5.5 : Types of Aggregate Grading
Aggregate grading is crucial in economically obtaining a concrete mix with adequate strength, reasonable workability, and minimal segregation. There are four types of aggregate gradation: well-graded, uniformly (or one-sized) graded, gap-graded, and open-graded.
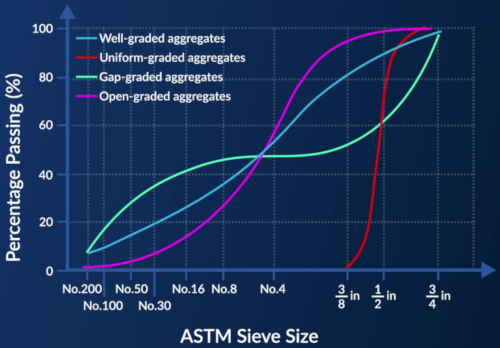
Well-graded aggregates include a complete range of necessary size fractions that fit together to create a dense matrix with minimal voids, represented by a smooth, continuous gradation curve. This type of grading ensures good workability and stability for the concrete.
In contrast, one-sized or uniformly graded aggregates consist predominantly of particles of the same size, which is evident from a nearly vertical gradation curve. While these aggregates provide good permeability, they lack stability and are typically used in specific applications like chip seals in pavements.
Gap-graded aggregates are characterized by the absence of certain size fractions, causing a significant portion of particles to pass through two vastly different sieves. This results in a gradation curve with a nearly horizontal section, indicative of missing intermediate sizes. Due to the missing material sizes, these aggregates can lead to issues with concrete stability.
Open-graded aggregates, missing smaller sizes that fill voids between larger aggregates, exhibit a flat gradation curve with minimal values in the smaller size range. These aggregates are highly permeable but have reduced stability.
From Chapter 5:

Now Playing
5.5 : Types of Aggregate Grading
Aggregates and Water
345 Views

5.1 : Unsoundness of Aggregate due to Volume Change
Aggregates and Water
90 Views

5.2 : Deleterious Substances in Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
134 Views

5.3 : Sieve Analysis and Grading Curves
Aggregates and Water
269 Views

5.4 : Fineness Modulus
Aggregates and Water
229 Views

5.6 : Maximum Size of Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
64 Views

5.7 : Quality of Water
Aggregates and Water
75 Views

5.8 : Testing Water Quality
Aggregates and Water
97 Views

5.9 : Aggregates Classification
Aggregates and Water
292 Views

5.10 : Shape and Texture of Coarse Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
177 Views

5.11 : Bonding and Strength of Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
124 Views

5.12 : Toughness and Hardness of Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
232 Views

5.13 : Specific Gravity of Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
190 Views

5.14 : Bulk Density of Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
379 Views

5.15 : Porosity and Absorption of Aggregate
Aggregates and Water
240 Views
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved