A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Measuring Neural Mechanisms Underlying Sleep-Dependent Memory Consolidation During Naps in Early Childhood
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes methods used to examine neural mechanisms underlying sleep-dependent memory consolidation during naps in early childhood. It includes procedures for examining the effect of sleep on behavioral memory performance, as well as the application and recording of both polysomnography and actigraphy.
Abstract
Sleep is critical for daily functioning. One important function of sleep is the consolidation of memories, a process that makes them stronger and less vulnerable to interference. The neural mechanisms underlying the benefit of sleep for memory can be investigated using polysomnography (PSG). PSG is a combination of physiological recordings including signals from the brain (EEG), eyes (EOG), and muscles (EMG) that are used to classify sleep stages. In this protocol, we describe how PSG can be used in conjunction with behavioral memory assessments, actigraphy, and parent-report to examine sleep-dependent memory consolidation. The focus of this protocol is on early childhood, a period of significance as children transition from biphasic sleep (consisting of a nap and overnight sleep) to monophasic sleep (overnight sleep only). The effects of sleep on memory performance are measured using a visuospatial memory assessment across periods of sleep and wakeful-rest. A combination of actigraphy and parent report is used to assess sleep rhythms (i.e., characterizing children as habitual or non-habitual nappers). Finally, PSG is used to characterize sleep stages and qualities of those stages (such as frequencies and the presence of spindles) during naps. The advantage of using PSG is that it is the only tool currently available to assess sleep quality and sleep architecture, pointing to the relevant brain state that supports memory consolidation. The main limitations of PSG are the length of time it takes to prepare the recording montage and that recordings are typically taken over one sleep bought. These limitations can be overcome by engaging young participants in distracting tasks during application and combining PSG with actigraphy and self/parent-report measures to characterize sleep cycles. Together, this unique combination of methods allows for investigations into how naps support learning in preschool children.
Introduction
Given sleep's prevalence in our daily routine, it is important to understand its function. Studies with this objective require precise measurement of sleep. Polysomnography (PSG) is the gold-standard measure of sleep. PSG allows for objective, quantitative measurement of sleep with high temporal resolution and can be useful for both research and clinical purposes. PSG is a combination of physiological recordings. At minimum, a PSG montage includes the following measures: electroencephalography (EEG), electrooculography (EOG), and electromyography (EMG). These measures assess electrical potentials from the brain, the eyes, and muscles respectively, and allow for classification of sleep stages (see Figure 1). Other measures, such as electrocardiography (ECG), respiration, and pulse oximetry may be included to identify the presence of disordered sleep.
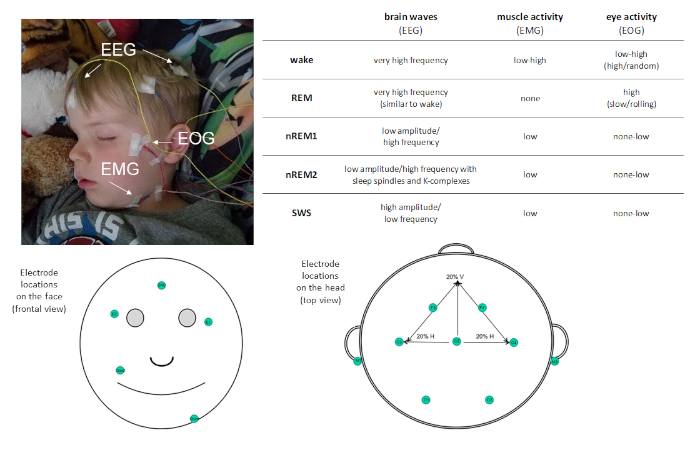
Figure 1: Example electrode placement and description of activity recorded via PSG. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
PSG allows sleep to be characterized into four distinct sleep stages: non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) stage 1 (nREM1; 4−7 Hz), non-REM stage 2 (nREM2; 12−15 Hz), and non-REM stage 3 (more commonly known as slow wave sleep [SWS]; 0.5−4 Hz), and rapid-eye movement (REM) sleep. nREM1 marks sleep onset, and is identified based on reduced muscle tone in the EMG recoding and mixed amplitude EEG oscillations relative to the alpha observed in resting wake. This is followed by nREM2, which can be distinguished by the presence of sleep spindles (short bursts of sigma frequency activity; 11−16 Hz) and K-complexes (single slow-waves that stand out from the surrounding activity) in the EEG. SWS is characterized by distinct slow-frequency high-amplitude EEG oscillations. REM sleep is characterized by fast low-amplitude oscillatory brain activity very similar to that observed during wake. However, what distinguishes REM sleep from wake is that it is also characterized by phasic rapid eye movements (hence the moniker REM) and muscle atonia. Over the course of a sleep bout, sleep stages are experienced cyclically, at a rate of about 90 min/cycle.
Sleep also follows the circadian rhythm, with sleep bouts taking place in 24-h cycles. Sleep timing and consistency may influence sleep function and are also important to assess. Although PSG is necessary to characterize sleep stages, it is time-consuming to apply and therefore not ideal for assessing multiple sleep bouts (e.g., multiple nights of sleep, naps and overnight sleep). For this, actigraphy is beneficial. Actigraphy uses a tri-axial accelerometer, typically on the wrist, to estimate sleep based on the absence of movement. Although actigraphy cannot be used to characterize sleep stages, it has been shown to be reliable at detecting sleep onset and wake onset (including sleep fragmentation or wake after sleep onset) in a range of populations from infants1 to older adults2. Both PSG and actigraphy are preferred methods over self/parent-report measures. Self/parent-report measures are easy to administer and relatively inexpensive, however, they are also subject to bias and non-compliance. Finally, it is worth noting that these methods can be used in combination to capitalize on the strengths of each. For example, PSG can be combined with actigraphy and/or self/parent-report to obtain both overnight sleep quality as well as verification of sleep quantities or sleep-wake cycles, especially over long durations (e.g., weeks or months).
One function of sleep that has garnered particular interest is sleep-dependent memory consolidation, the processing of memories that leaves them stronger and less vulnerable to interference3. Although memory consolidation can take place during wake in children4 and adults5, there is substantial evidence that consolidation is enhanced during sleep. Past research has provided behavioral examples of sleep-dependent memory consolidation by comparing changes in memory performance following an interval of sleep (e.g., 8 pm−8 am) to changes following an equivalent interval spent awake (e.g., 8 am−8 pm). In adults, memories are protected6 or even enhanced7 following an interval of sleep while memories typically decay over an equivalent interval of wake. Controls have been employed that dissociate performance changes from circadian influences8,9,10. For example, similar benefits of sleep are observed when comparing performance over a mid-day nap to an equivalent mid-day wake period9.
Although sleep was once thought to reflect a passive process, simply protecting memories from decay or interference, modern theories suggest sleep plays a more active role and actually promotes memory through reactivations11,12,13. Support for this comes from observed correlations between behavioral measures of memory consolidation over sleep (change in memory recall after sleep compared to before sleep) and specific aspects of sleep physiology. For many declarative memory tasks, memory consolidation is associated with aspects of non-REM sleep, specifically measures of SWS or sleep spindles found in nREM2 and SWS. If sleep's role was passive protection from interference, such a correlation would not be expected; rather a correlation between time asleep (regardless of sleep stage) and performance would be expected, as more time asleep would provide more protection from interference14.
Additional support for the active role of SWS in memory consolidation is evident in studies of targeted memory reactivation. In these studies, a memory is learned in the context of a perceptual cue, for instance an odor, and recall of the memory is greater following sleep if the cue is re-presented during sleep, SWS in particular15. Although the underlying mechanism is debated16,17, one prominent theory, systems consolidation theory, contends that memories encoded in the hippocampus are stabilized in the cortex though hippocampal-neocortical dialogue. Specifically, cortical slow waves and sleep spindles, occurring in conjunction with hippocampal ripples associated with memory reactivation, support the memory transfer3.
The role of sleep in memory consolidation during development is less clear. Early childhood is a period of particular interest as children begin to transition from a biphasic (consisting of a mid-day nap and an overnight sleep bout) to a monophasic sleep pattern. Recent research suggests that this transition may reflect brain maturation18. This argument is consistent with empirical data showing developmental changes in overnight sleep (i.e., topography of slow wave activity) mirrors that of cortical maturation19.
Although there are several behavioral demonstrations of overnight sleep-dependent consolidation in children20,21 and infants22, research on the neural underpinnings of memory consolidation with mid-day sleep are just beginning to be investigated. In ground-breaking work examining the role of mid-day naps on memory in preschool children, naps were shown to protect memories of recently learned information, whereas memory was reduced (by ~12%) when children stayed awake during the nap interval23. This "nap benefit" was greatest in children who napped habitually (i.e., 5 or more times per week as measured with actigraphy) regardless of their age. By recording PSG during the nap, the change in memory performance across the nap period was found to be specifically associated with sleep spindle density (the number of sleep spindles per minute of nREM), suggesting nap quality (not quantity) was a critical factor in promoting memory retention (see the representative results section).
This study highlights the significance of PSG in exploring relations between sleep and memory during development. It points to the importance of characterizing sleep macro- (sleep stages) and micro- (qualities of those stages such as frequencies and the presence of spindles) structures during naps for memory consolidation. It also highlights the importance of assessing sleep rhythms (characterizing children as habitual or non-habitual nappers). Although our work has characterized the function of naps in visuospatial learning (and more recently emotional24 and procedural25 learning), many questions remain. For instance, it will be important to examine other declarative memory tasks to assess the generalizability of these findings and to assess tasks used in preschool classrooms to understand specific parameters (e.g., amount of nap benefit relative to learning) for ecologically valid tasks. Additional work will also be necessary to understand when wake is sufficient for memory consolidation. Thus, our objective is to demystify the process of measuring sleep and sleep-dependent memory consolidation in children. We provide practical tips for examining the benefit of an afternoon nap on declarative memory in typically developing preschoolers (approximately 3 to 4 years of age) using a computerized visuospatial memory task as well as methods for assessing nap habituality using actigraphy, parent-report, and nap physiology using PSG. Although these methods were developed for preschool age children who nap with varying frequency, these methods could be adapted to any age group.
Protocol
Prior to beginning any research procedures, written consent should be obtained from the parent and verbal consent should be obtained from the child for all study procedures.
NOTE: See Figure 2 for an overview of the procedures.
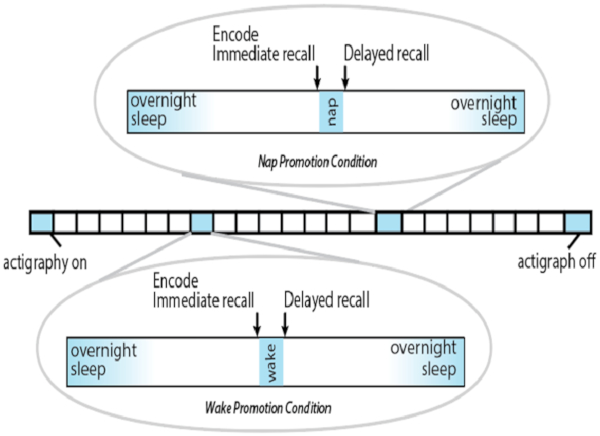
Figure 2: Overview of protocol. Each square represents one day. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
1. Nap promotion condition
- Ensure that the nap promotion condition is counterbalanced with the wake promotion condition across participants as discussed below.
- Schedule the nap promotion condition to begin approximately one hour before the child's typical nap period to allow time to apply PSG and to conduct the visuospatial memory task. Ensure that the time between immediate and delayed recall are the same between the wake promotion and nap promotion conditions.
- Explain the procedures for this session to children and parents using age-appropriate materials.
NOTE: Age appropriate materials include story books or short videos of another child undergoing the same procedures. - Apply polysomnography equipment (see section 3).
- Conduct the encoding and the immediate memory assessment for the visuospatial memory task (see section 4).
- Have the child use the restroom and then initiate the child's typical pre-nap routine.
- Allow the parent/caregiver to put the child to sleep as they usually would. Interfere as little as possible because most children fall asleep faster when provided with their normal routine.
- Allow the child to nap utilizing their typical nap location.
- Utilize nap promotion techniques, but only when necessary as these have proven less successful in the home if they deviate too far from the child's normal routine.
NOTE: Nap promotion techniques include using a weighted blanket, rubbing the participant's back, wrapping the child in a blanket (similar to swaddling), progressive muscle relaxation, and playing soothing music.
- Ensure that the amount of time the child sleeps in the nap promotion condition matches the amount of time they play in the wake promotion condition.
NOTE: If the nap promotion condition is first, allow the child to wake up naturally and use this duration to set the duration of the awake session. If the wake promotion condition is first, use this duration to determine the length of the nap. If the nap exceeds this time, wake the child as naturally as possible by opening the door, walking around outside the bedroom, and gradually speaking louder. - Conduct the delayed recall assessment for the visuospatial memory task, approximately 15−30 min after the child wakes to avoid sleep inertia.
- Collect child and experimenter rating for Visual Sleepiness Scale (VSS)26 and Visual Mood Scale (VMS)27.
- Remove PSG electrodes.
2. Wake promotion condition
- Ensure that the wake promotion condition is counterbalanced with the nap promotion condition discussed above.
- Schedule the wake promotion condition to begin approximately one hour before the child's typical nap period to equate time of day across conditions. Ensure that the time between immediate and delayed recall are approximate the same between the wake promotion and nap promotion conditions.
- Explain the procedures for this session to children and parents using age-appropriate materials.
- Apply PSG electrodes (see section 3) in order to equate the wake and nap promotion conditions.
NOTE: Although sleep is not expected, this equates conditions and can be used to verify the absence of sleep if in doubt. - Conduct the encoding and the immediate memory assessment for the visuospatial memory task (see section 4).
- Have the child use the restroom and then proceed to the location that they typically nap.
- Do not allow the child to nap, instead, have the child play quietly with non-stimulating toys in the same location as their typical nap.
NOTE: Acceptable non-stimulating toys include small sensorimotor toys such as wax sticks and age-appropriate interlocking plastic bricks. - Have the child play for their typical nap length or for the time they slept during the nap promotion condition (see step 1.7 for additional information).
- Record any unusual activity such as talking, leaving the room, and playing with toys that are not provided.
- Do not allow the child to nap, instead, have the child play quietly with non-stimulating toys in the same location as their typical nap.
- Ensure that the amount of time the child sleeps in the nap promotion condition matches the amount of time they play in the wake promotion condition.
- Conduct the delayed recall assessment for the visuospatial memory task, approximately 15−30 min after the child is finished playing in order to keep delay time similar between conditions.
- Collect child and experimenter rating for VSS26 and VMS27.
- Remove PSG electrodes.
3. Polysomnography (PSG)
- Preparation
- Facilitate PSG electrode application by having the child engage in a quiet activity such as reading a book, playing with playdough, eating a snack if they are hungry, or watching a short movie.
NOTE: If a movie is used, ensure that the movie is age appropriate but does not elicit rowdiness in the child (e.g., popular child-friendly animated films or shows). - Accessibility to a parent or guardian is not required. However, for shy and tentative children ensure that trusted caregivers are available.
NOTE: For a small number of children, parents and guardians may be distracting instead of helpful. If this is the case, ask the parent if they would be willing to step out of the child's sight.
- Facilitate PSG electrode application by having the child engage in a quiet activity such as reading a book, playing with playdough, eating a snack if they are hungry, or watching a short movie.
- Collect head measurements.
- Use a flexible tape measure and china marker to mark locations for subsequent electrode application.
- Measure the distance from the inion to nasion and place a mark at the halfway point. Measure the distance from preauricular notch in one ear to the preauricular notch in the other ear and place another mark at the halfway point. The intersection of these two marks is the "Reference" point (CZ).
- Measure 10% of the inion to nasion distance up from the inion. Then measure out 10% of the preauricular notch to preauricular notch measurement from this point on either side. Make two marks, one on each side (O3 and O4).
- Measure 20% of the preauricular notch to preauricular notch measurement from the reference point on either side of the head. Make two marks, one on each side (C3 and C4).
- Measure 20% of the inion to nasion distance up from the reference point. Then measure out 20% of the preauricular notch to preauricular notch measurement from this point on either side. Make two marks, one on each side (F3 and F4).
- Prepare one electrode at a time for placement.
- Clean each electrode location using an alcohol swab. Exfoliate using a slightly abrasive gel and then remove any residual cleaning material.
- Fill each electrode using electrode cream.
- For electrodes placed where hair is present, apply an additional drop of electrode cream to a gauze square and place it on the back of the electrode.
- For electrodes placed on the face, use medical tape to adhere the electrode to the skin.
- Place an electrode on each corresponding EEG, EOG, and EMG location.
- Place an electrode on each marked location on the scalp (CZ, O3, O4, C3, C4, F3, and F4).
- Place one electrode on each mastoid (small bony process behind the ear) and one in the center of the forehead.
- Place one EOG electrode adjacent to each eye. Place one of these electrodes slightly superior to the outside of the right eye (termed ROC) and one to the outside and slightly inferior to the left eye (termed LOC).
- Place two EMG electrodes around the chin area. Place one electrode on the right cheek just above the smile line. Place the other on the left side just above where the chin meets the neck, adjacent to the esophagus. Find the second location by having the participant say the word "milk" out loud while feeling for the location where muscle contractions in the neck and chin are maximal.
- Attach electrodes to the recording device and initiate recording.
- Record impedance readings for all electrodes. Ensure all electrodes pass the impedance test.
NOTE: Some devices may note a 'Pass' or 'Fail', while other devices may give numeric values. In the latter, impedances under 25 kΩ are acceptable. If an impedance fails or is too high, remove and replace the batteries. If this does not amend the issue, reapply that electrode. - At the completion of each conditions, remove the PSG electrodes.
- For electrodes applied in the hair, soak the location of the electrode with a water-based spray. Allow the spray to sit for about one minute then remove the electrode.
NOTE: Detangling hair spray is highly effective for the purpose of removing hair electrodes. - For electrodes applied with tape, typically on the face and mastoids, use a cotton pad with baby oil applied to it to saturate the tape. When the tape is completely covered in baby oil, gently pull the tape up from the corners.
- For electrodes applied in the hair, soak the location of the electrode with a water-based spray. Allow the spray to sit for about one minute then remove the electrode.
4. Visuospatial memory task
- Administer nine to-be-remembered stimuli arranged in a 3 x 3 matrix to children younger than 44 months of age. Administer the 12 to-be-remembered stimuli arranged in a 3 x 4 matrix to children older than 44 months of age.
NOTE: If a child assigned to the 12-item matrix is too challenged, the 9-item matrix can be used. Likewise, if it is evident that the 9-item matrix is too easy, the 12-item matrix can be used to avoid ceiling effects. This is justified because within-subject accuracy is of the variable of interest and not raw scores. Stimuli are typically cartoon-like pictures of common images (e.g., bear, car, scissors) arranged in a matrix and presented on a laptop screen. There are two sets of stimuli. This allows the task to be counterbalanced across the two conditions (i.e., nap versus wake promotion) so that children do not receive the same pictures in both conditions. - Administer the task in three phases: encoding, immediate recall, and delayed recall. For each phase allow the child to answer each question at their own pace.
NOTE: Typical durations are: 6 min for the encoding phase, 2 min for the immediate recall phase, and 2 min for the delayed recall phase.- In the encoding phase, direct the child to identify each image by name, then instruct the child to remember their location of each item on the grid. Following encoding, the cards are replaced with 'blank' images and the child must then locate the position of each image until they reach an encoding score ≥75%.
NOTE: A threshold of 75% was chosen based on studies in young adults28,29,30 and reflects a point when learning is clearly reached but not at ceiling.- During this block, participants receive visual feedback from the task after each response. After the child selects an image location, reveal the associated image, informing the child whether that was the correct or incorrect location.
- Provide verbal feedback on performance to motivate the child but ensure that the amount of feedback is consistent across both conditions. When the child succeeds at locating an image use language like "Great job, you got that one!" When a child fails use language that highlights the child's effort (e.g., "Whoops! Not quite but good try! Let's see if you can get the next one.").
- Provide children who are assigned to the 12-item matrix that cannot pass encoding after 4 rounds with an opportunity to stretch, do jumping jacks, and move for about 5 min. If the child still cannot pass encoding after an additional 2 rounds, restart encoding with the 9-item matrix.
- Provide children assigned to the 9-item matrix who receive an encoding score of 100% on the first round with the encoding task for the 12-item matrix. If they do not go through all the necessary steps to drop back to the 9-item matrix, use the 12-item matrix for the following two phases.
- During the immediate recall phase, present the images again, one at a time, and ask the child to recall the corresponding location. Do not provide visual or verbal feedback, and only probe each item once. However, do provide feedback on effort (i.e., "Good job giving your best effort").
- Conduct the delayed recall phase immediately after the wake or sleep condition.
NOTE: This phase is identical to the immediate recall phase.- At times children will become fussy during the delayed recall phase. If this happens, entice the child to complete the task with a prize or by offering more time to watch their movie during PSG removal. During this time do not allow the child to play with toys or engage in other tasks until the memory task is complete.
- In the encoding phase, direct the child to identify each image by name, then instruct the child to remember their location of each item on the grid. Following encoding, the cards are replaced with 'blank' images and the child must then locate the position of each image until they reach an encoding score ≥75%.
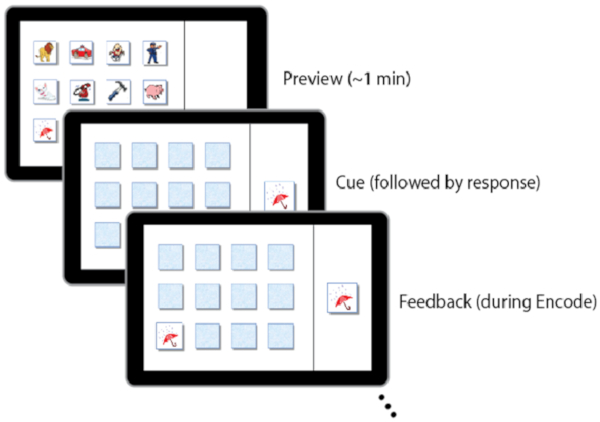
Figure 3: Examples of screen displays during the visuospatial memory task. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Actigraphy
- Program the activity watch.
NOTE: The activity watch is sampled at 32 Hz, with a sensitivity of <0.01 g. Activity is stored in 15-s epochs. - Provide each participant with a pre-programmed activity watch and instructions. Tell the parent that the watch should always be worn. Highlight that it is waterproof so there is no reason to remove the device.
- Instruct the child to wear the watch on their non-dominant hand continuously.
- Instruct the parent to press the button on the side of the watch face every time their child attempts to sleep, and then again when they wake.
NOTE: This generates an event marker in the data which assists with scoring actigraphy.
- Provide the parent with a sleep diary (similar to a log or spreadsheet) on which they can record sleep times and watch removal.
NOTE: This also assists with scoring actigraphy.- In the sleep diary, ask the parent to provide a complete log of all sleep for the number of days that the activity watch will be worn, including the time that the child goes to bed and when the child wakes up. The parent should provide this information for both naps and regular overnight sleep. Additionally, ask the parent to provide information about any time when the watch is removed.
6. Data analysis
- Visuospatial memory task
- Calculate accuracy for each recall phase as the percent of items recalled.
- Calculate change in recall over the nap and wake intervals as follows.
- Calculate change in recallnap by subtracting immediate recall accuracy (before nap) from delayed recall accuracy (after nap).
- Calculate change in recallwake by subtracting immediate recall accuracy (before wake) from delayed recall accuracy (after wake).
- PSG
- Characterize sleep stages in accordance with the standard scoring criteria (e.g., The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events v. 2.5).
- Detect sleep spindles at C3 using specialized software by marking spindle onsets and offsets.
- Verify sleep stages and spindle onsets and offsets with second trained researcher. In the event the scorings are not concordant, have a third trained scorer make the consensus decision.
- Analyze spindle density using specialized software and an in-house MATLAB code based on previous studies31. In brief, filter EEG data from 0.5−35 Hz. Consider the maximum voltage between the identified spindle onset and offset the peak spindle amplitude. Use a fast Fourier transform of each spindle to identify the peak spectral frequency between 9−15 Hz24,32.
- Actigraphy
- Score activity watch data using specialized software following standardized protocols20.
NOTE: Multiple days and nights of data are required to ensure reliability of the data. At minimum, participants need at least three days and three nights of actigraphy data (days and nights do not need to be consecutive); however, 5 nights is preferable, particularly when these data are of primary interest33. - Use sleep diary information and event markers (button presses) to verify sleep onset and offset.
NOTE: These two items must be within 20 min of each other in order to score the start and end of a rest interval.- If a participant is missing sleep diary information, event markers, or the diary and event markers are not within 20 min of each other, determine sleep onset and offset manually32: determine sleep onset by the first three minutes of continuous sleep33 and determine sleep offset by the last five minutes of continuous sleep34.
- Score activity watch data using specialized software following standardized protocols20.
Results
Using the procedures described here, Kurdziel and colleagues23 examined sleep-dependent memory consolidation during naps in preschool children. Results showed children's recall accuracy on the visuospatial memory task after a nap was better than their recall accuracy after a similar period during which they remained awake (i.e., signifying a "nap benefit", Figure 4). Moreover, those who spent the prior day in the wake condition did not ...
Discussion
This article describes how to investigate sleep-dependent consolidation of declarative memory during naps in early childhood. Methods include behavioral assessment of memory across nap and awake conditions, actigraphy and parent-report to assess sleep cycles, and PSG to assess sleep architecture. This unique combination is critical for assessing memory, characterizing sleep cycles, and examining the neural mechanisms underlying the benefit of sleep on memory. Representative results indicate that learning and memory were ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Neurocognitive Development Lab at the University of Maryland, College Park and the Somneuro Lab at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst for assistance with this project. Funding was provided by NIH (HD094758) and NSF (BCS 1749280) to TR and RS. Representative results were funded by NIH HL111695.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Actiwatch Spectrum Plus Starter Kit | Philips Respironics | 1109516 | Includes: Actiwatch Spectrum Plus Device, Actiware Software License, and manual |
| Actiware software | Philips Respironics | 1114828 | Alternatives may be available. |
| Brain Analyzer | Brain Products | BV-BP-170-1000 | Alternatives may be available. |
| Dell Latitude 5580 Laptop | Dell | X5580T [210-AKJR] | Laptop for running MatLab, Actiware, and RemLogic as well as storing/uploading data |
| EC2 cream | Grass | 12643 | Possible alternatives include Ten20 paste and Lic2 electride cream |
| Embla REMLogic software | Natus Medical Inc. | 21475 | Alternatives may be available. |
| Embletta MPR PG Sys - XR - US | Natus Medical Inc. | 12077 | Embletta system for PSG recordings |
| Embletta MPR ST + Proxy Kit | Natus Medical Inc. | 12696 | Attachment to Embletta to record PSG sensors |
| Nuprep cleaning solution | Natus Medical Inc. | 12643 | Possible alternatives may be available. |
| Sleep Supplies Starter Kit for Embletta MPR ST/ST + Proxy | Natus Medical Inc. | 12643 | Started kit for sleeping including guaze, EC2 cream, NuPrep cleaning solution, cotton swabs and more. |
References
- Sadeh, A., Acebo, C., Seifer, R., Aytur, S., Carskadon, M. A. Activity-based assessment of sleep-wake patterns during the 1st year of life. Infant Behavioral Development. 18 (3), 329-337 (1998).
- Sadeh, A., Urbach, D., Lavie, P. Actigraphically-based automatic bedtime sleep-wake scoring: Validity and clinical applications. Journal Ambulatory Monitoring. 2 (3), 209-216 (1989).
- Rasch, B., Born, J. About sleep's role in memory. Physiological Reviews. 93, 681-766 (2013).
- Werchan, D. M., Gómez, R. L. Wakefulness (not sleep) promotes generalization of word learning in 2.5-year-old children. Child Development. 85 (2), 429-436 (2014).
- Wang, J. Y., Weber, F. D., Zinke, K., Inostroza, M., Born, J. More effective consolidation of episodic long-term memory in children than adults-unrelated to sleep. Child Development. 89 (5), 1720-1734 (2018).
- Sonni, A., Spencer, R. M. C. Sleep protects memories from interference in older adults. Neurobiology of Aging. 36 (7), 2272-2281 (2015).
- Marshall, L., Helgadóttir, H., Mölle, M., Born, J. Boosting slow oscillations during sleep potentiates memory. Nature. 444 (7119), 610-613 (2006).
- Baran, B., Wilson, J., Spencer, R. M. C. REM-dependent repair of competitive memory suppression. Experimental Brain Research. 203 (2), 471-477 (2010).
- Diekelmann, S., Born, J. The memory function of sleep. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 11 (2), 114-126 (2010).
- Stickgold, R. Sleep dependent memory consolidation. Nature. 437 (27), 1272-1278 (2005).
- Dudai, Y., Karni, A., Born, J. The consolidation and transformation of memory. Neuron. 88 (1), 20-32 (2010).
- Feld, G. B., Born, J. Sculpting memory during sleep: concurrent consolidation and forgetting. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 44, 20-27 (2017).
- Staresina, B. P., et al. Hierarchical nesting of slow oscillations, spindles and ripples in the human hippocampus during sleep. Nature Neuroscience. 18 (11), 1679-1686 (2015).
- Ellenbogen, J. M., Payne, J. D., Stickgold, R. The role of sleep in declarative memory consolidation: passive, permissive, active or none?. Current Opinion Neurobiology. 16 (6), 716-722 (2006).
- Oudiette, D., Paller, K. A. Upgrading the sleeping brain with targeted memory reactivation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 17 (3), 142-149 (2013).
- Yonelinas, A. P., Ranganath, C., Ekstrom, A. D., Wiltgen, B. J. A contextual binding theory of episodic memory: systems consolidation reconsidered. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 20, 364-375 (2019).
- Antony, J. W., Schapiro, A. C. Active and effective replay: systems consolidation reconsidered again. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. , (2019).
- Lam, J., Mahone, E. M., Mason, T., Scharf, S. M. The effects of napping on cognitive function in preschoolers. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics. 32 (2), 90-97 (2011).
- Kurth, S., Ringli, M., Geiger, A., Lebourgeois, M., Jenni, O. G., Huber, R. High-density sleep electroencephalogram study. Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (40), 13211-13219 (2010).
- Backhaus, J., Hoeckesfeld, R., Born, J., Hohagen, F., Junghanns, K. Immediate as well as delayed post learning sleep but not wakefulness enhances declarative memory consolidation in children. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 89 (1), 76-80 (2008).
- Wilhelm, I., Diekelmann, S., Born, J. Sleep in children improves memory performance on declarative but not procedural tasks TT - Bei Kindern verbessert Schlaf die Gedächtnisleistung für deklarative aber nicht für prozedurale Aufgaben. Learning and Memory. 15 (5), 373-377 (2008).
- Seehagen, S., Konrad, C., Herbert, J. S., Schneider, S. Timely sleep facilitates declarative memory consolidation in infants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (5), 1625-1629 (2015).
- Kurdziel, L., Duclos, K., Spencer, R. M. C. Sleep spindles in midday naps enhance learning in preschool children. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (43), 17267-17272 (2013).
- Kurdziel, L. B. F., Kent, J., Spencer, R. M. C. Sleep-dependent enhancement of emotional memory in early childhood. Scientific Reports. 8 (12609), 1-10 (2018).
- Desrochers, P. C., Kurdziel, L. B. F., Spencer, R. M. C. Delayed benefit of naps on motor learning in preschool children. Experimental Brain Research. 234 (3), 763-772 (2016).
- Maldonado, C. C., Bentley, A. J., Mitchell, D. A pictorial sleepiness scale based on cartoon faces. Sleep. 27 (3), 541-548 (2004).
- Stern, R. A., Arruda, J. E., Hooper, C. R., Wolfner, G. D., Morey, C. E. Visual analogue mood scales to measure internal mood state in neurologically impaired patients: Description and initial validity evidence. Aphasiology. 11 (1), 59-71 (1997).
- Plihal, W., Born, J. Effects of early and late nocturnal sleep on indicators of procedural and declarative memory. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 9 (4), 534-547 (1997).
- Donohue, K. C., Spencer, R. M. C. Continuous re-exposure to environmental sound cues during sleep does not improve memory for semantically unrelated word pairs. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology. 10 (2), 167-177 (2015).
- Wilson, J. K., Baran, B., Pace-Schott, E. F., Ivry, R. B., Spencer, R. M. C. Sleep modulates word-pair learning but not motor sequence learning in healthy older adults. Neurobiology of Aging. 33 (5), 991-1000 (2012).
- Wamsley, E. J., et al. Reduced sleep spindles and spindle coherence in schizophrenia: Mechanisms of impaired memory consolidation?. Biological Psychiatry. 71 (2), 154-161 (2012).
- Mölle, M., Bergmann, T. O., Marshall, L., Born, J. Fast and slow spindles during the sleep slow oscillation: Disparate coalescence and engagement in memory processing. Sleep. 34 (10), 1411-1421 (2011).
- Acebo, C., et al. Sleep/wake patterns derived from activity monitoring and maternal report for healthy 1- to 5-year-old children. Sleep. 28 (12), 1568-1577 (2005).
- Acebo, C., et al. Estimating sleep patterns with activity monitoring in children and adolescents: How many nights are necessary for reliable measures?. Sleep. 22 (1), 95-103 (1999).
- Geiger, A., et al. The sleep EEG as a marker of intellectual ability in school age children. Sleep. 34 (2), 181-189 (2011).
- Wagner, U., Gais, S., Born, J. Emotional memory formation is enhanced across sleep intervals with high amounts of rapid eye movement sleep. Learning and Memory. 8, 112-119 (2001).
- Gómez, R. L., Bootzin, R. R., Nadel, L. Naps promote abstraction in language-learning infants. Psychological Science. 17 (8), 670-674 (2006).
- Konrad, C., Herbert, J. S., Schneider, S., Seehagen, S. Gist extraction and sleep in 12-month-old infants. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 134, 216-220 (2016).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved