Method Article
An Open Source Technology Platform to Manufacture Hydrogel-Based 3D Culture Models in an Automated and Standardized Fashion
In This Article
Summary
This protocol serves as a comprehensive tutorial for standardized and reproducible mixing of viscous materials with a novel open source automation technology. Detailed instructions are provided on the operation of a newly developed open source workstation, the usage of an open source protocol designer, and the validation and verification to identify reproducible mixtures.
Abstract
Current mixing steps of viscous materials rely on repetitive and time-consuming tasks which are performed mainly manually in a low throughput mode. These issues represent drawbacks in workflows that can ultimately result in irreproducibility of research findings. Manual-based workflows are further limiting the advancement and widespread adoption of viscous materials, such as hydrogels used for biomedical applications. These challenges can be overcome by using automated workflows with standardized mixing processes to increase reproducibility. In this study, we present step-by-step instructions to use an open source protocol designer, to operate an open source workstation, and to identify reproducible mixtures. Specifically, the open source protocol designer guides the user through the experimental parameter selection and generates a ready-to-use protocol code to operate the workstation. This workstation is optimized for pipetting of viscous materials to enable automated and highly reliable handling by the integration of temperature docks for thermoresponsive materials, positive displacement pipettes for viscous materials, and an optional tip touch dock to remove excess material from the pipette tip. The validation and verification of mixtures are performed by a fast and inexpensive absorbance measurement of Orange G. This protocol presents results to obtain 80% (v/v) glycerol mixtures, a dilution series for gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA), and double network hydrogels of 5% (w/v) GelMA and 2% (w/v) alginate. A troubleshooting guide is included to support users with protocol adoption. The described workflow can be broadly applied to a number of viscous materials to generate user-defined concentrations in an automated fashion.
Introduction
Reproducibility and replicability are of paramount importance in scientific work1,2,3,4. However, recent evidence has highlighted significant challenges in repeating high-impact biomedical studies in fundamental science as well as translational research4,5,6,7. Factors contributing to irreproducible results are complex and manifold, such as poor or biased study design6,8, insufficient statistical power3,9, missing compliance with reporting standards7,10,11, pressure to publish6, or unavailable methods or software code6,9. Amongst them, subtle changes in the protocol and human errors in the execution of experiments have been identified as further elements accounting for irreproducibility4. For instance, manual pipetting tasks introduce intra- and inter-individual imprecision12,13 and increase the probability of human errors14. While commercial liquid handling robots are able to overcome these drawbacks and have demonstrated increased reliability for liquids15,16,17, automated handling of materials with significant viscous properties is still challenging.
Commercial liquid handling robots commonly use air cushion pipettes, also known as air piston or air displacement pipettes. The reagent and the piston are separated by an air cushion which shrinks during dispensing steps and expands during aspirating steps. Using air cushion pipettes, viscous materials ‘flow’ only slowly into and out of the tip, and early withdrawal of the pipette from the reservoir may result in the aspiration of air bubbles. During dispensing tasks, the viscous material leaves a film on the inner tip wall which ‘flows’ only slowly or not at all when being forced by air. To overcome these issues, positive displacement pipettes were introduced commercially to actively extrude the viscous material out of the tip using a solid piston. Although these positive displacement pipettes enable accurate and reliable handling of viscous materials, automated solutions with positive displacement pipettes are still too expensive for academic laboratory settings, and, therefore, most workflows with viscous materials rely solely on manual pipetting tasks18.
In general, viscosity is defined as the resistance of a fluid to flow, and viscous materials are further being defined as materials with a greater viscosity of water (0.89 mPa·s s at 25 °C). In the field of biomedical applications, experimental setups often contain multiple materials with a greater viscosity than water, such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; 1.99 mPa·s at 25 °C), glycerol (208.1 mPa·s at 25 °C for 90% glycerol [v/v]), Triton X-100 (240 mPa·s at 25 °C), and water-swollen polymers, referred to as hydrogels19,20. Hydrogels are hydrophilic polymer networks arranged in a physical or/and chemical mode used for various applications, including cell encapsulation, drug delivery, and soft actuators19,20,21,22. The viscosity of hydrogels depends on the polymer concentration and molecular weight19. Routinely used hydrogels for biomedical applications exhibit viscosity values between 1 and 1000 mPa·s, while specific hydrogel systems have been reported with values of up to 6 x 107 mPa·s19,23,24. However, viscosity measurements of hydrogels are not standardized in terms of measurement protocol and sample preparation, and, therefore, viscosity values between different studies are difficult to compare.
Since commercially available automated solutions specifically designed for hydrogels are either missing or too expensive, current workflows for hydrogel depend on manual handling18. To understand the limitations of the current manual-based workflow for pipetting of hydrogels, it is important to comprehend essential handling tasks18. For example, once a novel hydrogel material has been synthetized, a desired concentration or a dilution series with varying concentrations is generated to identify reliable synthesis protocols and crosslinking characteristics with subsequent analysis of the mechanical properties25,26,27,28. In general, a stock solution is prepared or purchased, and subsequently mixed with a diluent and/or other reagents to obtain a mixture. The mixing tasks are mostly not performed directly in a well plate (or any output format), and are rather performed in a separate reaction tube, which is commonly referred to as master mix. During these preparation tasks, various aspirating and dispensing steps are required to transfer the viscous material(s), mix the reagents, and transfer the mixture to an output format (e.g., a 96 well plate). These tasks require a high amount of human labor18, long experimental hours, and increase the probability of human errors which could potentially manifest as inaccurate results. Moreover, manual handling prevents efficient preparation of high sample numbers to screen various parameter combinations for detailed characterization. The manual processing also impedes the usage of hydrogels for high-throughput screening applications, such as the identification of promising compounds during drug development. The current manual-based preparation steps are not feasible to screen drug libraries consisting of thousands of drugs. For these reasons, automated solutions are required to provide an efficient development process and enable the successful translation of hydrogels for drug screening applications.
To move from manual-based workflows to automated processes, we have optimized a commercial open source pipetting robot for the handling of viscous materials by the integration of temperature docks for thermoresponsive materials, the usage of off-the-shelf positive displacement pipettes using capillary piston tips, and an optional tip touch dock for pipette tip cleaning. This pipetting robot has been further integrated as a pipetting module into a newly developed open source workstation, which consists of ready-to-install and customizable modules18,29. Detailed assembly instructions for the developed workstation including hardware and software files are freely accessible from the GitHub (https://github.com/SebastianEggert/OpenWorkstation) and the Zenodo repository (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3612757). In addition to the hardware development, an open source protocol design application has been programmed and released to guide the user through the parameter selection process and generate a ready-to-use protocol code (https://github.com/SebastianEggert/ProtocolDesignApp). This code runs on the commercial open source pipetting robot as well as on the developed open source workstation.
Herein, a comprehensive tutorial is provided on the operation of the open source workstation to automate mixing tasks for viscous materials (Figure 1). The tutorial-specific protocol steps can be carried out with the developed open source workstation as well as the commercial open source pipetting robot. Supported by an in-house developed open source protocol design application, automated mixing and preparation of required concentrations for glycerol, gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) and alginate is demonstrated. Glycerol has been selected in this tutorial, since it is well characterized30,31, it is inexpensive and readily available, and, therefore, it is commonly used as viscous reference material for automated pipetting tasks. As examples for hydrogels used in biomedical applications, GelMA and alginate hydrogel precursor solutions have been applied for automated mixing experiments. GelMA presents one of the most commonly used hydrogels for cell encapsulation studies32,33, and alginate was selected in this study to demonstrate the ability to manufacture double network hydrogels34,35. Using Orange G as a dye, a fast and inexpensive procedure was implemented to validate and verify the mixing results with a spectrophotometer16.
A commercial open source pipetting robot has been integrated as a pipetting module into the developed open source workstation (Figure 2a), and therefore, the name ‘pipetting module’ is further used to describe the pipetting robot. A detailed description of the installed hardware is beyond the scope of this protocol and is available via the provided repositories which also include step-by-step instructions for the general assembly of the open source platform. The pipetting module can be equipped with two pipettes (single- or 8-channel pipette) which are installed on axis A (right) and axis B (left) (Figure 2b). The pipetting module offers a 10-deck capacity according to American National Standards Institute/Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening (ANSI/SLAS) standards, and the following location positions are defined on the deck: A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2, D1, D2, E1, E2 (Figure 2c). To initiate photo-induced polymerization of hydrogel solutions, a separate crosslinker module is required and has been added to the workstation. The crosslinker module is equipped with LEDs with a wavelength of 400 nm and, therefore, substances that excite at a visible light wavelength can be used with the current systems, such as lithium phenyl-2,4,6 trimethylbenzoylphosphinate (LAP)36,37. The intensity (in mW/cm2) of the LEDs can be addressed by the user in the protocol design application to study the crosslinking behavior38. The workstation includes also a storage module to enable increased throughput studies; however, this module is not used within this study and, therefore, not further described. In general, it is recommended to operate the pipetting module in a biological safety cabinet to avoid sample contamination. The main power circuit to operate the pipetting module is a 12 V circuit, which is considered as a low-voltage application in most countries. All electrical components are based in a dedicated control box preventing users from coming into contact with the source of an electrical hazard.
By following these standardized mixing protocols, researchers are able to achieve reliable mixtures for viscous as well as non-viscous materials in an automated fashion. The open source approach allows users to optimize mixing sequences and share newly developed protocols with the community. Ultimately, this approach will facilitate the screening of multiple parameter combinations to investigate the interdependencies between different factors and, thereby, accelerate the reliable application and development of viscous materials for biomedical applications.
Protocol
NOTE: The protocol starts with an introduction to (1) the software and (2) the hardware setup to familiarize the user with required installations and the workstation. Following a section on (3) material preparation and (4) the usage of the protocol designer application, (5) the calibration of the pipetting module and (6) the execution of the automated protocol is highlighted in detail. Finally, (7) validation and verification procedures are described, including absorbance reading and data analysis. A general protocol workflow with individual tasks is displayed in Figure 1.
1. Software setup
NOTE: This section includes a detailed instruction to install the application programming interface (API) as well as the required protocol designer application and the calibration terminal. The following instructions are written for a Raspberry Pi (RPi) single-board computer; however also Windows 8, 10 and macOS 10.13+ have been successfully used with the API and the applications.
- Set up the computer environment.
NOTE: Be familiar with the basics of Python39, how to set up and use a Raspberry Pi40,41, and how to connect to the internet42. The following tutorial steps focus on protocol-specific steps and additional information on the usage of a Raspberry Pi is available online40.- Open a terminal window from the taskbar or application menu.
- Update the system’s package list:
sudo apt-get update - Upgrade all the installed packages:
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade - Restart the Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot - Check installed Python version:
python3 --version
Make sure that at least Python 3.5 is installed; if not, install the latest version43. - Install python pip, which publishes Python packages with the Python Package Index44:
sudo apt-get install python3-pip - Install dependencies:
pip install numpy
pip install python-resize-image
NOTE: If you are using Windows, you need to install the windows-curses package via: python -m pip install windows-curses
- Install the application programming interface (API).
NOTE: The API provides a simple Python framework designed to write experimental protocols script and operate the workstation. The following two APIs are required to successfully execute the generated protocol code.- Install workstation API:
pip install openworkstation - Install Opentrons API to operate the pipetting module:
pip install opentrons==2.5.2 - Verify, if API is installed successfully:
python3
>>> import openworkstation
>>> import opentrons
NOTE: The size of the API and the protocol design application is 2.2 MB and 1.2 MB, respectively. No issues were experienced during the installation when used with limited disk space (200 MB). However, the disk space requirements depend on the operating system.
- Install workstation API:
- Select a directory for file download (calibration terminal, protocol design application, etc.).
NOTE: Files can be copied and pasted elsewhere afterwards. - Clone files from GitHub repository:
git clone https://github.com/SebastianEggert/OpenWorkstation
NOTE: The ‘git clone’ command clones and subsequently saves all files into the directory, which is open in the terminal at this time. Since the repository also includes the hardware files for the assembly, not the entire repository is required to execute the presented protocols. All required files to replicate the experiments are available as Supplemental File and in the GitHub repository under “/examples/publication-JoVE”. - Open the downloaded folder. If the entire repository was downloaded, navigate to the ‘publication-JoVE’ folder via
cd openworkstation/examples/publication-JoVE
NOTE: This folder includes files required for the operation of the workstation and the usage of the protocol designer application and the calibration terminal.
2. Hardware setup
- Place the workstation in a biological safety cabinet to avoid sample contamination.
- Install pipettes on the workstation.
- Select the pipette size based on the experimental setup. In general, take a pipette size which volume to be aspirated is on the higher end of the range. If mixing tasks with volumes greater than 1 mL are required for a specific setup (e.g., aspirating/dispensing of 2 mL), choose the M1000E with a maximal aspirating/dispensing volume of 1,000 µL to minimize pipetting steps and save time.
NOTE: A detailed instruction for air-displacement pipettes is available online45. The developed pipetting module is able to integrate the following off-the-shelf positive displacement pipettes: M10E (1–10 µL), M25E (3–25 µL), M50E (20–50 µL), M100E (10–100 µL), M250E (50–250 µL), M1000E (100–1,000 µL). - Use an M4 Allen key to loosen and tighten screws.
- Attach the two pipette fixation plates (white acrylic plates) to the aluminum rail and tighten M5 screws loosely.
- Insert the pipette into the two pipette fixation plates and ensure that the ergonomic tail of the pipette is resting on the opposite side of the acrylic mounting plate.
- Tighten the four screws of the two pipette fixation plates firmly.
- Slide the two square fastening nuts, which are attached to the acrylic mounting plate, into the extrusion slot of the z-axis and tighten screws.
NOTE: Fasten pipette tightly to avoid any movement during operation.
- Select the pipette size based on the experimental setup. In general, take a pipette size which volume to be aspirated is on the higher end of the range. If mixing tasks with volumes greater than 1 mL are required for a specific setup (e.g., aspirating/dispensing of 2 mL), choose the M1000E with a maximal aspirating/dispensing volume of 1,000 µL to minimize pipetting steps and save time.
3. Material preparation
NOTE: The viscous materials (glycerol, GelMA, alginate) are used for the experiments presented in this study, and, therefore, prepared volumes and handling tasks (e.g., add 5 mL of stock solution in 5 mL reaction tubes) are specifically for this experimental setup.
- Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA)
NOTE: GelMA functionalization, dialysis, and lyophilization are not the scope of this paper, and a step-by-step protocol is available in Loessner et al.33. The protocol starts using lyophilized GelMA, which can be prepared in-house or purchased commercially.- Calculate required mass of GelMA (mGelMA) based on the desired final stock concentration (cGelMA) and volume (VGelMA) using the equation:
mGelMA = cGelMA x VGelMA
NOTE: VGelMA depends on the experimental setup and it is recommended to prepare 20−30% excess material. The presented protocols start with 5 mL of 20% (w/v) GelMA as a stock solution. - Weigh the required amount of lyophilized GelMA, add it into a 50 mL reaction tube and add the required amount of phosphate buffered saline (PBS).
- Mix GelMA either by soaking into the solvent at 4 °C overnight or by heating to 60 °C for 6 h in a water bath.
NOTE: Sterile GelMA solutions can be stored protected from light at 4 °C for at least six months. - Fill 5 mL of GelMA into 5 mL reaction tubes.
- Calculate required mass of GelMA (mGelMA) based on the desired final stock concentration (cGelMA) and volume (VGelMA) using the equation:
- Photoinitiator: Lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate (LAP)
NOTE: Avoid additional exposure to room light, since LAP is light sensitive.- Calculate required mass of LAP (mLAP) based on the desired final stock concentration (cLAP) and required volume (VLAP) using the equation:
mLAP = cLAP x VLAP
NOTE: It is recommended to prepare a 3% (w/v) stock solution. - Weigh the required amount of LAP, add it into a 15 mL reaction tube and add PBS.
- Wrap the tube in aluminum foil to prevent photo-induced decomposition.
- Dissolve LAP by placing the reaction tube in a water bath at 37 °C for 2 h or until fully dissolved.
- Fill 1 mL of LAP stock solution in 5 mL tubes.
- Calculate required mass of LAP (mLAP) based on the desired final stock concentration (cLAP) and required volume (VLAP) using the equation:
- Alginate
- Calculate required amount of alginate (malginate) based on the desired final stock concentration (calginate) and volume (Valginate) using the equation:
malginate = calginate x Valginate
NOTE: Valginate depends on the experimental setup and it is recommended to prepare 20−30% excess material. The presented protocols start with 5 mL of 4% (w/v) alginate as a stock solution. - Weigh the required mass of alginate, add it into a 50 mL reaction tubes, and add PBS.
- Place the alginate mix into a water bath at 37 °C for 4 h.
NOTE: The usage of a vortex mixer will accelerate the dissolution process, but also generate air bubbles. Dissolved alginate can be stored at 4 °C for at least six months. - Fill 5 mL of alginate into 5 mL reaction tubes.
- Calculate required amount of alginate (malginate) based on the desired final stock concentration (calginate) and volume (Valginate) using the equation:
- Fill 5 mL of glycerol in 5 mL reaction tubes.
- Orange G solution
- Prepare a 10 mg/mL stock solution of Orange G in a 50 mL reaction tube.
NOTE: The volume depends on the number of experiments. Depending on the diluent type, prepare stock solution either in ultrapure water, PBS or a suitable diluent reagent. In the presented experiments, ultrapure water was used for diluting glycerol and PBS for diluting GelMA and alginate. PBS was used as a diluent for GelMA and alginate, and can be either prepared using tablets or purchased off-the-shelf. - Mix for 10 s by vortexing.
- Wrap the tube in aluminum foil to prevent photo-induced decomposition.
NOTE: Stock solution can be used after 24 h to ensure proper dissolution of Orange G. - Dilute stock solution to a 1 mg/mL working solution in a 50 mL reaction tube.
- Transfer working solution to appropriate flasks/tubes for the experimental setup.
NOTE: For the presented experiments, the working solution was filled into 5 mL tubes. Orange G stock and working solution can be stored at 4 °C and used within three months upon preparation. - Fill 5 mL of the 1 mg/mL Orange G working solution in 5 mL reaction tubes.
- Prepare a 10 mg/mL stock solution of Orange G in a 50 mL reaction tube.
4. Generate protocol code with the protocol designer application
NOTE: The specified parameters in steps 4.2−4.7 are the same for all conducted experiments, except for the material’s stock concentration and the final output concentration. These parameters are summarized in Table 1 and, in the following, parameters are used to prepare double network hydrogels with 5% (w/v) GelMA, 2% (w/v) alginate, 0.15% (w/v) LAP, and PBS as a diluent.
- Open the protocol designer application by running ‘ProtocolDesignApp.html’.
NOTE: The app “ProtocolDesignApp.html” guides the user through the parameter selection process and automatically generates the ready-to-use protocol to operate the workstation. The user interface runs on every commonly used internet browser (i.e. Chrome, Firefox, Safari, edge, Internet Explorer). - Enter protocol name (e.g., double-network-hydrogels) on setup page.
- Click ‘Continue’ to confirm protocol name and proceed to the next step.
- Define input tray by selecting ‘3x4 Heating Block’ from drop-down menu and the following input parameters:
- Select ‘Gel 1’ from drop-down menu, enter name ‘GelMA’, enter stock-concentration ‘20%’, set ‘Number of Samples’ to ‘3’ to fill one column. Click ‘+add’ to save entries.
- Select ‘Gel 2’ from drop-down menu, enter name: ‘Alginate’, enter stock-concentration ‘4%’, set ‘Number of Samples’ to ‘3’ to fill one column. Click ‘+add’ to save entries.
- Select ‘Photoinitiator’ from drop-down menu, enter name: ‘LAP’, enter stock-concentration ‘3%’, set ‘Number of Samples’ to ‘3’ to fill one column. Click ‘+add’ to save entries.
- Select ‘Diluent 1’ from drop-down menu, enter name: ‘PBS’, set ‘Number of Samples’ to ‘3’ to fill one column. Click ‘+add’ to save entries.
NOTE: The visualization of the input tray automatically updates, once ‘+add’ is clicked. If more inputs are added than the tray’s capacity, the warning ‘Too many samples for this tray’ will be shown to the user.
- Define crosslinking parameters by checking ‘Photo crosslinking’ and typing the time in seconds, ‘30’, and the intensity W/m2 with ‘2’.
- Finish the input setup by clicking ‘CONTINUE’.
- Define output tray setup by selecting ’96 well plate’ in the drop-down menu for well plate type.
- Click on ‘Group1’ to define outputs by creating a group of samples.
- Specify output composition by entering desired concentrations and sample volume into the fields for each input: GelMA = ‘5’, Alginate = ‘2’, LAP = ‘0.15’, Total Volume = ‘60’.
- Check box to apply advanced mixing protocol.
- Specify number of samples by entering the number of samples into the field ‘Number of Samples’: ‘96’.
NOTE: The visualization of the sample tray automatically updates, once ‘+add group’ is clicked. If more samples are added than the tray’s capacity, the warning ‘Too many samples for this tray’ will be shown to the user. - Finish the output setup by clicking ‘CONTINUE’.
- Select tray position on the deck layout and prepare the platform accordingly:
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT A1’ and select ‘Empty_Cell’ from drop-down menu.
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT A2’ and select ‘Trash_Cell’ from drop-down menu.
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT B1’ and select ‘Tips_Cell_100µL’ from drop-down menu.
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT B2’ and select ‘Tips_Cell_1000µL’ from drop-down menu.
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT C1’ and select ‘Input_Cell’ from drop-down menu.
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT C2’ and select ‘Empty_Cell’ from drop-down menu.
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT D1’ and select ‘Mixing_Cell’ from drop-down menu.
- Check checkmark in field ‘SLOT D2’ and select ‘Output_Cell’ from drop-down menu.
- Define type and characteristics of first pipette (M100E) by checking ’Pipette Left’, selecting ‘10-100µL positive displacement’ from drop-down menu and setting aspirating speed = ‘600’, dispensing speed = ‘800’.
- Define type and characteristics of second pipette (M1000E) by checking ’Pipette Right’, selecting ‘100-1000µL positive displacement’ from drop-down menu and setting aspirating speed = ‘800’, dispensing speed = ‘1200’.
- Click on ‘GENERATE PROTOCOL’ to confirm the setup and generate the protocol script.
NOTE: The developed protocol designer app generates automatically a new folder whenever a new protocol is generated. All files which are required for this experiment and to operate the workstation are saved in this folder which is named after the protocol name. The folder can be copied into different directories without causing issues. - Do not close the interface, as it will be used to execute the protocol (see step 6.6.).
5. Calibration of the pipetting module
NOTE: Containers (e.g., well plates, tip rack, trash) and pipettes (e.g., M1000E) must be calibrated initially. If a container and/or a pipette position are modified/changed, the new position must be calibrated.
- Navigate to the protocol folder and open the calibration terminal by executing the file ‘calibrate.py’ in a terminal windox (see step 1.1.1):
phython.calibrate.py
NOTE: The 'calibrate.py' interface guides the user through the calibration of the deck setup and pipettes. Make sure that the file is in the same folder as the protocol file and the module files. It is automatically generated in step 4.10. - Select movement increments for plungerx,y,z movement with the numeric keypad (1−8): ‘1’ for 0.1 mm, ‘2’ for 0.5 mm, ‘3’ for 1 mm, ‘4’ for 5 mm, ‘5’ for 10, ‘6’ for 20 mm, ‘7’ for 40 mm, and ‘8’ for 80 mm.
- Calibrate the pipette.
- Press keyboard shortcut P to select pipette size.
- Press keyboard shortcut V to enter the plunger calibration mode.
NOTE: It is recommended to start with small increments (2, 5, and 10 mm) to get familiar with the increment size and movement action of the pipette head. - Calibrate the following plunger positions for a positive displacement pipette: T–Top = rest position; B–Bottom = plunger is pushed until resistance is met; P–Pick-up = plunger is pushed to a position where a piston tip can be attached; E–Eject = plunger is pushed until an attached tip is ejected. Vary plunger positions using the upwards and downwards arrows on the keyboard, and save the final position using S on the keyboard.
- Leave the pipette plunger calibration mode by pressing keyboard shortcut V.
- Calibrate container position relative to the pipette tip.
- Press keyboard shortcut P to select pipette type. Make sure that a tip is connected to the selected pipetted.
- Press keyboard shortcut C to select container type.
- Select an appropriate movement increment and move pipette tip to the following positions. For well plates, calibrate to the ‘A1’ well position at the bottom; For tip rack, calibrate to the ‘A1’ position; For trash, choose a position (defined as a point) where the tip can be ejected into the trash.
- Press keyboard shortcut S to save position.
- Repeat steps 5.3.1−5.3.3 for all containers listed under ‘C’ for the selected pipette type.
- Repeat 5.3.1−5.3.5 for the second pipette type.
- Close the calibration script.
6. Protocol execution with the workstation
NOTE: Protocol files are accessible via the repository and are also available as Supplemental File.
- Position trash container, tip racks, input tray, mixing tray, and output on the deck (defined in step 4.3).
- Calibrate pipettes and instruments as defined in section 5.
- If required, switch the temperature dock ON and select the temperature for input and mixing tray.
NOTE: The experiments in this tutorial were conducted without temperature control and at 40 °C for glycerol, and 37 °C for GelMA and alginate pipetting. - Position tubes with input reagents in the aluminum blocks on the temperature docks according to the selected setup.
- Wait until input reagents have reached the desired temperature.
NOTE: To ensure proper temperature distribution, an incubation time of 30 min is recommended for GelMA and alginate. - Execute the protocol file by clicking on ’RUN PYTHON SCRIPT’
NOTE: The selected protocol is now executed by the workstation. The accompanying video highlights automated mixing of GelMA and the distribution of 60 µL into a 96 well plate. - Run is completed, when ‘Finished’ is displayed.
7. Validation and verification process
- Remove the well plate from workstation and transport the well plate with the samples to a spectrophotometer.
- Read absorbance with a spectrophotometer at 450 nm. Read each plate 2x to compare results and ensure consistent results.
- Export and save absorbance readings.
- Data analysis.
NOTE: Experimental data can be processed individually or copied and pasted into the provided template to evaluate the mean, standard deviation, and coefficient of variance (CV) value using spreadsheet software.- Open the Supplemental File ‘supplementary_template-analysis.xlsx”, which is also vailable within the GitHub repository under ‘openworkstation/examples/publication-JoVE.
- Copy absorbance readings into the ‘raw data’ sheet, ensure that all cell references are correctly defined in all tables, and click on the ‘analysis’ sheet for information on the average, standard deviation, and coefficient of variance (CV) values.
NOTE: Depending on the sample distribution on a well plate, the following preset evaluation types are available with the template: the ‘Uniform’ type is used when all samples have the same composition, the ‘By rows’ type is used when samples in different rows have different compositions, the ‘By columns’ type is used when samples in different columns have different compositions, and the ‘Customized’ type is used when the sample positions are user specific.
Results
This tutorial presents results for experiments with glycerol (Figure 3) and GelMA with LAP and alginate (Figure 4).
The generation of an 80% (v/v) glycerol solution was investigated either without temperature control (room temperature, 22 °C) and without tip touch (defined as setup 1), with temperature control (40 °C) and without tip touch (setup 2), or with temperature control (40 °C) and with tip touch (setup 3) (Figure 3a-i). These two temperature settings were chosen to evaluate the handling difference, since glycerol’s viscosity is decreasing almost by a factor of 3 when heated from 22 °C (139.5 mPa·s) to 40 °C (46.6 mPa·s)30. An 85% (v/v) stock solution of glycerol was diluted to a final concentration of 80% and uniformly distributed into a 96 well plate (n = 96 per setup). The experimental time, which includes the dispensing of each material into the mixture tube, the respective mixing tasks, and sample distribution into a 96 well plate, was 30 min 42 s. To identify differences between dilution mixtures, ultrapure water–as the diluent for glycerol–was prepared with 1 mg/mL Orange G. The absorbance readings highlight that the integration of the temperature control and the tip touch significantly impacts the mixtures (p < 0.0001). In addition to the performed two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), the CV values were calculated to evaluate the relative standard deviation. The coefficient of variation describes a standardized indicator to identify the degree of deviation in relation to the mean and is expressed as a percentage. If the sample means are not particularly the point of interest, but the variability within the measurements, the coefficient of variation provides additional insights to identify reproducible mixtures46. Within this experiment with three different setups, the absorbance values showed decreasing CV values from 5.6%, 4.2%, to 2.0% for setup 1, setup 2, and setup 3, respectively, demonstrating the significant influence of the temperature dock and the tip touch function on producing reliable results (Figure 3a-ii). Plotting of sample absorbance values for setup 3 (sample number #1 to #96 in a 96 well plate) yields no increasing or decreasing values throughout the experiment and, therefore, indicates no influence of the sample position on the absorbance values (Figure 3a-iii). Visualizing the data for each measured well plate with heat maps provides additional insights to identify heterogeneities for a specific row or column, or varying absorbance values throughout the dispensing tasks. The visualized heatmaps for the three setups display decreased heterogeneities across the entire well plates from setup 1 to setup 3 (Figure 3b). Finally, the replicability of the conducted mixing was evaluated within eight independent runs (Figure 3c-i,ii), where each run took 6 min 57 s. Single mixing runs showed low CV values between 1.1% to 2.6%, which indicate very reliable mixing and dispensing tasks for the individual runs. Absorbance values of all eight runs yielded a CV value of 3.3% and demonstrated the reproducibility of the established mixing protocol.
GelMA dilution series were prepared by diluting a 20% (w/v) stock solution with PBS to 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2, and 0% (w/v) and adding LAP to a constant concentration of 0.15% (w/v) (Figure 4a-i), which took in total 55 min 12 s. As specified in the experimental protocol script, the hydrogel was crosslinking for 30 s with an intensity of 2.0 mW/cm2 at 400 nm. To evaluate the differences between the mixtures, PBS―as the diluent for GelMA and alginate―was prepared with 1 mg/mL Orange G. Hence, absorbance difference between samples within one mixture as well as between the serial dilutions are identified with a spectrophotometer. Measured absorbance values of each concentration step are significantly different (p < 0.0001) and have very low CV values between 1.2% and 3.4% throughout the concentration steps (n = 12 per concentration step). Linear regression demonstrated high fit with an R² value of 0.9869 (Figure 4a-ii) and a heatmap confirmed the homogenous distribution for each concentration and the difference between the concentrations (Figure 4a-iii). Automated mixing of four reagents was conducted for the generation of 5% (w/v) GelMA, 2% (w/v) alginate, 0.15% (w/v) LAP, and PBS as diluent without (setup 2) and with (setup 3) touch tip (n = 96 for each setup) with the same crosslinking parameters (30 s, 2.0 mW/cm2, 400 nm). Dispensing of the four materials, mixing, and distributing into a 96 well plate took 32 min 22 s. All experiments with GelMA and alginate were conducted at 37 °C to prevent thermal gelling which prevents pipetting of GelMA. With the tip touch option, the CV value was reduced from 5.2% to 3.4% and, especially, outliers in the lower region were prevented by removing excess material from the tip (Figure 4b-i). Although the mean value of 1.927 and 1.944 for setup 2 and setup 3 are very close, the coefficient of variation highlights the decreasing deviation in relation to the mean. Single rows of the 96 well plate can be compared with each other using a heatmap visualization to detect row and/or column differences (Figure 4b-ii).
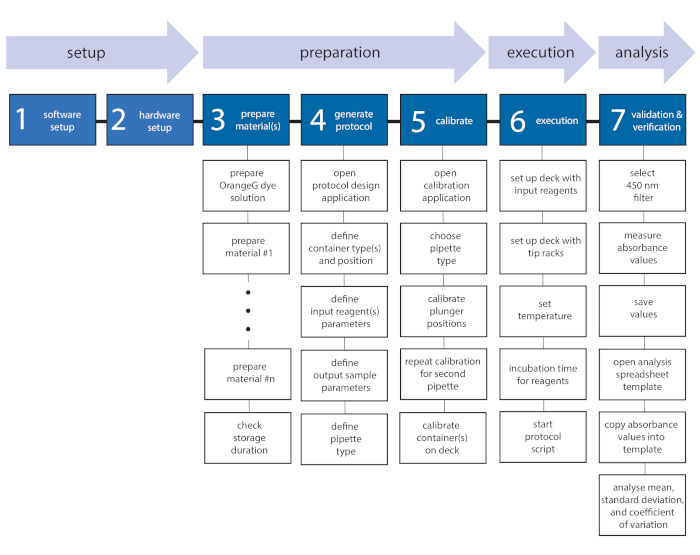
Figure 1: Protocol workflow with individual tasks. The described workflow is divided into seven tasks, which are separated into setup, preparation, execution, and analysis. In the beginning, the software (task 1) as well as the hardware (task 2) must be set up. After the preparation of the materials (task 3) and the generation of the protocol script (task 4), the pipetting module is calibrated by defining the pipette and container positions (task 5). Next, the protocol script is executed on the workstation (task 6) and validation and verification (task 7) of mixtures are carried out to evaluate mixtures. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
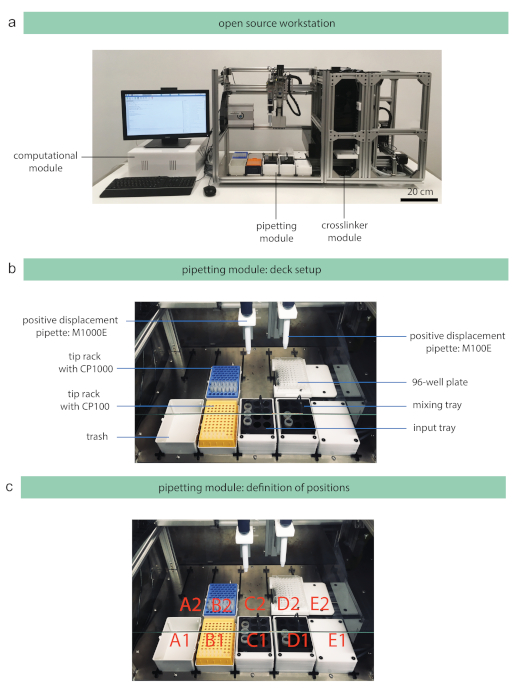
Figure 2: Open source workstation and deck setup of the pipetting module. (a) The developed workstation is inspired by an assembly line approach, where samples are being transported through different modules, and consists of the following modules: pipetting, crosslinker, storage, transport, and computational module. (b) The deck of the pipetting module is set up depending on the experimental layout (e.g., well plate type, tube volume, etc.). The displayed deck setup was used for the presented experiments and consists of positive displacement pipettes with a range from 10−100 µL (M100E) and 100−1,000 µL (M1000E), the tip racks with capillary pistons (CP) for 100 µL (CP1000) and 1,000 µL (CP1000), a trash container, a mixing tray, and an input tray for the input reagents. (c) The available deck positions are defined with the displayed numbers. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
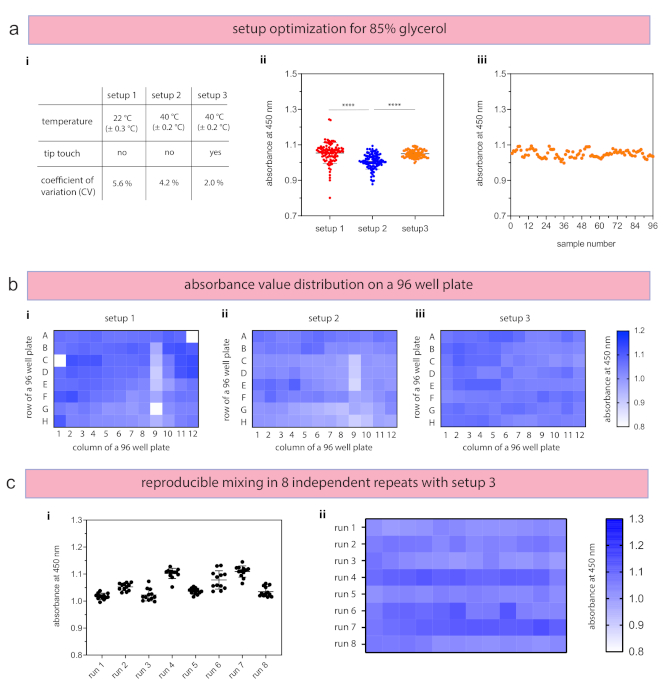
Figure 3: Results for automated pipetting of glycerol mixtures. (a) The flexible workstation design enables the evaluation of three different setups (i) to identify optimal parameters for reproducible results. (ii) The addition of a tip touch and heating of the material resulted in a decreased coefficient of variance (CV) values and highly reproducible mixtures for setup 3. Each experiment was conducted with 96 samples. (iii) Plotting of single sample values showed no influence on the pipetting sequence. (b) Experimental results of each setup were visualized with heat maps to identify the influence on raw/column differences, edges, or master mixture. (c) The reproducibility of setup 3 was analyzed within eight independent runs using (i) median, standard deviation, CV value, and (ii) heatmaps. Data in panels a-ii (n = 96) and b-i (n = 12) are presented with the means and the single data points. Statistical significance was defined as ****p < 0.0001 using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
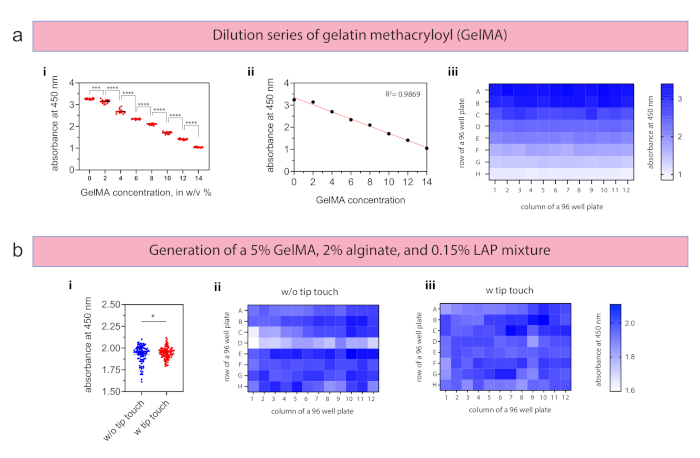
Figure 4: Results for mixing tasks with hydrogels. (a) From a gelatin metacryloyl (GelMA) 20% (w/v) stock solution, a serial dilution of 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2, and 0% (w/v) was generated within one experimental run using a 96 well plate (n = 12 per concentration). (i) The coefficient of variance (CV) values varied between 1.2% and 3.4% throughout the prepared concentrations, and (ii) linear regression showed a high fit with an R² value of 0.9869. (iii) Homogenous dilutions were confirmed visually with the generated heatmap. (b) Double network hydrogels were generated with 5% (w/v) GelMA, 2% (w/v) alginate, and 0.15% (w/v) LAP (i) with and without tip touch (n = 96 for each setup) and crosslinked for 30 s with an intensity of 2.0 mW/cm2 at 400 nm. The integration of the tip touch resulted in decreasing CV values from 5.2% to 3.4%. (ii,iii) Heatmaps confirm fewer deviations when using tip touch to remove excess material from tip. Data in panels a-i and b-i are presented with the means and the single data points. Statistical significance was defined as *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
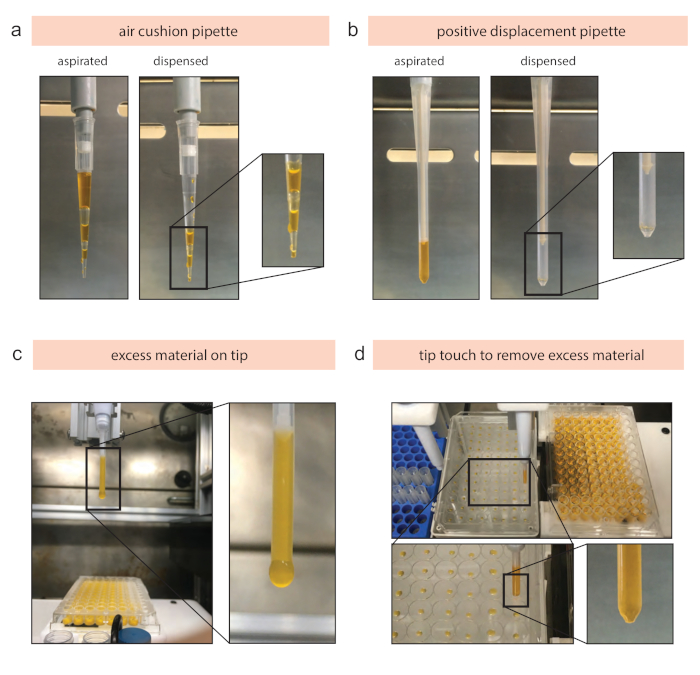
Figure 5: Summary of the pipette type difference and issues with viscous biomaterials. (a) The reagent and the piston are separated by an air cushion that shrinks during dispensing steps and expands during aspirating steps. When aspirating and dispensing viscous materials, the slow ‘flow’ introduces problems such as air bubbles and irregular pipetting behavior. (b) Positive displacement pipettes enable reliable aspirating and dispensing of viscous material by the usage of a piston inside the tip. (c) Pipetting of highly viscous materials (e.g., 4% (w/v) alginate) can result in the accumulation of excess material on the tip, which leads to inaccuracy throughout the experiments. (d) The implementation of a simple tip touch tray enables the removing of the excess material on the tip and results in accurate aspirating and dispensing volumes. This is realized by using the inner side of the well plate lid placed onto a tip rack container. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Material #1 (stock concentration) | Final concentration of material #1 | Material #2 (stock concentration) | Final concentration of material #2 | Materials #3 (stock concentration) | Final concentration of material #3 | Diluent (Orange G working solution) | Final Orange G concentration in mixture | Displayed in figure |
| Glycerol (85% (w/v)) | 80% (w/v) | water (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.059 mg/mL | Figure 3a−c | ||||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 0% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 1 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 2% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.85 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 4% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.75 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 6% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.65 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 8% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.55 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 10% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.45 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 12% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.35 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 14% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.25 mg/mL | Figure 4a | ||
| GelMA (20% (w/v)) | 5% (w/v) | Alginate (4% (w/v)) | 2% (w/v) | LAP (3% (w/v)) | 0.15% (w/v) | PBS (1 mg/mL Orange G) | 0.2 mg/mL | Figure 4b |
Table 1: Parameter overview for the conducted experiments.
| Protocol step | Problem | Possible reason | Solution |
| 1.1 | Software cannot be installed or updated | Running out of disk space on SD card | Check disk space on SD card. If required, remove unnecessary items, empty bin, or use an appropriately sized SD card |
| 1.2 | API cannot be installed | Users ability for installation is restricted (no root user permission) | Use ‘sudo’ command in front of specified commands to gain admin rights. In Linux, this kind of access is known as the superuser. |
| 3.1 | Troubles with GelMA | Functionalization, dialysis or lyophilization | Detailed step-by-step protocol including troubleshooting list available in Loessner et al.33. |
| 5.1 and 6.2 | Workstation is not reacting to commands | Connection issues | Turn of everything and shut down the computer. Switch off the power supply for 10 s. Power computer and workstation back on. |
| 5.1 and 6.2 | Workstation is not reacting to commands | Connection issues | Check if the computer is recognizing the USB connection and the USB port is defined correctly. Make sure that firewall is not preventing the connection process (see the link below Table 2). |
| 5.1 and 6.2 | Cannot open file | Wrong directory | Check director (folder path) to ensure that the right path is being used. If a file (e.g., interface.py) cannot be found, it is likely that the wrong path is being used. |
| 6.6.2 | Tip is not properly attached or falls during movement | Calibration issue | Repeat calibration steps for the pipette and make sure that the capillary piston is connected properly with the pipette. |
| 6.6.2 | Tip is not properly attached or falls during movement | Attachment issue | Pipette is not properly connected to the pipette axis and moves during the movement steps. Tighten screws firmly to prevent this. |
| 6.6.2 | Tip is aspirating above material | Calibration issue | Repeat calibration of this tray type to define height properly. |
| 6.6.2 | Tip is aspirating above material | Calibration issue | Check volume in tube and make sure that the volume equals the volume defined in the protocol designer application. |
| 6.6.2 | Material is dipping during movement | Too much excess material on tip | Add tip touch dock option; optionally, also the time for tip touch can be increased. |
| 6.6.2 | Material is solid or too viscous for pipetting | Thermoresponsive behaviour of material | Check thermoresponsive material characterization and adjust heating/cooling temperature of temperature dock accordingly. |
| https://support.opentrons.com/en/articles/2687601-c-having-trouble-connecting-try-this-basic-troubleshooting | |||
Table 2: Troubleshooting table with identified issues, possible reasons as well as solutions to solve the problems.
Supplemental File. Please click here to download this file.
Discussion
Pipetting of viscous materials, especially hydrogels for biomedical applications19,20,21,33,47, are routine tasks in many research labs to prepare a user-defined concentration or a dilution series with varying concentrations. Although it is repetitive and the execution is rather simple, it is mostly performed manually with low sample throughput18. This tutorial is introducing the operation of an open source workstation, which has been specifically designed for viscous materials, to enable automated mixing of viscous materials for reproducible generation of desired concentrations. This workstation is optimized for pipetting of hydrogels to enable automated and highly reliable handling by the integration of temperature docks for thermoresponsive materials, positive displacement pipettes for viscous materials, and an optional tip touch dock to remove excess material from the tip. The pipetting module has been specifically optimized to enable the processing of viscous material in a standardized and automated manner. In comparison to air cushion pipettes (Figure 5a), positive displacement pipettes (Figure 5b) dispense viscous materials without leaving residual material left in the tip, resulting in accurate aspirating and dispensing volumes. The optional tip touch dock removes excess sample material from the tip (Figure 5c,d), which is useful for gluey materials (e.g., 4% (w/v) alginate).
The protocol designer application has been specifically programmed for hydrogels and allows the dilution of up to four reagents with different concentrations and up to two diluents. The risk of errors in the calculation of final dilutions is prevented in this application, as users only choose the desired concentration or the serial dilution steps. Required aspirating and dispensing volumes are calculated automatically, saved in a separate documentation text file, and then filled into the protocol script. This protocol design application gives the user full control of all experimental parameters (e.g., pipetting speed) and ensures internal documentation of the important parameters. The protocol design app takes the filling level of the reservoir (e.g., well) into account and varies the aspirating/dispensing height to prevent unnecessary dipping into the viscous materials. This integrated feature avoids material accumulation on the outer wall of the tip, and, thereby, ensures reliable aspirating and dispensing tasks throughout the protocol. Although the protocol designer application has been developed for hydrogel dilution steps, it can be also used for dilution of nonviscous liquids, such as Orange G dyes. The protocol designer application, which is accessible via the repository under ‘/examples/publication-JoVE’, is the version which is explained in the protocol section and highlighted in the video. This version will not be updated. However, an updated version of the protocol designer application is available via the main repository page. The calibration terminal was initially developed by Sanderson48 and has been optimized for the calibration of positive displacement pipettes.
As described in the protocol section 4, pipettes as well as containers must be calibrated initially. This calibration process is crucial to define and save the positions which are then used to calculate the movement increments. Therefore, successful protocol execution relies on well-defined calibration positions, as wrong calibration points could result in crashing of the tip into a container. Since the plunger positions of the pipettes must be calibrated manually, pipetting accuracy and precision depend greatly on the performed calibration. These calibration procedures depend highly on the user experience with the pipetting module, and, therefore, training with experienced staff is recommended at the beginning to ensure proper calibration procedures. In addition to the manual calibration on the pipetting module, the pipette itself must be calibrated to ensure accurate pipetting. It is recommended to calibrate the pipettes at least every 12 months to meet to acceptance criteria as specified in ISO 8655. To evaluate the pipette calibration internally, validation and verification are available as described by Stangegaard et al.16.
For the generation of a reliable data set, it is crucial to start with reagents of high quality. This is especially important for hydrogel processing tasks, as batch-to-batch variations might impact the generated results within this protocol. In addition to batch-to-batch variations, subtle changes in the preparation of small volumes may also contribute to property differences. To prevent this, preparation of larger volumes is recommended, which can be used for the entire experiments.
The validation and verification procedures rely on the usage of a dye to identify reliable mixtures. The presented protocol describes the application of Orange G, but the general protocol and analysis workflow can be also adapted to fluorescent dyes49,50. The usage of Orange G reduces the technical requirements of the spectrophotometer and eliminates precautions taken to prevent bleaching of the fluorescent dyes after exposure to light. Issues in the dissolving behavior or cluster formation of the dye have not been observed with the presented materials during experiments but might appear with other materials. Potential cluster formation and, therefore, the interaction between dye and material could be easily detected with a microscope.
The procedures and techniques presented in this tutorial add automation capability to current workflows for viscous materials to achieve highly reliable tasks with minimal human labor. The provided troubleshooting table (Table 2) includes identified issues and presents possible reasons as well as solutions to solve the problems. The presented workstation has been successfully applied to natural (gelatin, gellan gum, matrigel) and synthetic (e.g., poly(ethylene glycol) [PEG], Pluronic F127, Lutrol F127) polymeric materials for automated pipetting tasks. In particular, the combination of an open source workstation and an open source protocol design application designed for viscous materials will be very useful for researchers working in the fields of biomedical engineering, material science, and microbiology.
Disclosures
CM and DWH are founders and shareholders of Gelomics Pty Ltd. CM is also the Director of Gelomics Pty Ltd. The authors declare no conflict of interests relevant to the subject of this article. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the article apart from those disclosed.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the members of the Centre in Regenerative Medicine at QUT, in particular, Antonia Horst and Pawel Mieszczanek for their helpful suggestions and feedback. This work was supported by the QUT’s Postgraduate Research Award for SE, and by the Australian Research Council (ARC) under grant agreement IC160100026 (ARC Industrial Transformation Training Centre in Additive Biomanufacturing). NB was supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Peter Doherty Early Career Research Fellowship (APP1091734).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 15 reaction tubes | Fisher Scientific, Inc. (USA) | 14-959-53A | |
| 5 mL tubes | Pacific Laboratory Products Australia Pty. Ltd. (Australia) | SCT-5ML | size depends on experimentl protocol; also Eppies (0.5, 1, 1.5 mL) or Falcon tubes (15, 50mL) can be used; product is manufactured by Axygen, Inc. https://www.pacificlab.com.au/shop/tubes-plastic/sct-5ml-tubewith-screwcap-blue-unassembled-5ml-self-standing/1/name |
| 50 mL reaction tubes | Fisher Scientific, Inc. (USA) | 14-432-22 | |
| 70% w/w Ethanol | LabChem, Inc. (USA) | aja726-5Lpl | |
| 96-well plate | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (USA) | https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/168055 | |
| Alginate | NovaMatrix | 4200001 | https://www.novamatrix.biz/store/pronova-up-lvg/ |
| Demineralized or ultrapure (MilliQ) water | |||
| Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) | Synthetized in-house | detailed protocol (incl materials and references) is available in Loessner et al. (2016), Nature Protocols. https://www.nature.com/articles/nprot.2016.037 | |
| Lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate (LAP) | Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. (USA) | 900889 | |
| M4 and M5 Allen key | OpenBuilds, inc. (USA) | 179, 190 | also available in every hardware store. https://openbuildspartstore.com/allen-wrench/ |
| OrangeG | Fisher Scientific (USA) | O267-25 | https://www.fishersci.com/shop/products/orange-g-certified-biological-stain-fisher-chemical/O26725 |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (USA) | 14190-144 | alternativly: PBS tablets: 18912014 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) |
| Equipment | |||
| Aluminium blocks for temperature dock | Ratek Instruments Pty. Ltd. (Australia) | SB16 | blocks for different tube sizes are available. http://www.ratek.com.au/products/SB16-Block-with-12x16mm-holes.html |
| Analytical balance | Sartorius AG (Germany) | ED224S | |
| Open source liquid handling robot: commercial product | Opentrons Laboratories, Inc. (USA) | OT-One S Pro | https://shop.opentrons.com/products/ot-one-pro |
| Open source liquid handling robot: open source hardware | Assembled in-house following an open source approach | hardware and software files are freely accessible on GitHub and Zenodo (links provided); building instructions are provided. https://github.com/SebastianEggert/OpenWorkstation. https://zenodo.org/record/3612757#.XipEjBV7F24 | |
| Positive displacement pipette: MicromanE | Gilson, Inc. (USA) | FD10006 | depends on required size. https://www.gilson.com/default/shop-products/pipettes/positive-displacement.html |
| Spectrophotometer | BMG LABTECH GmbH (Germany) | CLARIOstar | |
| Tips: capillary pistons | Gilson, Inc. (USA) | F148180 | depends on required size. https://www.gilson.com/default/shop-products/pipette-tips.html?technique_en_ww_lk=191 |
References
- Jarvis, M. F., Williams, M. Irreproducibility in Preclinical Biomedical Research: Perceptions, Uncertainties, and Knowledge Gaps. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 37 (4), 290-302 (2016).
- Collins, F. S., Tabak, L. A. Policy: NIH plans to enhance reproducibility. Nature. 505 (7485), 612-613 (2014).
- Freedman, L. P., Cockburn, I. M., Simcoe, T. S. The economics of reproducibility in preclinical research. PLoS Biology. 13 (6), 1-9 (2015).
- Niepel, M., et al. A Multi-center Study on the Reproducibility of Drug-Response Assays in Mammalian Cell Lines. Cell Systems. 9 (1), 35-48 (2019).
- Prinz, F., Schlange, T., Asadullah, K. Believe it or not: how much can we rely on published data on potential drug targets. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 10 (9), 712(2011).
- Baker, M. 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Nature. 533 (7604), 452-454 (2016).
- Begley, C. G., Ellis, L. M. Raise standards for preclinical cancer research. Nature. 483 (7391), 531-533 (2012).
- Sena, E. S., van der Worp, H. B., Bath, P. M. W., Howells, D. W., Macleod, M. R. Publication Bias in Reports of Animal Stroke Studies Leads to Major Overstatement of Efficacy. PLoS Biology. 8 (3), 1000344(2010).
- Ioannidis, J. P. A., Kim, B. Y. S., Trounson, A. How to design preclinical studies in nanomedicine and cell therapy to maximize the prospects of clinical translation. Nature Biomedical Engineering. 2 (11), 797-809 (2018).
- Enserink, M. Sloppy reporting on animal studies proves hard to change. Science. 357 (6358), 1337-1338 (2017).
- Freedman, L. P., Inglese, J. The Increasing Urgency for Standards in Basic Biologic Research. Cancer Research. 74 (15), 4024-4029 (2014).
- Lippi, G., Lima-Oliveira, G., Brocco, G., Bassi, A., Salvagno, G. L. Estimating the intra- and inter-individual imprecision of manual pipetting. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM). 55 (7), 962-966 (2017).
- Hentz, N. G., Knaide, T. R. Effect of Liquid-Handling Accuracy on Assay Performance. Journal of Laboratory Automation. 19 (2), 153-162 (2014).
- Reason, J. Understanding adverse events: human factors. Quality and Safety in Health Care. 4 (2), 80-89 (1995).
- Schober, L., et al. Cell Dispensing in Low-Volume Range with the Immediate Drop-on-Demand Technology (I-DOT). Journal of Laboratory Automation. 20 (2), 154-163 (2015).
- Stangegaard, M., Hansen, A. J., Frøslev, T. G., Morling, N. A Simple Method for Validation and Verification of Pipettes Mounted on Automated Liquid Handlers. Journal of Laboratory Automation. 16 (5), 381-386 (2011).
- Crombie, D. E., et al. Development of a Modular Automated System for Maintenance and Differentiation of Adherent Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. SLAS Discovery. 22 (8), 1016-1025 (2017).
- Eggert, S., Hutmacher, D. W. In vitro disease models 4.0 via automation and high-throughput processing. Biofabrication. 11 (4), 043002(2019).
- Malda, J., et al. 25th Anniversary Article: Engineering Hydrogels for Biofabrication. Advanced Materials. 25 (36), 5011-5028 (2013).
- Zhang, Y. S., Khademhosseini, A. Advances in engineering hydrogels. Science. 356 (6337), (2017).
- Kratochvil, M. J., et al. Engineered materials for organoid systems. Nature Reviews Materials. 4 (9), 606-622 (2019).
- Caliari, S. R., Burdick, J. A. A practical guide to hydrogels for cell culture. Nature Methods. 13 (5), 405-414 (2016).
- Pati, F., et al. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nature Communications. 5, 1-11 (2014).
- Gao, G., Huang, Y., Schilling, A. F., Hubbell, K., Cui, X. Organ Bioprinting: Are We There Yet. Advanced Healthcare Materials. 7 (1), 1701018(2018).
- Schuurman, W., et al. Gelatin-Methacrylamide Hydrogels as Potential Biomaterials for Fabrication of Tissue-Engineered Cartilage Constructs. Macromolecular Bioscience. 13 (5), 551-561 (2013).
- Lim, K. S., et al. New Visible-Light Photoinitiating System for Improved Print Fidelity in Gelatin-Based Bioinks. ACS Biomaterials Science and Engineering. 2 (10), 1752-1762 (2016).
- Müller, M., et al. Development and thorough characterization of the processing steps of an ink for 3D printing for bone tissue engineering. Materials Science and Engineering C. 108, 110510(2020).
- Sewald, L., et al. Beyond the Modification Degree: Impact of Raw Material on Physicochemical Properties of Gelatin Type A and Type B Methacryloyls. Macromolecular Bioscience. 18 (12), 1-10 (2018).
- Eggert, S., Mieszczanek, P., Meinert, C., Hutmacher, D. W. A modular open source technology for automated in vitro workflows. Zenodo. , (2020).
- Volk, A., Kähler, C. J. Density model for aqueous glycerol solutions. Experiments in Fluids. 59 (5), 75(2018).
- Zhang, H., Grinstaff, M. W. Recent Advances in Glycerol Polymers: Chemistry and Biomedical Applications. Macromolecular Rapid Communications. 35 (22), 1906-1924 (2014).
- Klotz, B. J., Gawlitta, D., Rosenberg, A. J. W. P., Malda, J., Melchels, F. P. W. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends in Biotechnology. 34 (5), 394-407 (2016).
- Loessner, D., et al. Functionalization, preparation and use of cell-laden gelatin methacryloyl-based hydrogels as modular tissue culture platforms. Nature Protocols. 11 (4), 727-746 (2016).
- Ansari, S., et al. Regulation of the fate of dental-derived mesenchymal stem cells using engineered alginate-GelMA hydrogels. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A. 105 (11), 2957-2967 (2017).
- Axpe, E., Oyen, M. Applications of Alginate-Based Bioinks in 3D Bioprinting. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 17 (12), 1976(2016).
- Ma, X., et al. 3D printed micro-scale force gauge arrays to improve human cardiac tissue maturation and enable high throughput drug testing. Acta Biomaterialia. 95, 319-327 (2019).
- Bas, O., et al. Rational design and fabrication of multiphasic soft network composites for tissue engineering articular cartilage: A numerical model-based approach. Chemical Engineering Journal. 340, 15-23 (2018).
- O'Connell, C. D., et al. Tailoring the mechanical properties of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels through manipulation of the photocrosslinking conditions. Soft Matter. 14 (11), 2142-2151 (2018).
- LearnPython.org. , Available from: https://www.learnpython.org (2020).
- Raspberry Pi Foundation: Using your Raspberry Pi. , Available from: https://projects.raspberrypi.org/en/projects/raspberry-pi-using (2020).
- Raspberry Pi Foundation: Setting up your Raspberry Pi. , Available from: https://projects.raspberrypi.org/en/projects/raspberry-pi-setting-up/4 (2020).
- Raspberry Pi Foundation: Connect your Raspberry Pi. , Available from: https://projects.raspberrypi.org/en/projects/raspberry-pi-setting-up/3 (2020).
- Python Software Foundation: python.org. , Available from: https://www.pthon.org (2020).
- Python Software Foundation: pypi.org. , Available from: https://pypi.org (2020).
- Opentrons Labworks, Inc: Installing pipettes. , Available from: https://support.opentrons.com/en/articles/689945-installing-pipettes (2020).
- Kang, C. W., Lee, M. S., Seong, Y. J., Hawkins, D. M. A Control Chart for the Coefficient of Variation. Journal of Quality Technology. 39 (2), 151-158 (2007).
- Annabi, N., et al. 25th Anniversary Article: Rational Design and Applications of Hydrogels in Regenerative Medicine. Advanced Materials. 26 (1), 85-124 (2014).
- Theo Sanderson: OpenTronsTerminalCalibration. , Available from: https://github.com/theosanderson/OpentronsTerminalCalibration (2020).
- Rhode, H., et al. An Improved Method for Checking HTS/uHTS Liquid-Handling Systems. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 9 (8), 726-733 (2004).
- Taylor, P. B., et al. A Standard Operating Procedure for Assessing Liquid Handler Performance in High-Throughput Screening. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 7 (6), 554-569 (2002).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved