Methods Article
A Rapid In Vivo Bioassay for Developmentally Active Enhancers
Not Published
In This Article
Summary
With the increased use of transcription factor-specific ChIP-seq technology, techniques to validate potential regulatory regions are critical. The authors describe a rapid chick bioassay to validate the activity of regulatory sequences functioning during development.
Abstract
A potential regulatory sequence (PRS) can be identified by several approaches including conservation analysis and transcription factor-specific chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next generation sequencing (TF ChIP-seq). TF ChIP-seq generates a large data set (TF-regulatome) that includes PRSs and background interactions. These approaches require secondary low throughput validation in model systems that replicate the temporal and spatial specificity of the PRS.
In this report, a protocol is described to rapidly validate activity of PRSs in their developmental context. Following selection of candidate PRSs, the associated sequences are isolated, cloned into a GFP reporter construct, and then transfected into chick embryos. For PRSs that are anticipated to be functional during early development, from gastrulation through early organogenesis, whole embryo electroporation (EP) is recommended. With this technique transfection, incubation and monitoring occurs ex ovo during early gastrulation. The entire embryo is transfected and as structures form, they can be monitored live for PRS activity. This ex ovo approach supports development up to early limb bud outgrowth.
If the functional activity of a PRS is expected to be later in development or if the investigation is to ascertain its activity during the development of a specific organ, targeted regional electroporation (TREP) is used. This approach requires injection of construct DNA directly into the developing organ, precursor or adjacent cavity prior to electroporation. An approach to transfect the presumptive limb bud using TREP is also outlined and illustrated. TREP supports a rapid organ-specific validation of a PRS' activity. Both techniques can also be used to investigate regulatory domains by site-directed mutagenesis of the PRS-reporter construct.
The chick as a bioassay offers a rapid effective tool for PRS validation, functional domain determination, and further characterization of the regulatory events responsible for development.
Introduction
Evaluation of systems biology by big data sets (i.e., genome-wide) offers new insights and tool sets for the curation of relevant regulatory molecules and pathways.1,2 Transcription factor-specific chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next generation sequencing (TF ChIP-seq) generates a genome-wide data set (TF regulatome) of potential regulatory sequences. However, not all of the recovered sites are functionally relevant. The ability to discern signal from noise is a significant limitation of the "omic" data sets.3
With an increasing number of completed genomes available for comparison, one approach is to determine whether a potential regulatory sequence (PRS) is conserved across species and thereby implicate functional relevance. This approach can accelerate discovery in a variety of disciplines, but is particularly helpful in developmental biology where establishing the basic body plan in vertebrate development is controlled by conserved gene sets.4 Furthermore, associated regulatory elements are also typically conserved and clustered within introns or associated gene deserts.5-7 Comparison of the PRS with enhancer-associated marks, such as p300 or H327Ac, are additional tools for the prediction of enhancer activity.8,9 Although these added screening techniques increase the likelihood that PRSs are functionally relevant, confirmation is still required.
Timmer and coworkers first reported the use of in ovo electroporation as a rapid bioassay for demonstrating enhancer-promoter activity.10 They injected -PRS linked to reporters into chick neural tubes at Hamburger and Hamilton11 stage (HH) 15 - 17 using various enhancer-promoter combinations and then followed for enhancer activity. Uchikawa generated an inducible reporter construct with a basal herpes simplex thymidine kinase promoter linked to an enhanced GFP reporter (ptk-EGFP).12 The basal level of activity of this promoter is very low in most tissues allowing for faithful enhancer driven localization of activity. Uchikawa also extended developmental reporting to other tissue involved in early development using a whole embryo electroporation technique at HH 4.13 Oberg, Pira and colleagues further extended the capacity of in ovo electroporation to other tissues at later stages of development.14,15 Thus, the capacity to evaluate enhancer activity in various tissues through a range of developmental stages has been demonstrated.
In this report, the chick as a bioassay is used at multiple stages and sites to determine the activity of PRSs during development. This technique can be used to validate an isolated PRS as the target of a hypothesis driven question or to validate several candidates from a large data set before further analysis.
Protocol
The protocol described below was performed in accordance with Loma Linda University's policy on research involving animals and followed the recommendations within the Federation of Animal Science Societies' (FASS) Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Research and Teaching, 3rd ed. and the National Research Council's Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. It is important to check with the local institution regarding their requirements for vertebrate animal use approval when using chick embryos since they are not considered as a vertebrate animal within the FASS guide; however, recommendations for appropriate avian embryo euthanasia are described and adhered to in this lab.
1. Construction of the Reporter Vector
- Design primers to the potential regulatory sequence (PRS) to contain the restriction endonuclease sequence recognition site for XhoI (CTCGAG) and KpnI (GGTACC). 16
- Amplify the region by performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using genomic DNA template as previously reported.17,18
- Clone the PCR product into the ptk-EGFP expression vector.19
- Use the empty ptk-EGFP expression vector as a negative control to indicate the basal level of expression within a given tissue. Use theβ-actin-driven RFP reporter plasmid as a positive control and an indicator of transfection efficiency.
2. Whole Embryo Electroporation
- Preparations
- Prepare filter paper supports. Punch 4 holes in a cloverleaf pattern onto a 2.2 x 2.2 cm filter paper using a standard hole punch. Sterilize by autoclaving.
- Prepare the albumin-agar culture dish.
- Dissolve 0.18 g of agar in 30 ml 0.9% sodium chloride on a hotplate, with stirring. Cool in a 42 °C water bath.
- Extract the thin albumin by first cracking the narrow end of an unincubated egg and removing the eggshell. Pour out the thick albumin and transfer the thin albumin into a sterile 50 ml conical tube using a large bore plastic transfer pipet. Use enough eggs to get 30 ml of thin albumin (~ 4 eggs). Add 150 µl of 10,000 U/ml penicillin-streptomycin and warm the albumin in a 42 °C water bath.
- Combine the albumin and agar and mix by swirling. Transfer 2 ml aliquots to a 35 mm Petri dish, gently swirling the dish to ensure even coverage. Allow the agar to set at room temperature for at least 10 min. Store at 4 °C.
- Prepare the cloned PRS vector cocktail: 1 µg/µl of PRS plasmid, 0.3 µg/µl of reporter plasmid, and 0.025% Fast Green FCF stain.
- Protocol for In Vitro Culturing of Hamburger-Hamilton Stage (HH) 4 Chick Embryos
- Incubate fertilized White Leghorn eggs at 39 °C for 18 - 19 hr, according to Hamburger-Hamilton chick staging11.
- Spray the surface of the egg with a light mist of 70% ethanol and air-dry.
- Crack the egg and empty its content into a 15 cm Petri dish. Carefully remove the thick albumin on the yolk using the blunt end of forceps.
- If the embryo is on the side of the yolk, roll the yolk around with the blunt end of forceps until the embryo is in the middle of the yolk.
- Place the filter paper on the yolk, with the embryo centered. Cut the vitelline membrane at the edges of the filter paper. Lift the filter paper from the yolk.
Note: It is important that the vertical orientation of the primitive streak is maintained so that the embryo does not tear. - Place the filter paper on the albumin-agar plate with the hypoblast (yolk side) up. Carefully remove excess yolk with the blunt end of forceps. Gently rinse the embryo with warmed Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS).
- Electroporation Protocol
- Position the electrodes and pulled glass capillary needle attached to a syringe under a dissecting microscope. Set the 3 mm round platinum cathode at the base of a ~ 2 mm deep chamber under the embryo suspension silicone platform. Mount the 2 mm round platinum anode in a micromanipulator and suspend above the silicone platform. The syringe contains mineral oil as the hydraulic fluid.
- Add 100 - 200 µl HBSS into the cathode cavity of the silicone platform. Place the filter paper supporting embryo on the platform with the hypoblast (yolk side) up.
- Inject 1 µl PRS vector cocktail between the blastoderm and the vitelline membrane using a pulled glass capillary needle. Follow with a small amount of mineral oil to seal the injection point.
- Position the anode about 2 mm above the embryo. Drop ~ 100 µl of HBSS directly over the electrode and embryo. Electroporate with 5 pulses of 5 V for 50 msec at intervals of 100 msec.
CAUTION: The electroporator can produce high levels of voltage and current. Observe basic lab safety and common sense to prevent injury. This includes not touching the exposed electrodes with bare hands or materials that can conduct electricity while the electroporator is on. Refer to the equipment manual for other safety precautions and potential hazards. - Return the embryo to the agar-albumin plate, with hypoblast up, and incubate in a humidified chamber.
- Clean the cathode after each electroporation by aspirating any remaining liquid and yolk. Clean the anode by wiping with a lab tissue.
3. Targeted Regional Electroporation: Neural Tube of HH10 Chicken Embryo
- Protocol for Windowing the Egg and Staining the Embryo
- Incubate fertilized White Leghorn eggs at 39 °C for 33 - 38 hr, according to Hamburger-Hamilton chick staging11.
- Spray a light mist of 70% ethanol onto the eggs and air-dry.
- Place the egg on its side on an egg holder. Using a dissecting probe, poke a small hole at the blunt end of the egg. Insert a syringe with an 18 gauge needle through this hole at a downward angle and withdraw 1 - 2 ml of albumin, taking care not to remove any yolk.
- Without breaking the underlying shell membrane, poke a shallow hole on the top side of the egg. Carefully remove small portions of the eggshell with the dissecting probe, until ~ 0.5 cm diameter of the underlying membrane is exposed. Break the shell membrane by pushing down on it with the dissecting probe.
- Cover the hole with a strip of tape and cut the hole bigger, to ~ 2 cm diameter, using small scissors.
- Under a dissecting microscope, identify the blood island surrounding the embryo and add 6 µl of neutral red solution to the middle of this blood island. Wait 2 - 3 min.
- Carefully remove the vitelline membrane overlying the embryo using a tungsten needle.
- Electroporation Protocol
- Align the two electrodes in parallel with a fixed inter-electrode distance of 4 mm and mount on a micromanipulator. Position the electrodes on the yolk membrane so that the embryo is centered between the electrodes.
- Inject ~ 0.1 µl PRS vector cocktail into the neural tube lumen of the embryo. Add 1 - 2 drops of 1x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) using a transfer pipet. Reposition the electrodes so that they touch the yolk membrane, if necessary.
- Apply 5 pulses of 20 V each lasting 50 msec at 950 msec intervals. Add 1 drop of 1x PBS and remove electrodes.
- Seal the egg with a piece of transparent tape and return to the egg incubator.
- Clean electrodes after each electroporation in bleach, RNase-free water, and 1x PBS to remove residual yolk.
4. Targeted Regional Electroporation: Lateral Plate Mesoderm of HH14 Chicken Embryos
- Electroporation Protocol
- Incubate fertilized White Leghorn eggs at 39 °C for 50 - 53 hr, according to Hamburger-Hamilton chick staging11.
- Open and stage the embryos as described above in in Steps 3.1.2 to 3.1.7.
- Using a tungsten needle, make a slit onto the yolk membrane outside the periphery of the blood vessel at the tail end of the embryo.
- Slide the cathode rod into the yolk through this slit. Position the cathode parallel to and along the length of the embryo. Do not place the cathode directly under the lateral plate mesoderm.
- Inject ~ 0.2 µl PRS vector cocktail into the intraembryonic coelom at the level of somite 18, followed by a small amount of mineral oil. The DNA will travel anteriorly and posteriorly along the coelom.
- Position the cathode directly under the lateral plate mesoderm, spanning somites 15 - 20. Position the anode above the lateral plate mesoderm with an inter-electrode distance of ~ 2.5 mm. Add 3 - 5 drops of 1x PBS so as to submerge the anode. Adjust the electrodes so that they are not touching the embryo.
- Apply 3 pulses of 8 V, 60 msec in duration at 50 msec intervals.Remove cathode from the yolk through the slit.
- Add 40 µl 2,500 U/ml of penicillin/ streptomycin. Seal the egg with transparent tape and return to the egg incubator.
- Clean electrodes after each electroporation in bleach, RNase-free water, and 1x PBS to remove residual yolk.
5. Fluorescence Analysis
- Whole Embryo Electroporation
- Using forceps, lift the filter paper from the plate and replace the embryo onto the same plate with the hypoblast down. Position the embryo away from residual yolk and cloudy portions of the agar-albumin plate. Alternatively, place the embryo in a new plate for imaging.
- Examine the embryos with a fluorescence microscope to visualize transfection efficiency and PRS activity 6 - 48 hr after transfection. To optimize fluorescence intensity, visualize the embryos under high magnification.
- Targeted Regional Electroporation (TREP)
- Carefully dissect the embryo from the egg by cutting the yolk membrane around the embryo with microscissors and transfer to a 35 mm dish containing 1x PBS.
- Under a dissecting microscope, remove the extraembryonic membrane with microscissors and forceps.
- Keep the microscissors flat and parallel to the embryo to prevent accidentally cutting the embryo. Do not pull or tear the membranes with forceps as the embryo might tear otherwise.
- Visualize the embryo in a new 35 mm dish with 1x PBS under bright field and fluorescence microscopy. Use high magnification (40X) to optimize fluorescence intensity.
- At high magnification, stitch the images together using an image-editing software to generate the complete image of the targeted tissue.
Results
The ptk-EGFP vector provides an inducible reporter with low levels of background activity in the developing chick embryo. The vector links the Herpes Simplex virus minimal thymidine kinase promoter (ptk) to an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter (Figure 1A). The potential regulatory sequence is cloned into the multiple cloning site (MCS) upstream of the promoter. The construct is then transfected into the chick embryo by electroporation. Transfection efficiency is determined by co-electroporation with a β-actin promoter-driven RFP reporter plasmid (Figure 2D). RFP can be detected within 6 hr of transfection indicating the lag time needed before enhancer activity can be assayed with certainty. When assaying for activity during early development, whole embryo electroporation ex ovo at HH 4 during gastrulation is used (Figure 1B). Activity can then be localized and followed through gastrulation and basic body plan formation, up until about stage HH 16 or 17 just prior to wing outgrowth.
Whole embryo electroporation was used to assay potential regulatory sequences (PRS) associated with the RTN4/NOGO gene. A PRS 88.5 kb upstream of RTN4/NOGO demonstrated enhancer activity in the neural tube (Figure 2). The product of RTN4/NOGO, NOGO-A, is associated with neurite outgrowth inhibition. NOGO-A is also expressed within the neural tube coincident with the activity of the PRS. To assay the activity of this NOGO-A associated enhancer element (NAEE) at later stages of development, targeted regional electroporation (TREP) was used to transfect the neural tube at HH 10 (Figure 1C). TREP demonstrated that NAEE activity became restricted to the cranial spinal cord by HH18 (Figure 2N).
There are three predicted binding sites within this short 125 bp, enhancer; POU1F1, HNF3B, and SOX. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SOX binding site silenced enhancer activity suggesting that a SOX transcription factor is required for enhancer activity (Figure 2 I & J). The ZPA regulatory sequence (ZRS) has been described as the most distant regulatory enhancer located 1Mb upstream of Sonic hedgehoh (Shh).20 Thus, of the genes within the vicinity (~ 1 Mb) of the NAEE, only RTN4/NOGO is expressed within the neural tube. Thus, RTN4/NOGO is the most likely target of NAEE regulation.
In addition, transcription factor-targeted ChIP-seq data (reported as genomic intervals or peaks) are considered potential regulatory sequences. Genomic-wide sites of Lmx1b binding within the developing murine limb bud were analyzed at embryonic day 12.5 (e 12.5). The genomic intervals were screened for conservation and a PRS 60 kb upstream of Lmx1b itself was identified (Figure 3A). To validate that this PRS could function as an enhancer during limb development, a ptk-EGFP reporter construct was transfected into the presumptive chick limb using TREP (Figure 1D). After 48 hr of incubation, the emerging limb bud (HH 24; developmentally similar to e12.5) demonstrated enhancer activity restricted to the dorsal limb mesoderm corresponding to the expression domain of Lmx1b (Figure 3D & E). Enhancer activity was abolished by mutation of the predicted Lmx1b binding site, implying a requirement for Lmx1b binding for enhancer activity (Figure 3H).
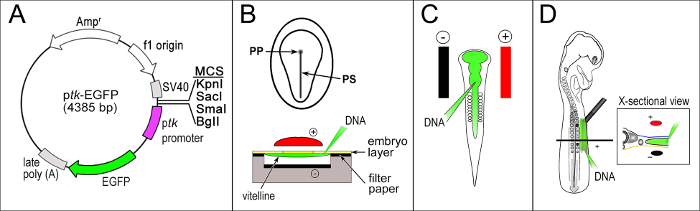
Figure 1: Reporter Construct and Electroporation Setup. A) The ptk-EGFP vector illustrating the multiple cloning site (MCS), the thymidine kinase promoter (ptk) linked to the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter. Potential regulatory sequences (PRS) are cloned into the MCS just upstream of the minimal promoter. The PRS-ptk-EGFP can then be transfected into chick embryos and assayed for activity using one of the following three approaches. B) Whole embryo electroporation. A Hamburger-Hamilton stage (HH) 4 embryo is mounted on a filter paper support and placed hypoblast up on a silicone platform encasing the cathode (-). The DNA is injected into the space between the vitelline membrane and the epiblast and the anode (+) is suspended above the embryo (PP=primitive pit, PS=primitive streak). C) Targeted regional electroporation of the neural tube. DNA is injected into the lumen of the neural tube of HH 10 chicken embryo. Paired parallel electrodes (+, -) are placed flanking the embryo. D) Targeted regional electroporation of the lateral plate mesoderm of HH 14 chicken embryos. DNA (PRS-ptk-EGFP) is injected into the intraembryonic coelom underlying the lateral plate mesoderm between somite levels 15 and 20 (black squares). The cathode (-) is placed underneath the embryo and the anode (+) is placed above the embryo, as shown in the transverse section at the level indicated in D with a black line (inset) (Cathode - colored black, Anode - colored red, Injected DNA - colored green). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
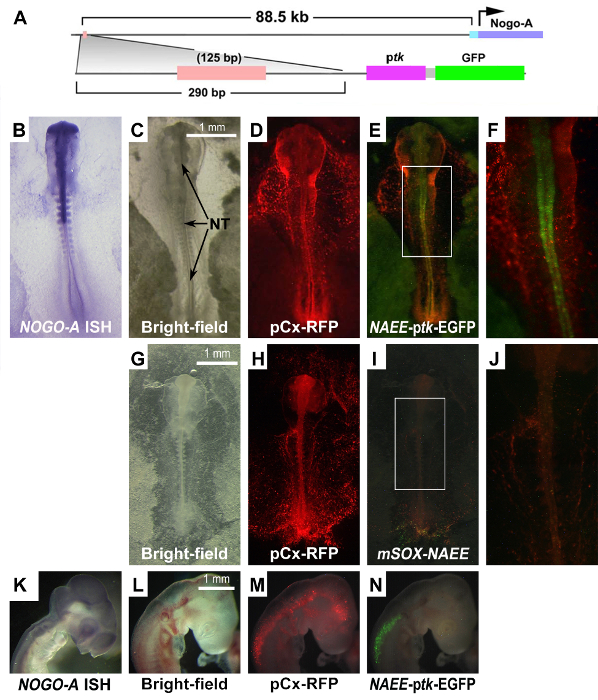
Figure 2: Activity of the NOGO-A-Associated Enhancer Element (NAEE) During Development. A) Schematic of the potential regulatory sequence upstream of the RTN4/NOGO gene that encodes for NOGO-A and its reporter construct. ptk- basal thymidine kinase promoter B) in situ hybridization (ISH) for NOGO-A mRNA at HH 10. C) Bright-field light of a HH 10 embryo transfected with the NAEE-ptk-EGFP reporter. D) Co-transfection of the embryo with an RFP reporter plasmid demonstrates transfection efficiency. E) Activity of the NAEE sequence within the neural tube (NT). F) Boxed region from "E" magnified. NAEE activity (E) co-localizes with NOGO-A expression (B). G) Bright-field of a similarly staged embryo assaying NAEE activity with the SOX binding site mutated (mSOXNAEE) showing loss of activity (I). J) Boxed region in I magnified. H) RFP is diffuse indicating good transfection. K) NOGO-A expression in a later stage (HH 18) embryo. L) Bright-field of the HH 18 embryo. N) Enhancer activity is accentuated in the spinal cord whereas RFP is detected throughout the neural tube (M). Scale bars in C, G and L are 1 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
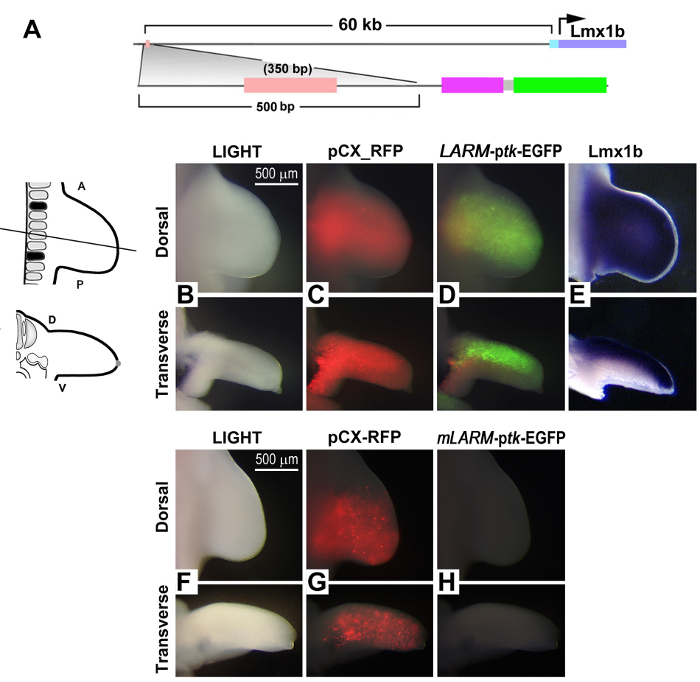
Figure 3: Validation of an Lmx1b-Associated Regulatory Element (LARM) Identified by ChIP. A) Schematic of the conserved sequence found by Lmx1b-specific ChIP-seq and its reporter construct (ptk- basal thymidine kinase promoter). At HH 24 (48 hr after transfection of the presumptive limb mesoderm), the limb is examined. B) Morphology of the HH 24 limb bud with bright-field light (scale bar = 500 µm). C) Distribution and transfection efficiency is demonstrated by an RFP reporter plasmid. D) Activity of the conserved ChIP-identified genomic interval is evident and localized to dorsal mesoderm corresponding to the expression domain of Lmx1b (E, in situ hybridization to Lmx1b mRNA). F) Bright-field of an HH 24 limb transfected with the LARM containing a mutated Lmx1b binding site (mLARM; scale bar = 500 µm). G) Diffuse distribution of RFP indicating transfection efficiency. H) Loss of activity when the Lmx1b binding site is mutated. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
This report describes a bioassay to validate potential regulatory sequences active during development. The approach incorporates the use of a reporter construct, transfection via electroporation and chicken embryos. The process, from sequence determination to validation of activity, can typically be completed within two to four weeks. A critical aspect of this protocol is the efficient transfection of construct into the target tissue. Several steps ensure efficient transfection. The use of endotoxin-free plasmids minimizes post-operative deformation and embryonic death. Cleaning electrodes well after each EP optimizes and standardizes transfection. The voltage and pulses of the electroporator may also need to be adjusted to optimize transfection yet minimize EP related tissue damage. These parameters, once established should be consistently used. For whole embryo EP, removing as much of the yolk from the embryo and filter paper as possible optimizes current flow and keeps the embryo from sagging or tearing from the filter paper. Removing the yolk also makes it easier to visualize the embryo and PRS activity during evaluation.
For targeted regional electroporation (TREP), injection of DNA into a cavity is ideal, since the cavity can retain the concentrated DNA during the time between injection and electroporation. Every attempt should be made to keep this interval short irrespective of the target, but a restricted space is helpful. When an associated cavity or restricted space is not available, a cavity or bubble within the target tissue should be created. For example, Oberg and co-workers created a cavity within limb bud mesoderm by injecting a bolus of DNA followed by a bubble of mineral oil.14 Retention of DNA by this approach promoted efficient transfection of limb bud mesoderm. If direct tissue contact by the electrodes is necessary to direct current to the target tissue, insulate the electrodes as described by Oberg and co-workers to minimize short circuits that can reduce transfection efficiency.14 Be aware that direct contact will also cause some local tissue damage. If TREP of an organ has yet to be described, the approach should be optimized first with the RFP construct to ensure effective transfection of the targeted tissue with minimal tissue damage. The major limitation of this approach is the transfection of organs that form in more advances stages of development or are physically difficult to target within the embryo such as the metanephric kidney.
A number of in vitro and in vivo approaches have been used to validate potential regulatory sequences. Validation of an enhancer element can be accomplished in a relevant in vitro cell line.21 Although this approach can be useful, cell lines are immortal and out of context from their original derivation and thus, may not represent in vivo activity. Even primary cells grown in culture are out of context to their in situ relationships and rapidly lose some of their differentiated features.22,23 For a transcription factor that has precise spatial and temporal expression during development, context is critical for functional validation. Analysis of enhancer activity in transgenic mice follows a protocol similar to what is described in this report with generation of a reporter construct, typically using the LacZ reporter, although GFP has also been described.24,25 The mouse transgenic approach requires the injection of the construct into mouse embryonic stem cells, typically injecting 100 - 300 cells for recovery 3 - 5 embryos, 3 - 7 week after construct generation, and costs of around $ 2,500 per construct. Furthermore, since evaluation occurs post-harvesting only one developmental stage can be examined per embryo. Thus, using the mouse transgenic approach to evaluate developmentally active vertebrate enhancers is limited by embryonic stage, cost, time and efficiency. The zebrafish model is a more assessable and accessible model for enhancer activity but is also a vertebrate model that is more divergent from human than either mouse or chicken.7 Thus, for the analysis of limb development related enhancers, the chick or mouse models would be more informative. The zebrafish model also requires establishing a fish facility to breed and maintain a colony, which is not a trivial undertaking.
The chick is a common well-studied vertebrate developmental model for several major organ systems including brain, heart and limbs. Fertile eggs are readily available and require only an avian incubator for development. Similar to the zebrafish model, assessment of enhancer activity in chick embryos is rapid, within 6 hr after transfection, and as in zebrafish, enhancer activity can be followed through multiple stages of development. The most expensive item required to setup up a chick bioassay system for enhancer activity in most labs is the electroporation unit that is presently around $ 14 k, which can be used for hundreds of transfections and bioassays of potential regulatory sequences. Considering the cost of mouse transgenics or establishing a fish facility, the chick bioassay is quite cost effective. Overall, the chick bioassay as described provides a rapid system for validating enhancers active during vertebrate development. The approach can be used to supplement high throughput techniques to confirm functional relevance of data sets. Alternatively, this approach can be used to validate targets extracted from genomic data sets that are to be used in hypothesis-driven, mechanistic investigations.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the members of the Soriano lab for critical review of this technique. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Uchikawa for the kind gift of the ptk-EGFP plasmid. Funded in part by grants from the LLU Pathology Research Endowment, National Organization of Rare Diseases, and from the NICHD (HD39421).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Bacto-Agar | BD Biosciences | 204010 | |
| Sodium chloride | Sigma | S9888 | |
| Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) | Sigma | H6136 | Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS), Without sodium bicarbonate |
| Penicillin-streptomycin | Life Technologies | 15140-122 | |
| Ethanol 200 proof | dilute to 70% | ||
| Endofree Maxiprep Plasmid Kit | Qiagen | 12362 | EndoFree Plasmid Maxi Kit |
| White Leghorn fertilized eggs | Chino Valley Ranchers | ||
| Whatman Grade 4 filter paper | GE Healthcare Life Sciences | 1004-240 | filter paper support (a range of grades are ssufficent to provide stability during growth) |
| 50ml conical tube | VWR | 21008-242 | |
| 35mm petri dish | VWR | 627161 | Sterile Petri Dishes, 35W x 10H mm |
| 15cm petri dish | VWR | 82050-600 | Sterile Petri Dishes, 145W x 20H mm |
| Transfer pipet | VWR | 414004-042 | |
| Capillary tube | World Precision Instruments | 1B100F-6 | |
| Terasaki dish | VWR | 82050-706 | dish from which to aspirate DNA |
| mineral oil | |||
| Standard hole punch | |||
| Hotplate stirrer | |||
| Stir bar | |||
| Water bath | |||
| Round Platinum 3mm Petri dish electrode | Protech International Inc | CUY700-P3E | electrode for whole embryo electroporation |
| Round Platinum 2mm cover electrode | Protech International Inc | CUY700-P2L | electrode for whole embryo electroporation |
| Humidified chamber | |||
| Dissecting microscope | |||
| Dissecting fluorescence microscope | |||
| Forceps | ` | ||
| Standard surgical scissors | |||
| CUY21-EDIT Square Wave Electroporator | Protech International | CUY21-EDIT | electroporator |
| Micropipette | Hamilton Company | ||
| Micromanipulator | |||
| Egg holder (nest) | modeling clay shaped on a 10cm petri dish | ||
| Dissecting probe | to window the egg | ||
| Parallel Fixed Needle Electrode | Protech International Inc | CUY610-P4.4 | 4mm Gap & Platinum 4mm Tip, electrode for electroporation of neural tube |
| Tungsten wire | Omega Engineering, Inc | W5W26-010 | Tungsten 5% Re vs. Tungsten 26% Re, 0.010, unsheathed, used to make fine cuts on embryo |
| Needle holder | |||
| Platinum Z-Shape Blunt Needle Electrode | Protech International Inc | CUY611-P7.4 | 7mm Length x 4mm Exposed Tip, electrode for electroporation of lateral plate mesoderm |
| 18 gauge needle | |||
| 10cc syringe | |||
| Scotch transparent tape | Office Depot | 305324 | |
| Neutral red solution 0.25% | Fisher Scientific | N12925 | to stain the embryo |
| Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline | Sigma aldrich | D5773 | Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline, Without sodium bicarbonate |
| Household bleach | for electrode cleaning | ||
| Fast green FGF (0.25%) | Specrtum Chemical Mfg Corp | FA105 | |
| Predicted regulatory region Plasmid | |||
| Reporter pasmid | Several options | The ptkEGFP was a kind gift from Uchikawa and Kondoh, but Adgene has a ptkRFP that could be used for the reporter and pCAG-GFP for the transfection control. | |
| TE buffer | Qiagen | included in Endofree Maxiprep Plasmid Kit | for dilution of DNA |
References
- Li, Y., Chen, L. Big biological data: challenges and opportunities. GPB. 12, 187-189 (2014).
- Howe, D., et al. Big data: The future of biocuration. Nature. 455, 47-50 (2008).
- Khoury, M. J. Genomics and Health Impact Blog. , (2014).
- Irie, N., Sehara-Fujisawa, A. The vertebrate phylotypic stage and an early bilaterian-related stage in mouse embryogenesis defined by genomic information. BMC Biol. 5 (1), (2007).
- Boffelli, D., Nobrega, M. A., Rubin, E. M. Comparative genomics at the vertebrate extremes. Nat Rev Genet. 5, 456-465 (2004).
- Noonan, J. P., McCallion, A. S. Genomics of long-range regulatory elements. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 11, 1-23 (2010).
- Woolfe, A., et al. Highly conserved non-coding sequences are associated with vertebrate development. PLoS Biol. 3, 7 (2005).
- Visel, A., et al. ChIP-seq accurately predicts tissue-specific activity of enhancers. Nature. 457, 854-858 (2009).
- Cotney, J., et al. Chromatin state signatures associated with tissue-specific gene expression and enhancer activity in the embryonic limb. Genome Res. 22, 1069-1080 (2012).
- Timmer, J., Johnson, J., Niswander, L. The use of in ovo electroporation for the rapid analysis of neural-specific murine enhancers. Genesis. 29, 123-132 (2001).
- Hamburger, V., Hamilton, H. L. A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J Morphol. 88, 49-92 (1951).
- Uchikawa, M. Enhancer analysis by chicken embryo electroporation with aid of genome comparison. Dev Growth Differ. 50, 467-474 (2008).
- Uchikawa, M., Takemoto, T., Kamachi, Y., Kondoh, H. Efficient identification of regulatory sequences in the chicken genome by a powerful combination of embryo electroporation and genome comparison. Mech. Dev. 121, 1145-1158 (2004).
- Oberg, K. C., et al. Efficient ectopic gene expression targeting chick mesoderm. Dev. Dyn. 224, 291-302 (2002).
- Pira, C. U., et al. . 15, 319-323 (2008).
- Ye, J., et al. Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinformatics. 13, 134 (2012).
- Frey, B. Amplification of genomic DNA by PCR. Methods Mol Med. 13, 143-156 (1998).
- Lorenz, T. C. Polymerase chain reaction: basic protocol plus troubleshooting and optimization strategies. J Vis Exp. (e3998), (2012).
- Uchikawa, M., Ishida, Y., Takemoto, T., Kamachi, Y., Kondoh, H. Functional analysis of chicken Sox2 enhancers highlights an array of diverse regulatory elements that are conserved in mammals. Dev. Cell. 4, 509-519 (2003).
- Lettice, L. A., et al. A long-range Shh enhancer regulates expression in the developing limb and fin and is associated with preaxial polydactyly. Hum Mol Genet. 12, 1725-1735 (2003).
- Smith, A. M., et al. Integration of Elf-4 into stem/progenitor and erythroid regulatory networks through locus-wide chromatin studies coupled with in vivo functional validation. Mol Cell Biol. 32, 763-773 (2012).
- Carlson, B. M. The preservation of the ability of cultured quail wing bud mesoderm to elicit a position-related differentiative response. Dev Biol. 101, 106-115 (1984).
- Hayamizu, T. F., Bryant, S. V. Retinoic acid respecifies limb bud cells in vitro. J Exp Zool. 263, 423-429 (1992).
- Suda, Y., et al. The same enhancer regulates the earliest Emx2 expression in caudal forebrain primordium, subsequent expression in dorsal telencephalon and later expression in the cortical ventricular zone. Development. 137, 2939-2949 (2010).
- Ros, M. A., et al. The chick oligozeugodactyly (ozd) mutant lacks sonic hedgehog function in the limb. Development. 130, 527-537 (2003).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved