13.8 : Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Median of Single Population
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test for the median of a single population is a nonparametric test used to evaluate whether the median of a population differs from a specified value. Unlike parametric tests, it does not require data to follow a normal distribution, making it suitable for non-normal or small samples. The test begins by calculating the difference (d) between each observation and the hypothesized median. The absolute values of these differences are ranked in ascending order, with ties averaged. Each rank is then assigned the original sign of the corresponding d-value, creating a set of signed ranks.
The next step is to separately sum the positive and negative signed ranks. The test statistic is based on the smaller of these two sums (absolute value), which reflects the degree of symmetry around the hypothesized median. The sample size (n) is the number of non-zero d-values (differences that are not exactly zero). Based on n and the distribution of signed ranks, the test statistic is evaluated against critical values for a given significance level to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis that the sample median equals the hypothesized value. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is particularly useful for data that deviates from normality, as it accounts for both the magnitude and direction of differences, unlike the simpler sign test, which only considers direction
- If n is smaller than 30, the test statistic T is taken as the smallest of the two sums obtained;
- If n is higher than 30, the test statistic T is calculated using the formula
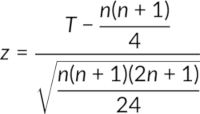
In both cases, the critical Z-value is obtained from its table for a particular significance level and sample size n. The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic, T, is lower than the critical value.
Du chapitre 13:

Now Playing
13.8 : Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Median of Single Population
Nonparametric Statistics
101 Vues

13.1 : Introduction to Nonparametric Statistics
Nonparametric Statistics
663 Vues

13.2 : Ranks
Nonparametric Statistics
226 Vues

13.3 : Introduction to the Sign Test
Nonparametric Statistics
690 Vues

13.4 : Sign Test for Matched Pairs
Nonparametric Statistics
102 Vues

13.5 : Sign Test for Nominal Data
Nonparametric Statistics
70 Vues

13.6 : Sign Test for Median of Single Population
Nonparametric Statistics
89 Vues

13.7 : Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Matched Pairs
Nonparametric Statistics
87 Vues

13.9 : Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
Nonparametric Statistics
151 Vues

13.10 : Bootstrapping
Nonparametric Statistics
583 Vues

13.11 : The Anderson-Darling Test
Nonparametric Statistics
665 Vues

13.12 : Spearman's Rank Correlation Test
Nonparametric Statistics
679 Vues

13.13 : Kendall's Tau Test
Nonparametric Statistics
590 Vues

13.14 : Kruskal-Wallis Test
Nonparametric Statistics
561 Vues

13.15 : Wald-Wolfowitz Runs Test I
Nonparametric Statistics
606 Vues
See More