, take out 2 ml of the freshly made fixative solution and pour it on the slide so that the entire surface of the slide is covered.
- Leave the solution on the slide for 1 min. Rinse the slide for 1 min with tap water and leave it to air dry.
4. Making the Amylase Solution for Negative Control
- Take 0.25 g of amylase powder and dissolve in 50 ml of distilled water. Pour the solution in a clean 100 ml beaker.
- Immerse the slide in the beaker so that half of the slide receives the treatment and the other half remains untreated and then incubate for 15 min at room temperature (Figure 1C).
- Make a note on which side of the slide is receiving the amylase treatment. Draw a line on the back of the slide indicating the border between the treatment and control.
- Wash the slides with ddH2O to remove the amylase solution and leave the slide to air dry.
5. Perform Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) Staining and Imaging
NOTE: PAS reagents are toxic by inhalation and are corrosive, so the steps need to be done in a chemical fume hood, and the waste products must be properly disposed of according to institutional guidelines.
- Place the slide on a flat surface and pour 1.50-2.00 ml of Periodic Acid Solution on the sample. Incubate for 5 min at room temperature.
- Rinse the slides in several charges of distilled water.
- Pour 1.50-2.00 ml of Schiff’s reagent on the slide and incubate it at room temperature for 15 min.
- Wash the slide with distilled water for 5 min and leave it to air dry.
- Apply 10 µl mounting media on the slide and cover with two small coverslips, or apply 50 µl and use one large coverslip.
- Apply clear nail polish on the edges of the coverslip, let dry overnight.
6. Obtain Images with the Binocular Light Microscope Using the 100X Objective
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
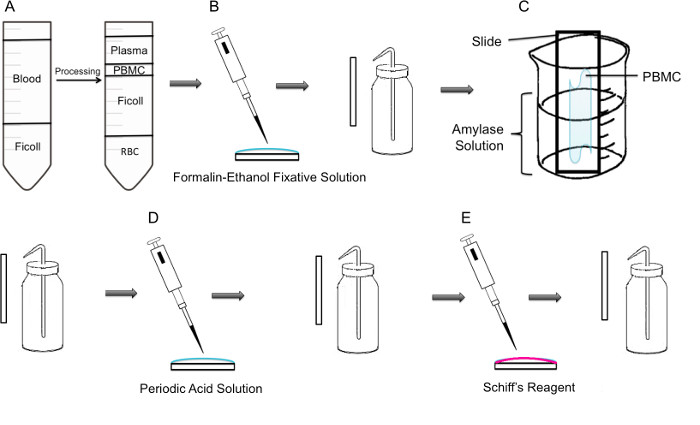
Figure 1: Step by step methodology of PAS staining on PBMC. (A) First, isolation of PBMC is achieved through ficoll gradient, the left panel shows the preparation before centrifugation, the right panel shows it after centrifugation where the buffy coat containing the PBMC is observed in the center of the tube. (B) Isolated PBMCs are fixed onto the slide using formalin-ethanol fixative solution. The slide is gently rinsed with distilled water from a plastic wash bottle. (C) The slide is then placed in a 100 ml beaker half way filled with amylase solution, which will dissolve glycogen. The slide is gently rinsed. (D) The slide is treated with periodic acid solution, where oxidation of saccharides takes place. Slides are gently rinsed; this will remove the excess periodic acid and stop the oxidation step. (E) When the Schiff reagent is added to the slides, it will react with aldehydes created during the oxidation step. This colorless reagent will then result in a deep red magenta product. Slides are gently rinsed to remove the excess Schiff reagent.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Periodic Acid Shiff Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | 395B | Bring to room temperature prior to use. Materials in this kit are toxic and harmful. Use caution. |
| α-Amylase from porcine pancreas | Sigma-Aldrich | A3176 | |
| Binocular Microscope | Carl Zeiss Microscopy | Axio Lab A0 | |
| Glycogen Assay Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | MAK016 | |
| Ficoll-Paque PLUS | VWR, GE Healthcare | 17-1440-02 | Nonionic synthetic polymer of sucrose. |
| Centrifuge | For PBMC isolation, swing buckets were used. |
References
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Tabatabaei Shafiei, M., et al. Detecting Glycogen in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells with Periodic Acid Schiff Staining. J. Vis. Exp. (2014).
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved