Method Article
Quantifying Spontaneous Ca2+ Fluxes and their Downstream Effects in Primary Mouse Midbrain Neurons
In This Article
Summary
Here we present a protocol to measure in vitro Ca2+ fluxes in midbrain neurons and their downstream effects on caspase-3 using primary mouse midbrain cultures. This model can be employed to study pathophysiologic changes related to abnormal Ca2+ activity in midbrain neurons, and to screen novel therapeutics for anti-apoptotic properties.
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a devastating neurodegenerative disorder caused by the degeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons. Excessive Ca2+ influx due to the abnormal activation of glutamate receptors results in DA excitotoxicity and has been identified as an important mechanism for DA neuron loss. In this study, we isolate, dissociate, and culture midbrain neurons from the mouse ventral mesencephalon (VM) of ED14 mouse embryos. We then infect the long-term primary mouse midbrain cultures with an adeno-associated virus (AAV) expressing a genetically encoded calcium indicator, GCaMP6f under control of the human neuron-specific synapsin promoter, hSyn. Using live confocal imaging, we show that cultured mouse midbrain neurons display spontaneous Ca2+ fluxes detected by AAV-hSyn-GCaMP6f. Bath application of glutamate to midbrain cultures causes abnormal elevations in intracellular Ca2+ within neurons and this is accompanied by caspase-3 activation in DA neurons, as demonstrated by immunostaining. The techniques to identify glutamate-mediated apoptosis in primary mouse DA neurons have important applications for the high content screening of drugs that preserve DA neuron health.
Introduction
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide, with no known cure. Estimates suggest that PD prevalence will continue to increase and is projected to surpass 1 million diagnoses by the year 2030 in the United States alone1. With few effective treatments currently available to combat PD, there is a pressing need to develop more effective therapies. PD is characterized by a rapid and progressive loss of midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons2. The mechanisms that underlie neurodegeneration in PD are poorly understood. Evidence suggests a likely convergence of multiple mechanisms, such as oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, etc. that contribute to the initiation of apoptotic signaling cascades and eventual cell death3.
One such convergent mechanism, glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity has been implicated in multiple neurodegenerative diseases, including PD4. While glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity is thought to work mainly through stimulation of NMDA receptors via an excessive increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration and eventual initiation of apoptosis, Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors have also been implicated in the excitotoxic response5,6,7. Therefore, it is of interest to determine the contribution of AMPA receptors to glutamate-mediated apoptosis within a PD model. This can be achieved using NBQX, an AMPA and kainate blocker, which at micromolar concentrations is selective for AMPA receptors8. Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity and apoptotic signaling cascades are an ideal downstream target to measure the extent of cell death, and a potential target for therapeutic intervention. Therefore, developing a high-content method for assessing glutamate-mediated modulation of calcium activity and associated downstream signaling in primary ventral mesencephalic (VM) neurons would be valuable for screening novel treatment methods on their ability to preserve neuronal health.
Here, we have developed a protocol in which we express the genetically encoded calcium indicator (GECI), GCaMP6f, using AAV2/5 with the human synapsin (hSyn) promotor to measure the Ca2+ activity of mouse VM primary neurons in response to glutamate application which can be measured at the physiological and molecular level. This high-content screening can be adapted for discovering pharmaceuticals or treatments that modulate Ca2+ activity to preserve the health of VM neurons. We propose that this primary culture model is an effective way to screen for novel PD interventions, based on their ability to preserve the health of VM neurons and mitigate the progression of PD.
Protocol
All procedures involving the use of animal subjects have been approved by the Texas A&M University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (25th Nov 2019; AUP# 2019-0346).
NOTE: Preparation of cell culture solutions should be done using sterile procedure in a biological safety cabinet and filtered at 0.2 µm to prevent contamination.
1. Preparation of solutions and culture medium
- Prepare laminin coating solution by diluting 20 µL of 1 mg/mL laminin stock into 2 mL of sterile distilled H2O. Prepare on the day of dissection.
- Prepare 10% equine (horse) serum (ES) stop solution by adding 5 mL of ES to 45 mL of 1x Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS). Sterile filter using a 0.2 µm filter system or syringe filter tip. Store at 4 °C.
- Prepare 4% bovine serum albumin (BSA) stock solution by adding 2 g of BSA powder to 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and bringing to a final volume of 45 mL. Sterile filter using a 0.2 µm filter system or syringe filter tip. Store at 4 °C.
- Prepare papain stock solution by diluting papain to 3 mg/mL in 1x HBSS. Sterile filter using a 0.2 µm filter system or syringe filter tip. Store at -20 °C.
- Prepare deoxyribonuclease (DNase) solution by adding 20 mg of DNase powder to sterile H2O and bringing to a final volume of 20 mL. Sterile filter using a 0.2 µm filter system or syringe filter tip. Store at -20 °C.
- Prepare ascorbic acid stock solution by adding 352 mg of ascorbic acid to sterile distilled H2O and bringing to a final volume of 20 mL. Heat in 37 °C bath to dissolve if necessary. Sterile filter using a 0.2 µm filter system or syringe filter tip. Store at -20 °C.
- Prepare Cell Culture Medium by adding the following to 50 mL of Neurobasal medium: 500 µL of Glutamax (100x), 500 µL equine serum, 1 mL of B-27, 100 µL of ascorbic acid, 500 µL of penicillin-streptomycin, 50 µL of kanamycin and 50 µL of ampicillin. Sterile filter using a 0.2 µm filter system. Store at 4 °C.
- Prepare 0.01% Triton X-100 Solution by adding 1 mL of Triton X-100 into 9 mL of 1x PBS to make a 10% solution. As Triton X-100 is viscous, pipette slowly to allow tip to fill completely. Heat in 37 °C bath to dissolve if necessary. Store at 4 °C.
- To dilute 10% Triton X-100 stock to 0.01%, perform 3 serial 1:10 dilutions. Dilute 1 mL of 10% stock into 9 mL of 1x PBS to make 1% solution. Dilute 1 mL of 1% solution into 9 mL of 1x PBS to make 0.1% solution. Dilute 1 mL of 0.1% solution into 9 mL of 1x PBS to make a 0.01% solution.
- Prepare 10% and 1% normal goat serum (NGS) solution by adding 1 mL of NGS to 9 mL of 1x PBS for a 10% solution. Add 100 µL of NGS to 9.9 mL of 1x PBS to make 1% solution.
- Prepare glutamate stock solution (100 mM) by adding 735 mg of L(+)-Glutamic acid to sterile distilled H2O and bring to a final volume of 50 mL. Solubility at this concentration will be an issue. Adding small volumes (100 µL) of 1 M hydrochloric acid is sufficient to increase solubility.
- Prepare NBQX stock solution (10 mM) by adding 50 mg of NBQX to sterile distilled H2O and bring to a final volume of 13 mL.
2. Preparation of culture dishes and coverslips (Done the day before dissection)
NOTE: We have found that combining three coating agents, poly-L-lysine, poly-L-ornithine, and laminin allows for ideal cell adhesion and viability.
- Place 10 35 mm Petri dishes in a biological safety cabinet. Place two circular 12 mm coverslips in each dish and fill with 70% EtOH for 10 min. Use a vacuum line to aspirate the remaining EtOH from each dish, allowing the EtOH to evaporate completely.
- Pipette ~90-100 µL of 0.1% poly-L-lysine solution onto each coverslip, making sure that the entire coverslip is covered by the poly-L-lysine solution. Cover the dishes with lids and place in a 37 °C incubator for 1 h.
- Aspirate remaining poly-L-lysine solution from each coverslip and rinse with sterile H2O.
- Repeat steps 2.2 – 2.3 with 0.1% poly-L-ornithine solution.
- Again, repeat steps 2.2 – 2.3 with 0.01% laminin solution. Place in a 37 °C/5% CO2 incubator until ready for cell plating on the following day.
3. Mouse embryonic dissections
NOTE: We use between 4 to 6 timed pregnant mice per culture. While much of the dissection process occurs outside of a biological safety cabinet it is still important to maintain sterile procedure. Plentiful use of 70% EtOH on surfaces near the dissection microscope and on surgical tools is ideal. A mask may also be worn during the dissection to further prevent contamination. Additionally, we use 4 separate antibiotics in the culture medium, so contamination is unlikely. However, if use of antibiotics is problematic, this dissection setup could be moved inside a sterile hood. To preserve cell viability all dissection solutions should be pre-chilled at 4 ˚C, and dissections should be completed as quickly as possible. We do not perform the dissections on ice. The method for dissection of mouse embryonic midbrain neurons is identical to previously described methods9,10.
- Prepare a space on a bench near a dissection microscope with an absorbent pad and spray liberally with 70% EtOH.
- Spray two 100 x 15 mm glass Petri dishes and one 50 x 10 mm glass Petri dish with 70% EtOH and allow EtOH to evaporate. Once evaporated, place 50 mL of sterile 1x HBSS into each 100 x 15 mm Petri dish.
- Submerge surgical scissors, forceps, and microtome blade in 70% EtOH for 10 min minimum to sterilize. Place instruments on the absorbent pad to dry.
- Using CO2 followed by cervical dislocation, euthanize 2-3 month old timed pregnancy mice on embryonic day 14.
- Spray the abdomen of the euthanized mice with 70% EtOH. Using forceps grab the lower abdomen and open the abdominal cavity using surgical scissors. Start cutting near where the forceps are holding the abdomen, making lateral cuts on each side until the abdominal wall can be folded back and the uterus is clearly visible.
- Using surgical scissors, cut both ends of the uterine horn. Then remove the uterus and place into Petri dish with 1x HBSS.
- Using straight-tip forceps carefully remove embryos from the uterus. Leave embryos in HBSS throughout this process. Using either the forceps or a microtome blade, quickly decapitate embryos by cutting near the neck. Making as level a cut as possible.
- Under a dissecting microscope, move an embryo head to a dry 50 mm Petri dish and place on the ventral side. Stabilize the head with forceps by placing and penetrating near the eyes/snout. Forceps should be angled downward at ~45° to avoid penetrating the mesencephalon.
- Using the forceps in the other hand, carefully remove the translucent layer of skin and skull just before the prominent ridge of the mesencephalon. Start near the midline and remove skin and skull caudally until the mesencephalon is fully exposed.
- Hold the forceps perpendicular to the exposed mesencephalon with one tip between the cortex and mesencephalon and the other near the cerebellum. Press down and pinch the forceps together to remove the entire midbrain. The midbrain segment should be approximately 0.5 mm thick. Place the midbrain segment into the second Petri dish filled with fresh 1x HBSS. Repeat this process for each embryo.
- Using the dissection microscope, position the brain segment with the ventral side facing up. If the meninges are still attached, carefully remove it by grabbing with the forceps and lifting up and away from the brain segment.
- The brain segment should have 4 visible quadrants. Place the segment in such a manner that the two smaller quadrants are positioned superior to the two larger quadrants. There is a prominent ridge separating the superior two (small) quadrants from the inferior two (large) quadrants.
- Using the forceps pinch and separate the superior quadrants from the inferior quadrants, and then discard the superior quadrants. The remaining inferior quadrants will have excess tissue laterally on the dorsal side, this tissue will look less opaque than the remaining ventral tissue. Remove the less dense dorsal tissue and discard. The remaining segment should contain both the Substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA).
- Using the forceps cut the remaining ventral tissue segment into 4 smaller pieces and using a 1mL wide bore pipette transfer these segments in a 15 mL conical tube with 1x HBSS. Keep the conical tube with brain segments on ice throughout the procedure.
- Repeat this process for all remaining brain segments.
4. Dissociation of cells
- Enzymatic digestion of cells
- Carefully aspirate the HBSS from the 15 mL conical tube containing midbrain segments, leaving the segments at the bottom of the tube.
- Add ~800 µL of papain solution to the tube and place in a 37 °C incubator for 7 min. Resuspend cells by flicking the tube and replace to the 37 °C incubator for an additional 7 min.
- With a wide-bore 1 mL pipette tip remove only the midbrain segments into a 1 mL aliquot of DNase. Allow the segments to reach the bottom of the aliquot or about 1 min of exposure.
- With a wide-bore 1 mL pipette tip remove only the midbrain segments into a 15 mL conical tube containing 2 mL of stop solution. Allow segments to settle at the bottom of the tube and repeat the rinse in an additional conical tube filled with stop solution.
- Mechanical trituration of cell suspension
- In the second stop solution rinse tube, using a wide-bore 1 mL pipette tip, pipette the cells up and down 10 times until there are no large tissue segments visible. It is important to avoid over trituration for minimal cell lysis.
- Slowly pipette 300 µL of 4% BSA solution to the bottom of the 15 mL conical tube containing brain segments. Carefully remove the pipette tip to maintain a suspension layer. Centrifuge at 0.4 x g for 3 min. Then carefully aspirate the supernatant and resuspend cells in 400 µL of cell culture medium.
5. Plating the cells
NOTE: Based on experience, about 100,000 viable cells per embryo are collected. 2-3 month old timed pregnant mice typically have litter sizes of 8-10 embryos; therefore, a rough estimate for total yield of cells per timed pregnant mouse is approximately 1 million cells.
- Using a hemocytometer preform a cell count and then dilute the suspension to 2,000 cells/µL using cell culture medium. Triturate briefly to mix.
- Remove coverslips with laminin solution from step 2 from the incubator and aspirate the remaining laminin solution from the coated coverslips using a vacuum. Plate quickly to avoid the coverslips from drying completely. Pipette 100 µL (2.0 x 105 cells/coverslip) onto each coverslip and place Petri dishes into a 37 °C incubator for 1 h.
- Carefully add 3 mL of cell culture medium to each dish and place back into the 37 °C incubator. Preform half medium changes 2 times per week for 2 weeks.
6. Infection of cell culture at 14 DIV with adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors
- For each dish prepare 1 mL of serum free DMEM medium with 1 µL of hSyn-GCaMP6f AAV (1.0 x 1013 titer)
- Aspirate the cell culture medium from each dish and replace with 1 mL of serum free DMEM containing hSyn-GCaMP6f. Place dishes back into the 37 °C incubator for 1 h.
- Aspirate the serum free medium containing AAVs and replace with 3 mL of cell culture medium. Place dishes back into the 37 °C incubator. We have found that 5-7 days of AAV infection allows for ideal levels of GCaMP expression. Continue to change medium every 2-3 days throughout this period of viral infection.
7. Live confocal Ca2+ imaging between 19-21 DIV
NOTE: As mentioned in step 6.3, imaging can be done between 5-7 days following viral infection. This is the ideal window to achieve visible expression of the fluorophore at levels which allow for detection of spontaneous Ca2+ activity.
- Preparation of recording buffers
- To make 1 L of HEPES recording buffer, add: 9.009 g of NaCl, 0.3728 g of KCl, 0.901 g of D-glucose, 2.381 g of HEPES, 2 mL of 1 M CaCl2 stock solution, and 500 µL of 1 M MgCl2 stock solution to 800 mL of sterile distilled H2O. Bring the pH to 7.4 with NaOH. Bring to a final volume of 1 L.
- To make 200 mL of 20 µM glutamate recording buffer, dilute 40 µL of 100 mM glutamate stock solution into 200 mL of HEPES recording buffer described above.
- To make 200 mL of 10 µM NBQX recording buffer, dilute 200 µL of 10 mM NBQX stock solution into 200 mL of HEPES recording buffer.
- Confocal imaging
- Fill a sterile 35 mm Petri dish with 3 mL of recording buffer.
- Remove a 35 mm Petri dish with infected cultures from the 37 °C incubator. Using fine tip forceps, carefully grab the edge of one coverslip and transfer it quickly into the Petri dish filled with recording buffer. Place the remaining coverslip in medium back into the 37 °C incubator. Transport the dish with recording buffer to the confocal microscope.
- Start the imaging software. Proceed to next step while it initializes.
- Start the peristaltic pump and place the line into the recording buffer. Calibrate the speed of flow to be 2 mL/min.
- Transfer the infected coverslip from the 35 mm Petri dish into the recording bath.
- Using the 10x water immersion objective and BF light, find the plane of focus and look for a region with a high density of neuron cell bodies. Switch to the 40x water immersion objective and using BF light refocus the sample.
- In the “Dyes list” window within FluoView select AlexaFluor 488 and apply it.
- AAV expression can be variable; therefore, in order to prevent overexposure and photobleaching of the fluorophores, start with low HV and laser power settings. For the AlexaFluor 488 channel, set the high voltage (HV) to 500, the gain to 1x, and offset to 0. For the 488 laser line set the power to 5%. In order to increase the effective volume imaged in the z-plane, increase the pinhole size to 300 µm. Use the “focus x2” scanning option to optimally adjust emission signals to sub-saturation levels. From here, settings can be adjusted until ideal visibility of each channel is achieved.
NOTE: To accurately capture the full range of Ca2+ fluxes with GCaMP, adjust the baseline HV and laser power settings in order to allow for an increase in fluorescent intensity without oversaturating the detector. - Once microscope settings are optimized, move the stage in order to locate a region with multiple cells displaying spontaneous changes in GCaMP6f fluorescence and focus to the desired plane for imaging.
- Use the “Clip rect” tool to clip the imaging frame to a size that can achieve a frame interval of just under 1 second. This is necessary to set the imaging interval at 1 frame per second.
- Set the “Interval” window to a value of 1.0 and the “Num” window to 600.
NOTE: In order to deliver different recording buffers at the desired time point (300 s), it is important to calibrate the latency of the pump to deliver the new solution to the bath. This will be dependent on the solution perfusion rate (2 mL/min) and the length of the line used to pump solution. - To capture a t-series movie select the “Time” option and then use the “XYt” scanning option to begin imaging.
- Watch the imaging progress bar and move the line from the HEPES recording buffer into the 20 µM glutamate recording buffer at the appropriate time point (e.g., if the latency of the pump is calibrated to deliver solution at 60 s, move the line into the glutamate buffer at 240 frames in order to deliver glutamate at 300 s).
- When imaging is complete, select the Series Done button and save the finished t-series movie. Continue to perfuse 20 µM Glutamate for an additional 5 min, so that the cultured neurons have been exposed to glutamate for a total of 10 min. Repeat this process for each coverslip to be imaged.
- Following the additional 5 min exposure to 20 µM Glutamate, remove the coverslip from the bath and place back into the 35mm Petri dish containing recording buffer until the day of imaging is completed. When finished, proceed to step 8.
- Ca2+ trace analysis
- Perform image analysis in ImageJ. Install the BIO-FORMATS plugin for ImageJ, which will allow .OIB image files to open.
- In the ImageJ toolbar, click Analyze | Set Measurements, and select the box for Mean gray value (MGV).
- In ImageJ, open a t-series movie as a hyperstack.
- Drag the slider for the movie and identify the frame with maximal glutamate response to visualize all neurons that respond to glutamate. Use the polygon tool to trace all visible neuron cell bodies, adding their ROIs to the “ROI manager” list.
- When finished tracing and adding ROIs, select all ROIs within the ROI Manager window and use the Multi measure selection in the more list of options. Copy and paste these data into a spreadsheet. Complete this process for all movies to be analyzed.
- For each ROI, convert the raw MGV data from each frame to ΔF/F0 values using the equation: ΔF/F0 = [F(t) – F0] / F0. Where F(t) = MGV of any given frame, and F0 = average baseline MGV of ~10 frames where no Ca2+ fluxes are present.
- Using a statistical software such as OriginPro 2020, converted ΔF/F0 traces can be made into line graphs. The “Peak analyzer” function can be used (or similar function if using a different software) to measure the peak amplitude of glutamate response, latency to respond to glutamate, and area under the curve.
8. Immunostaining of cultures
NOTE: Following fixation with formalin, coverslips can be stored in 1x PBS at 4 °C until ready to be processed for immunostaining. Primary and secondary antibody incubation was done in a serial manner, as such incubation with anti-Caspase-3 primary antibody and its complementary secondary antibody preceded incubation with the anti-TH primary antibody and its complementary secondary antibody.
- Immediately following glutamate exposure, place the coverslip back into its 35 mm Petri dish, aspirate the recording buffer, and add 3 mL of 10% formalin. Let sit for 40 min at room temperature (RT).
- Rinse the dish 3 times with 1x PBS.
- Aspirate the PBS and permeabilize cells in 1 mL of 0.01% Triton X-100 in PBS for 2 min.
- Rinse the dish 3 times with 1x PBS.
- Aspirate the PBS and block cells in 1 mL of 10% NGS in PBS for 40 min.
- Rinse the dish 3 times with 1x PBS.
- Add 1 µL of rabbit anti-Caspase-3 primary antibody to 1 mL of 1% NGS in PBS (1:1000 dilution). Aspirate PBS from the dish and replace with the primary antibody solution. Place on a shaker and incubate for 1.5 h at RT.
- Rinse the dish 3 times with 1x PBS.
- Add 1 µL of goat anti-rabbit AlexaFluor 488 secondary antibody to 1 mL of 1% NGS in PBS (1:1000 dilution). Aspirate PBS from the dish and replace with the secondary antibody solution. Place on a shaker and incubate for 1 h at RT. Moving forward protect the samples from light.
- Rinse the dish 3 times with 1x PBS.
- Repeat steps 8.7 – 8.10, but using the chicken anti-TH primary antibody (1:1000) in step 8.7 and the goat anti-chicken AlexaFluor 594 secondary antibody (1:1000) in step 8.9.
- Following the final PBS rinse, place 30 µL of mounting medium onto a microscope slide. Using forceps grab a coverslip from the 35 mm Petri dish and place the coverslip with the cells facing down into the mounting medium. Both coverslips will fit on a single microscope slide if placed correctly. Place in a dry, dark area and allow the mounting medium to dry overnight.
9. Confocal imaging of immunostained cultures
- Confocal imaging
- Start the imaging software. Place the sample onto the microscope stage.
- With the microscope eyepieces, using a 20x magnification objective and epifluorescent light with a TRITC filter, focus the sample and search for a TH+ cell body.
- Once locating a TH+ cell body, center it in the field of view and then move to the 60x magnification objective.
- Select the AlexaFluor 488 and AlexaFluor 594 dyes in the “dye list” window.
- As with live imaging, start with low HV, gain, offset, and laser power settings to prevent photobleaching. Use the “focus x2” scan option to assess the fluorescent intensity of each channel and adjust accordingly. As these images will later be quantified for fluorescent intensity it is necessary to keep the imaging settings consistent across all fields of view. Therefore, it is best to look at a few examples of each condition to get an idea of the range of fluorescent intensity across samples.
- Once ideal imaging settings are determined, select the “focus x2” scan option and move the cell of interest into the center of the field of view. Increase the digital zoom to 3x using the “zoom” slider.
- Using the focus knob, find the plane of focus with the brightest fluorescence and capture a single plane XY image. Save the image to finish.
- Switch back to the 20x magnification objective to search for another TH+ cell. Repeat this process until the desired number of cells have been sampled from each condition.
- Image analysis
- In the ImageJ toolbar, click Analyze | Set Measurements, and select the boxes for Area, Integrated density, and Mean gray value.
- Open an image as a hyperstack with each channel separated by dragging and dropping into the ImageJ toolbar or selecting the image via the file menu.
- Use the TH channel (594 nm) to draw ROIs around the cell body. Using the polygon tracing tool in ImageJ, closely trace the outer edge of the cell body. Where the distance between the cell membrane and cell nucleus is the smallest, trace a straight line through the cytosol to the edge of the nucleus and then closely follow the outline of the nucleus in order to exclude it. Then trace a straight line back to the external membrane, bordering the initial line as closely as possible, and continue to follow the outline of the cell body until the ROI is complete.
- Using the keyboard shortcut “T” or using the toolbar menu path Analyze | Tools | ROI Manager, open the ROI manager and add the ROI that was just drawn to the list.
- Select the window of the caspase-3 channel (488 nm), and then select the added ROI in the “ROI Manager” list.
- In the ROI Manager window, select the Measure button. The results window will appear with the measurements set previously. Copy these to a spreadsheet and repeat this process for each cell.
Results
Following initial culturing of cells, we treated VM culture dishes at 14 DIV with 1 µL of AAV hSyn-GCaMP6f and allowed for 5 days of viral expression. On the day of imaging HEPES recording buffer was prepared fresh. We used two conditions; in one condition 20 µM glutamate was applied for 10 min, while in the other condition 5 min of 10 µM NBQX application preceded a 10 min co-application of 10 µM NBQX + 20 µM glutamate. In both conditions, we observed heterogenous and spontaneous changes in GCaMP6f fluorescence, which indicate spontaneous Ca2+ fluxes, as shown in the representative traces (Figure 1A,B, Supplemental Movie 1-2). Application of 20 µM glutamate generated a robust and sustained Ca2+ response in both spontaneously active and quiescent neurons (Figure 1A, Supplemental Movie 1). Application of 10 µM NBQX reduced spontaneous activity, and partially blocked the glutamate response (Figure 1B, Supplemental Movie 2). The extent to which glutamate application stimulated a Ca2+ response in each condition was quantified using area under the curve, peak amplitude, and latency to respond. Both area under the curve and peak amplitude were similar for both the glutamate and NBQX + glutamate treated conditions (Figure 1C), while latency to response was significantly increased in the NBQX + glutamate condition (Figure 2A,B). In addition to quantifying the Ca2+ response to glutamate treatment, we fixed and stained samples with an anti-caspase-3 antibody as a measure of glutamate-mediated apoptosis. We observed a range of caspase-3 activation across the conditions (Figure 3A,B). Caspase-3 activation was quantified by measuring area and mean caspase-3 intensity. When compared to untreated control cells, the average area of cells with caspase-3 activation under glutamate and NBQX + glutamate conditions trended towards significance (Figure 3B). Mean caspase-3 intensity was significantly higher in the glutamate and NBQX + glutamate conditions as compared to untreated controls (Figure 3B). Together, these results demonstrate a high-content framework in which apoptosis of neurons can be measured by quantifying Ca2+ responses to excitotoxic agents and followed up with an analysis of downstream apoptotic events such as caspase-3 activation in the same set of cultures.
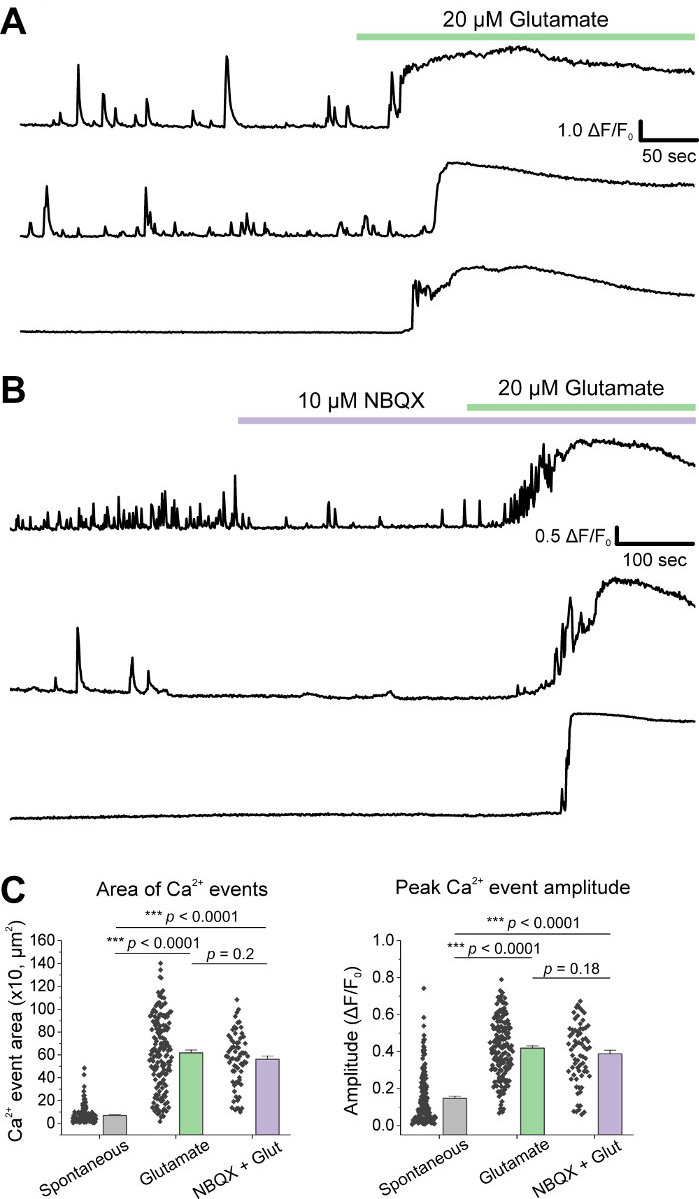
Figure 1: Cultured ventral mesencephalic neurons display spontaneous Ca2+ activity and are robustly stimulated by glutamate application. (A) Representative traces of spontaneous Ca2+ activity in VM neurons and their response to 20 µM Glutamate application. (B) Representative traces of spontaneous Ca2+ activity in VM neurons and their response to 10 µM NBQX + 20 µM Glutamate application. (C) Population data showing area under the curve and peak amplitude of Ca2+ traces. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
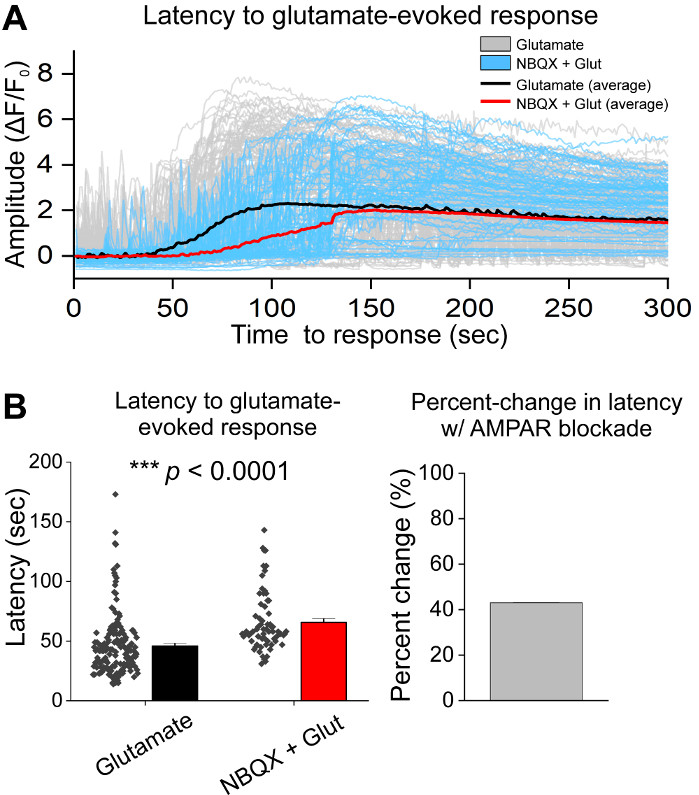
Figure 2: AMPAR blockade with NBQX delays response to glutamate application in cultured ventral mesencephalic neurons. (A) Representative Ca2+ traces of glutamate (gray) and NBQX + glutamate (blue) evoked responses. Average Ca2+ traces of glutamate (black) and NBQX + glutamate (red) are shown overlaid. (B) Population data showing latency to response for glutamate and NBQX + glutamate evoked responses. Percent change between glutamate and NBQX + glutamate conditions is displayed in the right panel. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
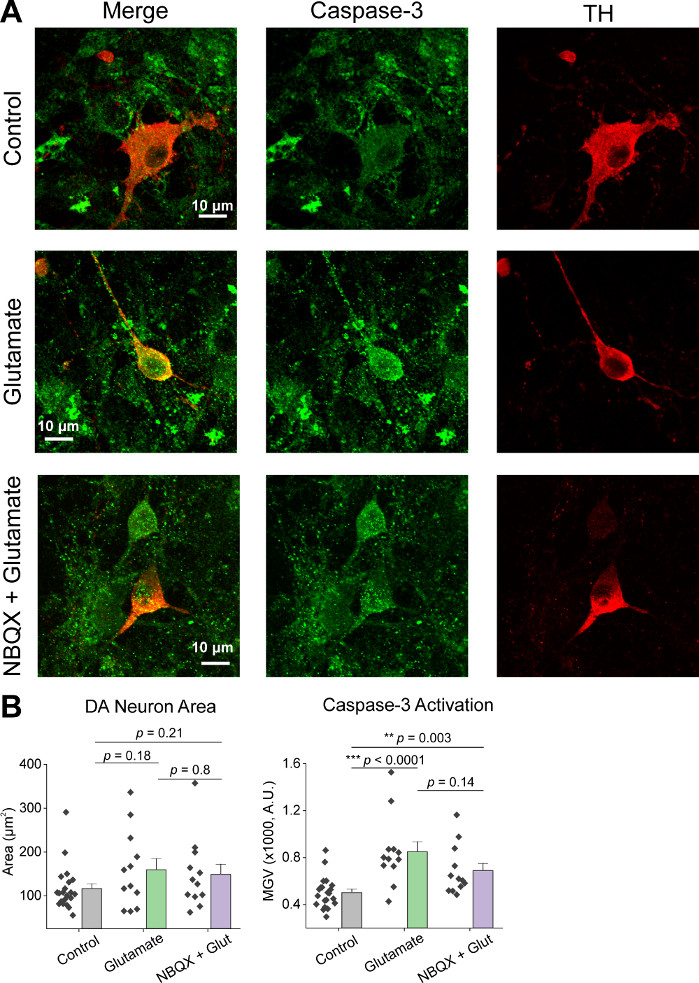
Figure 3: Glutamate application increases caspase-3 expression in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) positive ventral mesencephalic neurons. (A) Representative confocal images of VM cultures immunostained for caspase-3 (green) and TH (red), scale bar = 10 µm. (B) Population data showing DA neuron area and mean gray value of caspase-3 expression in each condition. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Supplementary Movie 1: Spontaneous Ca2+ activity and response to glutamate application.
Spontaneous Ca2+ fluxes in the presence of HEPES recording buffer (0-300 s) followed by application of 20 µM glutamate (301-600 s). Scale bar = 50 µm. Please click here to download this video.
Supplementary Movie 2: Spontaneous Ca2+ activity and response to NBQX + glutamate application.
Spontaneous Ca2+ fluxes in the presence of HEPES recording buffer (0-300 s) followed by application of 10 µM NBQX (301-600 s), and 10 µM NBQX + 20 µM glutamate (601-900 s). Scale bar = 50 µm. Please click here to download this video.
Discussion
We describe a long-term primary ventral mesencephalic (VM) cell culture system for high-content analysis of glutamate-mediated apoptosis in neurons. Studies have employed primary midbrain dopaminergic cultures to elucidate excitotoxic mechanisms in the context of PD models11,12. In this study, we employ a combinatorial approach using Genetically Encoded Calcium Indicators (GECIs) to measure Ca2+ activity and further associate this activity with downstream molecular changes, such as initiation of apoptotic signaling cascades4. The method has multiple advantages to other similar cell culture systems. As we have particular interest in excitotoxicity within the context of Parkinson’s disease, using primary VM cell cultures is ideal. By using different field relocation techniques, such as gridded coverslips or a motorized XY microscope stage combined with TH immunostaining, we can directly study the cell type specific effects of glutamate-mediated apoptosis in ventral midbrain neurons. Additionally, the 3-week cell culture model allows for neurons to develop their full, mature molecular profile, reflecting adult DA neurons9. Previous methods have mainly focused on molecular changes following glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity13,14. The model is unique in its ability to correlate acute changes in neuronal physiology with downstream molecular events in identified cell types. One limitation of the primary culture model is that the dissection technique captures the entire ventral midbrain, including DA and GABAergic neurons as well as neurons from the SNc and VTA. Evidence now suggests that DA neurons of the SNc have selective vulnerability to calcium and eventual cell death compared to DA neurons of the neighboring VTA15. Unfortunately, differentiating SNc from VTA neurons in embryonic cultures has proven difficult with few anatomical landmarks to define these structures in the embryonic brain.
We demonstrate that the primary culture technique allows for quantification of heterogenous spontaneous Ca2+ activity (Figure 1). Therefore, this is an ideal cell culture system model to study tonically active cells, such as pacemaking dopaminergic neurons of the midbrain, neocortical neurons, and GABAergic neurons of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)16,17. In most applications, Ca2+ imaging does not achieve the same temporal resolution as electrophysiology. Therefore, it is likely that a single Ca2+ event is analogous to a burst of neuronal action potentials. This can be interpreted to mean that Ca2+ imaging allows for relatively accurate measures of abnormal bursting activity in pacemaking cells and is therefore appropriate for a high content screen of Ca2+-mediated excitotoxic cell death.
To achieve and maintain spontaneous Ca2+ activity, it is important to address two key points in the protocol. First is the plating density of the cells following dissection. For primary VM neurons, previous studies have used around 100,000 cells/cm2 9,10. We have adapted the protocol to plate a density of 200,000 cells/cm2, which creates a heterogenous range of spontaneous activity and increases the number of dopaminergic VM neurons present on each coverslip. Since different pacemaking neurons have distinct firing properties16, the plating density needs to be customized to the cell type being studied and optimized in order to achieve ideal levels of spontaneous activity. Second is the incubation time following viral infection of AAVs. Like plating density, this will be dependent on the specific context of the research question and type of AAV being used. For the specific AAV used here, 5 days of incubation following viral infection is ideal to achieve the desired protein expression levels, which allows for dynamic changes in GCaMP fluorescence in order to record Ca2+ activity. Many factors determine how quickly and efficiently an AAV will express its cargo, much of which is outside the scope of this method, but briefly, it is important to consider promoter activity and the rate at which the cargo protein matures and folds.
Another advantage of the method is that it allows for considerable flexibility in format, expression vectors, use of imaging equipment, and the range of scientific questions that can be addressed. In addition, the method enables inquiry into a wide range of specific questions that surround glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity in PD, and other models of nervous system dysfunction. For example, glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity involves multiple receptors and signaling cascades5. By using the method, and as demonstrated with the AMPAR blocker, NBQX in Figure 1, it is possible to dissect out specific components of the excitotoxic glutamate response at a physiological and molecular level. Conceivably, a similar approach using inhibitors of second messenger systems could be used to determine their contribution to excitotoxicity. Additionally, the AAVs used here could be adapted to express GECIs with cell-specific promoters or AAV-expressed optogenetic sensors that could be used to measure other parameters such as neurotransmitter release.
Apart from primary embryonic dissections and confocal imaging, much of the protocol uses basic laboratory skills that do not require specialized training. Therefore, the limitations to the model include the difficulty of the embryonic dissection technique, the length of time the cells must be cultured to reach maturity, and access to a confocal microscope, or similar imaging apparatus. The many benefits and flexibility of the method outweighs these limitations, making this an ideal model to study the role glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity in nervous system disorders. Finally, this model could be an effective tool to screen novel compounds for anti-apoptotic effects and their ability to preserve DA neuron health.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Supported by grants from the American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA) and NIH R01NS115809-01 to RS. We thank the Texas A&M Institute for Genomic Medicine (TIGM) for providing timed pregnant mice to generate primary dopaminergic cultures.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 10% Formalin/PBS | VWR | 100496-506 | |
| 10X NA 0.3 water-immersion objective | Olympus | UMPLFLN10XW | |
| 12 mm circular cover glass No. 1 | Phenix Research Products | MS20-121 | |
| 20X NA 0.85 oil-immersion objective | Olympus | UPLSAPO20XO | |
| 35 mm uncoated plastic cell culture dishes | VWR | 25382-348 | |
| 40X NA 0.3 water-immersion objective | Olympus | LUMPLFLN40XW | |
| 60X NA 1.35 oil-immersion objective | Olympus | UPLSAPO60XO | |
| Ampicillin (sodium) | Gold Bio | A-301-25 | |
| B-27 supplement | ThermoFisher | 17504044 | 50x stock |
| Binolcular Microscope | Kent Scientific | KSCXTS-1121 | |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Sigma-Aldrich | A7030 | |
| Calcium Chloride (CaCl2), anhydrous | Sigma-Aldrich | 746495 | |
| Chicken polyclonal anti-Tyrosine Hydroxylase | Abcam | ab76442 | |
| Deoxyribonuclease I (DNase) | Sigma-Aldrich | DN25 | |
| D-glucose, andydrous | Sigma-Aldrich | RDD016 | |
| DMEM + GlutaMAX medium | ThermoFisher | 10569010 | 500 mL |
| Equine serum | ThermoFisher | 26050088 | heat-inactivated |
| Fiber Optic Illuminator, 100V | Kent Scientific | KSC5410 | |
| Filter System, PES 22UM 250ML | VWR | 28199-764 | |
| Fluoview 1000 confocal microscope | Olympus | ||
| Fluoview 1200 confocal microscope | Olympus | ||
| GlutaMAX supplement | ThermoFisher | 35050061 | |
| Goat polyclonal anti-chicken Alexa Fluor 594 | Abcam | ab150176 | |
| Goat polyclonal anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 | Abcam | ab150077 | |
| Hanks-balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) 1x | ThermoFisher | 14175095 | 500 mL |
| HEPES | VWR | 101170-478 | |
| HeraCell 150 CO2 incubator | Heraeus (ThermoFisher) | ||
| ImageJ v1.52e | NIH | ||
| IRIS-Fine Scissors (Round Type)-S/S Str/31*8mm/13cm | RWD | S12014-13 | |
| Kanamycin monosulfate | Gold Bio | K-120-25 | |
| Laminin | Sigma-Aldrich | L2020 | |
| L-Ascorbic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | A7506 | |
| L-glutamic acid | VWR | 97061-634 | |
| Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2), andydrous | Sigma-Aldrich | M8266 | |
| MPII Mini-Peristaltic Pump, 115/230 VAC, 50/60 Hz | Harvard Apparatus | 70-2027 | |
| MULLER Micro Forceps-Str, 0.15mm Tips, 11cm | RWD | F11014-11 | |
| NBQX | Hello Bio | HB0443 | |
| Neurobasal medium | ThermoFisher | 21103049 | 500 mL |
| Normal goat serum (NGS) | Abcam | ab7481 | |
| Origin 2020 | OriginLab | ||
| pAAV.Syn.GCaMP6f.WPRE.SV40 | Addgene | 100837-AAV1 | Titer: 1.00E+13 gc/ml |
| Papain | Worthington Biomedical Corporation | LS003126 | |
| Penicillin streptomycin | ThermoFisher | 15140122 | 10,000 U/mL |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) 1x | ThermoFisher | 10010049 | 500 mL |
| Poly-L-lysine | Sigma-Aldrich | P4832 | |
| Poly-L-ornithine | Sigma-Aldrich | P4957 | |
| Potassium Chloride (KCl), anhydrous | Sigma-Aldrich | 746436 | |
| Pump Head Tubing Pieces For MPII | Harvard Apparatus | 55-4148 | |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-caspase-3 | Abcam | ab32351 | |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl), anhydrous | Sigma-Aldrich | 746398 | |
| Sucrose | Sigma-Aldrich | S7903 | BioXtra, ≥99.5% (GC) |
| Time-pregnant female C57BL/6 mice | Texas A&M Institue for Genomic Medicine | ||
| Triton X-100 | Sigma-Aldrich | X100 | 500 mL |
| Wide-bore blue pipette tips P1000 | VWR | 83007-380 |
References
- Marras, C., et al. Prevalence of Parkinson's disease across North America. NPJ Parkinson's Disease. 4, 21 (2018).
- Poewe, W., et al. Parkinson disease. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 3, 17013 (2017).
- Mehta, A., Prabhakar, M., Kumar, P., Deshmukh, R., Sharma, P. L. Excitotoxicity: bridge to various triggers in neurodegenerative disorders. European Journal of Pharmacology. 698 (1-3), 6-18 (2013).
- Ambrosi, G., Cerri, S., Blandini, F. A further update on the role of excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neural Transmission (Vienna). 121 (8), 849-859 (2014).
- Dong, X. X., Wang, Y., Qin, Z. H. Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 30 (4), 379-387 (2009).
- Vieira, M., et al. Excitotoxicity through Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors requires Ca2+-dependent JNK activation. Neurobiology of Disease. 40 (3), 645-655 (2010).
- Sebe, J. Y., et al. Ca(2+)-Permeable AMPARs Mediate Glutamatergic Transmission and Excitotoxic Damage at the Hair Cell Ribbon Synapse. Journal of Neuroscience. 37 (25), 6162-6175 (2017).
- Brickley, S. G., Farrant, M., Swanson, G. T., Cull-Candy, S. G. CNQX increases GABA-mediated synaptic transmission in the cerebellum by an AMPA/kainate receptor-independent mechanism. Neuropharmacology. 41 (6), 730-736 (2001).
- Srinivasan, R., et al. Smoking-Relevant Nicotine Concentration Attenuates the Unfolded Protein Response in Dopaminergic Neurons. Journal of Neuroscience. 36 (1), 65-79 (2016).
- Henley, B. M., et al. Reliable Identification of Living Dopaminergic Neurons in Midbrain Cultures Using RNA Sequencing and TH-promoter-driven eGFP Expression. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (120), e54981 (2017).
- Douhou, A., Troadec, J. D., Ruberg, M., Raisman-Vozari, R., Michel, P. P. Survival promotion of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons by depolarizing concentrations of K+ requires concurrent inactivation of NMDA or AMPA/kainate receptors. Journal of Neurochemistry. 78 (1), 163-174 (2001).
- Lavaur, J., et al. The noble gas xenon provides protection and trophic stimulation to midbrain dopamine neurons. Journal of Neurochemistry. 142 (1), 14-28 (2017).
- Kritis, A. A., Stamoula, E. G., Paniskaki, K. A., Vavilis, T. D. Researching glutamate - induced cytotoxicity in different cell lines: a comparative/collective analysis/study. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 9, 91 (2015).
- Gupta, K., Hardingham, G. E., Chandran, S. NMDA receptor-dependent glutamate excitotoxicity in human embryonic stem cell-derived neurons. Neuroscience Letters. 543, 95-100 (2013).
- Surmeier, D. J., Obeso, J. A., Halliday, G. M. Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 18 (2), 101-113 (2017).
- Ramirez, J. M., Tryba, A. K., Pena, F. Pacemaker neurons and neuronal networks: an integrative view. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 14 (6), 665-674 (2004).
- Guzman, J. N., Sanchez-Padilla, J., Chan, C. S., Surmeier, D. J. Robust pacemaking in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Journal of Neuroscience. 29 (35), 11011-11019 (2009).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved