Consistent with the law of mass action, an equilibrium stressed by a change in concentration will shift to re-establish equilibrium without any change in the value of the equilibrium constant, K. When an equilibrium shifts in response to a temperature change, however, it is re-established with a different relative composition that exhibits a different value for the equilibrium constant.
To understand this phenomenon, consider the elementary reaction:
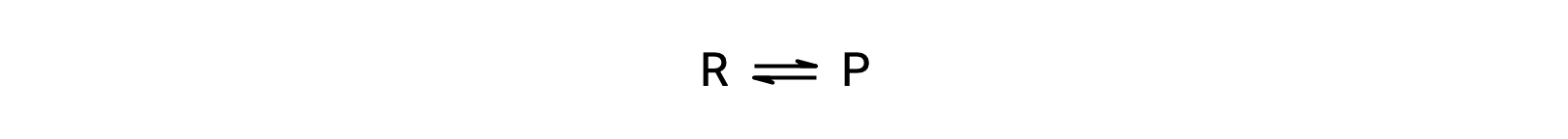
Since this is an elementary reaction, the rates laws for the forward and reverse may be derived directly from the balanced equation’s stoichiometry:
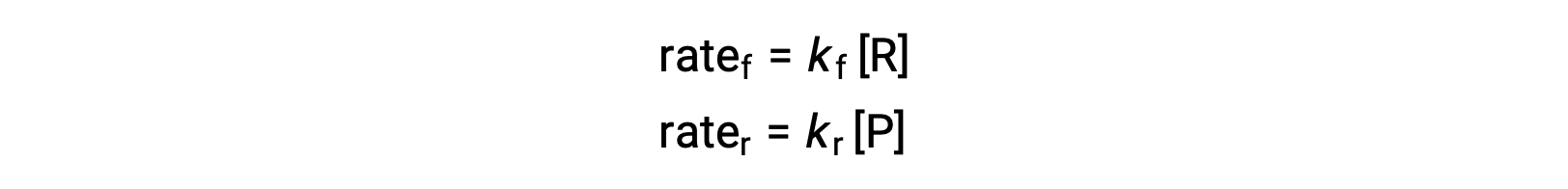
When the system is at equilibrium,
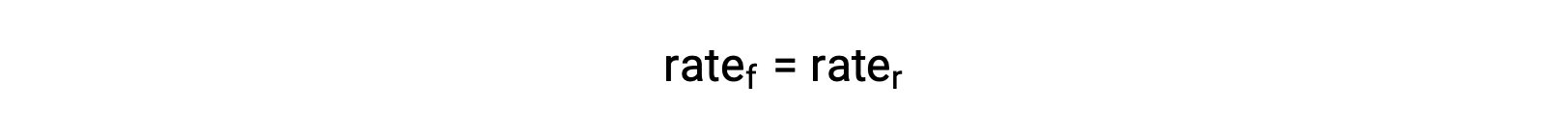
Substituting the rate laws into this equality and rearranging gives
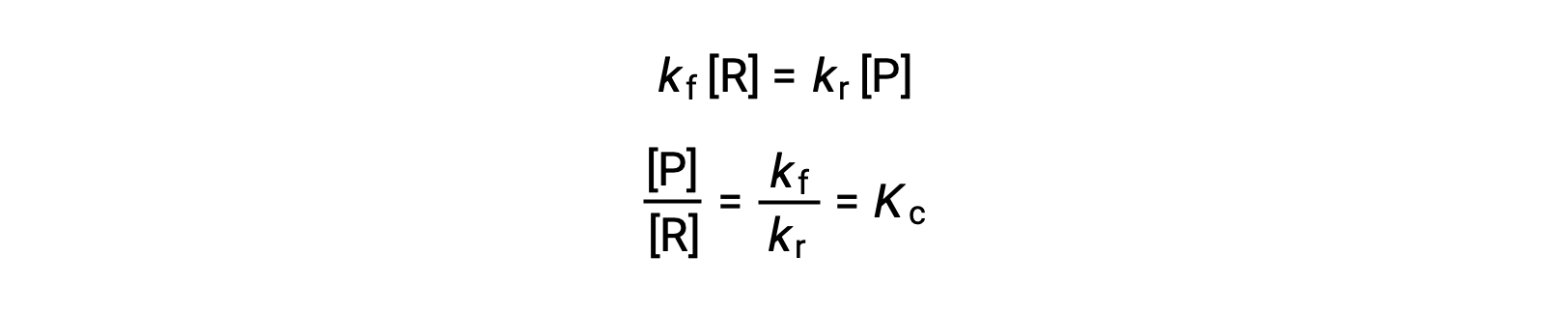
The equilibrium constant can be expressed as a mathematical function of the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions. Since the rate constants vary with temperature as described by the Arrhenius equation, it stands to reason that the equilibrium constant will likewise vary with temperature (assuming the rate constants are affected to different extents by the temperature change). For more complex reactions involving multistep reaction mechanisms, a similar but more complex mathematical relation exists between the equilibrium constant and the rate constants of the steps in the mechanism. Regardless of how complex the reaction may be, the temperature-dependence of its equilibrium constant persists.
Predicting the shift an equilibrium will experience in response to a change in temperature is most conveniently accomplished by considering the enthalpy change of the reaction. For example, the formation of ammonia by the Haber’s process is an exothermic (heat-producing) process:
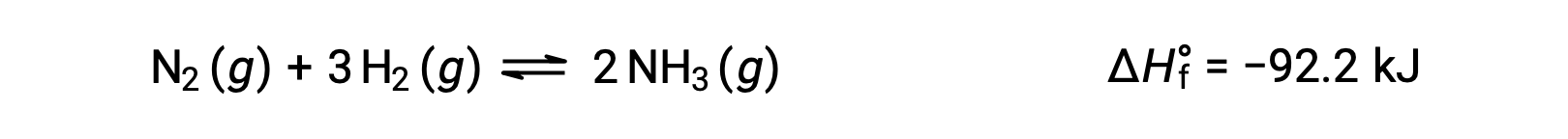
For purposes of applying Le Châtelier’s principle, heat, q, may be viewed as a product:
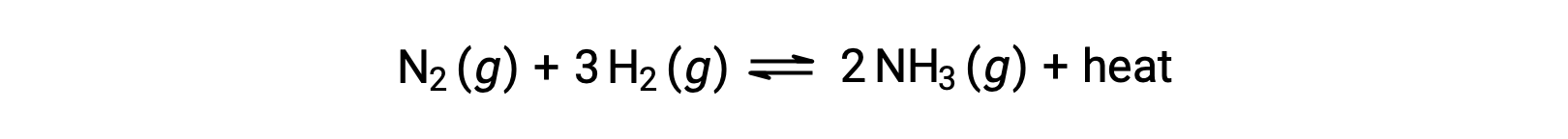
Raising the temperature of the system is akin to increasing the amount of a product, and so the equilibrium will shift to the left. Lowering the system temperature will likewise cause the equilibrium to shift right. For endothermic processes, heat is viewed as a reactant of the reaction and so the opposite temperature dependence is observed.
This text has been adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 13.3 Shifting Equilibria: Le Châtelier’s Principle.
Aus Kapitel 14:

Now Playing
14.9 : Le Chatelier's Principle: Changing Temperature
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
28.5K Ansichten

14.1 : Fließgleichgewicht
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
49.1K Ansichten

14.2 : Die Gleichgewichtskonstante
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
45.6K Ansichten

14.3 : Homogene Gleichgewichte für gasförmige Reaktionen
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
23.7K Ansichten

14.4 : Berechnung der Gleichgewichtskonstante
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
30.2K Ansichten

14.5 : Reaktionsquotient
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
47.4K Ansichten

14.6 : Berechnung von Gleichgewichtskonzentrationen
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
46.5K Ansichten

14.7 : Das Prinzip von Le Chatelier: Veränderte Konzentration
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
56.8K Ansichten

14.8 : Das Prinzip von Le Chatelier: Ändern des Volumens (Druck)
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
33.5K Ansichten

14.10 : Die kleine x Annahme
Chemisches Gleichgewicht
45.4K Ansichten
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten