A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Biaxial Mechanical Characterizations of Atrioventricular Heart Valves
In This Article
Summary
This protocol involves characterizations of atrioventricular valve leaflets with force-controlled, displacement-controlled, and stress-relaxation biaxial mechanical testing procedures. Results acquired with this protocol can be used for constitutive model development to simulate the mechanical behavior of functioning valves under a finite element simulation framework.
Abstract
Extensive biaxial mechanical testing of the atrioventricular heart valve leaflets can be utilized to derive optimal parameters used in constitutive models, which provide a mathematical representation of the mechanical function of those structures. This presented biaxial mechanical testing protocol involves (i) tissue acquisition, (ii) the preparation of tissue specimens, (iii) biaxial mechanical testing, and (iv) postprocessing of the acquired data. First, tissue acquisition requires obtaining porcine or ovine hearts from a local Food and Drug Administration-approved abattoir for later dissection to retrieve the valve leaflets. Second, tissue preparation requires using tissue specimen cutters on the leaflet tissue to extract a clear zone for testing. Third, biaxial mechanical testing of the leaflet specimen requires the use of a commercial biaxial mechanical tester, which consists of force-controlled, displacement-controlled, and stress-relaxation testing protocols to characterize the leaflet tissue's mechanical properties. Finally, post-processing requires the use of data image correlation techniques and force and displacement readings to summarize the tissue's mechanical behaviors in response to external loading. In general, results from biaxial testing demonstrate that the leaflet tissues yield a nonlinear, anisotropic mechanical response. The presented biaxial testing procedure is advantageous to other methods since the method presented here allows for a more comprehensive characterization of the valve leaflet tissue under one unified testing scheme, as opposed to separate testing protocols on different tissue specimens. The proposed testing method has its limitations in that shear stress is potentially present in the tissue sample. However, any potential shear is presumed negligible.
Introduction
Proper heart function relies on appropriate mechanical behaviors of the heart valve leaflets. In situations where heart valve leaflet mechanics are compromised, heart valve disease occurs, which may lead to other heart-related issues. Understanding heart valve disease requires a thorough understanding of the leaflets' proper mechanical behaviors for use in computational models and therapeutic development, and as such, a testing scheme must be developed to accurately retrieve the healthy leaflets' mechanical properties. In previous literature, this mechanical characterization has been conducted using biaxial mechanical testing procedures.
Biaxial mechanical testing procedures for soft tissues vary throughout the literature, with different testing frameworks utilized to retrieve different characteristics1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19. Testing methods have been extended for investigations of the mechanical characteristics of heart valve leaflets. In general, biaxial mechanical testing involves loading the heart valve tissue with simultaneous forces in the two principal directions, but how this testing is performed varies based on the biomechanical properties to be observed. Some of these testing protocols include (i) strain-rate, (ii) creep, (iii) stress-relaxation, and (iv) force-controlled testing.
First, strain-rate testing has been utilized to determine the time-dependent behaviors of the tissue leaflets18,20. In this testing protocol, leaflets are loaded to a maximum membrane tension at different half-cycle times (i.e., 1, 0.5, 0.1, and 0.05 s) to determine if there is a significant difference in peak stretch or hysteresis between loading times. However, these tests have demonstrated a negligible difference in the observed stretch with varying strain-rates. Second, in creep testing, the tissue is loaded to the peak membrane tension and held at peak membrane tension. This testing allows a demonstration of how the tissue's displacement creeps to maintain the peak membrane tension. However, it has been shown that the creep is insignificant for heart valve leaflets under physiologically functioning3,20. Third, in stress-relaxation testing, the tissue is loaded to the peak membrane tension and the associated displacement is held constant for an extended period of time3,21,22. In this type of testing, the tissue stress has a notable reduction from the peak membrane tension. Lastly, in force-controlled testing, tissues are cyclically loaded at various ratios of the peak membrane tension in each direction17,23. These tests reveal the material's anisotropy and nonlinear stress-strain response, and by loading the tissue under various ratios, potential physiologic deformations may be better understood. These recent investigations made it apparent that stress-relaxation and force-controlled protocols prove most beneficial to perform a mechanical characterization of heart valve leaflets. Despite these advances in heart valve biomechanical characterization, the testing has not been performed under one unified testing scheme, and there are limited methods to investigate the coupling between directions.
The purpose of this method is to facilitate a full material characterization of the heart valve leaflets by a unified biaxial mechanical testing scheme. A unified testing scheme is considered as one where each leaflet is tested under all testing protocols in one session. This is advantageous, as tissue properties are inherently variable between leaflets, so a full characterization for each leaflet proves more accurate as a descriptor than performing each protocol independently on various leaflets. The testing scheme consists of three main components, namely (i) a force-controlled biaxial testing protocol, (ii) a displacement-controlled biaxial testing protocol, and (iii) a biaxial stress-relaxation testing protocol. All testing schemes utilize a loading rate of 4.42 N/min, and 10 loading-unloading cycles to ensure stress-strain curve replicability by the 10th cycle (as found in previous work)23. All protocols are also constructed based on the membrane tension assumption, which requires that the thickness be less than 10% of the effective specimen lengths.
The force-controlled protocol used in this presented method consists of 10 loading and unloading cycles with peak membrane tensions of 100 N/m and 75 N/m for the mitral valve (MV) and tricuspid valve (TV), respectively15,17. Five loading ratios are considered in this force-controlled testing protocol, namely 1:1, 0.75:1, 1:0.75, 0.5:1, and 1:0.5. These five loading ratios prove useful in describing the stresses and strains correspondent to all potential physiologic deformations of the leaflet in vivo.
The displacement-controlled protocol presented in this method consists of two deformation scenarios, namely (i) constrained uniaxial stretching and (ii) pure shear. In the constrained uniaxial stretching, one direction of the tissue is displaced to the peak membrane tension while fixing the other direction. In the pure shear setup, the tissue is stretched in one direction and judiciously shortened in the other direction, so the area of the tissue remains constant under deformation. Each of these displacement-controlled testing procedures is performed for each of the two tissue directions (circumferential and radial directions).
The stress-relaxation protocol used in the presented method is achieved by loading the tissue to the peak membrane tension in both directions and holding the tissue at the correspondent displacements for 15 min to monitor the tissue's stress relaxation behavior. The detailed experimental procedures are discussed next.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All methods described were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at The University of Oklahoma. All animal tissues were acquired from a United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)-approved slaughterhouse (Country Home Meat Co., Edmond, OK).
1. Tissue acquisition and cleaning
- Retrieve the animal hearts on the same day as the animal is slaughtered and store the hearts in an ice chest to ensure the tissue freshness. Transport the hearts to the laboratory space.
- Upon arrival at the lab, submerge the heart in a bucket of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution to rinse off any excess blood. Retrieve forceps, a placemat, a surgical blade, a bucket of PBS solution, bleach, and a plastic bag. Prepare the placemat by laying it on the dissection counter, allowing for an easier cleanup of blood-related mess. After the heart has been sufficiently rinsed, place the heart on the placemat (Figure 1a).
- Using the forceps, locate the parting line between the atria and the ventricle on each side of the heart. Using a razor blade, carefully make an incision along this parting line and reveal the heart valves and the ventricles (Figure 1b). Make the incision along the entire outer circumference of the heart, such that the atria and all heart material superior to the ventricles may be removed.
- With the forceps, carefully pull out any observed blood clots in the ventricles (Figure 1c). If an attempt is made to remove a blood clot but it does not move, ensure the chordae tendineae or leaflets have not been grabbed. Place blood clots in the biohazard bag for waste disposal.
- When all blood clots have been removed from the ventricles, rinse the heart one final time in a bucket with PBS solution. Place the clean heart in the plastic bag and store it in a freezer.
- Using a solution of 10% bleach and 90% water, mix the blood with the bleach solution and stir continuously for approximately 10 min. Look for a successful bleach treatment, indicated by the solution transitioning from red to yellow. Dispose of the bleach-treated blood through drainage.
CAUTION: Bleach is a toxic substance and can be harmful if ingested.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here.
2. Heart dissection and examination of anatomy
- Retrieve the previously cleansed heart and allow it to thaw in a warm water bath. The required materials for dissection include forceps, surgical blades, placemats, PBS, and small storage containers. After the heart is completely thawed, put it on a placemat to absorb any remaining blood.
- Hold the heart for a top-down (superior) view to optimally observe the valve structures. Beginning with the MV on the left side of the heart, use forceps to carefully manipulate the leaflets and identify a commissure, or parting line, between the leaflets.
- Make an incision along the commissure and carefully cut through the ventricular wall, making sure not to damage the leaflets. It may be necessary to cut the chordal attachments during this process to fully open the ventricle. Once the full incision is made, open the ventricle (Figure 2a).
- Identify the MV anterior and posterior leaflets and use a surgical blade to sever the chordal attachments to the papillary muscles. Using forceps, stretch the leaflets taut and make cuts to separate the leaflets from the annulus. Place the excised leaflets in an appropriately labeled container filled with PBS solution and store it in a refrigerator at approximately 4 °C.
- Hold the heart for a top-down view and identify the TV on the right side of the heart. Locate the commissures and make an incision through one of the commissures and the ventricular wall (Figure 2b).
- Identify the TV septal, posterior, and anterior leaflets, and perform the leaflet extraction as done in step 2.4. Place all obtained leaflets in a labeled container filled with PBS solution and store the container in a refrigerator at approximately 4 °C.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here. However, tissue biomechanical testing and the subsequent histology analyses should occur within 2 days of the heart dissection.
3. Tissue dissection
- Retrieve a leaflet from the fridge, the tissue cutter for the specified sectioning size, a surgical pen, forceps, razor blades, and a cutting mat.
- Using forceps, remove the specimen from the PBS solution and lay it flat on the cutting mat with the radial direction (R) aligned to the Y-direction, and the circumferential direction (C) aligned to the X-direction (Figure 3a). Identify the leaflet’s central region as the testing section.
- Align the tissue cutter so that the desired tissue testing region is within the boundaries of the razor blades. Make one cut horizontally and another vertically to form a square region of the desired dimensions (Figure 3b). Using the surgical pen, label the tissue’s radial direction (Figure 3b).
- Using the razor blade, trim any chordal attachments by stretching the chordae from the leaflet with the forceps and making a careful cut without causing any damage to the leaflet.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here. If the protocol is paused, store the sectioned tissue in a labeled container filled with PBS solution, and store the container in a refrigerator at approximately 4 °C (as explained in step 2.6). However, tissue testing should occur within 2 days of the dissection.
4. Thickness measurement and biaxial tester setup
- Retrieve the sectioned tissue specimen, digital calipers, and a small metal spatula. Using the digital calipers, measure and record the thickness of the metal spatula.
- Using forceps, lay the tissue specimen flat on the metal spatula. Using the digital calipers, measure the thickness of the spatula-tissue pair (Figure 3c) at three different leaflet locations. Subtract the spatula’s thickness from each measurement and record the average thickness.
- Prepare a PBS bath at 37 °C, which corresponds to the tissue’s physiological conditions.
5. Tissue mounting and fiducial marker placement
- Retrieve forceps, the tissue specimen, mounting hardware, a fine-tipped tool, glass beads (with diameters of 300–500 µm), and super glue.
- Mount the tissue to the biaxial testing system (Figure 3d,e). While mounting, ensure that the tissue’s circumferential and radial directions are aligned with the machine’s X- and Y-directions.
- For the fiducial marker placement, place glass beads into one small open-faced container and a small pool of super glue in another container. Using the fine-tipped tool, coat the tip with a small amount of super glue and stick an individual bead to the tip of the tool.
- Carefully use the tool to transfer the bead to one corner of the middle third of the tissue’s testing region (Figure 3f). Repeat this step until a square array of four beads is formed (Figure 3g).
NOTE: It is crucial that excess glue is avoided, and that the fiducial markers do not stick together as later digital image correlation (DIC) techniques will produce useless tracking results. It is important that the square array must be within the middle third of the tissue’s testing region.
6. Preconditioning step and duration timing
- To compute the appropriate membrane tension, obtain the tissue’s effective testing edge length and use the following equation.
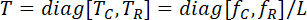 (1)
(1)
NOTE: Here, T is the membrane tension in a unit of force/length, f is the force, and L is the specimen’s effective testing length. - Create a preconditioning protocol so that the tissue will undergo 10 loading/unloading cycles at the forces associated with peak membrane tension at a loading rate of 4.42 N/min, including a preload of 2.5% of the maximum force (Figure 4).
- Create a new arbitrary testing directory to temporarily store the preconditioning data, because it is not necessary for future calculations. Establish a loading rate of 4.42 N/min for subsequent testing.
- Create a new set of testing parameters and set the name of the protocol as Preconditioning0 (Figure 4a). For the X- and Y-axes, set the control mode to be force and the control function to be step. Set the load magnitude as the force associated with targeted peak membrane tension (cf. step 6.1) (Figure 4b). Set the preload magnitude as 2.5% of the maximum force for the first repetition only (Figure 4c). Set the stretch duration and recovery duration both to be 25 s. Set the number of repetitions to be 10 (Figure 4e).
- When the preconditioning step finishes, make a note of the tissue’s deformation in the X- and Y-directions. Prepare a protocol to move the specimen to the maximum force, beginning from the recorded size.
- Retrieve a stopwatch for timing purposes. Begin the maximum force loading protocol and start the stopwatch simultaneously when the machine begins actuation (Figure 5a). Stop the stopwatch when the actuation stops. Stopping will be obvious through auditory cues.
- Record the post-preconditioning peak tissue deformation alongside the time from the stopwatch representing the tissue’s optimal stretch time (Figure 5b).
7. Biaxial mechanical testing
- Prepare a force-controlled protocol at a loading rate of 4.42 N/min.
- Open a new testing directory and name the test. Set the data to save to a known location for use in later stress and strain calculations. Move the specimen back to the original mounting configuration.
- Create a protocol set titled FirstImage. Set the X-axis and Y-axis control mode to force and the control function to step. Set the load magnitude to 0 mN. Set the stretch duration and recovery duration each to 1 second. Set the number of repetitions to 1. Set the data output frequency and image output frequency each to 1 Hz.
- Construct a new testing set, named PreconditioningA. Establish the testing parameters such that the tissue will undergo 10 repetitions of cyclic loading/unloading to the targeted force for the desired membrane tension exactly as was prepared in step 6.2. Note that now, the stretch time and recover time should be the time recorded in step 6.3.2. No images are captured in the A testing set, but data is captured at 15 Hz.
- Construct another testing set, named PreconditioningB. All testing parameters should be identical to those as mentioned in the previous step, with the exception that image output frequency is set to 15 Hz, and no preload is applied.
- After the preconditioning protocol, create testing protocols so that the tissue is loaded to the peak membrane tension in the following circumferential-to-radial loading ratios at a loading rate of 4.42 N/min: 1:1, 0.75:1, 1:0.75, 0.5:1, and 1:0.5 (Figure 6). Retrieve data from the last two cycles of each loading ratio for subsequent data processing and analyses described in section 10. Refer to Table 1 for a detailed description of the protocols to be established.
- Prepare a displacement-controlled testing protocol at a loading rate of 4.42 N/min as follows. (i) Biaxial stretching in the X-direction and Y-direction to the displacements associated with the peak circumferential and radial stretches, respectively (Figure 7a). (ii) Pure shear along the X-direction—stretching in the X-direction associated with the peak circumferential stretch and shortening in the Y-direction, while keeping the dashed area constant under deformation (Figure 7b). (iii) Constrained uniaxial stretching along the X-direction (Figure 7c). (iv) Pure shear along the Y-direction (Figure 7d). (v) Constrained uniaxial stretching along the Y-direction (Figure 7e).
- Between each of these steps, construct a rest “cycle” of 1 min that holds the tissue at the original mounted configuration. Retrieve data from the last two cycles of each loading ratio for data processing and analyses (section 9). Refer to Table 2 for a detailed description of the protocols to be established.
- Prepare a stress-relaxation protocol so that the tissue is loaded in each direction, at a loading rate of 4.42 N/min, to the displacements associated with the peak membrane tensions (step 7.2) and held at that displacement for 15 min (Figure 8 and Figure 9). After 15 min, the protocol should be set to recover the tissue to its original mounting configuration.
NOTE: In the case of tissue tearing, abort the test immediately to prevent any potential damage caused to the biaxial testing system.
8. Tissue fixation for histology analysis
- Unmount the tissue from the biaxial testing system. Place the tissue into a container filled with 10% formalin, and then place the container in a refrigerated environment at approximately 4 °C. Fix the tissue for 24–48 h, depending on the tissue’s thickness.
CAUTION: Formalin is a known carcinogen and, if breathed in, an excess may cause lungs to become fixed. All work with formalin should be performed in a fume hood with adequate ventilation. - After the tissue has been fixed in formalin for 24–48 h, transfer the tissue to an 80% ethanol solution for later histology. The tissue should be stored in solution in a refrigerated environment at 4 °C.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here. Once the tissues are fixed, the specimens can be analyzed at any time. If the protocol is paused, store the tissue in a labeled container filled with 80% ethanol, and store the container in a refrigerator at approximately 4 °C (as explained in step 8.2). - Prepare the tissue for commercial histology analysis as per the vendor’s instructions. If a certain leaflet constituent, such as collagen, elastin, glycosaminoglycans, etc., is of the study’s interest, ensure that the appropriate histology stain is employed.
NOTE: Histology slides may be visualized using a microscope to observe desired constituents (Figure 10). - Using the image processing program ImageJ, perform color deconvolution methods to determine the percentage of each stained constituent in the tissue. For more details on these procedures, please refer to Ruifrok and Johnston24.
9. Biaxial testing data post-processing procedures
- Perform DIC-based tracking on the four fiducial markers from the images taken during the biaxial mechanical testing (Figure 11) to determine the time-dependent marker positions.
 (2)
(2)
- If it is desired to perform the analysis with respect to the mounting configuration, let XI be the marker positions in the undeformed state at the beginning of the biaxial test. If it is desired to perform the analysis with respect to the post-preconditioning deformation, let XI be the marker positions at the end of the preconditioning protocol.
NOTE: The subsequent steps will be conducted in the same manner, regardless of the reference configuration chosen.
NOTE: Here, XI and xI are the undeformed and deformed positions of the markers, respectively, and dI is the displacement vector of each marker.
- If it is desired to perform the analysis with respect to the mounting configuration, let XI be the marker positions in the undeformed state at the beginning of the biaxial test. If it is desired to perform the analysis with respect to the post-preconditioning deformation, let XI be the marker positions at the end of the preconditioning protocol.
- Compute the deformation gradient (F) of the fiducial markers using a four-node bilinear finite element2,23,25.
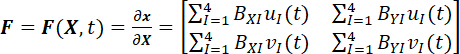 (3)
(3)
NOTE: Here, BxI’s and ByI’s are the finite element shape function derivatives in the X- and Y-directions for node I, respectively, and uI(t) and vI(t) are the time-dependent X- and Y-displacements, respectively, as previously determined from step 9.1. Note that the X- and Y- coordinates are aligned to the tissue’s circumferential and radial directions. - Compute the right Cauchy–Green deformation tensor (C) and the Green strain tensor (E).
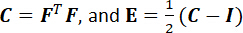 (4)
(4)
NOTE: Here, I is the second-order identity tensor. Determine the circumferential and radial stretches by taking the square roots of the principle values of C. - Determine the first Piola-Kirchhoff (1st-PK) stress tensor (P).
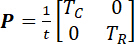 (5)
(5)
NOTE: Here, t is the specimen’s thickness, and TC and TR are the applied membrane tensions in the circumferential and radial directions, respectively. - Also, compute other stress tensors, such as the Cauchy stress tensor (σ) and the second Piola-Kirchoff (2nd-PK) stress tensor (S).
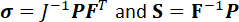 (6)
(6)
NOTE: Here, J is the Jacobian of the deformation gradient tensor F.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Stress-stretch data from the force-controlled biaxial mechanical testing reveals a nonlinear curve with some resemblance to an exponential curve (Figure 12). Regarding the response in each principal direction, the material behavior is transversely isotropic, with the radial stretch greater than the circumferential deformation. In some cases, the anisotropy's directions may flip, with the circumferential direction exhibiting greater compliance than the rad...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Critical steps for this biaxial mechanical testing include (i) the proper orientation of the leaflet, (ii) proper biaxial tester setup for negligible shear, and (iii) a careful application of the fiducial markers. The orientation of the leaflet is crucial to the obtained mechanical characterization of the leaflet tissue as the material is anisotropic in nature. Thus, the radial and circumferential directions need to be known for properly aligning the tissue specimens with the testing X- and Y-directions. It is also ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the American Heart Association Scientist Development Grant 16SDG27760143. The authors would also like to acknowledge the Mentored Research Fellowship from the University of Oklahoma's Office of Undergraduate Research for supporting both Colton Ross and Devin Laurence.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 10% Formalin Solution, Neutral Bufffered | Sigma-Aldrich | HT501128-4L | |
| 40X-2500X LED Lab Trinocular Compound Microscope | AmScope | SKU: T120C | |
| BioTester - Biaxial Tester | CellScale Biomaterials Testing | 1.5N Load Cell Capacity | |
| ImageJ | National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD | Version 1.8.0_112 | |
| LabJoy | CellScale Biomaterials Testing | Version 10.66 | |
| MATLAB | MathWorks | Version 2018b | |
| Phosphate-Buffered Saline | n/a | Recipe for 1L 1X PBS Solution: 8.0g NaCl, 0.2g KCl, 1.44g Na2HPO4, 0.24g KH2PO4 | |
| Single Edge Industrial Razor Blades (Surgical Carbon Steel) | VWR International | H3515541105024 | Razord blades for tissue retrieval and preparation procedures |
References
- May-Newman, K., Yin, F. Biaxial mechanical behavior of excised porcine mitral valve leaflets. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 269 (4), H1319-H1327 (1995).
- Billiar, K., Sacks, M. A method to quantify the fiber kinematics of planar tissues under biaxial stretch. Journal of Biomechanics. 30 (7), 753-756 (1997).
- Grashow, J. S., Sacks, M. S., Liao, J., Yoganathan, A. P. Planar Biaxial Creep and Stress Relaxation of the Mitral Valve Anterior Leaflet. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 34 (10), 1509-1518 (2006).
- Humphrey, J. D., Vawter, D. L., Vito, R. P. Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. Journal of Biomechanics. 20 (1), 59-65 (1987).
- Sacks, M. A method for planar biaxial mechanical testing that includes in-plane shear. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 121 (5), 551-555 (1999).
- Sacks, M., Chuong, C. Biaxial mechanical properties of passive right ventricular free wall myocardium. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 115 (2), 202-205 (1993).
- Stella, J. A., Sacks, M. S. On the biaxial mechanical properties of the layers of the aortic valve leaflet. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 129 (5), 757-766 (2007).
- Lanir, Y., Fung, Y. Two-dimensional mechanical properties of rabbit skin-II. Experimental results. Journal of Biomechanics. 7 (2), 171-182 (1974).
- Sun, W., Sacks, M. S., Sellaro, T. L., Slaughter, W. S., Scott, M. J. Biaxial mechanical response of bioprosthetic heart valve biomaterials to high in-plane shear. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 125 (3), 372-380 (2003).
- Sommer, G., Regitnig, P., Költringer, L., Holzapfel, G. A. Biaxial mechanical properties of intact and layer-dissected human carotid arteries at physiological and supraphysiological loadings. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 298 (3), H898-H912 (2009).
- Tong, J., Cohnert, T., Regitnig, P., Holzapfel, G. A. Effects of age on the elastic properties of the intraluminal thrombus and the thrombus-covered wall in abdominal aortic aneurysms: biaxial extension behaviour and material modelling. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 42 (2), 207-219 (2011).
- Billiar, K. L., Sacks, M. S. Biaxial mechanical properties of the natural and glutaraldehyde treated aortic valve cusp-Part I: Experimental results. Transactions-American Society of Mechanical Engineers Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 122 (1), 23-30 (2000).
- Jett, S., et al. Biaxial mechanical data of porcine atrioventricular valve leaflets. Data in Brief. 21, 358-363 (2018).
- Pham, T., Sun, W. Material properties of aged human mitral valve leaflets. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A. 102 (8), 2692-2703 (2014).
- Pierlot, C. M., Moeller, A. D., Lee, J. M., Wells, S. M. Biaxial creep resistance and structural remodeling of the aortic and mitral valves in pregnancy. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 43 (8), 1772-1785 (2015).
- Potter, S., et al. A Novel Small-Specimen Planar Biaxial Testing System With Full In-Plane Deformation Control. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 140 (5), 051001(2018).
- Khoiy, K. A., Amini, R. On the biaxial mechanical response of porcine tricuspid valve leaflets. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 138 (10), 104504(2016).
- Grashow, J. S., Yoganathan, A. P., Sacks, M. S. Biaixal stress-stretch behavior of the mitral valve anterior leaflet at physiologic strain rates. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 34 (2), 315-325 (2006).
- Huang, H. -Y. S., Lu, J. Biaxial mechanical properties of bovine jugular venous valve leaflet tissues. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology. , 1-13 (2017).
- Stella, J. A., Liao, J., Sacks, M. S. Time-dependent biaxial mechanical behavior of the aortic heart valve leaflet. Journal of Biomechanics. 40 (14), 3169-3177 (2007).
- Sacks, M. S., David Merryman, W., Schmidt, D. W. On the biomechanics of heart valve function. Journal of Biomechanics. 42 (12), 1804-1824 (2009).
- Sacks, M. S., Yoganathan, A. P. Heart valve function: a biomechanical perspective. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences. 362 (1484), 1369-1391 (2007).
- Jett, S., et al. An investigation of the anisotropic mechanical properties and anatomical structure of porcine atrioventricular heart valves. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 87, 155-171 (2018).
- Ruifrok, A. C., Johnston, D. A. Quantification of histochemical staining by color deconvolution. Analytical and Quantitative Cytology and Histology. 23 (4), 291-299 (2001).
- Sacks, M. S. Biaxial mechanical evaluation of planar biological materials. Journal of Elasticity. 61 (1), 199(2000).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved