24.7 : Calculations of Electric Potential II
An electric dipole is a system of two equal but opposite charges, separated by a fixed distance. This system is used to model many real-world systems, including atomic and molecular interactions. One of these systems is the water molecule, but only under certain circumstances. These circumstances are met inside a microwave oven, where electric fields with alternating directions make the water molecules change orientation. This vibration is equivalent to heat at the molecular level.
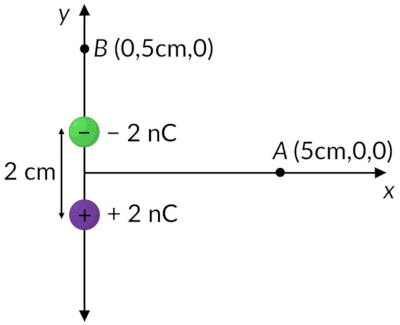
Consider a dipole with charges 2 nC and -2 nC, with a separation of 2 cm between them, situated at the origin. What will be the electric potential due to this dipole at positions A (5 cm, 0, 0), and B (0, 5 cm, 0)?
The electric potential due to the dipole is given by the following equation
For position A, the electric potential is calculated on the x-axis, for which the angle between the position vector and the dipole moment is 90 degrees. Therefore the electric potential due to the given electric dipole at position A is
For position B, the electric potential is calculated on the y-axis, for which the angle between the position vector and the dipole moment is 0 degrees. Therefore the electric potential due to the given electric dipole at position B is
From Chapter 24:

Now Playing
24.7 : Calculations of Electric Potential II
Electric Potential
1.6K Views

24.1 : Electric Potential Energy
Electric Potential
5.6K Views

24.2 : Electric Potential Energy in a Uniform Electric Field
Electric Potential
4.5K Views

24.3 : Electric Potential Energy of Two Point Charges
Electric Potential
4.4K Views

24.4 : Electric Potential and Potential Difference
Electric Potential
4.2K Views

24.5 : Finding Electric Potential From Electric Field
Electric Potential
3.9K Views

24.6 : Calculations of Electric Potential I
Electric Potential
1.9K Views

24.8 : Equipotential Surfaces and Field Lines
Electric Potential
3.6K Views

24.9 : Equipotential Surfaces and Conductors
Electric Potential
3.3K Views

24.10 : Determining Electric Field From Electric Potential
Electric Potential
4.3K Views

24.11 : Poisson's And Laplace's Equation
Electric Potential
2.5K Views

24.12 : Van de Graaff Generator
Electric Potential
1.6K Views

24.13 : Energy Associated With a Charge Distribution
Electric Potential
1.5K Views

24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
Electric Potential
386 Views

24.15 : Second Uniqueness Theorem
Electric Potential
945 Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved