Method Article
Erratum: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP)
July 9th, 2021
Summary
An erratum was issued for: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP). A figure was updated.
Abstract
An erratum was issued for: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP). A figure was updated.
Figure 4 was updated from:
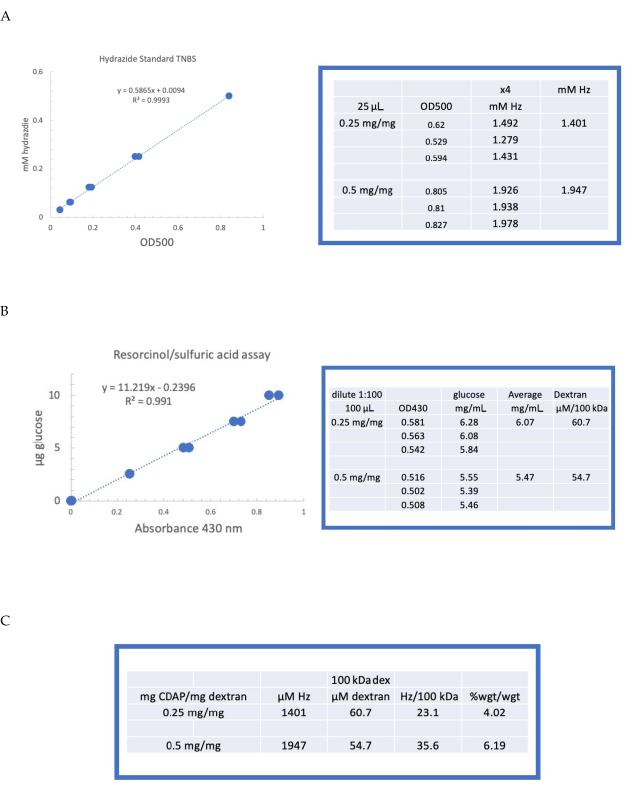
Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
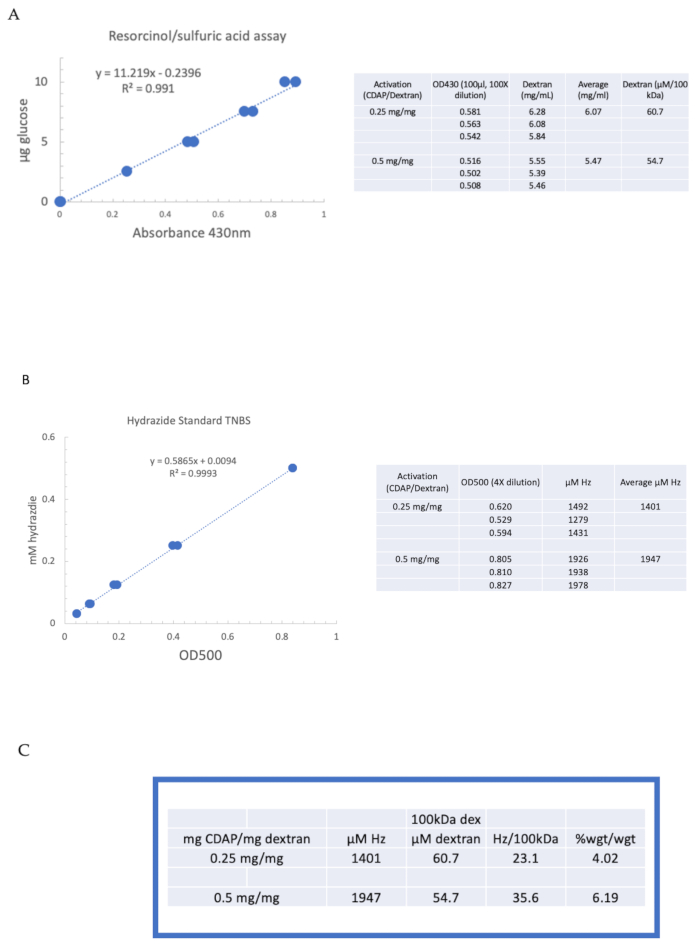
Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
An erratum was issued for: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP). A figure was updated.
Figure 4 was updated from:

Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:

Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Disclosures
References
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionCopyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved