A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA Amplicons Post PCR: A Method to Analyze Products of Multiplex PCR and Evaluate PCR Reaction Success
In This Article
Overview
In this video, we demonstrate the separation of bacterial PCR-amplified DNA using agarose gel electrophoresis. Agarose gel functions as a molecular sieve, enabling the negatively-charged DNA to migrate based upon their size under an applied electric field.
Protocol
1. PCR Amplicon Confirmation by Gel Electrophoresis
- According to the manufacturer's recommendations, prepare a volume of 1.5% (w/v) agarose gel in 1x tris-borate-EDTA (TBE) buffer appropriate for the number of PCR reactions to be tested. Prior to casting, add 5 µL of fluorescent nucleic acid dye per 50 µL of gel solution and mix. Use trays and combs as appropriate for casting, leaving an appropriate number of wells free for DNA reference ladders.
- After setting, submerge the gel in 1x TBE-buffer in a GE system. Mix 5 µL of PCR product together with 2 µL of loading dye and transfer to gel wells. Add 5 µL of DNA ladder in empty wells for reference.
- Run the gel at 110 V per 15 cm for approximately 1 h and use a UV-based gel imaging/visualisation system to verify the presence of multiple (up to five) bands representing PCR amplicons (see example in Figure 1). Discard the gel. Store remaining PCR products at 4 °C until further processing.
Results
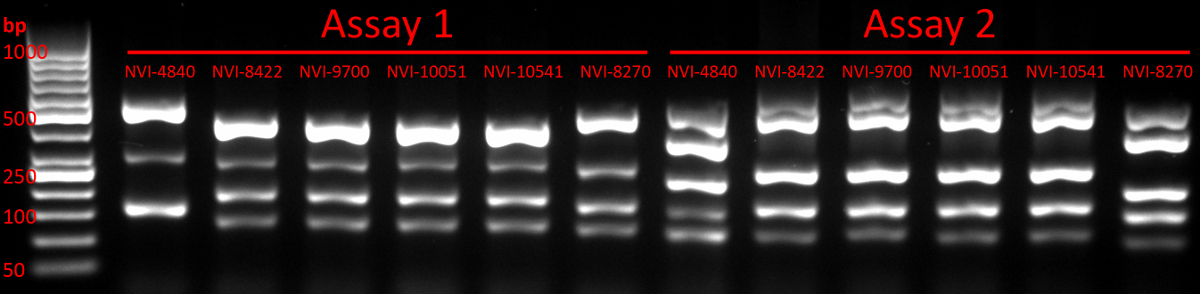
Figure 1: Gel electrophoresis verifying the presence of multiple PCR products. The image confirms the presence of multiple PCR amplicons in all 12 lanes containing samples, with the first lane representing the DNA ladder used. The sizes of selected ladder fragments have been indicated, as have the PCR assay and strain affiliation of each lane.
Disclosures
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Agarose, universal, peqGOLD | VWR | 732-2789P/732-2788 | |
| Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE) buffer | NA | NA | Standard recipe; produced in-house. |
| DNA Gel Loading Dye (6X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | R0611 | |
| Gel electrophoresis system | As preferred | NA | |
| GelRed Nucleic Acid Stain, 10,000X in water | Biotium | 41003 | Fluorescent nucleic acid dye |
| GeneRuler 50 bp DNA Ladder, ready-to-use | Thermo Fisher Scientific | SM0373 | DNA ladder |
| UV-based gel imaging/visualisation system | As preferred | NA |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Gulla, S. et al. Multi-locus Variable-number Tandem-repeat Analysis of the Fish-pathogenic Bacterium Yersinia ruckeri by Multiplex PCR and Capillary Electrophoresis. J. Vis. Exp. (2019)
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved