A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Substrate Oxidation Assay in Cultured Cells: An In Vitro Assay to Quantify Substrate Oxidation in Cells by Measuring Radioactive Signals from Trapped CO2
In This Article
Overview
This video demonstrates a quantification technique for CO2 released during substrate oxidation using 14C-radiolabeled substrates. The released 14CO2 is trapped in an alkaline solution and quantified by a scintillation counter. The oxidation of different substrates varies between tissues and reflects the pathophysiological condition of the tissue.
Protocol
The use of radioactive materials (RAM) requires prior approval by a designated safety committee at each institution.
1. Preparation of stock solutions for 14C-labeled substrates
- Make 4 mM bovine serum albumin (BSA) stock solution by mixing 11 g of BSA and 33.1 mL of Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) and shaking it gently at room temperature for ~3 h until BSA is fully dissolved. Warm the BSA stock solution in a 70 °C water bath before use.
- Air-dry 50 µCi 14C-oleate (50 µCi/µmol in ethanol) in the vial with the lid off for 8 h in a designated RAM working hood. Add 312.5 µL of H2O and then 3.5 mg (11.5 µmol) of sodium oleate. Mix thoroughly.
- Warm the resulting solution to 70 °C in a water bath. Add 0.9375 mL of the prewarmed BSA stock solution to yield 10 mM hot oleate stock solution (containing a 1:11.5 ratio of 14C-oleate to unlabeled oleate). Aliquot the stock solution and store it at -20 °C for long-term use.
- Use 14C-glucose and 14C-glutamine directly after thawing.
2. Preparation of medium containing 14C-labeled substrates
NOTE: To ensure reliable concentrations of energy substrates in the media, custom-made media must be used with fresh substrates added shortly before use. Here, a custom-made Minimum Essential Medium (MEMα) without glucose, pyruvate, glutamine, phenol red, or sodium bicarbonate is used. However, an optimal medium should be determined for each cell type.
- Reconstitute 8.67 g of the medium powder in 1 L of purified water. Add 2.2 g of sodium bicarbonate to achieve a pH of 7.4 and filter the solution using 0.22 µm vacuum filtration.
- Add fresh ingredients to obtain the complete medium (cMEMα) with final concentrations of 5.5 mM glucose, 2 mM glutamine, 1 mM pyruvate, and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Further supplement cMEMα with 100 mM L-carnitine and 10 µM HEPES to facilitate fatty acid oxidation.
- Immediately before use, add 14C-labeled substrates to freshly prepared cMEMα to make hot media. To make the oleate hot medium, add the 10 mM hot oleate stock solution to cMEMα for a final concentration of 100 µM oleate (1:100 dilution, final radioactivity 0.4 µCi/mL).
NOTE: The 10 mM hot oleate stock containing a 1:11.5 ratio of hot: cold oleate (see step 1.3) is used to achieve a physiological level of 100 µM total oleate in the media while minimizing the amount of radioactive material. - Make 10 mM unlabeled oleate stock by adding 24.36 mg of sodium oleate to 2 mL of H2O in a water bath at 70 °C for ~20 min until completely dissolved before mixing quickly with 6 mL of the 4 mM BSA stock solution prewarmed to 70 °C. Transfer to a 37 °C water bath for 1 h and filter through a 0.22 µm filter. Aliquot and store at -20 °C for long-term use.
- To make glucose hot medium, add 14C-glucose to a final concentration of 1.333 µM (1:4,125 dilution, final radioactivity 0.4 µCi/mL). To make glutamine hot medium, add 14C-glutamine to the final concentration of 2 µM (1:1,000 dilution, final radioactivity 0.4 µCi/mL).
- Supplement the glucose and glutamine hot medium with a 10 mM stock solution of unlabeled oleate from step 2.4 to achieve the final concentration of 100 µM oleate, the same as that in the oleate hot medium.
3. Preparation of cells
NOTE: Calvarial preosteoblasts and bone marrow macrophages are used as examples here. Users should prepare their cell type of choice according to appropriate protocols. Optimize the concentration of collagenase II to be used for digestion in pilot experiments as the enzymatic activity may vary among different lots.
- Isolation and culture of calvarial preosteoblasts
- Sacrifice postnatal day 3-5 (P3-5) pups by decapitation and transfer them to ice-cold DPBS containing Penicillin-Streptomycin (P/S).
- Expose the calvaria by removing the skin and soft tissue. Collect the middle region by cutting away the surrounding tissues from back to front in DPBS (Figure 1A). Scratch the inner and outer surfaces of the calvaria gently using tweezers to help release the cells upon subsequent digestion.
- Prepare a 2 mg/mL and a 4 mg/mL solution of Collagenase type II in DPBS and filter each solution with a fresh 0.22 µm filter. Digest the cleaned calvaria first with the 2 mg/mL collagenase solution for 15 min and discard the digestion solution. Digest the cleaned samples in 4 mg/mL collagenase solution 3 times for 15 min each time, pooling and saving the digestion solution.
- Filter the digestion solution through 70 µm cell strainers and centrifuge the filtrate at 300 × g for 5 min. Resuspend the cell pellet in cMEMα (see step 2.2) containing 10% FBS and P/S.
- Count and seed the cells at 4 × 104 cells/cm2 in 10 cm plates. Culture the cells in a 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2 for 3 days.
- Dissociate the cells at 37 °C with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA. Count and seed the cells in 24-well cell culture plates with cMEMα containing 10% FBS and P/S at 7.5 × 105/cm2. Seed at least 4 wells per cell type per substrate and at least three extra wells for each cell type for cell counting before the assay.
- Culture the cells at 37 °C overnight before the substrate oxidation assays.
- Isolation and culture of BMMs
NOTE: Culture of BMMs requires macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), which can be purchased commercially as a recombinant protein. Conditioned medium from the cell line CMG14-12 engineered to express M-CSF is an economical alternative used here.- Collect femurs and tibias from 8-week-old mice after removing the muscle and connective tissues. Cut and discard both ends of the bones with sharp scissors.
- Flush out the bone marrow from one femur and one tibia into a 10 cm Petri dish with a syringe fitted with a 23 G needle containing 15 mL of cMEMα with 10% FBS, P/S, and 10% CMG14-12 conditioned medium (BMM medium). Culture the cells in the Petri dish in a 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2.
- After 3 days, discard the culture media and rinse with DPBS. Dissociate the attached cells at 37 °C with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA for 5 min. Centrifuge and resuspend the cell pellet in the BMM medium.
- Count and seed the cells in 24-well cell culture plates at 7.5 × 105/cm2 in the same way as described in 3.1.6. Culture at 37 °C overnight in the BMM medium before starting the assays.
4. Substrate oxidation assay with CO2 trap
NOTE: An appropriate seeding density should be determined for each cell type to achieve 80-90% confluence before the start of the assay. Note that cell density can affect the metabolic state of the cells.
- Wash the cells in the extra wells twice with DPBS. Dissociate the cells with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA and mixed 20 µL cells resuspended in DPBS with 20 µL of acridine orange/propidium iodide (AO/PI) ready-to-use commercial dye solution. Determine the number of live cells with an automated cell counter and record the number for final calculations.
- Wash the cells in the assay wells twice with DPBS. Add 500 µL of hot medium to each assay well in the RAM-designated tissue culture hood. Seal the plates with parafilm and incubate the cells in a RAM-designated incubator at 37 °C for 4 h.
- During incubation, cut filter paper into circular pieces slightly bigger than the area inside the cap of 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes and insert the paper snugly into the cap (Figure 1B). Add 200 µL of 1 M perchloric acid to each tube and 20 µL of sodium hydroxide to the filter paper fitted inside the cap.
- After incubation of the cells, transfer 400 µL of culture medium from each well to the prepared tubes and close the caps immediately. Leave the tubes in a tube rack at room temperature for 1 h.
- During incubation, set up a scintillation vial for each tube and fill it with 4 mL of scintillation fluid. Transfer each piece of filter paper to a scintillation vial and incubate at room temperature for 30 min.
- Perform wipe tests on the tissue culture hood, the water bath (used for 14C-oleate preparation), refrigerator, incubator, sink, ground, and any other working area for potential RAM contamination. Put the paper wipes into scintillation vials containing scintillation fluid.
- Measure 14C radioactivity in the scintillation vials with a scintillation counter. Record the reading results. Decontaminate the working environment according to radiation safety guidelines if necessary.
Results
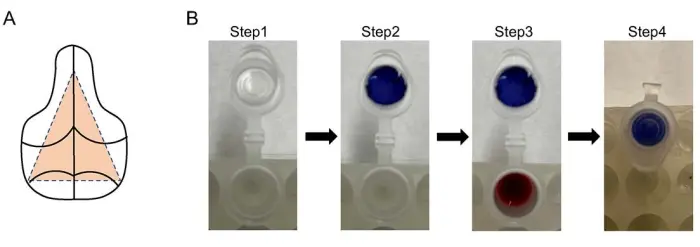
Figure 1: Diagrams for CO2 trapping assay and calvaria dissection. (A) The middle region of the calvaria, indicated by the orange dashed triangle, is harvested for cell isolation. (B) 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes are used for CO2 trapping (step 1). Filter papers (blue paper for illustration purposes) are cut to fit into tube caps (step 2). A...
Disclosures
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.22 µm filters | Sigma-Aldrich | SLGVM33RS | Used to filter BSA solution |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA | Gibco | 25200056 | Dissociate cells from cell culture plates |
| 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes | PR1MA | PR MCT17 RB | Used for reaction incubation |
| 10 cm plates | TPP | 93100 | Used for cell culture |
| 10 mL syringe | BD | 302995 | Used to flush marrow from long bones |
| 10% FBS | Atlanta biologicals | S11550 | For Cell culture medium preparation |
| 14C -Glucose | PerkinElmer | NEC042X050UC | Used to make hot media |
| 14 C-glutamine | PerkinElmer | NEC451050UC | Used to make hot media |
| 14 C-oleate | PerkinElmer | NEC317050UC | Used to make hot media |
| 23 G needle | BD | 305120 | Used to flush marrow from long bones |
| 24-well plates | TPP | 92024 | Used for cell culture |
| 70 μm cell strainers | MIDSCI | 70CELL | Used to filter supernatant during cavarial digestion |
| Acridine Orange/Propidium Iodide (AO/PI) dye | Nexcelom Biosciences | CS2-0106 | Stains live cells to determine seed density |
| Bovine Serum Ablumin | Proliant Biologicals | 68700 | Used for fatty acid conjugation |
| Cellometer Auto 2000 | Nexcelom Biosciences | Determine the number of viable cells | |
| Centrifuge | Thermo Fisher | Legend Micro 21R | Used to pellet cells |
| Collagenase type II | Worthington | LS004176 | Dissociate cells from tissue |
| Custom MEM alpha | GIBCO | SKU: ME 18459P1 | Used to create custom hot media |
| Dulbecco's Phosphate-Buffered Saline | Gibco | 10010023 | Used to dissolve and dilute reagents, and wash culture dishes |
| Filter Paper | Millipore-Sigma | WHA1001090 | Traps CO 2 with sodium hydroxide |
| Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | g7528 | Used to make custom media |
| HEPES | Gibco | 15630080 | Traps CO 2 during cell culture |
| L-carnitine | Sigma-Aldrich | C0283 | Supplemented for fatty acid oxidation |
| L-Glutamine | Sigma-Aldrich | g3126 | Used to make custom media |
| MEM alpha | Thermo | A10490 | Cell culture medium |
| Parafilm | Pecheney Plastic Packaging | PM998 | Used to seal cell culture dishes |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Thermo Fisher | 15140122 | Prevents contamination in cell culture |
| Perchloric Acid | Sigma-Aldrich | 244252 | Releases CO 2 during metabolic assay |
| Pyruvate | Sigma-Aldrich | p5280 | Used to make custom media |
| Scintillation Counter | Beckman Coulter | LS6500 | Determines radioactivity from the filter paper |
| Scintillation Fluid | MP Biomedicals | 882453 | Absorb the energy emitted by RAMs and re-emit it as flashes of light |
| Scintillation Vial | Fisher Scientific | 03-337-1 | Reaction containers for scintillation fluid |
| Sodium carbonate | Sigma-Aldrich | S5761 | Balance buffer for medium |
| Sodium Hydroxide | Sigma-Aldrich | 58045 | Traps CO2 during metaboilc assay |
| Sodium oleate | SANTA CRUZ | SC-215879 | BSA conjugated fatty acid preparation |
| Vaccum filtration 1000 | TPP | 99950 | Filter cMEMα |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Song, C. et al., Assessing Energy Substrate Oxidation In Vitro with 14CO2 Trapping. J. Vis. Exp. (2022)
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved