8.10 : Force and Potential Energy in Three Dimensions
Consider a particle moving under the action of a conservative force that has components along each coordinate axis. Each component of force is a function of the coordinates. The potential energy function U is also a function of all three spatial coordinates. Force in one dimension can be written as the negative ratio of potential energy change to the displacement along that coordinate. For minimal displacement, the ratios become derivatives. If a function has many variables, the derivative only takes the variable that the partial derivative specifies; the other variables are held constant. Thus, adding the force along the three spatial coordinates, the net force can be written as the vector sum of partial derivatives of potential energy with respect to each coordinate, multiplied by the corresponding unit vector. In other words, force in three dimensions can be expressed as the negative of the gradient of the potential energy function.
Let us understand this with the help of an example. The potential energy of a 3-dimensional force is given by
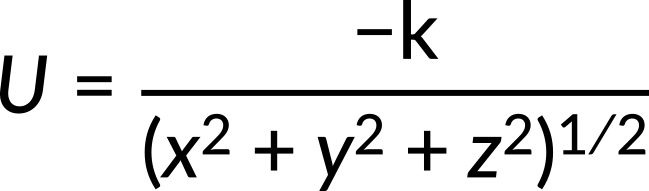
where k is a constant. Derive Fx, Fy, and Fz, and then describe the total force at each point in terms of its coordinates. Here, the known quantity is potential energy. The unknown quantities Fx, Fy,Fz, and the total force vector need to be calculated. Force is related to potential energy by the following equation:
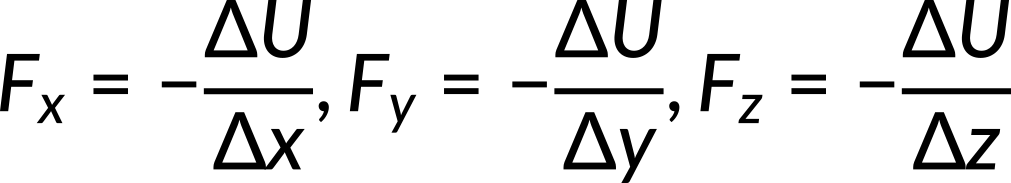
Substitution of U in the above equation gives the expression for Fx, Fy, andFz in terms of the coordinates x, y, and z. The vector force is the sum of the force along each coordinate. In other words,
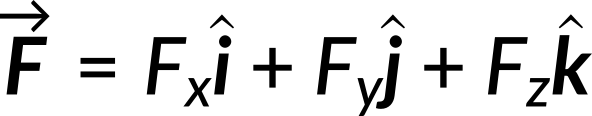
Substituting the values of Fx, Fy, andFz in the above equation, we get the net force vector as
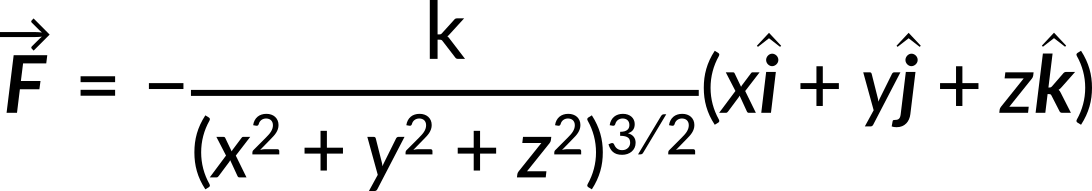
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 8.4: Potential Energy Diagrams and Stability.
Bölümden 8:

Now Playing
8.10 : Force and Potential Energy in Three Dimensions
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
4.8K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.1 : Yerçekimi Potansiyel Enerjisi
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
17.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.2 : Elastik Potansiyel Enerji
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
17.7K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.3 : Mekanik Enerjinin Korunumu
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
15.9K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.4 : Bir sistem üzerinde dış kuvvet tarafından yapılan iş
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
2.1K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.5 : Muhafazakar Güçler
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
12.1K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.6 : Muhafazakar Olmayan Kuvvetler
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
7.6K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.7 : Enerjinin Korunumu
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
8.9K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.8 : Enerjinin Korunumu: Uygulama
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
6.6K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.9 : Tek Boyutta Kuvvet ve Potansiyel Enerji
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
5.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.11 : Enerji Diyagramları - I
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
5.0K Görüntüleme Sayısı

8.12 : Enerji Diyagramları - II
Potansiyel Enerji ve Enerji Tasarrufu
4.6K Görüntüleme Sayısı
JoVE Hakkında
Telif Hakkı © 2020 MyJove Corporation. Tüm hakları saklıdır