A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Measurements of CO2 Fluxes at Non-Ideal Eddy Covariance Sites
In This Article
Summary
The presented protocol uses the eddy covariance method at non-typical locations, applicable to all types of short-canopy ecosystems with limited area, on a currently reforested windthrow site in Poland. Details of measuring site setup rules, flux calculations and quality control, and final result analysis, are described.
Abstract
This protocol is an example of utilizing the eddy covariance (EC) technique to investigate spatially and temporally averaged net CO2 fluxes (net ecosystem production, NEP), in non-typical ecosystems, on a currently reforested windthrow area in Poland. After a tornado event, a relatively narrow “corridor” was created within surviving forest stands, which complicates such kind of experiments. The application of other measuring techniques, such as the chamber method, is even more difficult under these circumstances, because especially at the beginning, fallen trees and in general great heterogeneity of the site provide a challenging platform to perform flux measurements and then to properly upscale obtained results. In comparison with standard EC measurements carried out in untouched forests, the case of windthrow areas requires special consideration when it comes to the site location and data analysis in order to ensure their representativeness. Therefore, here we present a protocol of real-time, continuous CO2 flux measurements at a dynamically changing, non-ideal EC site, which includes (1) site location and instrumentation setup, (2) flux computation, (3) rigorous data filtering and quality control, and (4) gap filling and net fluxes partitioning into CO2 respiration and absorption. The main advantage of the described methodology is that it provides a detailed description of the experimental setup and measurement performance from scratch, which can be applied to other spatially limited ecosystems. It can also be viewed as a list of recommendations on how to deal with unconventional site operation, providing a description for non-specialists. Obtained quality-checked, gap filled, half-hour values of net CO2, as well as absorption and respiration fluxes, can be finally aggregated into daily, monthly, seasonal or annual totals.
Introduction
Nowadays, the most commonly used technique in the atmosphere-land ecosystem carbon dioxide (CO2) exchange studies is the eddy covariance (EC) technique1. The EC method has been used for decades, and comprehensive descriptions of issues concerning all the methodological, technical and practical aspects have already been published2,3,4. Compared with other techniques used for similar purposes, the EC method allows for obtaining the spatially and temporally averaged net CO2 fluxes from automatic, point measurements that consider the contribution of all elements in complicated ecosystems, instead of laborious, manual measurements (e.g., chamber techniques) or the requirement of taking many samples1.
Among land ecosystems, forests play the most significant role in C cycling and many scientific activities have focused on investigating their CO2 cycle, carbon storage in woody biomass and their mutual relationships with changing climatic conditions by both direct measurement or modeling5. Many EC sites, including one of the longest flux records6, were set up above different types of forests7. Usually, the site location was carefully chosen before the measurements started, with the goal of the most homogenous and largest area possible. Although, in disturbed forest sites, such as windthrows, the number of EC measuring stations are still insufficient8,9,10. One reason is logistical difficulties in measuring site setup and, most of all, a small number of suddenly appearing locations. In order to obtain the most informative results at windthrow areas, it is crucial to start as soon as possible after such an incidental event, which may cause additional problems. In contrast to untouched forest sites, the EC measurements at windthrow sites are more challenging and can deviate from already established procedures3. Since some extreme wind phenomena create spatially limited areas, there is a need for a thoughtful measuring station location and careful data processing in order to derive as much reliable flux values as possible. Similar difficulties in EC method application have occurred (e.g., Finish studies performed above a long but narrow lake) where measured CO2 fluxes required rigorous data filtering11,12 in order to assure their spatial representativeness.
Hence, the presented protocol is an example of the use of the EC method at non-typical locations, designed not only for windthrow areas, but for all other types of short vegetation with the limited area (e.g., croplands situated between taller vegetation types). The biggest advantage of the proposed methodology is a general description of complicated procedures, requiring advanced knowledge, from the site location choice and instrumentation set up to the final outcome: a complete dataset of high-quality CO2 fluxes. The technical novelty of the measuring protocol is the use of a unique base construction for the EC system placement (e.g., tripod with a defined height that is a “mini- tower” with an adjustable, electrically operated mast, allowing changing the final height of sensors according to individual needs).
Protocol
1. Site location and instrumentation setup
- Choose a measuring site location in relatively homogeneous and flat terrain to meet basic requirements of the EC method. Avoid places with complicated landforms (depressions, slopes) or located near aerodynamic obstacles (e.g., surviving tree stands), which can distort the air flow.
- Check species composition and plant cover. Choose a place with the most similar characteristics: age and height of the main vegetation type.
- If possible, conduct some additional soil investigations, which help to choose homogeneous area. Compare soil types in a few locations (soil profiles), soil carbon and nitrogen content as well as moisture conditions (e.g., using regular grid for soil sampling). Avoid places with outstanding features in comparison with the average values from the soil investigation.
- Before deciding where to place the instruments, investigate prevailing wind directions (ideally for one year before site setup), or analyze data from the nearest meteorological station. If there are some restrictions regarding the extent of the area of interest, choose the location which is within prevailing wind sectors (upwind).
NOTE: In the case of Polish windthrow site, due to the shape of tornado path, it was decided to place the tower in the middle of its width dimension (ca. 400−500 m) and as far from neighboring, few-year-old pine plantation as possible in the east-west direction (ca. 200 m from the tower to their edges), since the prevailing wind direction was from north-west to south-west and from north-east to east (Figure 1). - Decide which EC system to use: open path or closed path (enclosed path = closed path with short intake tube) infrared gas analyzer (or two of them if possible). Each has advantages and disadvantages but in general, both are reliable to be used on a field. Use a three-dimensional (3D) orthogonal sonic anemometer. To use the EC method, high frequency measurements are required ― at least 10 Hz in the case of both instruments.
- Consider what kind of power supply is the most feasible to be used at the site (is there a power line nearby, solar panels or other power generator?). If there are no limitations, use the closed path (or enclosed) path gas analyzer.
NOTE: An open path system has much lower power consumption, but in harsh environments (very cold weather, icing, rainy locations) it would result in considerable loss of high-quality data. - Follow the rules to position both instruments relative to each other13. Avoid mounting any unnecessary elements close to the EC system, which can distort the air flow.
NOTE: An enclosed path analyzer (Table of Materials) and a 3D sonic anemometer (Table of Materials) were used in this experiment.
- Consider what kind of power supply is the most feasible to be used at the site (is there a power line nearby, solar panels or other power generator?). If there are no limitations, use the closed path (or enclosed) path gas analyzer.
- Once the location is chosen, place a tripod with a vertical pole (or another kind of base construction) to mount the EC system on top. Set the height of instruments considering two basic requirements: investigated surface roughness (in simplification the height of existing vegetation) and the area of influence (fetch/footprint ― the area “seen” by the EC system)4.
NOTE: At dynamically developing ecosystems, such as reforested windthrow site Tlen I, the change in instrument placement with time will be required to meet EC method requirements. As an alternative of a base construction for the EC system, an innovative infrastructure (i.e., “mini-tower”) was proposed here: an anchor aluminum construction (1.5-m-high rectangular truss (W x L) 1 m x 1.2 m) with a mast (triangular truss 30 cm x 30 cm x 30 cm) moving inside the structure along steel rails, powered by an electric motor.- First, mount both instruments of the EC system on a metal pole attached centrally to the mast. Remember to place the sonic anemometer at a perfectly vertical position. Tilt the gas analyzer slightly to allow rainwater to run off easily.
- Elevate instruments to a height twice the canopy height from the soil surface, and at least 1.5−2.0 m above the top of the canopy4. Make sure that the base construction is located in a way, which ensures that the investigated area extends at least 100 times the height of a sensor placement in each direction14.
- Remember to install lightning protection for a metal construction.
NOTE: To achieve maximal output from the EC measurement in Polish windthrow site (Tlen I), some compromises were made. The instruments were placed at the height of 3.3 m at the beginning of the experiment.
- For further computation and flux analysis, measure some auxiliary variables at the same time, including at least: air (Ta) and soil (Ts) temperature, relative humidity (RH) of the air, photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD), incoming solar radiation (Rg) and precipitation (P). Usually, at EC sites a great number of other variables are also obtained.
- Place radiation sensors (PPFD and Rg) to the south. Use a horizontal pole to move them away from the tripod. Check the view angle of the sensors and adjust the length of the pole and the mounting height to ensure that only the investigated surface is seen.
- Use air temperature and humidity sensors with radiation shields, mounted at a similar height as the EC system.
- Install tipping-bucket rain gauges (at least two) in relatively open spaces, near the EC tower, 1 m above the ground level. Bury soil temperature sensors at several different depths (three or more depending on the soil type). Remember to have some repetitions for each depth. Place some sensors at the shallowest possible level.
2. CO2 flux computation
- Use commercially available, free software (e.g., EddyPro15) for EC flux computation that includes correction applications.
NOTE: This software was selected due to its complexity, popularity and user-friendliness and is recommended especially for the non-experts. - First, create a new project and then in the project info tab, specify the raw data file format and choose metadata file. If raw data were obtained as “.ghg” files, the individual metadata file is already embedded, and no further action is required. In other cases, use alternative file option and type all information manually.
NOTE: The metadata file specifies the order of measured variables, their units and some additional information needed for flux computation. If any of the setup details or site characteristics change, remember to change it in the metadata section. - Go to the flux info tab, choose the dataset and output directories, specify the raw file name format and check the list of items for flux computation.
- Go to processing options tab and choose raw data processing settings.
- Choose the method for the correction of anemometers’ measurements (rotation method), which allows accounting for any misalignment of the sonic anemometer with respect to the local wind streamline15. Tick the first planar fit approach16 (suggested for non-ideal, heterogeneous locations).
- Choose the 0-1-2 type of flagging policy17 (the approach which presents results of a quality check procedure).
- Select the preferred footprint method (the area of the influence on measured fluxes) (e.g., the Kljun18 approach). Leave all other setting unchanged (default options).
NOTE: Here one can choose from the list of options regarding corrections to be applied, fluxes footprint calculation method or the structure of output files. Although, it is suggested not to change standard options during the preliminary run of the selected EC software, except for the ones listed here.
- In case of any problems/questions, use the question mark (?) button next to the option of interest to find out more. Remember that incorrect or missing information in one tab will prevent movement to another.
- Click Run an Advanced mode to start fluxes computation at the end. In case of using only default settings click Run an Express mode.
3. Filtering and quality control of fluxes
- Avoid data loss by using a regular maintenance plan. According to individual capabilities, clean sensors as frequently as possible using water or mild detergent.
- Carry out calibration of gas analyzers at least once every 6 months using CO2 standards (0 ppm and at least one other concentration, e.g., 360 ppm). A minimum of 24 h before each calibration, change CO2 and H2O absorbing agents (sodium hydroxide coated silica and magnesium perchlorate, respectively) that are present in two small bottles inside the sensor head.
NOTE: The calibration procedure is relatively easy and well described in the gas analyzer manual. In the software dedicated to LI-7200 and LI-7500, there is a tab, which contains all step-by-step guidelines of the whole process. In case of any difficulties, analyzers can always be sent for a factory calibration performed by the producer, but it requires sensor demounting and results in long gaps in the flux dataset. - Create a common file (e.g., .csv, .xlsx) that contains all results from the flux calculation software and auxiliary measurements. Make sure that corresponding 30-min averages (fluxes and meteorological variables) are measured at the exact same time.
NOTE: To simplify and speed up the filtering procedure, use additional programs (e.g., Matlab or free R software), depending on users’ skills, rather than work in a spreadsheet. - Perform all filtering steps described below (sections 3.5-3.7) on data from this file. Use either filtering tools in the spreadsheet (or embedded “if” function) or create custom filtering functions utilizing other software.
- Determine unfavorable weather conditions and instrument malfunctions.
- Use instrument’s performance indicators to filter out data subjected to errors due to gas analyzer contamination. For an enclosed-path analyzer, check the average signal strength (ASS) value given in the output file from the fluxes’ calculation software. Then, mark and discard all fluxes (co2_flux) measured below, e.g., ASS = 70% (10% higher threshold than suggested in the instrument’s manual).
- Optionally, set a constant range for fluxes, which allows exclusion of outliers (e.g., from -15 to 15 µmol∙m-2∙s-1 at Tlen I site). One of the possible ways to remove fluxes outside the normal range is to use a limit of 2−3 standard deviations from the mean flux value, calculated individually for each season.
NOTE: The authors do not strongly advise using an a priori range as done in the case of Tlen I site by non-specialist. The statistical approach is much more reliable and objective. - Discard fluxes measured during any rain events (or other type of precipitation); delete fluxes when P ≥ 0.1 mm.
- Account for inappropriate conditions for eddy covariance method application.
- Use results of the steady-state test and the well-developed turbulence test17,19 performed during fluxes computation in the software (see step 2.4.2). Discard flux data with poor quality (CO2 flag values: qc_co2_flux > 1) in the common results file.
- Use the nighttime period indicator (daytime = 0) given in the output file to filter out CO2 fluxes values measured at night. Plot all nighttime CO2 fluxes against corresponding friction velocity values (u* measured at the same time) and find the u* value at which these fluxes stopped increasing.
- Mark the obtained value as the friction velocity threshold (u*thr) to be used as a measure of insufficient turbulence conditions. Discard all CO2 fluxes with corresponding u* values < u*thr from the dataset
NOTE: The presented method for u*thr determination is the simplest but also the most subjective. There are few, more precise, complicated and reliable methods to define the friction velocity threshold21,22 than the simple visual inspection which can be used here. Also, it must be mentioned that at very heterogeneous sites defining u*thr might not be easy. Some other measures must be considered in such cases, which are well described in the literature3,4.
- Flux spatial representativeness constraints
- First, plot the wind rose, obtained from measurements or from the nearest meteorological station, on the map of investigated area. Specify which wind sectors should be excluded from the final analysis (due to the existence of any potential burden or different vegetation type than investigated). Use a custom method or utilize ready functions from other mathematical software (e.g., windRose function in R software).
- According to the estimation of crosswind integrated footprints chosen during fluxes computation (step 2.4.3), decide which footprint characteristic will be used for further analysis (x_10%, x_30%, x_50%, x_70% or x_90% level). To simplify, each 30-min footprint value provides information on what is the distance (upwind) to the edge of the area, from which the measured signal (flux) originated with a given probability level.
NOTE: Here footprint values representing 70% (x_70%) probability was chosen as the limit, since the highest possible 90% level in spatially limited sites results in going well beyond the area of investigation. - Choose wind direction sectors that are most representative of the measuring site. Do the same with the footprint values, bearing in mind that the furthest distance (the highest footprint value) cannot exceed the area of interest (Figure 1). Filter out flux values that do not meet both requirements.
NOTE: Since the windthrow Tlen I site was located between the forest stands that survived the tornado, only two sectors of wind direction were accepted as representative: 30−90° and 210−300°. Thus, all CO2 fluxes originated from the area beyond these sectors were excluded. Furthermore, the distance to the nearest burden (distorting air flow) or different ecosystem type (with different net CO2 exchange dynamics) in each direction should be the maximal footprint limit, although, it is recommended to decrease this value. At the centrally located Tlen I site, the distance to the surviving forest’s edges was ca. 200−250 m; therefore, the chosen footprint threshold was set to 200 m at most and applied equally in each direction.
4. Gap filling and net flux partitioning into CO2 respiration and absorption
- Choose the method for quality-checked CO2 flux gap filling and partitioning into absorption (gross primary production [GPP] fluxes) and respiration (ecosystem respiration [Reco] fluxes) from several commonly used approaches, which include three basic groups: process-based approach23,24, statistical methods25,26, and the use of neural networks27,28.
NOTE: Since the first two groups of methods (process-based and statistical approaches) are widely used among the scientific community, well described and discussed in the literature and in the case of the latter, recommended to be used in a global network of flux measurements sites (FLUXNET) and Integrated Carbon Observation System (ICOS) project (international initiatives aiming at trace gases monitoring, EC data collection and common processing protocols creation), the use of both was recommended here at the beginning. - As an example of the process-based approach, follow the procedure from the Fluxnet Canada Research Network (FCRN23,24).
- Select net CO2 fluxes (NEP) measured during nighttime periods as well as all flux values from outside the growing season. These are assumed to be entirely Reco fluxes.
NOTE: To differentiate between the nighttime and the daytime period, the PPFD threshold value can also be used (e.g., PPFD < 120 µmol∙m-2∙s-1 as a nighttime indicator29). Moreover, to estimate when the vegetation period starts and ends, a simple thermal method was used here: when the average daily air (at 2 m height) and soil temperature (at 2 cm depth) were greater than 0 °C, the beginning of the vegetation season was noted and ended when both temperatures fell below 0 °C again. In case of different vegetation species, a different temperature threshold should be used regarding plants physiology. The onset of photosynthetic activity is different for coniferous and deciduous trees, crops and grasses, which comes from the fact, that different vegetation species react differently to air temperature. - Using the temperature (T) of soil, air or the combination of the two, determine the relationship between temperature and Reco. Use any software that allows fitting non-linear functions to the data (e.g., Matlab software). In principal, choose the best fit regression model (use e.g., Akaike information criterion (AIC) to decide on the function which fits best to the data); although in practice, one of the most commonly utilized functions is a Lloyd-Taylor30 model:

where Reco is the ecosystem respiration flux value,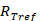 is the respiration rate in a reference temperature, Tref is the reference temperature, T is the measured air or soil temperature, T0 is the temperature which is a threshold for biological activity to initiate (estimated parameter of the model), and E0 is the parameter describing activation energy.
is the respiration rate in a reference temperature, Tref is the reference temperature, T is the measured air or soil temperature, T0 is the temperature which is a threshold for biological activity to initiate (estimated parameter of the model), and E0 is the parameter describing activation energy.
NOTE: In the case of FCRN procedure, some of these variables are set in advance: Tref and E0, which in case of Tlen I windthrow site were equal to 283.25 K and 309 K, respectively. Some studies suggest the use of soil temperature measured at the shallowest depth for the Reco vs. T relationship25, which for a short vegetation seemed to be the best choice, since a great part of emission comes from the heterogenic respiration from the soil and roots. Unlike in tall forest, the autotrophic respiration of foliage, branches and boles, driven by air temperature, does not play a major role (if present). - Using the obtained Reco vs T regression function, fill the gaps in nighttime and non-growing season NEP fluxes and calculate the function value for missing fluxes using corresponding temperature measurements. Note that in these cases Reco = NEP, and GPP = 0. The same function with daytime temperatures will give daytime Reco fluxes for each half-hour value.
- Calculate GPP values according to the equation: GPP = NEP + Reco for each available NEP flux during daytime in the growing season or set to zero during nighttime and the non-growing season. Then, find the relationship between PPFD and GPP fluxes. Use any software that allows fitting non-linear functions to the data. Again, there is one widely used equation to achieve such relationship- rectangular hyperbola of Michaelis-Menten, here in a modified form26:
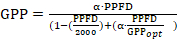
where GPP is the 30-min averaged gross primary production flux value, α is the ecosystem quantum yield, and GPPopt is the GPP flux rate at an optimum PPFD (2000 µmol∙m-2∙s-1).
NOTE: Use the obtained function to model GPP values for measured daytime, growing season NEP fluxes values. - At the end of the whole procedure, use modelled GPP and Reco fluxes to calculate missing NEP fluxes values as follows: NEP = GPP - Reco.
NOTE: Some small gaps (a few missing fluxes) can be filled with a simple linear regression function, a moving mean approach or other statistical methods before entering the models. The gaps in ancillary variables (temperature, solar radiation) must be filled before entering the models. Thus, the multiplied measurement of the same or surrogate variables are useful, helping to avoid big gaps in datasets.
- Select net CO2 fluxes (NEP) measured during nighttime periods as well as all flux values from outside the growing season. These are assumed to be entirely Reco fluxes.
- To fill the gaps not only in the CO2 but also other EC flux values (sensible and latent heat), as well as in the important meteorological elements, use the ReddyProc25 online tool (available also as an R software package).
NOTE: In contrast to the previous method, first missing NEP fluxes are filled and then each half-hour net flux is partitioned into GPP and Reco. The type of model used for Reco fluxes partitioning is the same as in the previous technique.- To use an online tool, prepare data according to the rules concerning their format and order. The data needed include 30-min averages of net CO2 (NEP), latent heat (LE) and sensible heat (H) fluxes, water vapor deficit (VPD) and friction velocity values calculated using EC measurements, as well as soil or air temperature (Tair or Tsoil), incoming solar radiation (Rg) and relative humidity of the air (RH).
- Go to the Processing page and fill all needed information regarding the measuring site (name, coordinates, altitude, time zone).
- Decide whether to estimate u* threshold additionally with this software (see steps 3.6.2 and 3.6.3), which method to use and for which period of time: the whole year or separately for each season.
- Select one or both methods for net fluxes partitioning (nighttime-25 or daytime-based31) and run the computation process.
- Compare obtained results in terms of both method performances in NEP flux gap filling and partitioning by creating artificial gaps in NEP, and check how precisely they were modeled.
- Calculate daily, monthly and annual totals of all gap filled CO2 fluxes including NEP, GPP, and Reco, on the basis of which the changes of ecosystem functioning can be traced. Use the users’ own function to aggregate these fluxes separately into the chosen time domain and sum up all values.
NOTE: At the Tlen I windthrow site, annual totals, as well as monthly fluxes allowed to analyze not only net CO2 exchange dynamics but also post-disturbance recovery mechanisms of the managed forest.
Results
One of the crucial steps in flux filtering and quality control at non-ideal EC sites is the assessment of the measured fluxes’ spatial representativeness. The simplest way to perform such analysis, given the fact that calculations were done using commercial, widely applied software, is to include measurements from desired area only, on the basis of wind direction and footprint estimations (see section 3.7). Thus, the wind rose plot, with a chosen wind direction and maximal acceptabl...
Discussion
This protocol presents the eddy covariance (EC) method to be used at non-ideal sites (here a reforested windthrow site): site location and measuring infrastructure setup, net CO2 fluxes computation and post-processing, as well as some issues regarding gap filling and fluxes partitioning procedures.
Even though the EC technique is commonly used at many measuring sites around the world, most of them are non-disturbed ecosystems, where the design and the following data processing can b...
Disclosures
The authors would like to mention, that presented protocol is mostly a simplification of a well-known and widely described issues regarding EC measurements. All sufficient references were given when required. Our main aim was to promote the use of this method, as well as our new and unique adjustable, electrically operated mast for EC measurements, among non-specialists with a step-by-step approach. We hope, that it makes it easier to realize and imagine that however strict requirements need to be met, EC technique can be satisfactorily applied also in non-typical, spatially limited ecosystems. With already broad literature concerning EC theory and methodology, presented protocol can potentially also be an encouragement to further knowledge acquisition on this subject.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by funding from General Directorate of the State Forests, Warsaw, Poland (project LAS, No OR-2717/27/11). We would like to express our gratitude to the entire research group from the Department of Meteorology, Poznan University of Life Sciences, Poland, involved in this protocol implementation and their help during creating its visual version.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Adjustable mast with metal rails and electric engine (24 V) | maszty.net | - | Alternative basic construction. To be designed and made by professionals |
| EddyPro | LI-COR, Inc. | ver. 6.2.0. | Free commercial software for fluxes calculation. Available on a website: https://www.licor.com/env/products/eddy_covariance/software.html, on request |
| Enclosed-path infrared gas analyzer | LI-COR, Inc. | LI-7200 | One of two instruments of the eddy covariance system (EC) used for CO2 fluxes measurements. Other types of fast analyzers (>10Hz sampling frequency) can be used |
| REddyProc | - | - | Free software for EC fluxes gap filling and partitioning. Available on Max Planck Institute for Biogeochmistry: https://www.bgc-jena.mpg.de/bgi/index.php/Services/REddyProcWeb. Both online tool and R package are provided. |
| Short aluminum tower base with concrete foundation | maszty.net | - | Alternative basic construction (pioneering solution). To be designed and made by professionals |
| Sonic anemometer | Gill Instruments | Gill Windmaster | One of two instruments of the eddy covariance system (EC) used for wind speed measurements. Other types of three-dimensional sonic anemometers can be used |
| Stainless-steel tripod | Campbel Scientific, Inc. | CM110 10 ft | The basic construction for eddy covariance (EC) system. Can be constructed by yourself- materials to be found in a hardware store |
| Sunshine sensor | Delta-T Devices Ltd. | BF5 | One of the exemplary instruments for photosynthetic photon flux density measurements (PPFD). To be bought from several commercial companies. Remember to place it above the canopy, far from reflective surfaces. |
| Thermistors | Campbel Scientific, Inc. | T107 | One of the exemplary instruments for soil temperature measurements. To be bought from several commercial companies. It is advisable to have a profile of soil temperature |
| Thermohygrometer | Vaisala Oyj | HMP155 | One of the exemplary instruments for air temperature and humidity measurements. To be bought from several commercial companies. Remember to place it inside radiation shield at similar height as the EC system. |
References
- Baldocchi, D. Measuring fluxes of trace gases and energy between ecosystems and the atmosphere - the state and future of the eddy covariance method. Global Change Biology. 20, 3600-3609 (2014).
- Aubinet, M., et al. Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of European forests: the EUROFLUX methodology. Advances in Ecological Research. 30, 113-174 (2000).
- Aubinet, M., Vesala, T., Papale, D. . A practical guide to measurements and Data Analysis. , (2012).
- Burba, G. . Eddy Covariance Method for: Scientific, Industrial, Agricultural, and Regulatory Applications. A Field Book on Measuring Ecosystem Gas Exchange and Areal Emission Rates. , (2013).
- Pan, Y., et al. A Large and Persistent Carbon Sink in the World’s Forests. Science. 333, 988-993 (2011).
- Wofsy, S. C., et al. Net exchange of CO2 in a midlatitude forest. Science. 260 (5112), 1314-1317 (1993).
- Luyssaert, S., et al. CO2 balance of boreal, temperate, and tropical forests derived from a global database. Global Change Biology. 13, 2509-2537 (2007).
- Knohl, A., et al. Carbon dioxide exchange of a Russian boreal forest after disturbance by wind throw. Global Change Biology. 8, 231-246 (2002).
- Lindauer, M., et al. Net ecosystem exchange over a non-cleared wind-throw-disturbed upland spruce forest-Measurements and simulations. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. 197, 219-234 (2014).
- Schulze, E. D., et al. Productivity of forests in the Eurosiberian boreal region and their potential to act as a carbon sink - a synthesis. Global Change Biology. 5, 703-722 (1999).
- Mammarella, I., et al. Carbon dioxide and energy fluxes over a small boreal lake in Southern Finland. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences. 120, 1296-1314 (2015).
- Vesala, T., et al. Eddy covariance measurements of carbon exchange and latent and sensible heat fluxes over a boreal lake for a full open water period. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences. 111, 1-12 (2006).
- Burba, G., Anderson, D. . A brief practical guide to Eddy Covariance Flux Measurements. Principles and workflow examples for scientific and industrial applications. , (2010).
- Businger, J. Evaluation of the accuracy with which dry deposition could be measured with current micrometeorological techniques. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology. 25, 1100-1124 (1986).
- . Eddy Pro Software Instruction Manual Available from: https://www.licor.com/documents/1ium2zmwm6hl36yz9bu4 (2017)
- Wilczak, J. M., Oncley, S. P., Stage, S. A. Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Boundary-Layer Meteorology. 99, 127-150 (2001).
- Foken, T., Lee, X., et al. Post-field quality control. Handbook of Micrometeorology: A Guide for Surface Flux Measurements. , (2004).
- Kljun, N., Rotach, M. W., Schmid, H. P. A three-dimensional backward Lagrangian footprint model for a wide range of boundary-layer stratifications. Boundary Layer Meteorology. 103, 205-226 (2002).
- Foken, T., Wichura, B. Tools for quality assessment of surface-based flux measurements. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. 78, 83-105 (1996).
- Mauder, M., Foken, T. Impact of post-field data processing on eddy covariance flux estimates and energy balance closure. Meteorologische Zeitschrift. 15, 597-609 (2006).
- Gu, L., et al. Objective threshold determination for nighttime eddy flux filtering. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. 128 (3-4), 179-197 (2005).
- Papale, D., et al. Towards a standardized processing of Net Ecosystem Exchange measured with eddy covariance technique: algorithms and uncertainty estimation. Biogeosciences. 3 (4), 571-583 (2006).
- Barr, A. G., et al. Interannual variability in the leaf area index of a boreal aspen-hazelnut forest in relation to net ecosystem production. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. 126, 237-255 (2004).
- Krishnan, P., Black, T. A., Jassal, R. S., Chen, B., Nesic, Z. Interannual variability of the carbon balance of three different-aged Douglas-fir stands in the Pacific Northwest. Journal of Geophysical Research. 114, 1-18 (2009).
- Reichstein, M., et al. On the separation of net ecosystem exchange into assimilation and ecosystem respiration: Review and improved algorithm. Global Change Biology. 11, 1424-1439 (2005).
- Falge, E., et al. Gap filling strategies for defensible annual sums of net ecosystem exchange. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. 107, 43-69 (2001).
- Ooba, M., Hirano, T., Mogami, J. I., Hirata, R., Fujinuma, Y. Comparisons of gap-filling methods for carbon flux dataset: A combination of a genetic algorithm and an artificial neural network. Ecological Modelling. 198, 473-486 (2006).
- Papale, D., Valentini, R. A new assessment of European forests carbon exchanges by eddy fluxes and artificial neural network spatialization. Global Change Biology. 9, 525-535 (2003).
- Baldocchi, D. D., Vogel, C. A., Hall, B. Seasonal variation of carbon dioxide exchange rates above and below a boreal jack pine forest. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. 83, 147-170 (1997).
- Lloyd, J., Taylor, J. On the Temperature Dependence of Soil Respiration. Functional Ecology. 8, 315-323 (1994).
- Lasslop, G., et al. Separation of net ecosystem exchange into assimilation and respiration using a light response curve approach: critical issues and global evaluation. Global Change Biology. 16, 187-208 (2010).
- Kljun, N., Calanca, P., Rotach, M. W., Schmid, H. P. A simple two-dimensional parameterisation for Flux Footprint Prediction (FFP). Geoscientific Model Development. 8, 3695-3713 (2015).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved