A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Adsorptive Bioprocess Improves Yield of Melanin from Pseudomonas stutzeri
In This Article
Summary
Here we present a protocol on adsorptive bioprocess to produce a biological product, especially a pigment that inhibits its own biosynthesis and inhibits the growth of the microorganism that produces it.
Abstract
Melanins are natural pigments, and the presence of indole ring and numerous functional groups makes melanin an ideal choice for many applications such as UV protective agents, skincare, cosmetics etc. A marine Pseudomonas stutzeri produces melanin without the addition of tyrosine. The feedback inhibition was observed by melanin in the culture of a melanin-producing marine bacterium, Pseudomonas stutzeri. Melanin also demonstrated microbial growth inhibition. The Han-Levenspiel model-based analysis identified uncompetitive type product inhibition of melanin on the cell growth. Tyrosinase enzyme, which produces melanin, was inhibited by melanin. The double reciprocal plot of the enzymatic reaction in the presence of different melanin concentrations revealed uncompetitive product inhibition. An adsorbent-based adsorptive bioprocess was developed to reduce the feedback inhibition by melanin. Different adsorbents were screened to select the best adsorbent for melanin adsorption. Dosage amount and time were optimized to develop the adsorptive bioprocess, which resulted in an 8.8-fold enhancement in melanin production by the marine bacteria Pseudomonas stutzeri (153 mg/L to 1349 mg/L) without supplementation of tyrosine and yeast extract.
Introduction
Melanins are polyphenol compounds whose monomeric unit is the indole ring. Melanins are responsible for most of the black, brown, and grey colorations of plants, animals, and microorganisms1. The most common melanins are eumelanins, which are dark brown or black pigments widely distributed in vertebrates and invertebrates2. Cephalopods, plants, and microbes are the major sources of melanin3. Melanin obtained from microorganisms has several advantages over melanin from cephalopods and plants. They are fast in growth and do not cause any problems of seasonal variations. Also, they modify themselves according to the growth medium and the operating conditions provided. Considering all these facts, the microbial sources are exploited as a major source of melanin with potential commercial applications4,5,6. Guo et al. used recombinant Streptomyces kathirae SC-1 to produce melanin up to 28.8 g/L in an optimized medium7. Lagunas-Muñoz et al. Obtained about 6 g/L of melanin in recombinant E. coli8. Wang et al. obtained about 4.2 g/L of soluble melanin after medium optimization9. Researchers also investigated marine cultures to produce melanin. Kiran et al. produced melanin from marine Pseudomonas species10. Kumar et al. isolated Pseudomonas stutzeri HMGM-7 from marine seaweed, which produced melanin in nutrient broth. All the reported melanin producers require medium supplements, yeast extract and/or peptone for melanin production, which may hinder the scale-up of the bioprocess. Raman et al. investigated melanin production from Aspergillus fumigatus AFGRD105, which did not require costly additives11.
A marine bacterium known as Pseudomonas stutzeri, isolated from seaweed, was selected for melanin production. This microorganism does not require additional supplementation of tyrosine and yeast extract for the production of soluble melanin and grows in seawater-based media, thereby reducing the potable water footprint and medium cost. Thaira et al. reported an optimized bioprocess using coconut cake meal for melanin nanopigment production using this marine bacterium in a previous publication12. The produced melanin was used for the highly efficient removal of heavy metals from the synthetic groundwater. However, during medium optimization, plausible feedback inhibition of melanin on the growth and product formation was identified. Therefore, in this protocol, feedback inhibition of melanin is investigated and quantified using the generalized Han-Levenspiel model. A simple and effective adsorptive bioprocess protocol is developed to reduce feedback inhibition to the maximum extent.
Protocol
1. Growth and maintenance of Pseudomonas stutzeri culture.
- Obtain the bacteria Pseudomonas stutzeri from MTCC Chandigarh (supplied as freeze-dried ampoule).
- Disinfect the surface of the ampoule with alcohol (70%). Mark the ampoule near the middle of the gauge and break at the marked area.
NOTE: Care should be taken in opening the ampoule as the contents are in vacuum. Take precautions while breaking the ampoule, as a snap opening will draw the cotton plug to one end and a hasty opening will release the lyophilized fine particles of the microbe into the air. - Carefully remove the cotton plug with sterilized tweezers and add 0.3 mL of Luria Bertani (LB) broth to the ampoule. Let it stand for 30 min.
- Inoculate 100 µL of the suspension to 10 mL of LB broth (in 100 mL conical flask) and place it in the incubator shaker at 180 rpm maintained at 37 °C. Simultaneously transfer 100 µL of the suspension to the solid LB agar and spread to obtain isolated colonies. Incubate it at 37 °C for overnight.
- Disinfect the surface of the ampoule with alcohol (70%). Mark the ampoule near the middle of the gauge and break at the marked area.
- Once the culture has grown, store them at 4 °C.
- Do subculture after every 4 weeks by streaking a colony onto a fresh LB agar plate and incubating the plate at 37 °C for overnight for the colonies to appear.
2. Inhibition studies of melanin on the growth and enzyme activity
- Prepare the culture medium by adding 51.4 g/L glucose, 49.8 g/L coconut cake meal, 0.09 g/L, 0.03 g/L and 0.05 g/L of CuSO4, FeSO4 and MgSO4, respectively, in artificial seawater (Table of Materials). Perform all the experiments in a 250 mL shake flask with 15 mL filling volume at 200 rpm, 37 °C, and initial pH of 7.
- Add different concentrations of melanin (100 mg/L, 200 mg/L, 500 mg/L, and 1000 mg/L) into each culture medium at the start of the bioprocess.
- Measure specific growth rate, the enzyme activity of the cells, and melanin at different time intervals of the bioprocess for each added melanin concentration (section 3.2).
3. Modeling melanin inhibition kinetics
- Use the following generalized equation of Han and Levenspiel13 to model the inhibition kinetics of melanin production,
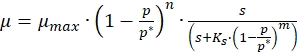 (1)
(1)
Where,
µ = apparent specific growth rate (1/h)
µmax = maximum specific growth rate (1/h)
p = product concentration (g/L)
p *= critical product concentration at which growth ceases (g/L)
s = substrate concentration (g/L)
m,n = parameters
Above equation can be rewritten as
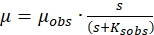 (2)
(2)
Where,
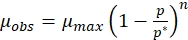 (3)
(3)
and (4)
(4)
The above equation can be rearranged to a double reciprocal plot of 1/µ versus 1/s, as given below
 (5)
(5) - Draw a straight line using the data of different specific growth rates and substrate concentrations using the above equation. The intercept on the Y- and the X-axis, respectively, give μmax and Ks, which can be substituted in eqution 3 and 4 respectively to obtain µobs and Kobs.
Equation (3) can be written as
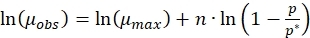 (6)
(6) - Calculate the specific growth rate of culture grown in step 2.2 and name it as µobs.
- Use the value of the specific growth rate obtained in step 3.3 in equation (6). Fit the data to a linear equation and calculate the slope and intercept.
- Use equation (3) to calculate the maximum specific growth rate in the absence of melanin.
4. Development of the adsorptive bioprocess
- Perform all the experiments in a 250 mL shake flask with 15 mL filling volume at 200 rpm, 37 °C, and initial pH of 7.
- Conduct the final optimized bioprocess in a 5 L stirred tank bioreactor with a 3 L filing volume. Maintain the pH of the culture between 7-7.5 and dissolved oxygen between 50%- 60% of the saturation in the bioreactor studies.
5. Selection of the best adsorbent from different available adsorbents
- Add different adsorbents such as alumina, zeolite, celite, fuller's earth, and activated carbon in different flasks containing the culture broth.
- Add each adsorbent separately at a concentration of 1 g/L to the culture broth and keep it in a rotary shaker at 150 rpm for 12.
- Separate the adsorbents by centrifugation at 5000 x g for 10 min and measure the absorbance of the supernatant at 400 nm using a spectrophotometer.
- Select the adsorbent which adsorbs the maximum amount of melanin from the culture broth.
6. Effect of dosage time of the adsorbent
- Start the bioprocess and add the adsorbent yielding the highest adsorption of melanin from the culture (selected after section 5). The concentration selected at the initial step is 1 g/L.
- Measure the maximum melanin production according to the previously published protocol12.
- Repeat step 6.1 by adding the adsorbent after 12 h of the start of the bioprocess and measure the melanin production at different times of the bioprocess.
- Repeat step 6.3 by adding the adsorbent after 24 h, 36 h, and 48 h of the start of the bioprocess.
- Compare the melanin produced in each bioprocess run and identify the best dosage time for the maximum melanin production and recovery.
7. Effect of amount of adsorbent dosage
- Add different concentrations of the best adsorbent (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 g/L) to the cultures at the time identified in section 6.
- Harvest the bioprocess by centrifugation at 5000 x g for 10 min.
- Collect the supernatant and calculate the amount of melanin by measuring absorbance at 400 nm.
- Wash the pellet containing adsorbent two times each with distilled water and ethanol to remove cells and other compounds attached to the adsorbent. Perform the washing step by centrifugation at 5000 x g for 10 min.
- Add a 0.1 M NaOH solution to the washed adsorbent to desorb the melanin.
- Centrifuge the mixture at 5000 x g for 10 min and measure the melanin amount in the supernatant at 400 nm by a spectrophotometer.
- Repeat the desorption process thrice or until the adsorbent is back to its normal color.
- Reduce the pH of this concentrated desorbed melanin solution to 3 or less by adding 1 N HCl using a stirrer with magnetic beads to precipitate melanin. Store the acidic solution in the refrigerator for 1 h to increase precipitation, if required.
- Wash the precipitated melanin thus obtained three times with distilled water by centrifugation at 5000 x g for 10 min, dry and store at 4 °C.
8. Mathematical modeling of the bioprocess
- Biomass growth kinetics
- Quantify the biomass growth rate using the following modified Verhulset model developed for product inhibition, as described by the equation given below14,15,16,17,
 (7)
(7)
Where,
x = biomass concentration (g/L)
xm = maximum biomass concentration (g/L)
µobs = maximum specific growth rate (1/h) as given by equation (2)
Vazques et al. (2008) further derived the following equation for biomass concentration from equation (7)
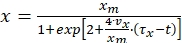 (8)
(8)
Where,
vx = biomass growth rate (g/L/h) = µobs·x
µobs = observed specific growth rate (1/h)
τx = lag time (h)
t = time (h) - Use Equation (8) to calculate the biomass concentration at different times of the bioprocess and simulate the growth profile of Pseudomonas stutzeri.
- Quantify the biomass growth rate using the following modified Verhulset model developed for product inhibition, as described by the equation given below14,15,16,17,
- Substrate consumption kinetics
NOTE: The substrate is used for biomass growth, product formation, and maintenance in a bioprocess.- Use the following equation to balance substrate utilization in the bioprocess,
 (9)
(9)
The majority of the glucose is used for biomass generation; therefore, for simplification, neglecting substrate consumption for product formation would reduce equation (9) to,
 (10)
(10)
Where,
S = substrate concentration (g/L)
YP/S = product yield coefficient, i.e., melanin yield coefficient (g/g)
P = product concentration (g/L), i.e., melanin concentration (g/L)
YX/S = biomass yield coefficient (g/g)
ms = maintenance coefficient (g/g/h)
Integrating the above equation from time t = 0 to time t = t, and substituting the value of x from equation (8) gives the following equation for substrate concentration profile17,
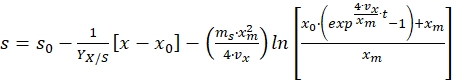 (11)
(11)
Where, s0 = initial substrate concentration (g/L) and x0 = initial biomass concentration (g/L) - Use equation (11) to calculate the substrate concentration at different time intervals of the bioprocess or if substrate concentration is known, then use the same equation to estimate the parameters given in the equation.
- Use the following equation to balance substrate utilization in the bioprocess,
- Melanin production kinetics
- Use Ludeking-Pirate equation to simulate melanin production. However, melanin is growth associated and therefore, the non-growth associated product formation term is neglected, and the simplified equation can be written as,
 (12)
(12)
Where,
α = Ludeking-Pirate constant linked to growth associated product formation (g/g)
Integrating equation (12) from time t = 0 to t = t result in the following equation for product concentration profile
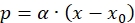 (13)
(13) - Use equation (13) to calculate α.
- Use Ludeking-Pirate equation to simulate melanin production. However, melanin is growth associated and therefore, the non-growth associated product formation term is neglected, and the simplified equation can be written as,
- Kinetic parameter estimation
- Estimate all parameters mentioned above by the nonlinear least square method of parameter estimation using any suitable software tool (e.g., Microsoft Excel solver tool).
- Use batch experiment data for parameter estimation and minimize the sum of squared error (SSE) using the Solver tool, as given by the following equation,
Minimize,
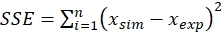 (14)
(14)
Where,
xsim = simulated value and xexp = experimental value
9. Analytical techniques
- Melanin extraction
- Centrifuge the growth culture at 5000 x g for 10 min to remove the biomass.
- Add an equal volume of 1 M NaOH to the supernatant.
- Acidify the alkaline supernatant to pH 2 by adding 1 N HCl to precipitate the melanin.
- Centrifuge the acidified supernatant at 12000 x g for 20 min to collect melanin.
- Wash the collected melanin thrice with 5 mL of distilled water, dry overnight at room temperature (RT) and store at 4 °C18.
- Melanin quantification
- Prepare different concentrations of melanin solutions (0-500 mg/L) by dissolving the appropriate amount of melanin in artificial seawater (pH 8).
- Measure the absorbance at 400 nm using spectrophotometer18.
- Prepare calibration curve using above data.
- Centrifuge the growth culture at 5000 x g for 10 min to remove the biomass and measure the absorbance of the supernatant at 400 nm. Calculate the melanin concentration in the growth culture using the calibration curve prepared in step 9.2.3
- Tyrosinase assay
- Follow the protocol given below for the tyrosinase enzyme assay developed by Ren et al. (2013)19 to determine the enzyme activity of tyrosinase extracted from Pseudomonas stutzeri culture broth.
- Centrifuge the bacterial culture at 5,000 x g to collect the cells.
- Sonicate the cells in cold 100 mM phosphate buffer of pH 6.5 and centrifuge the homogenate at 9000 x g for 15 min and collect the supernatant, a source of tyrosinase enzyme.
- Add 0.2 mL of the enzyme solution obtained in the above step to 2.8 mL of 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) containing 1 mM L-tyrosine (substrate).
- Observe the formation of dopachrome by measuring the absorbance at 475 nm.
- Calculate the tyrosinase activity as follows. One international unit (IU) of tyrosinase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to oxidize 1 µmol of L-tyrosine to dopachrome per minute. Calculate this by using the molar extinction coefficient of dopachrome (3600 L·M-1·cm-1) by the following equation,
 (15)
(15)
- Estimation of biomass
- Collect 5 mL of the samples at an interval of 4 h in the Biosafety cabinet, maintaining sterility. Flame the cotton plug of the flask before and after taking the samples to reduce the chances of contamination. Measure the optical density (OD) of the samples at 660 nm for all these samples.
NOTE: The uninoculated media serves as the blank. These readings will be used to study the growth of the microorganisms. - Centrifuge the culture broth at 5000 x g for 10 min and 4 °C, collect the cell pellet and dry the pellet for 8 h at 60 °C in a hot air oven to obtain the dry cell mass.
- Prepare calibration curve using the OD measured in step 9.4.1 and the corresponding biomass obtained in step 9.4.2
- Use the calibration curve (OD = 0.82٠Biomass (g/L)) to measure the unknown quantity of biomass by measuring the optical density of the culture broth at any given time.
- Collect 5 mL of the samples at an interval of 4 h in the Biosafety cabinet, maintaining sterility. Flame the cotton plug of the flask before and after taking the samples to reduce the chances of contamination. Measure the optical density (OD) of the samples at 660 nm for all these samples.
- Estimation of DNA
- Estimate the amount of DNA in the sample by measuring the optical density at 260 nm.
- Calculate the DNA using the following formula,
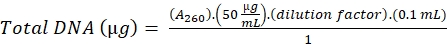 (16)
(16)
Where,
A260= Absorbance at 260 nm
0.1 = Volume of the sample
1 = Absorbance of DNA standard solution of concentration 50 µg/mL, at 260 nm
- Estimation of protein
- Estimate the amount of protein in the samples by using a Bradford protein estimation kit (Table of Materials).
- Add 5 mL of the Bradford reagent to 0.1 mL of the supernatant and keep it for 5 min. The proteins present in the supernatant reacts with the Bradford reagent to form a colored complex.
- Measure the absorbance at 595 nm20 using the spectrophotometer.
- Estimation of total reducing sugar (TRS)
- Measure the TRS by dinitrosalicylic (DNS) method21.
- Prepare the DNS solution by dissolving 1 g of DNS in 50 mL of distilled water. Add 30 g of sodium potassium tartarate to this solution in small amounts till the color of the solution becomes milky yellow, followed by transparent orange-yellow with the addition of 20 mL of 2 N NaOH. Bring the volume up to 100 mL using distilled water and store it in the dark.
- Prepare glucose working solution (0.01 M) by dissolving 180 mg of glucose in 100 mL of distilled water in a standard flask.
- Pipette out standard Glucose solution (0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1 mL) into 5 separate test tubes. Use a test tube containing distilled water (1mL) as a blank solution.
- Bring the volume up to 2 mL in each test tube by using distilled water.
- Add 1 mL of DNS reagent to each test tube and cover with aluminum foil.
- Heat the test tubes in a boiling water bath for 5 min and cool to RT.
- Add 9 mL of distilled water to each test tube and mix well. Measure the OD of the content at 575 nm using a spectrophotometer.
- Measure the concentration using a calibration chart prepared with the amount of glucose on the X-axis vs. absorbance at 575 nm (A575) on the Y-axis.
- Particle size analysis
- Disperse the biosynthesized melanin in distilled water (1 mL) using a sonicator.
- Add the dispersed sample solution (1 mL) into the nanoparticle analyzer and measure the particle size per the manufacturer's protocol.
- Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) analysis
- Dry the melanin powder obtained after extraction by keeping it at 60 °C for 8 h.
- Load the melanin powder in the TEM sample matrix and measure the size using the Transmission Electron Microscope following the operator protocol.
Results
Figure 1A,B demonstrates growth and melanin production under the influence of different initial melanin concentrations. The cell growth and melanin production decreased substantially with the increasing initial concentration of melanin. At 500 mg/L initial melanin concentration in the medium, the biomass and melanin reduced to almost 50% of the maximum value obtained in control. At 1000 mg/L of initial melanin concentration, there was marginal melanin production. The biomass...
Discussion
Product inhibition is a major bottleneck in bioprocessing which leads to reduced productivity. Several methods exist to reduce product inhibition, such as continuous bioprocess and in situ product removal techniques. However, these options require a complete overhaul of the existing bioprocessing facility23,24,25,26,27,28<...
Disclosures
The authors do not have any conflict of interest
Acknowledgements
We thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST/TSG/WP/2014/58), India, and the National Institute of Technology Karnataka for providing funding for the development of the above protocol.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Alumina+A15A26A3:A13A3:A16A3:A17 | HiMedia | GRM1909 | |
| Activated carbon | HiMedia | PCT1001 | |
| Artificial Sea Water Medium | HiMedia | M1942 | |
| Bradford reagent kit | HiMedia | ML106 | |
| Celite | HiMedia | GRM226 | |
| Centrifuge | REMI | CM-8 | |
| Centrifuge tubes | HiMedia | PW1207 | |
| Dinitrosalicylic acid | HiMedia | GRM1582 | |
| Erlenmeyer flask | Borosil | 4980021 | |
| fuller's earth | HiMedia | GRM232 | |
| Glucose | HiMedia | MB037 | |
| HCl | HiMedia | AS004 | |
| L-tyrosine | HiMedia | RM069 | |
| Microsoft Excel | Microsoft | ||
| Nanoparticle analyzer | HORIBA Scientific | Nanopartica SZ-100 | |
| Nutrient Agar medium | HiMedia | M001 | |
| Petri plate | HiMedia | PW054 | |
| Phosphate buffer | HiMedia | M1452 | |
| Sodium hydroxide | HiMedia | MB095 | |
| Spectrophotometer | Thermofisher | Genesys 10 | |
| Stirred tank bioreactor | Scigenics | Bioferm LS | |
| TE Buffer | HiMedia | ML060 | |
| Transmission Electron Microscope | JEOL | JEM-2100 | |
| Zeolite | HiMedia | GRM3834 |
References
- Langfelder, K., Streibel, M., Jahn, B., Haase, G., Brakhage, A. A. Biosynthesis of fungal melanins and their importance for human pathogenic fungi. Fungal Genetics and Biology. 38 (2), 143-158 (2003).
- Riley, P. A. Melanin. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 29 (11), 1235-1239 (1997).
- Madaras, F., Gerber, J. P., Peddie, F., Kokkinn, M. J. The effect of sampling methods on the apparent constituents of ink from the squid sepioteuthis australis. Journal of Chemical Ecology. 36 (11), 1171-1179 (2010).
- Tran-Ly, A. N., et al. Microbial production of melanin and its various applications. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology. 36 (11), 170 (2020).
- Pavan, M. E., López, N. I., Pettinari, M. J. Melanin biosynthesis in bacteria, regulation and production perspectives. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 104 (4), 1357-1370 (2019).
- Pombeiro-Sponchiado, S. R., Sousa, G. S., Andrade, J. C. R., Lisboa, H. F., Gonçalves, R. C. R. Production of melanin pigment by fungi and its biotechnological applications. Melanin. , 47-77 (2017).
- Guo, J., et al. Cloning and identification of a novel tyrosinase and its overexpression in Streptomyces kathirae SC-1 for enhancing melanin production. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 362, 41 (2015).
- Lagunas-Muñoz, V. H., Cabrera-Valladares, N., Bolívar, F., Gosset, G., Martínez, A. Optimum melanin production using recombinant Escherichia coli. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 101 (5), 1002-1008 (2006).
- Wang, L., Li, Y., Li, Y. Metal ions driven production, characterization and bioactivity of extracellular melanin from Streptomyces sp. ZL-24. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 123, 521-530 (2019).
- Kiran, G. S., Jackson, S. A., Priyadharsini, S., Dobson, A. D. W., Selvin, J. Synthesis of Nm-PHB (nanomelanin-polyhydroxy butyrate) nanocomposite film and its protective effect against biofilm-forming multi drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Scientific Reports. 7, 9167 (2017).
- Raman, N. M., Shah, P. H., Mohan, M., Ramasamy, S. Improved production of melanin from Aspergillus fumigatus AFGRD105 by optimization of media factors. AMB Express. 5 (1), 72 (2015).
- Thaira, H., Raval, K., Manirethan, V., Balakrishnan, R. M. Melanin nano-pigments for heavy metal remediation from water. Separation Science and Technology (Philadelphia). 54 (2), 265-274 (2018).
- Han, K., Levenspiel, O. Extended monod kinetics for substrate, product, and cell inhibition. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 32 (4), 430-447 (1988).
- Vázquez, J. A., Murado, M. A. Unstructured mathematical model for biomass, lactic acid and bacteriocin production by lactic acid bacteria in batchfermentation. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology. 83 (1), 91-96 (2008).
- Rohit, S. G., Jyoti, P. K., Subbi, R. R. T., Naresh, M., Senthilkumar, S. Kinetic modeling of hyaluronic acid production in palmyra palm (Borassus flabellifer) based medium by Streptococcus zooepidemicus MTCC 3523. Biochemical Engineering Journal. 137, 284-293 (2018).
- Nair, A. V., Gummadi, S. N., Doble, M. Process optimization and kinetic modelling of cyclic (1→3, 1→6)-β-glucans production from Bradyrhizobium japonicum MTCC120. Journal of Biotechnology. 226, 35-43 (2016).
- Reddy Tadi, S. R., Limaye, A. M., Sivaprakasam, S. Enhanced production of optically pure D (-) lactic acid from nutritionally rich Borassus flabellifer sugar and whey protein hydrolysate based-fermentation medium. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry. 64 (-), 279-289 (2017).
- Ganesh Kumar, C., Sahu, N., Narender Reddy, G., Prasad, R. B. N., Nagesh, N., Kamal, A. Production of melanin pigment from Pseudomonas stutzeri isolated from red seaweed Hypnea musciformis. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 57 (4), 295-302 (2013).
- Ren, Q., Henes, B., Fairhead, M., Thöny-Meyer, L. High level production of tyrosinase in recombinant Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnology. 13, 13-18 (2013).
- Kruger, N. J. The Bradford method for protein quantitation. The Protein Protocols Handbook. Springer Protocols Handbooks. , (2002).
- Miller, G. L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry. 31 (3), 426-428 (1959).
- Dutta, A., Diao, Y., Jain, R., Rene, E. R., Dutta, S. Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solution onto coffee grounds and wheat straw: Equilibrium and kinetic study. Journal of Environmental Engineering. 142 (9), 1-6 (2015).
- Dhillon, G. S., Brar, S. K., Verma, M., Tyagi, R. D. Recent advances in citric acid bio-production and recovery. Food and Bioprocess Technology. 4, 505-529 (2011).
- Roffler, S. R., Blanch, H. W., Wilke, C. R. In situ recovery of fermentation products. Trends in Biotechnology. 2 (5), 129-136 (1984).
- Maiti, S., et al. A re-look at the biochemical strategies to enhance butanol production. Biomass and Bioenergy. 94, 187-200 (2016).
- Prakash, G., Srivastava, A. K. Integrated yield and productivity enhancement strategy for biotechnological production of Azadirachtin by suspension culture of Azadirachta indica. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering. 6 (1), 129-137 (2011).
- Stark, D., von Stockar, U. In situ product removal (ISPR) in whole cell biotechnology during the last twenty years. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology. 80, 149-175 (2003).
- Kaur, G., Srivastava, A. K., Chand, S. Debottlenecking product inhibition in 1,3-propanediol fermentation by In-Situ Product Recovery. Bioresource Technology. 197, 451-457 (2015).
- Arun, G., Eyini, M., Gunasekaran, P. Characterization and biological activities of extracellular melanin produced by Schizophyllum commune (Fries). Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 53, 380-387 (2015).
- Bin, L., Wei, L., Xiaohong, C., Mei, J., Mingsheng, D. In vitro antibiofilm activity of the melanin from Auricularia auricula, an edible jelly mushroom. Annals of Microbiology. 62 (4), 1523-1530 (2012).
- Madhusudhan, D. N., Mazhari, B. B. Z., Dastager, S. G., Agsar, D. Production and cytotoxicity of extracellular insoluble and droplets of soluble melanin by Streptomyces lusitanus DMZ-3c. BioMed Research International. 2014, 1-11 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved