A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction to Enumerate Bacteriophages
In This Article
Overview
In this video, we discuss the quantitative polymerase chain reaction, qPCR, to enumerate T7 bacteriophages through DNA quantification. The fluorescent dye in the PCR mixture binds with the newly synthesized DNA strands and emits fluorescence, which is measured.
Protocol
1. Prepare qPCR reactions
NOTE: One PCR reaction is for one sample. Each PCR reaction contains 5 µL of qPCR master mix (see materials), 1 µL of 5 µM primer pair mix, 2 µL of H2O, and 2 µL of heat-treated T7 phage sample. For multiple PCR reactions, all the reagents except the phage sample are premixed in one 1.5 mL tube. The volume of each reagent in the premix depends on the number of phage samples for qPCR.
- Prepare the qPCR premix for 10 biopanned phage samples of unknown concentration and 7 samples of standard concentrations in triplicate. As a result, there are 51 total samples and therefore, 51 qPCR reactions (i.e., one reaction per sample). For 51 reactions, prepare a premix of 255 µL of qPCR master mix (51x 5 µL), 51 µL of primers (51x 1 µL), and 102 µL of H2O (51x 2 µL).
NOTE: It is recommended to prepare a few extra PCR reactions to compensate for the volume loss during aliquoting the PCR mix into each well of the 96-well qPCR plate. - Aliquot 8 µL of PCR premix into each well of 96-well qPCR plate for a total of 51 wells (i.e., 51 qPCR reactions). There is no need to change tips during aliquoting.
- Add 2 µL of heat-treated T7 phage samples or T7 phage reference DNA to each well (Figure 1B); change tips when adding different DNA samples to the well to prevent cross-contamination. Also, dispense the 2 µL DNA samples underneath the surface of the qPCR premix (i.e., into the 8 µL PCR premix).
- Seal the qPCR plate with adhesive film.
NOTE: This step is critical, regardless of the type of qPCR plate. Use the recommended kit to seal the plate completely; otherwise, any non-sealed region in the plate will cause volume loss during PCR cycling. - Wrap the qPCR plate with aluminum foil to minimize fluorescence photobleaching and proceed to run it on the qPCR equipment.
2. qPCR cycling conditions
NOTE: qPCR cycling conditions were set up on the specific qPCR equipment.
- Run the 96-well qPCR plate on the qPCR equipment. On the equipment, select settings from the menu to set up the following experimental conditions (Figure 1C).
- Set up cycling conditions as follows for a sample volume of 10 µL: one cycle at 50°C for 2 min, one cycle at 95°C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of (95°C for 15s, 60°C for 1 min). After, run the melt curve settings: one cycle of 95°C for 15 s, 60°C for 1 min, and 95°C 15 s.
- Proceed to analyze the data.
Results
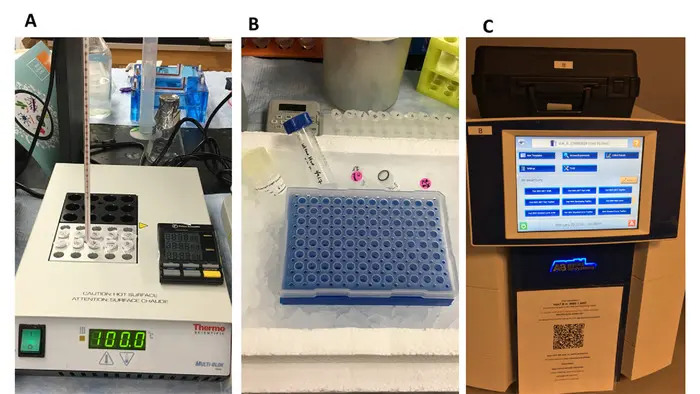
Figure 1: Phage sample treatment, qPCR reaction preparation, and qPCR run. DNase I pretreated T7 phage samples were heated at 100° C for 15 min to release the T7 DNA from intact phage particles (A); the qPCR mixture was prepared as described in the protocol. All the preparations were done on ice (A); qPCR equipment and compatible software (B...
Disclosures
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Primers for T7 genomic DNA | IDT | F: CCTCTTGGGAGGAAGAGATTTG R: TACGGGTCTCGTAGGACTTAAT | |
| T7 Select packaging control DNA | EMD Millipore | 69679-1UG | |
| MicroAmp optical 96-well reaction plate | ThermoFisher Scientific | N8010560 | |
| qPCR master mix-Power up SYBR Green master mix | Applied biosystems | Applied biosystems | |
| MicroAmp optical adhesive film kit | ThermoFisher Scientific | ThermoFisher Scientific | |
| UltraPure DNase/RNase-Free Distilled H2O | Invitrogen | 10977015 | |
| ViiA7 Real-Time PCR System with Fast 96-Well Block | ThermoFisher Scientific | 4453535 | |
| QuantStudio Real-time PCR software | ThermoFisher Scientific | v1.2 |
References
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Peng, X., et al., Quantitative PCR of T7 Bacteriophage from Biopanning. J. Vis. Exp. (2018)
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved