Method Article
العلاج المناعي تحت اللسان باعتباره البديل للحث على الحماية من التهابات الجهاز التنفسي الحادة
In This Article
Summary
The present work illustrates the convenience of using sublingual immunotherapy to boost the innate immune response in the lungs and confer protection against acute pneumococcal pneumonia in mouse.
Abstract
Sublingual route has been widely used to deliver small molecules into the bloodstream and to modulate the immune response at different sites. It has been shown to effectively induce humoral and cellular responses at systemic and mucosal sites, namely the lungs and urogenital tract. Sublingual vaccination can promote protection against infections at the lower and upper respiratory tract; it can also promote tolerance to allergens and ameliorate asthma symptoms. Modulation of lung’s immune response by sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) is safer than direct administration of formulations by intranasal route because it does not require delivery of potentially harmful molecules directly into the airways. In contrast to intranasal delivery, side effects involving brain toxicity or facial paralysis are not promoted by SLIT. The immune mechanisms underlying SLIT remain elusive and its use for the treatment of acute lung infections has not yet been explored. Thus, development of appropriate animal models of SLIT is needed to further explore its potential advantages.
This work shows how to perform sublingual administration of therapeutic agents in mice to evaluate their ability to protect against acute pneumococcal pneumonia. Technical aspects of mouse handling during sublingual inoculation, precise identification of sublingual mucosa, draining lymph nodes and isolation of tissues, bronchoalveolar lavage and lungs are illustrated. Protocols for single cell suspension preparation for FACS analysis are described in detail. Other downstream applications for the analysis of the immune response are discussed. Technical aspects of the preparation of Streptococcus pneumoniae inoculum and intranasal challenge of mice are also explained.
SLIT is a simple technique that allows screening of candidate molecules to modulate lungs’ immune response. Parameters affecting the success of SLIT are related to molecular size, susceptibility to degradation and stability of highly concentrated formulations.
Introduction
The overall goal of this work is to illustrate the benefits of sublingual immunotherapy for the treatment of acute respiratory infections (ARI) and present the advantages of this delivery route compared to other routes of administration, namely intranasal.
ARI cause millions of deaths every year especially in children under five. Streptococcus pneumoniae remains as one of the major etiological agents of bacterial pneumonia in infants and the elderly1,2. To present, the main available treatment relies on the use of antibiotics but resistant strains are continuously arising3,4.
SLIT induces broad responses at systemic and also mucosal level, particularly at the respiratory tract5. It has proven effectiveness against influenza infection, promoting long term protection with production of humoral and cellular responses6,7. Besides, it has been shown that prophylactic treatment with bacterial lysates delivered by sublingual route reduced exacerbations of chronic obstructive bronchitis in the elderly8 and prevented recurrent respiratory infections in children9. SLIT has been widely used for the treatment of allergies and asthma. Clinical studies had not only demonstrated its efficacy to modulate the immune response in the respiratory tract but also its safety10. Despite the growing interest of pharmaceutical companies and researchers in SLIT, the mechanisms involved in the induction of mucosal immune responses after sublingual delivery of compounds remain obscure. Recently, attention has been focused on the mechanisms promoting tolerance associated with allergen desensitization. It has been proposed that resident and recruited cells at the sublingual mucosa, like dendritic cells and macrophages, can promote tolerance after SLIT11-13. Dendritic cells of the oral mucosa can promote IFN-gamma and IL-10 producing T helper cells11 as well as recirculate to the distal genital mucosa and promote CD8+ T cells14. However, little is known about the impact of SLIT on innate cells or its capacity to improve pathogen clearance during acute respiratory infections.
The natural control of pneumococcal infection in the lungs greatly depends on the efficient and swift activation of local innate defences. We previously showed that enhancement of lungs’ innate immunity by a single intranasal dose of flagellin (FliC), a TLR5 and NLRC4 agonist, protects 75-100% of mice challenged with a lethal dose of a clinical isolate of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 1. This protection was shown to be dependent on local recruitment of GR1+ cells (likely polymorphonuclear neutrophils, PMNs) and not dependent on antibodies, B or T cells15.
Flagellin is the structural component of the bacterial flagellum. In its monomeric form it is recognized by two Pathogen Recognition Receptors (PRRs), TLR5 that senses extracellular FliC16 and NLRC4/NAIP5 inflammasome that detects intracellular flagellin17,18. When FliC is sensed by the PRRs an important inflammatory response is triggered. We and others have demonstrated that instillation of purified FliC from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium into the lungs drives swift production of chemokines and cytokines specially when recognized by the lungs’ epithelium that in turn orchestrate the recruitment of immune cells into the airways, mainly PMNs15,19-21. Although transient, the substantial neutrophil infiltration that takes place into the airways after nasal delivery of FliC could be a concern if moving towards clinical therapies for human use. Excessive inflammation could be detrimental for the lungs’ function. Moreover, it has been shown that intranasal delivery of immunostimulatory molecules may cause facial paralysis and/or brain toxicity22-24.
Sublingual immunotherapy offers a safer alternative to modulate the immune response in the respiratory tract compared to the intranasal route. It is non-invasive, painless, simple and has good patient compliance25. Furthermore, as mentioned before, it can induce protective responses in the respiratory mucosa without the risks associated to direct intranasal or intrapulmonary delivery of formulations. Sublingual route could be alternatively used to deliver molecules that have great effects onto the lung’s immune system but that have been proven to be toxic or to elicit great inflammation when administered intranasally. Besides these advantages, formulations for sublingual immunotherapy have lower cost of manufacture since non-sterile products can be delivered by this route and endotoxic shock is not a concern for SLIT. On the other hand, it is worth noticing that higher doses of the immunostimulatory compounds compared to those used by intranasal or parenteral routes are necessary to induce an immune response in the lungs; also highly concentrated solutions are needed when using the mouse model of SLIT since the anatomical site where the formulations are deposited is small.
Based on our previous published data, we developed a model of protection using sublingual immunotherapy with flagellin as model immunostimulant. We demonstrated that a single dose of flagellin induced 60% survival against invasive pneumococcal pneumonia caused by the serotype 1 strain while all mice in the control group died of infection within 5 days. Flow cytometry analysis showed that higher numbers of PMN are recruited into the airways of protected animals after sublingual treatment with flagellin suggesting that these cells might be involved in the mechanism of protection induced by sublingual immunotherapy.
This video shows in detail how to perform sublingual immunotherapy and also how to recover relevant tissue from the sublingual mucosa, draining lymph nodes as well as lungs and airways to perform further analysis. Additionally, it illustrates the general technique of cell preparation for FACS analysis and briefly shows how to prepare Streptococcus pneumoniae suspensions and how to perform intranasal infections in mouse to set up the acute infection model.
Protocol
تم تنفيذ الإجراءات التي تنطوي على الحيوانات وفقا للبروتوكولات N ° 08052010 071140-000821-12 وافقت عليها لجنة الفخرية للتجارب على الحيوانات ومجلس التوجيه من كلية الطب، جامعة دي لا ريبوبليكا - أوروغواي.
1. الإدارة تحت اللسان وكيل العلاجية
- تحضير محلول يحتوي على وكيل العلاجية لفحصها. ضبط تركيز على إدارة حجم الحد الأقصى من 10 ميكرولتر في الماوس.
ملاحظة: للحصول على فلاجيلين تنقيته من السالمونيلا الملهبة للضرب مصلي التيفية الفأرية الجرعة المثلى للحث على الحماية في الماوس المصابين أول جرعة قاتلة من S. الرئوية النمط المصلي 1 E1586، مما تسبب في وفيات 100٪ هو 10 ميكروغرام / الماوس. يجب أن تكون ساخنة حل فلاجيلين عند 65 درجة مئوية لمدة 5 دقائق لضمان الافراج عن أحادية. لمزيد من المعلومات حول تنقية فلاجيلين أنظر المرجع 26.- فارذ التركيز الفعال للعوامل المناعية مختلفة وفقا لحجمه الجزيئي، والنقاء، وقابلية التحلل البروتيني لواستخدام وكلاء mucoadhesive. ضبط تركيز الأمثل لكل مجمع لفحصها لتعظيم آثاره. إذا أجريت الدراسات السابقة من طريق الأنف لمركب معين، استخدام جرعة البداية 5 إلى 10 أضعاف لاختبار فعاليته من طريق تحت اللسان.
- تخدير الفئران عن طريق حقن كوكتيل يحتوي على 110 ملغ / كغ الكيتامين مع 5.5 ملغ / كغ Xylacine وترك بقية الحيوانات لمدة 7 إلى 10 دقيقة.
- تأكيد تخدير السليم عن طريق الضغط بلطف قاطع الطريق واحدة من رجليه الخلفيتين. إذا مخدرة بشكل صحيح والحيوان لا يتحرك ردا على التحفيز.
- نشر طبقة رقيقة من مرهم الطبيب البيطري على عيون كل فأر لمنع الجفاف بينما تحت التخدير.
ملاحظة: التخدير Inhalatory مثل Isofluorane يمكن أن تستخدم أيضا بدلا الكيتامين / Xylacine إذا كان نظام تجهيزPED مع التعريفي الغرفة والأنف المخاريط هو متاح. استخدام غرفة التعريفي لanaesthetise الحيوانات وإداراتها ومنبه المناعة من طريق تحت اللسان. اتصال فورا الحيوان إلى مخروط الأنف لمدة 15 دقيقة على الأقل لإبقائها تحت التخدير لتجنب البلع والسماح امتصاص المجمع العلاجي. - ماصة محلول يحتوي الحل منبه المناعة أو السيطرة على السيارة. باستخدام الإبهام والسبابة من اليد غير المسيطرة اتخاذ الماوس والاحتفاظ بها في الوضع الرأسي.
- باستخدام اليد المهيمنة مكان زوج من ملقط مغلقة تحت اللسان والاحتفاظ بها في مكانها باستخدام الأصابع الوسطى والبنصر، افتح قليلا ملقط لرفع اللسان.
- اتخاذ ماصة وإدارة الحل على الأرض من الجانب الظهري من الفم واللسان.
- إزالة ملقط والسماح للبقية الماوس لمدة 3 إلى 5 دقائق قبل وضعه مرة أخرى في قفص. ويحتفظ لضمان سوائية الحرارة في هيئة التصنيع العسكري مخدرةالإلكترونية، وربط أقفاص إلى نظام سخان القفص. إذا كان هذا النظام غير متوفر، الفئران مكان تابعة لمجموعة العلاج نفسها مرة أخرى في قفص واحد المقابلة بجانب بعضها البعض على الفراش وتغطي جزئيا لهم ورقة المناديل الورقية النظيفة لمساعدتهم على الحفاظ على درجة حرارة الجسم.
- جمع عينات الأنسجة في أي نقطة زمنية بعد تقطير من وكيل المناعية لتحليل التغيرات في السكان الخلية الناجمة عن العلاج.
تم إجراء هذه الإدارة في بروتوكول معينة من فلاجيلين 2 ساعة قبل التحدي: ملاحظة. تحديد الوقت الأمثل بين العلاج والتحدي لكل عامل علاجي معين، والممرض لفحصها.
2. التحدي إعداد تعليق البكتيرية وداخل الأنف مع العقدية الرئوية
ملاحظة: S. الرئوية هو الممرض الإنسان الطبيعي التي يمكن أن تسبب الأمراض التي تهدد الحياة مثل الالتهاب الرئوي الغازية، والإنتانوالتهاب السحايا. قد يحدث انتقال العدوى عند استنشاقه أو في اتصال مع الغشاء المخاطي. لذلك، جميع العينات التي قد تكون على اتصال مع S. الرئوية يجب أن يتم التعامل معها في المستوى المناسب منشأة السلامة البيولوجية II باستخدام مجلس الوزراء من الدرجة الثانية للسلامة الأحيائية. تحقق من إجراءات التشغيل الموحدة من مؤسستكم بشأن التعامل مع النوع الثاني لمسببات الأمراض الملابس الواقية والتخلص من النفايات والتدابير الأمنية الإضافية التي قد تنطبق. يجب أن تبقى الحيوانات المصابة في أقفاص التهوية بشكل فردي في العوازل مجهزة مرشحات HEPA. تتوفر اللقاحات المضادة للمكورات الرئوية والعلاج بالمضادات الحيوية. لمزيد من المعلومات انظر المراجع 27 و 1.
- ذوبان الجليد قسامة من تعليق عمل البورصة العقدية الرئوية من عدد البكتيريا المعروفة كفو أعد كما هو موضح في 15.
- أجهزة الطرد المركزي لمدة 5 دقائق عند 2،500 x ج وRT.
- تجاهل طاف ويغسل بيليه البكتيرية من خلال تعليق في 1 مل من شارعمحلول ملحي erile. نصائح استخدام مرشح عند إعداد تعليق البكتيرية، التخفيفات أو التحدي الحيوان.
- الطرد المركزي مرة أخرى كما هو موضح في الخطوة 2.2.
- تجاهل طاف و resuspend بيليه في حجم مناسب من ملحي معقم للحصول على تعليق 4x10 5 خلية / ميكرولتر 50. هذه الجرعة يتوافق مع الحد الأدنى من الجرعة البكتيرية S. الرئوية النمط المصلي 1 E1586 الذي يسبب وفيات 100٪ في BALB / ج الفئران وفقا لدراسات سابقة 15.
ملاحظة: عند إنشاء نموذج من الالتهاب الرئوي المكورات الرئوية في الفئران، والجرعة الدنيا البكتيرية تسبب يجب تحديد 100٪ من وفيات لكل تركيبة معينة من سلالة بكتيرية، والمصلي وسلالة الماوس. - تجانس تعليق البكتيرية قبل vortexing أو pipetting صعودا وهبوطا 5 مرات.
- تحميل 50 ميكرولتر من تعليق البكتيرية باستخدام تلميح تصفية العقيمة وغرس الحجم الإجمالي في فتحتي الأنف من الماوس مخدرة. عقد upri الماوسGHT لمدة 2 دقيقة وندعه يستريح في موقف الظهرية لمدة 2 دقيقة أكثر. تطبيق مرهم الطبيب البيطري على عيون الحيوانات والعودة إلى القفص. تأكد للحفاظ على سوائية الحرارة بينما تحت التخدير.
ملاحظة: في هذه الدراسة تم إجراء التحدي البكتيرية في حجم 50 ميكرولتر لضمان تسليم 90٪ على الأقل من إجمالي كفو إلى الرئتين كما هو محدد سابقا في 15،28. للحد من محنة حجم الحيوان أصغر (على سبيل المثال، 20 ميكرولتر) يمكن استخدامها. ومع ذلك، يجب أن يتم التحقق التنفيذ الفعال من البكتيريا في الرئتين. يمكن القيام بذلك عن طريق حصاد الرئتين 5 دقائق بعد التحدي والعد كفو الخليط في الرئتين عن طريق الطلاء التخفيفات المسلسل على لوحات أجار الدم. - تؤكد الأرقام كفو في تعليق البكتيرية المستخدمة في العدوى عن طريق طلي مسلسل التخفيفات 10 أضعاف على لوحات أجار الدم. احتضان O / N عند 37 درجة مئوية مع CO 2 5٪ وحساب عدد المستعمرات مخاطي تقديم سمة هالة آل الخضراءالبكتيريا البلا الانحلالي.
3. الأنسجة جمع وتحضير العينات للالتدفق الخلوي (FACS) تحليل
3.1) جمع الأنسجة
- الموت ببطء الحيوانية خلع عنق الرحم أو استخدام CO 2 غرفة. فتح التجويف الصدري وصولا إلى الرقبة وإجراء شق على طول الأرجل الأمامية لفضح الجانب البطني من الرقبة ومنطقة تحت الفك السفلي.
- مع تلميح منحنية ملقط غرامة سحب بلطف صعودا الغدد اللعابية والأنسجة اللينة المتاخمة لفضح الجانب الظهري من قاع الفم. باستخدام ملقط المنحنية غيض رقيقة، واتخاذ الفك السفلي والفك السفلي الغدد الليمفاوية الاكسسوار عن طريق سحب ما يصل بلطف ووضعها في أنبوب يحتوي على RPMI كاملة (cRPMI، 500 مل 10٪ الجنين مصل بقري، 5 مل من محلول يحتوي على 10،000 U / مل البنسلين و 10 ملغ / مل الستربتوميسين حل و 5 مل من L-الجلوتامين 200 ملم) أو حمض النووي حل حافظة وفقا للإجراءات التي سوف المصبيتعين الاضطلاع بها في وقت لاحق.
- لفتح التجويف الصدري إجراء شق في الحجاب الحاجز. باستخدام زوج من ملقط مسنن الفئران المشبك الغضروف سيفي الشكل من القص وبعناية قطع الأضلاع في كلا الجانبين الظهرية بدءا من الأضلاع الكاذبة على طول الطريق حتى الوصول إلى نقطة التقاء الأضلاع الحقيقية للقبضة من القص.
- من خلال عقد الغضروف سيفي الشكل من القص مع ملقط، سحب ما يصل بلطف لفضح أجهزة التجويف الصدري.
- إزالة الأضلاع تماما عن طريق خفض الأضلاع الأولى والترقوة. ستظهر الغدة الصعترية كهيكل الأبيض من فصين وتقع في الجزء أمامي بطني من قريب الصدر إلى قاعدة القلب.
- تأخذ واحدة من الفص بواسطة تحامل عليه مع زوج من ملقط واستخدام زوج من مقص لإزالة الأربطة بين جهها أدنى والتأمور. الشروع في إزالة الفص الثاني.
- تحديد تجويف البطن وفتحه عن طريق قطع على طول محور متوسط مجدار uscular لفضح الأجهزة. مع زوج من ملقط قطع الوريد الأجوف الخلفي والشريان الأبهر الصدري. إزالة الزائدة من الدم مع أنسجة ماصة.
- لتحليل المقيمين والتسلل السكان الخلية من الحويصلات الهوائية يؤدي غسيل القصبات (BAL). قطع العضلات في الجزء البطني من الرقبة لفضح القصبة الهوائية والمريء. للفصل بينهما جعل شقوق على الجانبين الجانبية والظهرية من الهياكل.
- رفع القصبة الهوائية مع ملقط وجعل شق صغير مع مشرط لإدخال ماصة نقل رقيقة طرف مليئة 1 مل من PBS دون الكالسيوم 2+ / المغنيسيوم 2+ زائد 1 ملي EDTA. غرس ونضح الحجم الإجمالي لا يقل عن ثلاث مرات؛ نضح ونقل تعليق خلية إلى أنبوب معقم 1.5 مل ووضعه على الجليد.
- لتحليل السكان الخلية موجودة في حمة الرئة، يروي أولا الرئتين عن طريق حقن 5 مل من PBS دون الكالسيوم 2+ / المغنيسيوم 2+ زائد 1 ملي EDTA إلى البطين الأيمنمن القلب.
ملاحظة: هذا سيقضي على معظم خلايا الدم الحمراء والخلايا المناعية الموجودة في الأوعية الدموية في الرئتين. إذا تم تنفيذ نضح بشكل صحيح، واللون الوردي من الرئتين تحول إلى اللون الأبيض. - عزل القلب من الرئتين عن طريق تحامل عليه من قاعدة البطين الأيسر وقطع بدقة الأوعية الدموية مع المقص لإزالته تماما. تأخذ الرئتين perfused لووضعها في cRPMI أو المواد الحافظة حمض النووي الحل اعتمادا على تحليل المصب التي يتعين القيام بها.
- لتحليل السكان الخلية في الغشاء المخاطي تحت اللسان، عزل رئيس الحيوان وإزالة الغدد اللعابية والأنسجة اللينة المجاورة إذا لم يتم القيام به في الخطوة 3.2.1.
- إجراء شق على كل جانب من الفم حتى تصل مفصل الفك السفلي وفصل الفك السفلي مع اللسان وأرضية الفم، باستخدام دبابيس إصلاحه على لوحة التشريح. سحب ما يصل اللسان. باستخدام مشرط إجراء شق فيها باحد ذاتها لسان تجتمع الكلمة من الفم حتى تصل إلى الأضراس الثالثة لفضح الغشاء المخاطي تحت اللسان.
- إزالة اللسان تماما. اتخاذ 0.5 ملم خزعة لكمة ووضعه بجانب القواطع السفلية. قطع من الإدراج اللثة من النسيج تحت اللسان واضغط بلطف حتى أرضية الفم قد قطع تماما.
- أكرر مرة أخرى وضع الآن لكمة خزعة بالقرب من الأضراس الثالثة لاستكمال إزالة الأنسجة تحت اللسان. وضع على أنبوب نظيفة تحتوي على مواد حافظة أو cRPMI الحمض النووي.
3.2) إعداد عينة للتحليل FACS.
- نقل أنسجة الرئتين "معزولة عن بعضها الماوس في لوحة 24 جيدا وتخطر لهم مع زوج من مقص نظيفة حتى الحصول على قطع صغيرة من النسيج حوالي 2 مم. إضافة 1 مل لكل بئر الهضم المتوسطة التي تحتوي على 30 ملغ من كولاجيناز من النوع الثاني، و 50 ميكروغرام الدناز-I في 1 مل من RPMI دون FBS. ماصة صعودا وهبوطا خمس مرات ويحضن في37 درجة مئوية و 5٪ CO 2 لمدة 40 دقيقة.
- لتحليل السكان الخلية في الأنسجة تحت اللسان، استبدل المتوسطة في الهضم 3.2.1 مع واحدة تحتوي على 2 وحدة من Dispase، 30 ملغ كولاجيناز من النوع الثاني، و 50 ميكروغرام الدناز-I في 1 مل من RPMI. احتضان الأنسجة التي تم جمعها من الماوس واحد في 500 ميكرولتر من الهضم متوسطة لمدة 20 دقيقة عند 37 درجة مئوية في شاكر المداري في 50 دورة في الدقيقة.
- بعد الحضانة، ماصة صعودا وهبوطا ما يصل إلى 10 مرات أو 30 ثانية حتى تعطلت معظم الأنسجة. تعليق تصفية خلية الرغم من الخلية 40 ميكرومتر مصفاة معقمة ويغسل مع 5 مل من برنامج تلفزيوني تستكمل مع 5 ملي EDTA.
لن يتحقق الهضم الكامل من المصفوفة خارج الخلية والأنسجة الليفية: ملاحظة. ومع ذلك، لا ينصح مرات أطول في الحضانة جود كولاجيناز و / أو dispase أو سحن العدواني لأنه سوف يؤدي إلى زيادة موت الخلايا وتدمير البروتينات خارج الخلية التي تؤثر على النتيجة الاجمالية للجمعةتحليل ACS. - الطرد المركزي في 400 x ج، 5 دقائق، 4 درجات مئوية.
- لتحليل السكان الخلية في BAL، الطرد المركزي الخلايا في 400 x ج، 5 دقائق، في 4 درجات مئوية، وانتقل إلى الخطوة 3.2.4.
- لتحليل السكان الخلية في الغدد الليمفاوية، ووضع مصفاة 70 ميكرومتر الخلية على طبق بتري معقمة ووضع الليمفاوية الليمفاوية مع 1 مل من cRPMI في مصفاة. إخراج يغرق من 2 مل حقنة معقمة واستخدامه بمثابة مدقة لسحق الغدد الليمفاوية ضد شبكة مصفاة ل. شطف مصفاة الخلية مع 1 مل من cRPMI جديدة ونقل الخلايا من طبق بتري لأنبوب العقيمة.
- اتخاذ قسامة كل عينة تمثيلية من وصمة عار مع التريبان الأزرق لتحديد عدد الخلايا قابلة للحياة.
- resuspend الخلايا في FACS-EDTA: PBS-5 ملي EDTA-1٪ مصل بقري Albumin- لتعويض تعليق 2X10 7 خلية / مل وإضافة 50 ميكرولتر في أنبوب عداد الكريات.
- إعداد مزيج الأجسام المضادة 2X تحتوي على appropriate مجموعات من الأجسام المضادة ضد علامات سطح fluorochromes وفقا للمتاح أداة FACS. إضافة 50 ميكرولتر من الأجسام المضادة مزيج 2X في كل أنبوب يحتوي على تعليق خلية.
ملاحظة: عاير كل الأجسام المضادة المسمى تألقي لتحديد الكمية المثلى لاستخدامها، لبروتوكول مفصل أنظر المرجع 29. - احتضان 30 دقيقة على الجليد في الظلام.
- يغسل مرة واحدة مع 3 مل من EDTA-FACS وتدور باستمرار في الخلايا عن طريق الطرد المركزي في 400 x ج لمدة 5 دقائق عند 4 درجات مئوية، resuspend الخلايا في 200 ميكرولتر من المخزن نفسه وتحليل في عداد الكريات التدفق.
ملاحظة: إذا كان التعامل مع عدد كبير من العينات، بروتوكول تلطيخ لتحليل نظام مراقبة الأصول الميدانية المذكورة أعلاه لا يمكن أن يؤديها في U-أسفل لوحات 96 جيدا بدلا من أنابيب عداد الكريات. ومع ذلك، إذا كان استخدام 96 جيدا الخطوات لوحات الغسيل يجب أن يؤديها من خلال إضافة ما يصل إلى 200 ميكرولتر من FACS-EDTA وتكرار ذلك 4 مرات الغزل أسفل الخلايا في 400 x ج لمدة 5 دقائق في 4 درجات مئوية بين كل اشيخطوة نانوغرام. - عند هذه النقطة، وتحديد العينات لتحليلها في وقت لاحق من تدفق عداد الكريات (إلى 72H بعد التثبيت).
- لإصلاح الخلايا، وبعد وضع العلامات مع الأجسام المضادة FACS غسل الخلايا في برنامج تلفزيوني لا كا 2 + / المغنيسيوم 2+، 1 ملم EDTA دون FBS. تعليق الخلايا في 50 ميكرولتر من نفس العازلة وإضافة 50 ميكرولتر من 4٪ من محلول بارافورمالدهيد الطازجة في مفرط التوتر (2X) PBS لا كا 2 + / المغنيسيوم 2+.
- احتضان لمدة 20 دقيقة في RT ويغسل 3 مرات في FACS-EDTA.
- resuspend الخلايا في 200 ميكرولتر من FACS-EDTA وتخزينها في 4 درجة مئوية، ومحمية من الضوء لمدة تصل إلى 72 ساعة.
ملاحظة: FSC-SSC يمكن أن تتأثر التثبيت. إذا تحديد الاختيار التوافق عينات من الأجسام المضادة fluorescently المسمى مع الشركة المصنعة منذ الأصباغ جنبا إلى جنب يمكن المتدهورة في حضور وكلاء تثبيتي. إذا نشأت عينات من الحيوانات المصابة ينصح بشدة تثبيت لضمان عدم وجود مسببات الأمراض القابلة للحياة سيكون حاضرا عندما analyالغناء العينات في الجهاز FACS منذ microaerosols يمكن أن تتولد خلال الاستحواذ على العينة.
4. إجمالي استخراج الحمض النووي الريبي، وكدنا] التجميعي في الوقت الحقيقي PCR.
4.1) استخراج الحمض النووي الريبي والتوليف [كدنا].
- تجانس الأنسجة في الحافظة حمض النووي حل الاختيار عن طريق تعطيل الميكانيكية (على سبيل المثال، باستخدام الخالط الدوار الموالي، وارتفاع سرعة اهتزاز الأنسجة ruptor والخرز، الخ). الطرد المركزي في 12،600 x ج لمدة 15 دقيقة و 4 درجات مئوية لإزالة الحطام الأنسجة. نقل طاف لأنبوب نظيفة.
- استخراج الحمض النووي الريبي مع أسلوب الاختيار التالية تعليمات الشركة المصنعة.
ملاحظة: RNA هو عرضة للتدهور، إذا لم يكن على وشك أن يستخدم على الفور بعد العزلة، وجعل مأخوذة وتخزينها في ريبونوكلياز أنابيب مجانية في -80 درجة مئوية. تجنب تكرار تجميد والذوبان. يجب التعامل مع قفازات الأنابيب في جميع الأوقات. بعد ذوبان العينات وlways الاحتفاظ بها على الجليد. - قياس امتصاص الأحماض النووية في 260 نانومتر وحساب تركيز في ميكروغرام / ميكرولتر.
- إعداد الدناز-I مزج بإضافة (لمدة 1 عينة): 7.6 ميكرولتر من الماء عالى النقاء، 1 ميكرولتر من 10X الدناز-I العازلة، 0.4 ميكرولتر من الدناز-I (التضخيم الصف) الأوراق المالية 1 U / ميكرولتر، وإضافة 8.4 ميكرولتر من والدناز-I مزج لكل عينة تحتوي على 1 ميكروغرام من الحمض النووي الريبي مجموع.
- استخدام الحمض النووي الريبي في تركيز 1 ميكروغرام / ميكرولتر وتنفيذ رد فعل retrotranscription (RT-PCR) وذلك بإضافة 1 ميكرولتر من الحمض النووي الريبي مجموع كقالب. إذا كانت العينات المخفف جدا وتركيز أقل مما كان متوقعا، إضافة كميات أكبر من الحمض النووي الريبي مجموع بدلا من الماء. لا تتجاوز 20٪ من حجم رد الفعل النهائي عند إضافة الحمض النووي الريبي خاصة إذا كان بروتوكول استخراج الحمض النووي الريبي الاختيار تشارك مزيج الفينول كلوروفورم منذ آثار الفينول يمكن أن تؤثر على العائد من RT-PCR.
- احتضان 15 دقيقة في RT تليها 10 دقيقة في 4 درجات مئوية أو طم. (لا تتجاوز فترة حضانة!)
- إضافة 1 ميكرولتر من EDTA 25 ملي (البيولوجيا الجزيئية الصف) إلى كل أنبوب واحتضان عند 65 درجة مئوية لمدة 10 دقيقة لإبطال نشاط الدناز-I.
- إعداد retrotranscription (RT) مزيج النحو التالي (1 رد الفعل): 1 ميكرولتر الأسهم الاشعال مسدوس العشوائي 0.2 ملغ / مل، 1 ميكرولتر dNTPs الأسهم 10 ملم، 4 ميكرولتر 5X M-MLV-RT العازلة، 2 ميكرولتر DTT M 0.1، 1 ميكرولتر ريبونوكلياز OUT الأسهم 40 U / ميكرولتر، و 1 ميكرولتر M-MLV retrotranscriptase الأسهم 200 U / ميكرولتر.
- إضافة 10 ميكرولتر من RT-PCR مزيج إلى 10 ميكرولتر الدناز-I أنبوب التفاعل.
- تنفيذ رد فعل PCR في cycler الحرارية وفقا للبرنامج التالي:
1X دورة: 10 دقيقة، 25 درجة مئوية؛ 50 دقيقة، 37 درجة مئوية؛ 15 دقيقة، 70 ° C - تمييع [كدنا] 1: 5 عن طريق إضافة 80 ميكرولتر من الماء عالى النقاء. تخزين في -20 درجة مئوية.
4.2) في الوقت الحقيقي PCR (QPCR).
- QPCR إعداد مزيج رد فعل على النحو التالي (1 رد الفعل): 5 ميكرولتر مزيج الرئيسي يحتوي على الحمض النووي طق Polymerase، SYBR الصبغة الخضراء، PCR العازلة، مزيج dNTP وMgCl 2 (انظر 4.2.2 أدناه). 0.9 ميكرولتر من حل 10 ميكرومتر الأسهم من التمهيدي إلى الأمام، 0.9 ميكرولتر من حل 10 ميكرومتر الأسهم من التمهيدي العكسي، 1.2 ميكرولتر الماء عالى النقاء، و 2 ميكرولتر من قالب [كدنا] المخفف سابقا كما هو موضح في الخطوة 4.1.10.
تم الأمثل تركيز كاشف والدراجات البروتوكولات المستخدمة في هذا القسم التي يتعين الاضطلاع بها على وجه التحديد مع الكواشف والأدوات الموصوفة في "جدول المواد والكواشف"، ماركات أخرى يمكن استخدامها ولكن حجم رد الفعل، تركيز كاشف وبروتوكول ركوب الدراجات قد تختلف: ملاحظة. تحقق إرشادات الشركة المصنعة قبل تنفيذ RT-QPCR. - إعداد أداة QPCR على النحو التالي:
1X دورة: 15 دقيقة، 95 ° C
40X دورات: 15 ثانية، 95 درجة مئوية تليها 1 دقيقة، 60 ° C (في هذه المرحلة يكتسب مضان).
ملاحظة: للحصول على القياس الكمي النسبي لمرنا وفقا لطريقة ط 30 على الاشارةيجب تحديد الجين البريد لتطبيع القيم ط. وينبغي اختبار إشارة الجينات من خيار في ظل ظروف معينة والفحص التعبير عنها قد تختلف، Actb، GAPDH أو 18S هي بعض من جينات منتقاة عادة كمراجع. - إعداد قيمة العتبة وتحليل البيانات.
النتائج
العلاج المناعي تحت اللسان يمكن استخدامها بنجاح لتعديل الاستجابة المناعية الرئتين. نحن أظهرت أن جرعة واحدة من فلاجيلين، وTLR5 وNLRC4 ناهض، يمكن أن تحدث upregulation كبير من مرنا ترميز CXCL1 كيموكينات، CCL20 وخلوى IL-6 مقارنة المالحة تعامل الضوابط. أضعاف تحريض مستويات مرنا بلغت ذروتها في 8 ساعات بعد SLIT والعودة إلى المستويات القاعدية بعد 20 ساعة (الشكل 1). ومع ذلك، عندما تم إجراء SLIT 2 ساعة عدوى الأنف مسبق مع S. الرئوية، ومستويات CXCL1 وIl6 مرنا ظلت upregulated بشكل ملحوظ حتى 24 ساعة بعد SLIT بالمقارنة مع الحيوانات غير المعالجة (الشكل 2).
وكشف تحليل للسكان الخلية في BAL وأنسجة الرئة بواسطة نظام مراقبة الأصول الميدانية أن الحيوانات تعامل مع فليك من طريق تحت اللسان قد ارتفع عدد العدلات في الشعب الهوائية ولكن ليس في أنسجة الرئتين "(الشكل 3).
ق = "jove_content"> وأخيرا، البقاء على قيد الحياة بعد التحدي المكورات الرئوية تمت مقارنة في الحيوانات تعامل سابقا مع فليك من طريق تحت اللسان أو بمحلول ملحي كمجموعة تحكم. كما هو مبين في الشكل 4، SLIT مع فلاجيلين الترويج حماية وزيادة البقاء على قيد الحياة ضد المكورات الرئوية الالتهاب الرئوي الحاد.
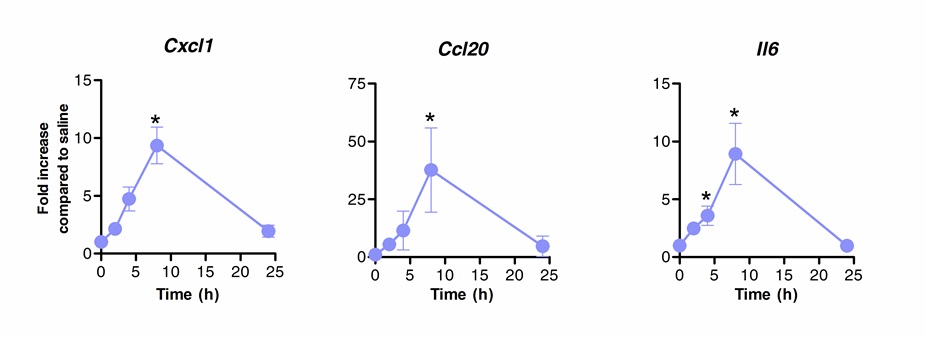
الرقم 1. حركية النسخي الرئتين "بعد العلاج المناعي تحت اللسان مع فلاجيلين. ثمانية إلى 10 أسابيع من العمر الفئران BALB / ج (ن = 4) عولجوا مع 10 ميكروغرام من فلاجيلين أو المالحة من طريق تحت اللسان تحت التخدير. تم جمع الرئتين عند نقاط زمنية مختلفة ووضعها في حافظة الحمض النووي. وقد أجريت إجمالي استخراج الحمض النووي الريبي وتم تصنيعه [كدنا]. تم تقييم مستويات مرنا من الوقت الحقيقي PCR باستخدام بادئات محددة مدرجة في طبلتم تنفيذ ه 1. الكمي النسبي حسب طريقة ΔCt باستخدام مستويات Actb مرنا للتطبيع. وتظهر النتائج على النحو أضعاف مقارنة مع المجموعة المعالجة والمالحة متوسط ± SEM. تشير العلامات النجمية فروق ذات دلالة إحصائية (P <0.05) المحسوبة وفقا لمان ويتني الاختبار. النتائج هي تمثيلية من 2 تجارب مستقلة.
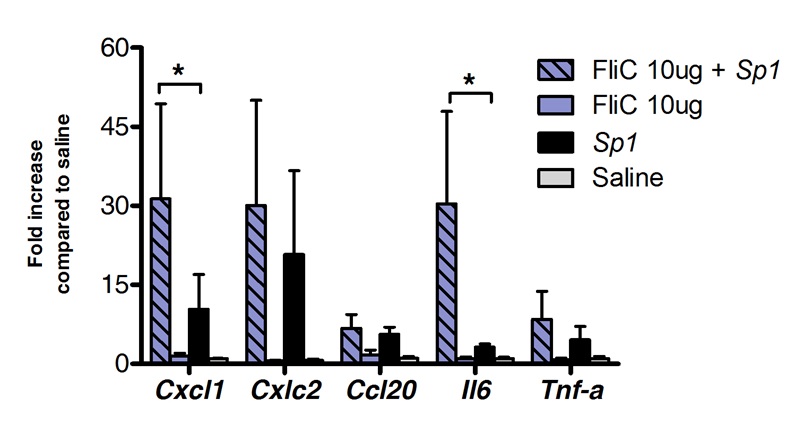
وعولج النسخي الشكل 2. الرئتين "خلال المكورات الرئوية الالتهاب الرئوي بعد العلاج المناعي تحت اللسان مع فلاجيلين. ثمانية إلى 10 أسابيع من العمر الفئران BALB / ج (ن = 4 لمجموعة التحكم و n = 7 لمجموعة المعالجة) مع 10 ميكروغرام من فلاجيلين أو المالحة بواسطة الطريق تحت اللسان تحت التخدير. 2 ساعة في وقت لاحق وقد تم الطعن الفئران من طريق الأنف مع الحد الأدنى من الجرعة المميتة (MLD) يسبب 10فيات 0٪ من عزل السريري للS. الرئوية النمط المصلي 1 E1585 الموافق 4x10 5 خلية / ميكرولتر 50. تم جمع الرئتين 24 ساعة بعد التحدي وتخزينها في حافظة الحمض النووي حتى تم تنفيذ استخراج الحمض النووي الريبي والتوليف [كدنا بها. في الوقت الحقيقي PCR أجريت خارج (انظر قائمة التمهيدي في الجدول 1) وأجري الكمي النسبي حسب طريقة ΔCt باستخدام مستويات Actb مرنا للتطبيع. وتظهر النتائج على النحو أضعاف مقارنة مع المجموعة المعالجة والمالحة متوسط ± SEM. تشير العلامات النجمية فروق ذات دلالة إحصائية (P <0.05) المحسوبة وفقا لمان ويتني الاختبار.
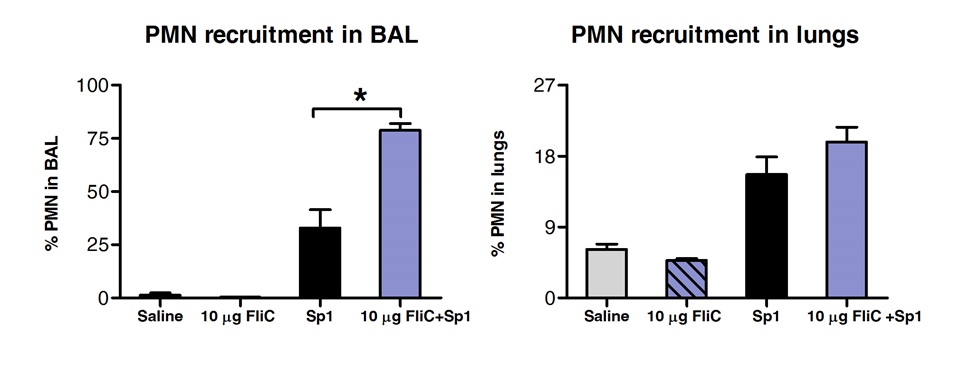
الرقم 3. تحليل النوى العدلات (PMN) التوظيف في أنسجة الرئتين والشعب الهوائية بعد SLIT. ثمانية ل10 أسابيع من العمر الفئران BALB / ج (ن = 4) وتعامل مع 10 ميكروغرام من فلاجيلين أو المالحة من طريق تحت اللسان تحت التخدير. 2 ساعة في وقت لاحق وقد تم الطعن الفئران من طريق الأنف مع MLD من S. الرئوية النمط المصلي 1 E1585. 24 ساعة بعد التحدي، تم تنفيذ BAL وتمت معالجة الرئتين لتحليل نظام مراقبة الأصول الميدانية. تم تحديد PMN كما Ly6G / CD11b خلايا السلبية عالية / CD11c وعالية واستنادا إلى بيان FCS-SSC. يتم التعبير عن النتائج كنسبة مئوية من PMN فيما يتعلق من إجمالي أعداد الخلايا في BAL أو الرئتين. القضبان تمثل متوسط ± SEM. تشير العلامات النجمية فروق ذات دلالة إحصائية (P <0.05) المحسوبة وفقا لاتجاه واحد مان ويتني الاختبار.
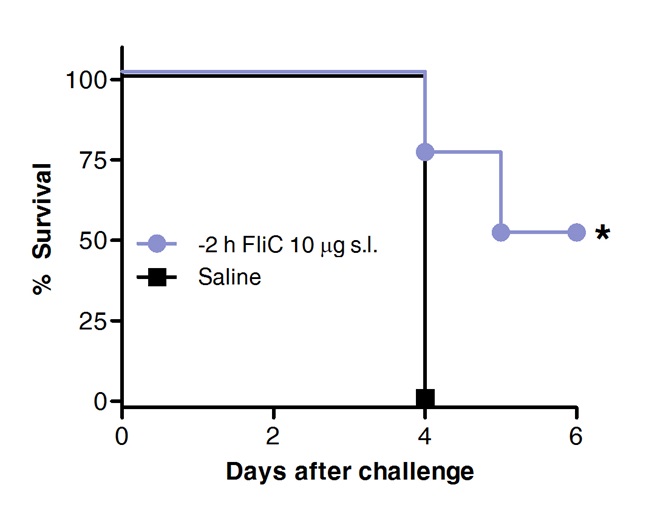
الرقم 4. SLIT مع فلاجيلين يحمي الفئران ضد المكورات الرئوية الالتهاب الرئوي الحاد. ثمانية إلى 10 أسبوعا من العمر BALB / ج الفئران (ن = 8) وتعامل مع 10 ميكروغرام من فلاجيلين أو المالحة من طريق تحت اللسان تحت التخدير. 2 ساعة في وقت لاحق وقد تم الطعن الفئران من طريق الأنف مع MLD من S. الرئوية النمط المصلي 1 E1585. تم تقييم البقاء على قيد الحياة على أساس يومي. وتمت مقارنة منحنيات كابلان ماير وفقا دخول رتبة الاختبار (رف الموقد كوكس). تشير العلامات النجمية فروق ذات دلالة إحصائية (P <0.05) .Results هي ممثل 2 تجارب مستقلة.
| اسم | تسلسل 5'-3 " | PCR طول المنتج (بي بي) |
| MB-actin_F | GCTTCTTTGCAGCTCCTTCGT | 68 |
| MB-actin_R | CGTCATCCATGGCGAACTG | |
| mCCL20_F | TTTTGGGATGGAATTGGACAC | 69 |
| mCCL20_R | TGCAGGTGAAGCCTTCAACC | |
| mCXCL1_F | CTTGGTTCAGAAAATTGTCCAAAA | 84 |
| mCXCL1_R | ACGGTGCCATCAGAGCAGTCT | |
| MIL-6_F | GTTCTCTGGGAAATCGTGGAAA | 78 |
| MIL-6_R | AAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCATACA | |
| mTNFalpha_F | CATCTTCTCAAAATTCGAGTGACAA | 63 |
| mTNFalpha_R | CCTCCACTTGGTGGTTTGCT | |
| mCxcl2_F | CCCTCAACGGAAGAACCAAA | 72 |
| mCxcl2_R | CACATCAGGTACGATCCAGGC |
الجدول قائمة 1. التمهيدي تستخدم في الوقت الحقيقي تحليل PCR. متواليات التمهيدي محددة تستخدم لتحليل QPCR. إلى الأمام والاشعال للماوس actb عكس، يتم عرض Cccl20، CXCL1، Il6، Tnfa وCXCL1 حسب تسلسل 5'-3 "ويشار طول المنتج المتوقع في الأزواج الأساسية (بي بي).
Discussion
وقد ثبت الإدارة تحت اللسان من العوامل العلاجية كوسيلة مفيدة لتعديل الاستجابة المناعية في الجهاز التنفسي. والميزة الرئيسية لSLIT لعلاج أمراض الجهاز التنفسي هي أنها لا تنطوي على التسليم المباشر من المركبات إلى الرئتين أو الأنف، كونها أكثر أمانا من العلاجات القائمة على إدارة الأنف 31.
العلاج المناعي تحت اللسان يمكن استخدامها لتعديل الاستجابة المناعية بطرق مختلفة، إما لتحريض استجابات التنظيمية التي يمكن تخفيف أعراض التهاب حساسية والربو 32 أو للحث على تفعيل عابرة آليات المناعة الفطرية لعلاج التهابات الرئة الحادة كما هو موضح هنا.
نموذج الفأر المقدمة في هذا الفيديو هو وسيلة مريحة لفحص مركبات مختلفة كعوامل علاجية لSLIT.
يقدم هذا النموذج الحيواني وسيلة مفيدة لتحديد أثرمن SLIT في الاستجابة المناعية الرئتين "وكذلك في الأجهزة الأخرى (على سبيل المثال، تجفيف الغدد الليمفاوية أو مواقع المخاطية البعيدة) التي لا يمكن أن تحاكي من خلال استخدام نماذج في المختبر. على الرغم من أن هناك العديد من الصحف التي تصف النتائج التي تم الحصول عليها باستخدام العلاج المناعي تحت اللسان، لم بذلت طرق مفصلة لإجراءات الإدارة تحت اللسان متاحة بعد. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن استخدام النموذج لتقييم اللقاحات تحت اللسان تهدف إلى منح الحماية النظامية وكذلك المحلية في الجهاز التنفسي.
كما هو مبين في شريط الفيديو المصاحب، والإدارة تحت اللسان من المركبات هو إجراء بسيط التي يمكن القيام بها بسهولة دون الحاجة إلى تدريب مكثف. عادة، فإن الشخص بارعا في التعامل مع الحيوانات تتطلب 1 ساعة لأداء SLIT في مجموعة من 10 الفئران باستخدام التخدير عن طريق الحقن كما هو موضح في هذا البروتوكول. إذا يتم تنفيذ التحدي المكورات الرئوية كذلك، سيطلب 90 دقيقة إضافية لإعدادتعليق البكتيرية وأداء التحدي الأنف من الحيوانات.
البروتوكولات FACS المقدمة هنا تسمح توصيف مناسب من تأثير SLIT في موقع الإدارة المحلية، واستنزاف الغدد الليمفاوية وكذلك تأثيرها على ديناميات خلايا الرئتين.
تحليل منفصل من القصبات والرئة حمة المحتوى مهم للتمييز الشعب الهوائية "مقيم المناعة، والتسلل أنواع الخلايا من تلك التي تبقى داخل الأنسجة. تحليل محتوى BAL يسمح دراسة البلاعم السنخية دوران فضلا عن ديناميات خلايا التجنيد في المساحات السنخية الناجمة عن العلاجات المختلفة، على سبيل المثال، PMNs، الحمضات، وحيدات. ويمكن أيضا BAL استخدامها لتقييم وجود السيتوكينات يفرز وكيموكينات بواسطة انزيم مرتبط المناعي فحص (ELISA) أو الكشف عن الأجسام المضادة ايغا يفرز أثار بعد التطعيم تحت اللسان. دراسة أنسجة الرئتين "سيسمح توصيف أنواع أخرى خلية، والخلايا الجذعية كلاسيكي، وخلايا T والخلايا B.
إعداد العينات BAL والغدد الليمفاوية للتحليل FACS بسيط. بعد جمع العينات، ويطلب عادة 60 دقيقة لاستكمال بروتوكول تلطيخ لمدة 10-20 العينات. في المقابل، سوف عزل الخلايا من أنسجة الرئتين أو تحت اللسان تتطلب المزيد من الوقت منذ مطلوب الهضم من المصفوفة خارج الخلية. امتصاص كيل العلاجية التي ألقاها الطريق تحت اللسان يمكن معالجتها من خلال تتبع جزيئات fluorescently أو المسمى بالإشعاع باستخدام أنظمة التصوير في الجسم الحي.
العلاج المناعي تحت اللسان هو وسيلة جذابة للحث على فعالية الاستجابات المناعية في الجهاز التنفسي وكذلك النظامية التي يمكن استخدامها لعلاج أو منع أمراض الجهاز التنفسي. توضيح آليات تحديد تفعيل مقابل التسامح من الاستجابة المناعية في الجهاز التنفسي بعد SLIT طق حاسمة للسماح التصميم الرشيد من الاستراتيجيات العلاجية الجديدة التي يمكن استخدامها وحدها أو في تركيبة مع العلاجات المتاحة ضد أمراض الجهاز التنفسي المختلفة.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Dr. Jean-Claude Sirard from the Center for Infection and Immunity of Lille, Institute Pasteur de Lille-France, for kindly providing the purified flagellin and Dr. Teresa Camou, Director of the National Reference Laboratory, Ministry of Health of Uruguay for kindly providing the pneumococcal strain.
The authors would like to express their acknowledgement to Mr. Diego Acosta and Mr. Ignacio Turel form BichoFeo Producciones-Uruguay for their commitment and hard work during the entire video production and edition.
This work was supported by the grants PR_FCE_2009_1_2783 and BE_POS_2010_1_2544 from the National Agency of Research and Innovation, ANII from Uruguay, the Program for Development of Basic Sciences, PEDECIBA of Uruguay and Sectoral Commission of Scientific research, CSIC-Universidad de la República, Uruguay.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Ketamine solution (50 mg/ml) | Pharma Service, Uruguay | ||
| Xilacine solution (2 %) | Portinco S.A., Uruguay | ||
| Sterile 1 ml syringe | Modern, Uruguay | ||
| Sterile 27 G needle | Modern, Uruguay | ||
| RPMI 1640 | General Electric Health Care | E15885 | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | ATCC | 302020 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin Solution | SIGMA | P4333 | |
| Sterile PBS without Ca2+/Mg2+ | PAA | H21002 | |
| Type-I Collagenase | Life Technologies/Gibco | 17100017 | |
| Deoxyribonuclease I (DNAse-I) | SIGMA | D4513 | |
| Dispase | Life Technologies/Gibco | 17105041 | |
| PerCP-Cy5.5 conjugated rat anti mouse IgG2b anti CD11b | BD | 550993 | Clone M1/70 |
| APC conjugated hamster anti mouse IgG1 anti CD11c | BD | 550261 | Clone HL3 |
| APC-Cy7 conjugated rat anti mouse IgG2a anti Ly6G | BD | 560600 | Clone 1A8 |
| Sterile Saline Solution | Laboratorio Farmaco Uruguayo, Uruguay | ||
| Tryptic Soy Agar | BD Difco, France | 236950 | |
| Defibrinated Sheep Blood | Biokey, Uruguay | ||
| Sterile Petri Dishes | Greiner | 633180 | |
| p10 Pipette | Gilson | F144802 | |
| p20 Pipette | Eppendorf | 3120000097 | |
| p200 Pipette | Gilson | F123601 | |
| p200 Pipette | Capp | C200 | |
| p200 Pipette | Eppendorf | 3120000054 | |
| p1000 Pipette | Eppendorf | 3120000062 | |
| Sterile Filter Tips p10 | Greiner | 771288 | |
| Sterile Filter Tips p200 | Greiner | 739288 | |
| Sterile Filter Tips p1000 | Greiner | 750288 | |
| Vortex | BIOSAN | V1-plus | |
| Stainless steel fine tip forceps | SIGMA | Z168785/Z168777 | Curved and straight |
| Dressing tissue forceps | SIGMA | F4392 | Length 8 inches |
| Micro-dissecting forceps | SIGMA | F4017 | Straight |
| Micro-dissecting forceps | SIGMA | F4142 | Curved |
| Mayo Scissors | SIGMA | Z265993 | |
| Scalpel | SAKIRA MEDICAL | ||
| Sterile Biopsy Punch Ø 3mm | Stiefel Laboratories Ltd. | 2079D | 5 mm diameter can also be used |
| Sterile 1.5 ml Tubes | Deltalab | 200400P | |
| Sterile 15 ml Tubes | Greiner | 188271 | |
| Sterile 50 ml Tubes | Greiner | 227261 | |
| Sterile serological pipettes 5 ml | Greiner | 606160 | |
| Sterile serological pipettes 10 ml | Greiner | 607160 | |
| Sterile serological pipettes 25 ml | Greiner | 760180 | |
| Biological safety cabinet, class II | Thermo Scientific | 1300 series, type A2 | |
| Micro-Isolator Rack | RAIR IsoSystem | 76144W | Super Mouse 1800 AllerZone |
| Refrigerated Microcentrifuge | Eppendorf | Legend Micro 21R | |
| Microcentrifuge | Heraeus | Biofuge-pico | |
| Centrifuge | Thermo Scientific | Sorval ST40R | |
| CO2 Incubator | Thermo Scientific | Model 3111 | |
| Sterile Thin-tip pasteur pipettes | Deltalab | D210022 | |
| Sterile pasteur pipettes | Deltalab | 200007 | |
| Sterile 24-well plate | Greiner | 662160 | |
| Trypan Blue Solution | Life Technologies | T10282 | |
| Automatic Cell Counter - Countess | Life Technologies | C10227 | |
| Countess Cell Counting Chamber Slides | Life Technologies | C10312 | |
| Flow Cytometry Tubes | BD | 343675 | |
| Flow Cytometer - FACS Canto-II | BD | ||
| Real Time PCR Instrument - Rotor Gene Q or ABI 7900 | Qiagen / Applied Biosystems | ||
| Trizol Reagent | Life Technologies | 15596-026 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| DNAse-I | Life Technologies | 18068-015 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| DNAse-I Buffer 10X | Life Technologies | 18068015 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| EDTA 25 mM | Life Technologies | 18068015 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| Ultra-Pure Water | Life Technologies | 10977 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| RNAse Out | Life Technologies | 100000840 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| Random Hexamer Primers | Life Technologies | N8080127 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| M-MLV-RT buffer | Life Technologies | 18057-018 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| M-MLV-RT enzime | Life Technologies | 28025-021 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| QuantiTect Syber Green PCR Kit | Qiagen | 204143 | Molecular Biology Grade |
| Specific primers | Life Technologies | Molecular Biology Grade |
References
- Pneumococcal vaccines WHO position paper--2012. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 14, 129-144 (2012).
- Pneumonia - Facts Sheet N°331. , WHO. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs331/en (2013).
- Appelbaum, P. C., et al. Carriage of antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae by children in eastern and central Europe-a multicenter study with use of standardized methods. Clin Infect Dis. 23, 712-717 (1996).
- Ramirez, J. A., Anzueto, A. R. Changing needs of community-acquired pneumonia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 66, 3-9 (2011).
- Cuburu, N., et al. Sublingual immunization induces broad-based systemic and mucosal immune responses in mice. Vaccine. 25, 8598-8610 (2007).
- Pedersen, G. K., et al. Evaluation of the sublingual route for administration of influenza H5N1 virosomes in combination with the bacterial second messenger c-di-GMP. PLoS One. 25, 1-12 (2011).
- Song, J. H., et al. Sublingual vaccination with influenza virus protects mice against lethal viral infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105, 1644-1649 (2008).
- Cogo, R., Ramponi, A., Scivoletto, G., Rippoli, R. Prophylaxis for acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis using an antibacterial sublingual vaccine obtained through mechanical lysis: a clinical and pharmacoeconomic study. Acta Biomed. 74, 76-87 (2003).
- Rosaschino, F., Cattaneo, L. Strategies for optimizing compliance of paediatric patients for seasonal antibacterial vaccination with sublingually administered Polyvalent Mechanical Bacterial Lysates (PMBL). Acta Biomed. 75, 171-178 (2004).
- Senna, G., Caminati, M., Canonica, G. W. Safety and tolerability of sublingual immunotherapy in clinical trials and real life. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 13, 656-662 (2013).
- Mascarell, L., et al. Oral dendritic cells mediate antigen-specific tolerance by stimulating TH1 and regulatory CD4+ T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 122, 603-609 (2008).
- Mascarell, L., et al. Mapping of the lingual immune system reveals the presence of both regulatory and effector CD4+ T cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 39, 1910-1919 (2009).
- Mascarell, L., et al. Oral macrophage-like cells play a key role in tolerance induction following sublingual immunotherapy of asthmatic mice. Mucosal Immunology. 4, 638-647 (2011).
- Hervouet, C., et al. Antigen-bearing dendritic cells from the sublingual mucosa recirculate to distant systemic lymphoid organs to prime mucosal CD8 T cells. Mucosal Immunology. 7, 280-291 (2014).
- Munoz, N., et al. Mucosal administration of flagellin protects mice from Streptococcus pneumoniae lung infection. Infect Immun. 78, 4226-4233 (2010).
- Hayashi, F., et al. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature. 410, 1099-1103 (2001).
- Lightfield, K. L., et al. Critical function for Naip5 in inflammasome activation by a conserved carboxy-terminal domain of flagellin. Nature Immunology. 9, 1171-1178 (2008).
- Lightfield, K. L., et al. Differential requirements for NAIP5 in activation of the NLRC4 inflammasome. Infect Immun. 79, 1606-1614 (2011).
- Honko, A. N., Mizel, S. B. Mucosal administration of flagellin induces innate immunity in the mouse lung. Infect Immun. 72, 6676-6679 (2004).
- Janot, L., et al. Radioresistant cells expressing TLR5 control the respiratory epithelium's innate immune responses to flagellin. Eur J Immunol. 39 (6), 1587-1596 (2009).
- Van Maele, L., et al. TLR5 signaling stimulates the innate production of IL-17 and IL-22 by CD3(neg)CD127+ immune cells in spleen and mucosa. J Immunol. 185, 1177-1185 (2010).
- Lee, S. J., et al. Neurologic adverse events following influenza A (H1N1) vaccinations in children. Pediatrics international: official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society. 54, 325-330 (2012).
- Lewis, D. J., et al. Transient facial nerve paralysis (Bell's palsy) following intranasal delivery of a genetically detoxified mutant of Escherichia coli heat labile toxin. PLoS One. 4, e6999(2009).
- Mutsch, M., et al. Use of the inactivated intranasal influenza vaccine and the risk of Bell's palsy in Switzerland. N Engl J Med. 350, 896-903 (2004).
- Kuo, C. H., Wang, W. L., Chu, Y. T., Lee, M. S., Hung, C. H. Sublingual immunotherapy in children: an updated review. Pediatr Neonatol. 50, 44-49 (2009).
- Nempont, C., Cavet, D., Rumbo, M., Bompard, C., Villeret, V., Sirard, J. C. Deletion of flagellin's hypervariable region abrogates antibody-mediated neutralization and systemic activation of TLR5-dependent immunity. J. Immunol. 181, 2036-2043 (2008).
- Pathogen Regulation Directorate, Public Health Agency of Canada . Streptococcus pneumoniae: Pathogen Safety Data Sheet - Infectious Substances. , Available from: http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/lab-bio/res/psds-ftss/streptococcus-pneumoniae-eng.php (2011).
- Marques, J. M., et al. Protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 1 acute infection shows a signature of Th17- and IFN-gamma-mediated immunity. Immunobiology. 217, 420-429 (2012).
- Stewart, C. C., Stewart, S. J., et al. Titering antibodies. Current Protocols in Cytometry. 4, Unit 4.1(2001).
- Kubista, M., et al. The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 27, 95-125 (2006).
- Pedersen, G., Cox, R. The mucosal vaccine quandary: intranasal vs. sublingual immunization against influenza. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 8, 689-693 (2012).
- Vitaliti, G., et al. Mucosal immunity and sublingual immunotherapy in respiratory disorders. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents. 26, S85-S93 (2012).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved