Step growth polymerization involves bi or multifunctional monomers. Bifunctional monomers react to form linear step growth polymers, whereas multifunctional monomers react to form non-linear or branched polymers.
As the step-growth polymerization involves step-wise condensation of monomers, the molecular weight also builds up eventually. Consequently, high molecular weight polymers are obtained at the late stages of the polymerization, where 99% of monomers have been consumed.
The extent of the reaction can be obtained from the Carothers equation.
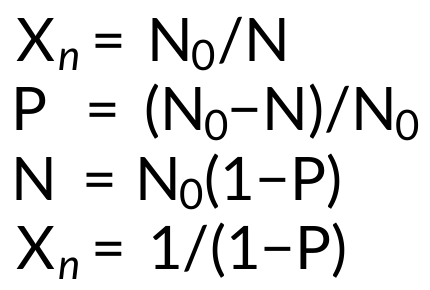
Here, Xn describes the average chain length, P describes the extent of the reaction, N0 is the number of molecules at the beginning of the polymerization, and N is the number of molecules left in the reaction after some time.
The equation above shows that in step-growth polymerization, a high monomer conversionis required to achieve a high degree of polymerization.
The polydispersity index(PDI) is a measure of the broadness of molecular weight distribution in a given polymer sample. PDI of a polymer is the ratio of the weight and number average of the molecular weight of the polymer. The PDI is unity if all the polymer molecules are of the same size.
In the case of step-growth polymers, the PDI is 2, indicating a broad molecular weight distribution.
Aus Kapitel 21:

Now Playing
21.16 : Molekülmasse von Stufenwachstumspolymeren
Synthetische Polymere
2.1K Ansichten

21.1 : Merkmale und Nomenklatur von Homopolymeren
Synthetische Polymere
2.9K Ansichten

21.2 : Merkmale und Nomenklatur von Copolymeren
Synthetische Polymere
2.4K Ansichten

21.3 : Polymere: Definition der Molekülmasse
Synthetische Polymere
2.7K Ansichten

21.4 : Polymere: Molmassenverteilung
Synthetische Polymere
3.1K Ansichten

21.5 : Klassifizierung von Polymeren: Architektur
Synthetische Polymere
2.6K Ansichten

21.6 : Klassifizierung von Polymeren: Kristallinität
Synthetische Polymere
2.7K Ansichten

21.7 : Klassifizierung von Polymeren: Stereospezifität
Synthetische Polymere
2.3K Ansichten

21.8 : Radikalische Kettenwachstumspolymerisation: Überblick
Synthetische Polymere
2.3K Ansichten

21.9 : Radikalische Kettenwachstumspolymerisation: Mechanismus
Synthetische Polymere
2.4K Ansichten

21.10 : Radikalische Kettenwachstumspolymerisation: Kettenverzweigung
Synthetische Polymere
1.9K Ansichten

21.11 : Anionische Kettenwachstumspolymerisation: Überblick
Synthetische Polymere
2.0K Ansichten

21.12 : Anionische Kettenwachstumspolymerisation: Mechanismus
Synthetische Polymere
2.0K Ansichten

21.13 : Kationische Kettenwachstumspolymerisation: Mechanismus
Synthetische Polymere
2.2K Ansichten

21.14 : Ziegler-Natta-Kettenwachstumspolymerisation: Überblick
Synthetische Polymere
3.2K Ansichten
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten