Newton's Laws of Motion
Overview
Source: Andrew Duffy, PhD, Department of Physics, Boston University, Boston, MA
This experiment examines at various situations involving two interacting objects.
First, the experiment examines the forces that two objects apply to one another while they collide. The objects are wheeled carts that have variable masses. The purpose of this experiment is to discover when the force the first cart exerts on the other is the same magnitude as the force the second cart exerts back on the first, as well as when these two forces have different magnitudes.
Second, it examines the forces that two objects exert on one another when one cart is pushing or pulling the second one. Again, the focus is on exploring the situations in which the two forces have the same magnitude and in which they have different magnitudes.
Principles
The primary goal of this experiment is to explore Newton's third law.
The apparatus consists of two carts, each with a force sensor mounted on top (Figure 1). The force sensors are connected to a computer via a dedicated computer interface. Each force sensor measures the force exerted upon it by the other force sensor during the collision or the push/pull situation.

Figure 1. The basic setup. Key components of the apparatus are the two wheeled carts, each with a force sensor mounted on top, and a computer interface.
Procedure
1. Collision Situations
- Screw a rubber bumper (Figure 1) into each force sensor.
- Set each force sensor on the 50-N setting.
- Zero the force sensors before each trial by pushing the "Zero" button next to the green arrow that starts data collection.
- Check to see that the positive direction (i.e., to the right) is defined appropriately for each force sensor.
- Push in on the force sensor mounted on the right of the cart; this should result in a positive force reading. Push in on the force sensor mounted on the left of the cart; this should result in a negative force reading.
- If both are wrong, simply reverse the position of the cart.
- If only one is wrong, go to the "Experiment menu" and select "Setup Sensors." Choose the appropriate force sensor and select "Reverse Direction."
- The first collision involves carts of equal mass. Designate one cart to be stationary prior to the collision. The other cart will be given an initial velocity toward the stationary cart so that the carts collide.
- Hit the "Collect" button (the green arrow) before pushing one cart toward the other. Give one cart a small shove, release the cart, and observe the collision. Peak force values between about 8 and 20 N should be observed in a typical trial. Adjust the push if the peak force values are much smaller than or much larger than this range.
- After the collision, the computer will display a graph of "force vs. time," as recorded by each force sensor.
- If the graphs do not appear, reverse the triggering.
- After hitting the "Collect" button, no data is actually recorded until one of the force sensors records a value above (or below) a certain trigger level. However, if the trigger level is set to a positive value and the force sensor is only giving negative force values, or vice versa, the computer will never receive the signal telling it to record data.
- To check, or reverse, the trigger setting, press the "Data Collection" icon (immediately to the left of the "Zero" button) and select the "Triggering" tab.
- The two options used in this experiment are "Increasing across 0.2 N" and "Decreasing across -0.2 N." If one of these settings is not causing the necessary triggering, switch to the other.
- In the second collision, the stationary cart should have 2-3 times the mass of the cart that is moving prior to the collision. To achieve this, add one or more weights to the stationary cart. Repeat the process (see the steps below).
- Designate the higher-mass cart to be stationary prior to the collision.
- Hit the "Collect" button and push the lower-mass cart toward the higher-mass cart.
- The computer will display the two "force vs. time" graphs.
In the third collision, the cart that moves prior to the collision should have 2-3 times the mass of the stationary cart. Achieve this by transferring the extra weight(s) from one cart to the other. Repeat the process of carrying out the collision and collecting the data.
2. Pushing and Pulling Situations
- Replace the rubber bumpers on each force sensor with hooks.
- Hook the carts together to allow one cart to push or pull the other cart.
- Reverse the triggering condition, as described in step 1.8.
- Start with carts of equal mass.
- Hit the "Collect" button.
- Either pull or push one of the carts so that it pulls or pushes the other cart, respectively, or rock it back and forth so that there both pulling and pushing occur.
- Give the cart being pulled and/or pushed 2-3 times the mass of the other cart. Repeat the data collection process.
- Record the "force vs. time" data for this pushing/pulling scenario.
- Give the cart doing the pulling and/or pushing 2-3 times the mass of the other cart. Repeat the data collection process.
- Record the "force vs. time" data in this pushing/pulling scenario.
Results
Newton's third law states that whenever two objects interact, the second object exerts a force on the first object that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force the first object exerts on the second. This is simple to state, but it can be hard to accept. For example, it is often assumed that the force a larger object exerts on a smaller object is larger than the force the smaller object exerts back on the larger object.
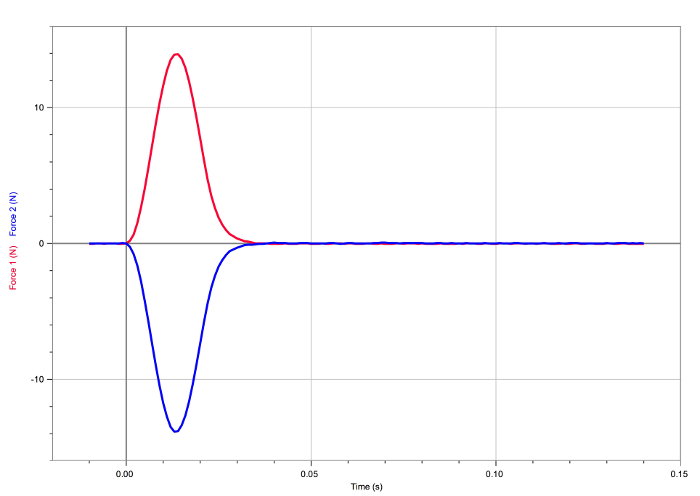
Figure 2. Result of the first collision. The forces experienced by the carts are equal and opposite.
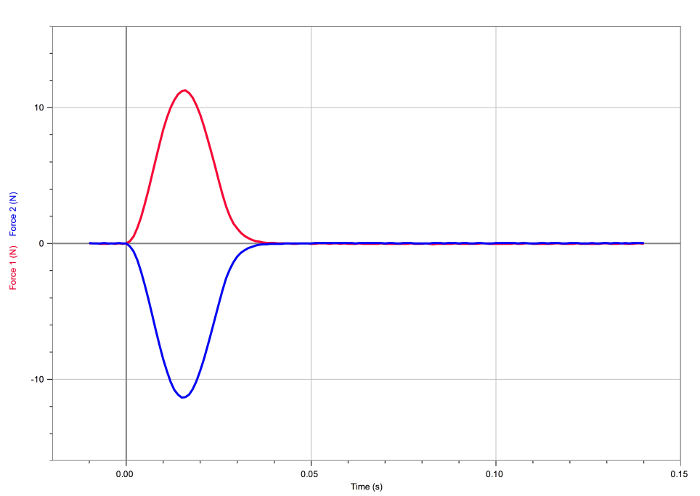
Figure 3. Result of the second collision. The forces experienced by the carts are equal and opposite.
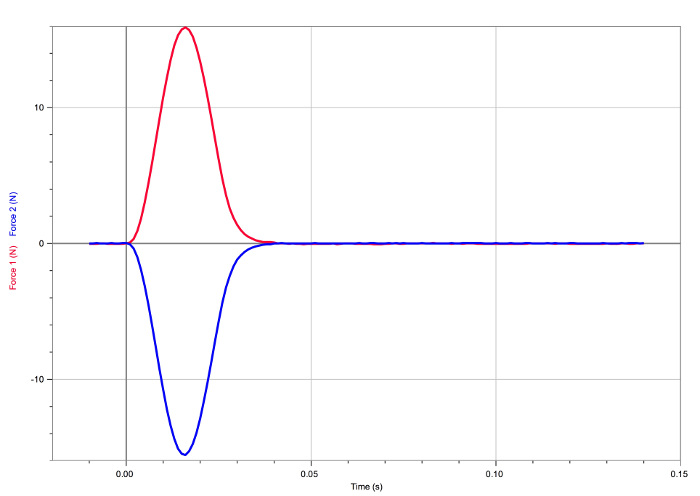
Figure 4. Result of the third collision. The forces experienced by the carts are equal and opposite.
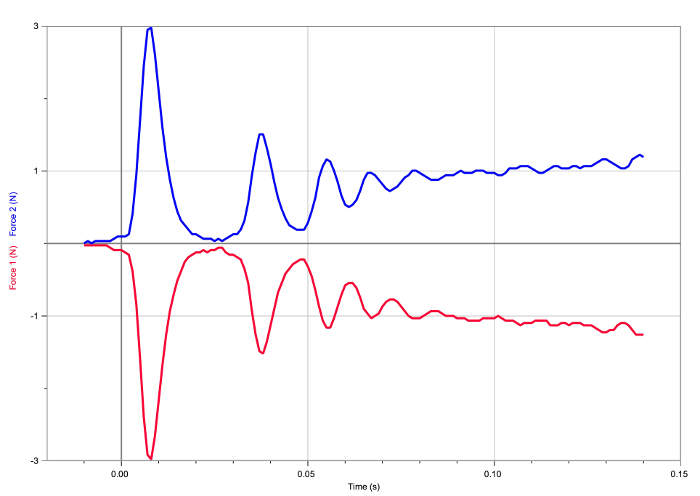
Figure 5. Result of the first pushing/pulling situation. The forces experienced by the carts are equal and opposite.
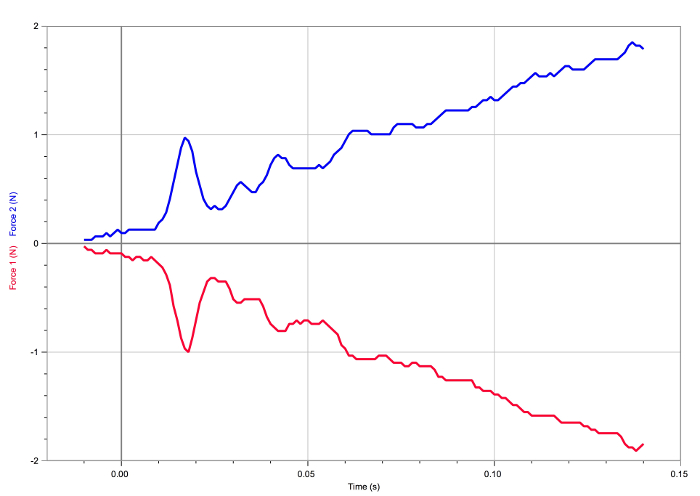
Figure 6. Result of the second pushing/pulling situation. The forces experienced by the carts are equal and opposite.
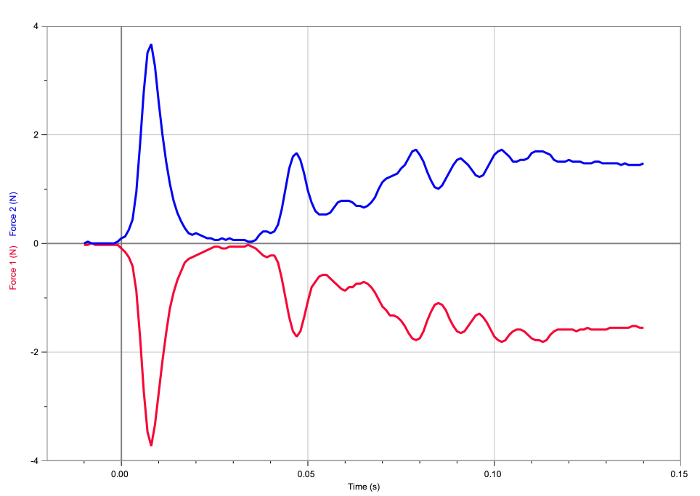
Figure 7. Result of the third pushing /pulling situation. The forces experienced by the carts are equal and opposite.
Application and Summary
The concept addressed in this experiment, namely that, in all interactions, the force one object applies to another is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force applied by the second object back on the first, has many applications. For example, (1) the gravitational force the Sun applies to the Earth is equal and opposite to the gravitational force the Earth applies to the Sun. (2) The gravitational force the Earth applies to the Moon is equal and opposite to the gravitational force the Moon applies to the Earth. (3) The gravitational force the Earth exerts on an apple is equal and opposite to the gravitational force the apple applies to the Earth. (4) In a collision, such as that between a car and a truck on the street or that between two football players, the forces are always equal and opposite, no matter how the masses compare. (5) When a person stands on a floor or sits on a chair, the force exerted on that person by the floor or the chair is equal and opposite to the force the person exerts on the floor or chair.
Tags
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
Newton's Laws of Motion
Physics I
75.7K Views

Force and Acceleration
Physics I
79.1K Views

Vectors in Multiple Directions
Physics I
182.3K Views

Kinematics and Projectile Motion
Physics I
72.6K Views

Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
Physics I
190.9K Views

Conservation of Momentum
Physics I
43.3K Views

Friction
Physics I
52.9K Views

Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion
Physics I
61.3K Views

Equilibrium and Free-body Diagrams
Physics I
37.3K Views

Torque
Physics I
24.4K Views

Rotational Inertia
Physics I
43.5K Views

Angular Momentum
Physics I
36.2K Views

Energy and Work
Physics I
49.7K Views

Enthalpy
Physics I
60.4K Views

Entropy
Physics I
17.6K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved