Un abonnement à JoVE est nécessaire pour voir ce contenu. Connectez-vous ou commencez votre essai gratuit.
Method Article
Une expérience utilisant la spectroscopie fonctionnelle proche infrarouge et les mouvements de pointage multi-articulaires assistés par robot du membre inférieur
* Ces auteurs ont contribué à parts égales
Dans cet article
Résumé
On estime qu'1 personne sur 6 dans le monde aura un accident vasculaire cérébral au cours de sa vie, entraînant une invalidité à long terme, dont les mécanismes de rééducation sont encore mal connus. Cette étude propose un protocole pour évaluer l’activation cérébrale par spectroscopie fonctionnelle proche infrarouge (fNIRS) lors d’une séance de thérapie robotique des membres inférieurs.
Résumé
L’AVC touche environ 17 millions de personnes dans le monde chaque année et constitue l’une des principales causes d’invalidité à long terme. La thérapie robotique s’est révélée prometteuse pour aider les patients victimes d’un AVC à retrouver les fonctions motrices perdues. Une avenue potentielle pour mieux comprendre comment la récupération motrice se produit est d’étudier l’activation cérébrale pendant les mouvements ciblés par la thérapie chez les individus en bonne santé. La spectroscopie fonctionnelle proche infrarouge (fNIRS) est devenue une technique de neuroimagerie prometteuse pour examiner les fondements neuronaux de la fonction motrice. Cette étude visait à étudier les corrélats neuronaux fNIRS des mouvements complexes des membres inférieurs chez des sujets sains. Les participants ont été invités à effectuer des cycles de repos et de mouvement pendant 6 minutes à l’aide d’un dispositif robotique pour la rééducation motrice. La tâche nécessitait des mouvements coordonnés des articulations du genou et de la cheville pour pointer vers des cibles affichées sur un écran d’ordinateur. Deux conditions expérimentales avec différents niveaux d’assistance au mouvement fournies par le robot ont été explorées. Les résultats ont montré que le protocole fNIRS détectait efficacement les régions du cerveau associées au contrôle moteur pendant la tâche. Notamment, tous les sujets présentaient une plus grande activation dans la zone prémotrice controlatérale pendant la condition sans assistance par rapport à la condition assistée. En conclusion, la fNIRS semble être une approche intéressante pour détecter les changements de concentration d’oxyhémoglobine associés aux mouvements de pointage multiarticulaires du membre inférieur. Cette recherche pourrait contribuer à la compréhension des mécanismes de récupération motrice de l’AVC et pourrait ouvrir la voie à de meilleurs traitements de réadaptation pour les patients victimes d’un AVC. Cependant, des recherches supplémentaires sont nécessaires pour élucider pleinement le potentiel de la fNIRS dans l’étude de la fonction motrice et de ses applications en milieu clinique.
Introduction
Les données épidémiologiques indiquent qu’il y a ~17 millions de nouveaux cas d’AVC chaque année dans le monde, avec une augmentation de l’incidence dans les pays à revenu faible et intermédiaire1. Le nombre de nouveaux cas devrait atteindre 77 millions d’ici 20302. La déficience motrice due à un AVC affecte souvent la mobilité du patient et sa participation aux activités de la vie quotidienne, contribuant à une faible qualité de vie. La rééducation motrice traditionnelle comprend la thérapie manuelle, mais au cours des dernières décennies, des systèmes robotiques de rééducation ont été développés. Ces systèmes peuvent fournir une thérapie à haute intensité, dose, quantifiabilité, fiabilité, répétabilité et flexibilité3 et ont montré leur potentiel en tant que traitements de réadaptation efficaces pour les patients victimes d’AVC aigu et chronique 4,5,6. En plus de l’administration de la thérapie, les systèmes robotiques de réadaptation peuvent être utilisés comme outils d’évaluation car ils peuvent être équipés de capteurs capables de mesurer les données cinématiques/cinétiques des mouvements du patient 7,8. Pour la rééducation motrice des membres supérieurs, ces données se sont non seulement avérées utiles pour évaluer le niveau de récupération motrice du patient induit par la thérapie robotique et ont servi d’outil supplémentaire aux évaluations cliniques traditionnelles 9,10, mais elles ont également contribué à faire progresser la compréhension du processus de récupération motrice après un AVC11, 12 ainsi que le contrôle neuronal du mouvement et l’apprentissage moteur chez des sujets sains 3,13,14. En conséquence, ces résultats ont fourni une base pour améliorer les traitements de réadaptation15.
Au cours des deux dernières décennies, de nombreux dispositifs robotiques pour la neuroréhabilitation des membres inférieurs ont été proposés, allant des exosquelettes qui supportent le poids corporel du patient pendant la marche (par exemple, sur un tapis roulant, comme Lokomat16) aux systèmes robotiques stationnaires qui permettent au patient d’exercer la cheville, le genou ou le pied sans marcher (tels que le Rutgers Ankle17, le robot de rééducation de la cheville à haute performance18 et le robot de rééducation cheville/pied de l’Institut des sciences et technologies de Gwangju (GIST)19) ou des orthèses plantaires actives qui sont des exosquelettes actionnés portés par le patient pour marcher sur le sol ou sur un tapis roulant (comme l’orthèse de marche motorisée20 et le MIT Anklebot21). Voir 22,23,4 pour une revue sur les robots pour la rééducation des membres inférieurs.
Les résultats des études cliniques sur les dispositifs robotiques pour la rééducation des membres inférieurs chez les patients victimes d’un AVC ont été encourageants et ont montré que ces systèmes peuvent améliorer l’amplitude des mouvements des articulations, la force musculaire ou la démarche, selon le dispositif spécifique et le protocole clinique (voir 24,25 pour une revue sur l’efficacité des robots des membres inférieurs pour la rééducation). Bien qu’il ait été postulé que la thérapie assistée par robot favorise les changements neuroplastiques, qui se traduisent finalement par une amélioration des capacités motrices26, la façon dont le processus de récupération motrice après un AVC se produit exactement et quels protocoles d’entraînement robotique optimisent le processus de récupération des capacités motrices des membres inférieurs, restent pour la plupart floues. En fait, il existe un écart important et croissant entre le développement croissant des robots de réadaptation (que ce soit par des chercheurs universitaires ou des entités commerciales) et la compréhension limitée des mécanismes neurophysiologiques qui sous-tendent la récupération motrice4. Les mesures de la cinématique du mouvement ou des couples articulaires prises avec des capteurs intégrés ont contribué à décrire quantitativement les changements de comportement moteur qui se produisent lorsque les patients récupèrent les capacités motrices des membres inférieurs 27,28,29, comblant partiellement cette lacune. Cependant, les corrélats neuronaux sous-jacents à ces changements ont été moins étudiés. Cela est dû à plusieurs raisons.
L’imagerie fonctionnelle cérébrale prend du temps et est parfois difficile à réaliser dans le contexte des essais cliniques, qui nécessitent souvent de réduire au minimum la charge des patients afin de maximiser la probabilité que les patients adhèrent à l’étude. Cela est particulièrement vrai pour les personnes ayant subi un AVC, étant donné que la fatigue post-AVC et la faiblesse musculaire sont fréquemment observées30. De plus, les modalités d’imagerie basées sur les champs magnétiques, telles que l’imagerie par résonance magnétique fonctionnelle (IRMf), nécessitent que le patient et le matériel robotique soient sans danger pour les aimants.
Parmi les modalités d’imagerie non invasives, la spectroscopie fonctionnelle proche infrarouge (fNIRS) est une technique d’imagerie particulièrement adaptée à l’évaluation des zones d’activation cérébrale chez les sujets subissant une thérapie robotique. Comme pour l’IRMf, la fNIRS mesure l’oxygénation/désoxygénation du sang dans le cerveau. Cependant, contrairement à l’IRMf, la fNIRS est entièrement compatible avec le matériel robotique et elle est souvent portable, voire utilisable au chevet du patient. De plus, la fNIRS a un faible coût et une sensibilité moindre aux artefacts de mouvement 31,32,33.
Malgré ses avantages évidents et son utilisation généralisée dans de nombreux contextes cliniques depuis son introduction à la fin des années 7034, seules quelques études ont utilisé la fNIRS pour quantifier l’activation cérébrale associée aux mouvements des membres inférieurs et à la récupération motrice de l’AVC. Les études FNIRS visant à élucider les mécanismes du contrôle neuronal du mouvement et/ou les mécanismes ou l’évaluation de la récupération motrice après un AVC ont principalement étudié les mouvements d’une seule articulation (par exemple, la dorsiflexion, la flexion plantaire ou les mouvements d’extension du genou 35,36,37), la marche 38,39,40,41,42,43 ou le cyclisme44. Voir45 pour une critique. De même, les études fNIRS sur la thérapie assistée par robot pour le membre inférieur se sont principalement concentrées sur la rééducation de la marche assistée par robot ; voir46 pour une critique. Quelques études se sont concentrées sur l’utilisation de la fNIRS dans le cadre d’un système d’interface cerveau-ordinateur (BCI) pour dériver des signaux de contrôle pour des dispositifs robotiques47,48 ; bien que ce domaine de recherche repose également sur le traitement des signaux fNIRS, son objectif est différent et principalement axé sur le décodage des intentions des patients (par exemple, les patients souffrant de handicaps moteurs sévères).
L’étude pilote présentée ici fait partie d’un effort initial visant à étudier les effets d’un système robotique pour la rééducation des membres inférieurs. Le robot peut offrir une rééducation ciblée des membres inférieurs qui implique un entraînement aux mouvements multiarticulaires quotidiens ainsi qu’une thérapie aux articulations uniques (par exemple, le genou ou la cheville) du membre inférieur (c’est-à-dire mettre en œuvre un programme de réadaptation ascendant).
L’étude visait à étudier la faisabilité d’un protocole expérimental nécessitant l’acquisition de données fNIRS lors de l’exécution de mouvements de pointage multi-articulaires des membres inférieurs. La durée de la période d’acquisition des données dans cette étude, qui a été limitée à 6 minutes, est plus courte que les protocoles fNIRS typiques. Il s’agissait d’un choix délibéré fait dans le but d’améliorer l’aspect pratique et l’applicabilité clinique de cette recherche, en particulier chez les patients à mobilité ou force limitées. L’identification des corrélats fNIRS de ces mouvements multi-articulaires complexes et la compréhension de la façon dont l’activation cérébrale était modulée par l’assistance robotique étaient également des points d’intérêt. À cette fin, deux sessions d’expérimentations ont été menées avec les mêmes participants : l’une sans assistance robotique et l’autre avec assistance robotisée. Enfin, il est important de noter que cette étude s’est concentrée sur des sujets sains afin d’établir une base pour les recherches futures en termes d’enregistrement de la faisabilité du protocole et d’évaluation de l’activation cérébrale lors des mouvements ciblés par la thérapie robotique.
Appareil
Un robot portable conçu pour assurer la rééducation des membres inférieurs (voir Figure 1) a été utilisé pour mener nos expériences. Le robot dispose d’un espace de travail accessible en 3D et est compact et léger, pesant environ 35 lb, ce qui le rend facile à transporter et à installer.

Figure 1 : Dispositif expérimental. (A) Le système robotique (installé au sol) conçu pour le membre inférieur. Un volontaire est montré en train d’utiliser l’interface avec son pied droit. (B) Structure de support pour le pied du sujet qui permet la fixation au système robotique. (C) Une capture d’écran du jeu Picnic. L’objectif du jeu est de déplacer le pied (chaussure verte et blanche) vers la cible (cercle jaune). Veuillez cliquer ici pour voir une version agrandie de cette figure.
Le système robotique est conçu pour aider un patient à effectuer des mouvements des membres inférieurs similaires à ceux effectués dans les tâches quotidiennes, telles que pointer ou donner des coups de pied. Il utilise des jeux interactifs de réalité virtuelle, qui sont affichés sur un écran d’ordinateur ou un écran de télévision placé devant le dispositif robotique (voir Figure 1). L’effecteur final du robot est fixé au membre inférieur du patient (par exemple, la cheville) et sa position est mappée à la position d’un curseur sur l’écran. Un jeu typique montre les cibles de mouvement du patient (par exemple, l’objet à pointer ou l’endroit où frapper le ballon).
Pour accomplir la tâche de mouvement, le robot peut aider le patient avec un niveau d’assistance qui peut aller d’une assistance complète à aucune. Le niveau d’assistance robotique est choisi au début de chaque séance de rééducation en fonction du niveau de déficience motrice du patient. Les mouvements effectués par le sujet sont utilisés par le jeu pour noter la performance du patient et lui fournir un retour sur sa performance (par exemple, ROM, nombre de mouvements et niveau d’assistance robotique). Les jeux sont conçus pour être interactifs et divertissants afin de maintenir l’intérêt et l’attention des patients. Dans cette étude, les participants ont joué au « jeu de pique- », dans lequel le joueur devait empêcher les insectes d’atteindre la serviette et de voler la nourriture (voir Figure 1, panneau inférieur, pour une capture d’écran).
L’acquisition des données a été effectuée avec un système d’acquisition fNIRS portable avec deux optodes à ondes continues différentes (760 nm et 850 nm), 8 sources LED à double pointe et 8 détecteurs actifs à double pointe. Les signaux ont été acquis à l’aide d’une fréquence d’échantillonnage de 10,17 Hz. Un ordinateur portable a été utilisé pour l’optimisation de l’étalonnage et l’enregistrement du signal à l’aide d’un réseau Wi-Fi créé par le système fNIRS.
Un capuchon a été utilisé pour maintenir les optodes aux endroits prédéterminés. Les sources et les détecteurs ont été placés selon le système EEG international 10-10 dans une distribution spatiale en grille. Chaque canal fNIRS a été défini par une paire source-détecteur avec des distances inter-optodes d’environ 30 mm. Les optodes ont été placés sur les zones supplémentaires du moteur, du prémoteur et du moteur aux endroits indiqués à la figure 2. Le nombre total de canaux était de 28, dont 8 étaient des canaux à courte distance couplés à chaque source à l’aide d’un adaptateur à fibre optique à un seul détecteur. Compte tenu de la configuration de multiplexage du matériel, il est possible d’acquérir des informations à courte distance à partir de toutes les sources en utilisant un seul détecteur.
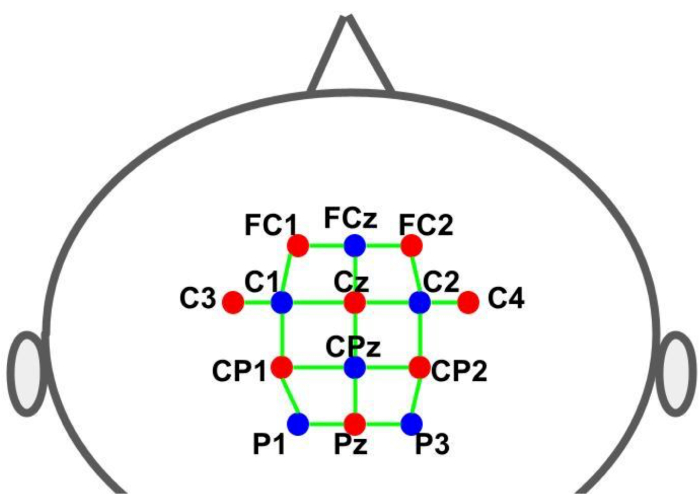
Figure 2 : Disposition du montage à l’aide du système EEG 10-10. Les lettres et les chiffres indiquent l’emplacement de la source/du détecteur. Les points rouges et bleus représentent respectivement la source et les optodes du détecteur. Les lignes vertes représentent les canaux fNIRS qui sont constitués de paires source et détecteur. Veuillez cliquer ici pour voir une version agrandie de cette figure.
Conception expérimentale
L’expérience a été menée dans deux conditions expérimentales distinctes, différant par le niveau d’assistance fourni par le robot pour les mouvements du sujet. Dans la première condition, le robot était programmé pour ne pas fournir d’assistance aux mouvements du sujet, tandis que dans la seconde condition, le robot contrôlait les mouvements des pieds et des jambes du sujet (mouvement assisté par robot).
Chaque expérience a suivi un paradigme de conception de blocs impliquant des cycles alternés d’une tâche motrice (jouer le jeu - 30 s) et de repos (30 s), comme illustré à la figure 3. Le début et la fin de chaque phase (jeu/jeu ou repos) étaient signalés visuellement au sujet par l’écran de l’ordinateur. Pendant la phase de repos, un message indiquant une pause s’est affiché. Chaque cycle (jeu/jeu + repos) a duré 60 s et a été répété six fois, ce qui a donné une durée totale de 360 s (6 min).
Les participants ont joué au « jeu du pique- », dont l’objectif était d’empêcher les insectes d’atteindre la serviette et de voler de la nourriture. Ce jeu impliquait une séquence de mouvements des membres inférieurs, partant d’une cible d’origine désignée (position initiale) et s’étendant vers l’une des trois cibles extérieures avant de revenir à la cible d’origine. Sur l’écran, les cibles extérieures étaient visuellement représentées sous forme d’insectes animés en mouvement, que les participants devaient atteindre et sur lesquels marcher. Il y avait trois cibles extérieures, chacune présentée au hasard un nombre égal de fois, ainsi qu’une cible commune pour chaque mouvement. La distance que le pied devait parcourir entre la cible d’origine et la position des cibles extérieures formait un arc mesurant environ 26 cm. La tâche motrice nécessitait l’exécution de mouvements multi-articulaires, exigeant une coordination entre les mouvements de flexion/extension du genou, de flexion plantaire et de dorsiflexion.
Les enregistrements de données fNIRS ont été synchronisés avec les stimuli visuels présentés par le jeu au sujet par le biais d’une impulsion transistor-transistor-logique (TTL) générée par le robot. Des impulsions ont été générées au début de chaque phase (jeu/jeu et repos). Ainsi, tout le contrôle du timing a été effectué par le jeu, qui a fourni des repères visuels (cibles) au participant pour commencer chaque mouvement, a envoyé des signaux TTL au système fNIRS pour marquer les enregistrements de l’activité cérébrale et, si l’expérience l’exigeait, a envoyé des signaux au système de contrôle du robot pour initier l’assistance au mouvement.
Protocole
Cette étude a été approuvée par le comité d’éthique local de l’UNICEP (Centro Universitario Paulista). Tous les participants ont donné leur consentement éclairé conformément à toutes les directives institutionnelles et aux normes fédérales concernant la recherche scientifique impliquant des humains. Ils n’ont reçu aucune compensation financière, comme l’exige la réglementation fédérale brésilienne.
1. Système fNIRS
- Préparez le capuchon à l’aide de 16 optodes : 8 sources lumineuses (760 nm et 850 nm) et 8 détecteurs de lumière (voir Figure 2 ; emplacement des sources : FC1, FC2, C3, Cz, C4, CP1, CP2 et Pz ; emplacement des détecteurs (FCz, C1, C2, CPz, P1 et P3). Fixez le huitième détecteur à l’adaptateur courte distance, qui est connecté à chacun des optodes sources.
- Ouvrez le logiciel d’acquisition fNIRS et chargez le montage avec le placement de chaque optode.
- Réglez la fréquence d’échantillonnage temporelle du signal fNIRS à 10,17 Hz.
2. Participants
- Expliquez brièvement la pertinence de la recherche et le protocole expérimental au participant.
- Si le participant accepte de faire du bénévolat, assurez-vous qu’il donne son consentement éclairé en suivant toutes les directives institutionnelles et les normes fédérales concernant la recherche scientifique impliquant des humains.
- Demandez au volontaire de s’asseoir sur un fauteuil devant le robot, positionné à environ 150 cm de l’écran de l’ordinateur.
- Après avoir retiré les chaussures, attachez confortablement le pied du participant au bras du robot avec des sangles velcro (voir Figure 1, panneau supérieur gauche).
- Placez le capuchon fNIRS avec les optodes dans la tête du participant et fixez-le solidement avec la fermeture auto-agrippante sous le menton.
- Placez le capuchon sur le capuchon d’optique pour réduire les interférences de la lumière ambiante.
3. Acquisition de données
- Demandez à chaque participant de ne pas faire de mouvements brusques de la tête pour minimiser le risque d’artefacts de mouvement.
- Calibrez le système fNIRS pour une qualité de signal optimale.
- Certifiez que tous les canaux sont de bonne qualité, comme le montre l’interface. Sinon, essayez d’enlever les cheveux entre le cuir chevelu et l’embout optode.
- Expliquez au participant comment jouer au jeu en déplaçant le pied attaché au robot pour atteindre les cibles indiquées à l’écran.
- Expliquez aux participants qu’il y aura deux conditions : sans et avec assistance robotique.
4. Système robotique
- Mettez le système sous tension en connectant le moniteur et le robot à la source du réseau électrique. Une fois le système d’exploitation initialisé, la première interface de jeu apparaît.
- Positionnez le bras robotique à l’emplacement standard et attendez de recevoir le message de retour d’information du bras robotique correctement positionné .
- Entrez des données descriptives sur le participant et l’expérimentateur dans le système pour vous connecter à l’interface de jeu du robot.
- Dans l’interface de sélection du jeu, configurez la durée de la session sur 6 min avec des intervalles de repos de 30 s.
- Sélectionnez la jambe appropriée (droite ou gauche) à utiliser par le participant.
- Sélectionnez le jeu de pique- et cliquez sur Aller pour jouer au jeu.
5. Analyse des données
- Convertir les signaux bruts en états hémodynamiques (oxyhémoglobine (HbO) et désoxyhémoglobine (HbR)) en utilisant l’équation de Beer-Lambertmodifiée 49.
- Créez des cartes d’activation individuelles à l’aide du modèle linéaire général (GLM) avec une estimation robuste et une estimation d’autocorrélation, qui est moins affectée par les artefacts de mouvement50. Utilisez le plan expérimental (repos = 0 ; jeu/jeu = 1) alambiqué par la fonction de réponse hémodynamique canonique (HRF) comme variable indépendante et le signal HbO ou HbR observé comme variable dépendante.
- Pour chaque canal, extrayez le coefficient bêta (qui reflète la force d’activation du canal) pendant le jeu/le jeu par rapport au reste.
- Fusionnez les canaux dans trois régions d’intérêt (ROI) et faites la moyenne des coefficients d’activation (bêta GLM) sur les canaux ROI. Définissez les ROI comme suit (voir Figure 2) : (1) zone prémotrice pour l’hémisphère gauche (canaux [FC1-FCz, C1-FC1, C1-Cz, C3-C1]) ; (2) aire somatomotrice de l’hémisphère gauche (canaux [C3-CP1, CP1-P1, CP1-CPz, P1-Pz]) ; et (3) surface motrice supplémentaire (SMA) (canaux [Cz-FCz, CPz-Cz]).
REMARQUE : D’après la littérature antérieure sur les tâches motrices similaires à celle étudiée ici 51,52,53 et étant donné que tous les participants ont exécuté la tâche motrice avec leur jambe droite, on a émis l’hypothèse que les régions prémotrice et somatomotrice gauche (controlatérale), ainsi que l’AS, présenteraient une activation pendant la performance de jeu/jeu dans les deux conditions, avec une activation plus forte dans la condition non assistée. - Appliquez le test de Wilcoxon non paramétrique à ces bêtas. Définissez l’erreur de type I à 5 % (analyse unilatérale).
Résultats
Les six sujets ont terminé les deux expériences. Dans la condition de non-assistance, une moyenne de 76,67 essais (std. 10,73) a été complétée par chaque sujet (notez que pour chaque sujet, le nombre d’essais dépendait du nombre d’atteintes réussies puisqu’une nouvelle cible n’était indiquée que si la précédente était atteinte). Dans la condition d’assistance, où le mouvement du sujet était entièrement aidé par le robot, tous les sujets ont effectué 70 essais. Les données fNIRS ont été enre...
Discussion
Dans cette étude de preuve de concept, la faisabilité de faire des inférences sur la cartographie de l’activation cérébrale à l’aide de données fNIRS de sujets sains pendant qu’ils s’entraînaient avec différents types de mouvements à l’aide d’un robot pour la rééducation des membres inférieurs a été étudiée. Les sessions d’enregistrement fNIRS typiques chez les adultes durent plus de 6 min54. Cependant, pour rendre les enregistrements réalisables dans le contexte d?...
Déclarations de divulgation
AMM est propriétaire de la société Vivax Ltda, qui a développé la machine de rééducation assistée Vivax (ARM). LD est un dirigeant de Highland Instruments, une société de dispositifs médicaux. Elle a des brevets en instance ou délivrés, personnellement ou en tant que dirigeant de l’entreprise, liés à l’imagerie, à la stimulation cérébrale, au diagnostic, à la modélisation et à la simulation. Les autres auteurs ne déclarent aucun conflit d’intérêts.
Remerciements
Les opinions, hypothèses, conclusions et recommandations de cette étude sont celles des auteurs et ne représentent pas nécessairement les opinions de l’organisme de financement. Le JRS est reconnaissant à la Fondation de recherche de São Paulo (FAPESP, numéros de subvention 2021/05332-8, 2018/04654-9, 2018/21934-5 et 2023/02538-0) et à Jackson Cionek pour leur soutien technologique. AMM et Vivax Ltda remercient la FAPESP (Fondation de recherche de São Paulo) et la FINEP (Agence brésilienne pour l’innovation). Ce projet a été financé par des subventions de la FAPESP (numéro de subvention 2018/09559-4) et du FINEP (numéro de subvention 2019/09933-6).
matériels
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 32 inch Smart TV | Samsung | N/A | TV connected to robot via HDMI cable |
| 8-detector silicon photodiode (SiPD) optodes for optical detection with dual tip | NIRx Medical Technologies (Glen Head, NY, USA) | https://nirx.net/nirsport | |
| 8-source optodes bundle for optical illumination with dual tip | NIRx Medical Technologies (Glen Head, NY, USA) | https://nirx.net/nirsport | |
| Aurora acquisition software | NIRx Medical Technologies (Glen Head, NY, USA) | https://nirx.net/nirsport | |
| Laptop Precision XPS 13 | Dell Technologies (Round Rock, TX, USA) | ||
| nirsLAB fNIRS Analysis software | NIRx Medical Technologies (Glen Head, NY, USA) | https://nirx.net/nirsport | |
| NIRSports2 fNIRS acquisition system | NIRx Medical Technologies (Glen Head, NY, USA) | https://nirx.net/nirsport | It has two different continuous wave optics (760 and 850 nm), 8 dual-ended LED sources and 8 dual-ended active detectors. |
| R | R-project.org (open source software) | https://www.r-project.org/ | |
| Standard cut cap, black color for up to 128 holders. | Easycap GmbH (Wörthsee, Germany) | https://www.easycap.de/ | |
| Vivax Assistive Rehabilitation Machine (ARM) | Vivax Ltda (São Paulo, Brazil) | https://vivaxbr.com/home/ | It is a portable robot designed to deliver lower limb rehabilitation. It has a 3D reachable workspace and is compact and light, weighing about 35 lb., which makes it easy to transport and to install. |
Références
- GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet. Neurology. 18 (5), 439-458 (2019).
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet. Neurology. 20 (10), 795-820 (2021).
- Huang, V. S., Krakauer, J. W. Robotic neurorehabilitation: a computational motor learning perspective. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation. 6, 5 (2009).
- Hobbs, B., Artemiadis, P. A Review of Robot-Assisted Lower-Limb Stroke Therapy: Unexplored Paths and Future Directions in Gait Rehabilitation. Frontiers in neurorobotics. 14, 19 (2020).
- Bertani, R., Melegari, C., De Cola, M. C., Bramanti, A., Bramanti, P., Calabrò, R. S. Effects of robot-assisted upper limb rehabilitation in stroke patients: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Neurological Sciences. 38 (9), 1561-1569 (2017).
- Warutkar, V., Dadgal, R., Mangulkar, U. R. Use of robotics in gait rehabilitation following stroke: A review. Cureus. 14 (11), e31075 (2022).
- Dipietro, L., et al. Changing motor synergies in chronic stroke. Journal of Neurophysiology. 98 (2), 757-768 (2007).
- Dipietro, L., et al. Learning, not adaptation, characterizes stroke motor recovery: evidence from kinematic changes induced by robot-assisted therapy in trained and untrained task in the same workspace. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 20 (1), 48-57 (2012).
- Bosecker, C., Dipietro, L., Volpe, B., Krebs, H. I. Kinematic robot-based evaluation scales and clinical counterparts to measure upper limb motor performance in patients with chronic stroke. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 24 (1), 62-69 (2010).
- Krebs, H. I., et al. Robotic measurement of arm movements after stroke establishes biomarkers of motor recovery. Stroke. 45 (1), 200-204 (2014).
- Volpe, B. T., et al. Robotic devices as therapeutic and diagnostic tools for stroke recovery. Archives of Neurology. 66 (9), 1086-1090 (2009).
- Hogan, N., et al. Motions or muscles? Some behavioral factors underlying robotic assistance of motor recovery. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 43 (5), 605-618 (2006).
- Shadmehr, R., Wise, S. P. . The Computational Neurobiology of Reaching and Pointing: A Foundation for Motor Learning. , (2005).
- Dipietro, L., Poizner, H., Krebs, H. I. Spatiotemporal dynamics of online motor correction processing revealed by high-density electroencephalography. J Cogn Neurosci. 26 (9), 1966-1980 (2014).
- Krebs, H., et al. Rehabilitation robotics: Performance-based progressive robot-assisted therapy. Autonomous Robots. 15, 7-20 (2003).
- Colombo, G., Joerg, M., Schreier, R., Dietz, V. Treadmill training of paraplegic patients using a robotic orthosis. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 37 (6), 693-700 (2000).
- Girone, M., et al. A Stewart platform-based system for ankle telerehabilitation. Autonomous Robots. 10, 203-212 (2001).
- Saglia, J. A., Tsagarakis, N. G., Dai, J. S., Caldwell, D. G. A high-performance redundantly actuated parallel mechanism for ankle rehabilitation. The International Journal of Robotics Research. 28 (9), 1216-1227 (2009).
- Yoon, J., Ryu, J. A novel reconfigurable ankle/foot rehabilitation robot. , 2290-2295 (2005).
- Ruthenberg, B. J., Wasylewski, N. A., Beard, J. E. An experimental device for investigating the force and power requirements of a powered gait orthosis. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 34 (2), 203-213 (1997).
- Forrester, L. W., et al. Clinical application of a modular ankle robot for stroke rehabilitation. NeuroRehabilitation. 33 (1), 85-97 (2013).
- Díaz, I., Gil, J. J., Sánchez, E. Lower-limb robotic rehabilitation: Literature review and challenges. Journal of Robotics. 2011, 759764 (2011).
- Zhang, X., Yue, Z., Wang, J. Robotics in lower-limb rehabilitation after stroke. Behavioural Neurology. 2017, 3731802 (2017).
- Zhang, M., Davies, T. C., Xie, S. Effectiveness of robot-assisted therapy on ankle rehabilitation - a systematic review. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation. 10, 30 (2013).
- Lo, K., Stephenson, M., Lockwood, C. Effectiveness of robotic assisted rehabilitation for mobility and functional ability in adult stroke patients: a systematic review protocol. JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports. 15 (1), 39-48 (2017).
- Belda-Lois, J. M., et al. Rehabilitation of gait after stroke: a review towards a top-down approach. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation. 8, 66 (2011).
- Bortole, M., et al. The H2 robotic exoskeleton for gait rehabilitation after stroke: early findings from a clinical study. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation. 12, 54 (2015).
- Banala, S. K., Kim, S. H., Agrawal, S. K., Scholz, J. P. Robot assisted gait training with active leg exoskeleton (ALEX). IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 17 (1), 2-8 (2009).
- Bartenbach, V., Wyss, D., Seuret, D., Riener, R. A lower limb exoskeleton research platform to investigate human-robot interaction. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR). 2015, 600-605 (2015).
- Hinkle, J. L., et al. Poststroke fatigue: Emerging evidence and approaches to management: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American heart association. Stroke. 48 (7), e159-e170 (2017).
- Balardin, J. B., Zimeo Morais, G. A., Furucho, R. A., Trambaiolli, L. R., Sato, J. R. Impact of communicative head movements on the quality of functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals: negligible effects for affirmative and negative gestures and consistent artifacts related to raising eyebrows. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 22 (4), 4601 (2017).
- Nazeer, H., Naseer, N., Mehboob, A., Khan, M. J., Khan, R. A., Khan, U. S., Ayaz, Y. Enhancing classification performance of fNIRS-BCI by identifying cortically active channels using the z-score method. Sensors. 20 (23), 6995 (2020).
- Ayaz, H., et al. Optical imaging and spectroscopy for the study of the human brain: status report. Neurophotonics. 9, S24001 (2022).
- Chen, W. L., et al. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy and its clinical application in the field of neuroscience: Advances and future directions. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 14, 724 (2020).
- Yamamoto, K., Miyata, T., Onozuka, A., Koyama, H., Ohtsu, H., Nagawa, H. Plantar flexion as an alternative to treadmill exercise for evaluating patients with intermittent claudication. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 33 (3), 325-329 (2007).
- Formenti, D., et al. Effects of knee extension with different speeds of movement on muscle and cerebral oxygenation. PeerJ. 6, 5704 (2018).
- Miyai, I., et al. Cortical mapping of gait in humans: a near-infrared spectroscopic topography study. NeuroImage. 14 (5), 1186-1192 (2001).
- Miyai, I., et al. Premotor cortex is involved in restoration of gait in stroke. Annals of Neurology. 52 (2), 188-194 (2002).
- Mihara, M., et al. Sustained prefrontal activation during ataxic gait: a compensatory mechanism for ataxic stroke?. NeuroImage. 37 (4), 1338-1345 (2007).
- Rea, M., et al. Lower limb movement preparation in chronic stroke: A pilot study toward an fNIRS-BCI for gait rehabilitation. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 28 (6), 564-575 (2014).
- Holtzer, R., Verghese, J., Allali, G., Izzetoglu, M., Wang, C., Mahoney, J. R. Neurological gait abnormalities moderate the functional brain signature of the posture first hypothesis. Brain Topography. 29 (2), 334-343 (2016).
- Kim, H. Y., Yang, S. P., Park, G. L., Kim, E. J., You, J. S. Best facilitated cortical activation during different stepping, treadmill, and robot-assisted walking training paradigms and speeds: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy neuroimaging study. NeuroRehabilitation. 38 (2), 171-178 (2016).
- Khan, H., Nazeer, H., Engell, H., Naseer, N., Korostynska, O., Mirtaheri, P. Prefrontal cortex activation measured during different footwear and ground conditions using fNIRS-A case study. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Mechatronics Systems (AIMS). , 1-6 (2021).
- Lin, P. Y., Chen, J. J., Lin, S. I. The cortical control of cycling exercise in stroke patients: an fNIRS study). Human Brain Mapping. 34 (10), 2381-2390 (2013).
- Yang, M., Yang, Z., Yuan, T., Feng, W., Wang, P. A systemic review of functional near-infrared spectroscopy for stroke: Current application and future directions. Frontiers in Neurology. 10, 58 (2019).
- Berger, A., Horst, F., Müller, S., Steinberg, F., Doppelmayr, M. Current state and future prospects of EEG and fNIRS in robot-assisted gait rehabilitation: A brief review. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 13, 172 (2019).
- Khan, R. A., Naseer, N., Qureshi, N. K., et al. fNIRS-based Neurorobotic Interface for gait rehabilitation. J NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 15 (1), 7 (2018).
- Khan, H., Naseer, N., Yazidi, A., Eide, P. K., Hassan, H. W., Mirtaheri, P. Analysis of Human Gait Using Hybrid EEG-fNIRS-Based BCI System: A Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 14, (2020).
- Delpy, D. T., Cope, M. Quantification in tissue near-infrared spectroscopy. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 352 (1354), 649-659 (1997).
- Huppert, T. J. Commentary on the statistical properties of noise and its implication on general linear models in functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Neurophotonics. 3, 010401 (2016).
- Alexandre, F., Heraud, N., Oliver, N., Varray, A. Cortical implication in lower voluntary muscle force production in non-hypoxemic COPD patients. PLoS One. 9 (6), 100961 (2014).
- Yoon, T., Vanden Noven, M. L., Nielson, K. A., Hunter, S. K. Brain areas associated with force steadiness and intensity during isometric ankle dorsiflexion in men and women. Experimental Brain Research. 232 (10), 3133-3145 (2014).
- Ciccarelli, O., et al. Identifying brain regions for integrative sensorimotor processing with ankle movements. Experimental Brain Research. 166 (1), 31-42 (2005).
- Udina, C., et al. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy to study cerebral hemodynamics in older adults during cognitive and motor tasks: A review. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 11, 367 (2020).
- Thickbroom, G. W., Phillips, B. A., Morris, I., Byrnes, M. L., Mastaglia, F. L. Isometric force-related activity in sensorimotor cortex measured with functional MRI. Experimental Brain Research. 121 (1), 59-64 (1998).
- Derosière, G., Alexandre, F., Bourdillon, N., Mandrick, K., Ward, T. E., Perrey, S. Similar scaling of contralateral and ipsilateral cortical responses during graded unimanual force generation. NeuroImage. 85 (1), 471-477 (2014).
- Shi, P., Li, A., Yu, H. Response of the cerebral cortex to resistance and non-resistance exercise under different trajectories: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 15, 685920 (2021).
- Dettmers, C., et al. Relation between cerebral activity and force in the motor areas of the human brain. Journal of Neurophysiology. 74 (2), 802-815 (1995).
- Keisker, B., Hepp-Reymond, M. C., Blickenstorfer, A., Kollias, S. S. Differential representation of dynamic and static power grip force in the sensorimotor network. The European Journal of Neuroscience. 31 (8), 1483-1491 (2010).
- Harada, T., Miyai, I., Suzuki, M., Kubota, K. Gait capacity affects cortical activation patterns related to speed control in the elderly. Experimental Brain Research. 193 (3), 445-454 (2009).
- Saleh, S., et al. The role of premotor areas in dual tasking in healthy controls and persons with multiple sclerosis: An fNIRS imaging study. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 12, 296 (2018).
- Bonnal, J., et al. Relation between cortical activation and effort during robot-mediated walking in healthy people: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy neuroimaging study (fNIRS). Sensors. 22 (15), 5542 (2022).
- Shibuya, K., Sadamoto, T., Sato, K., Moriyama, M., Iwadate, M. Quantification of delayed oxygenation in ipsilateral primary motor cortex compared with contralateral side during a unimanual dominant-hand motor task using near-infrared spectroscopy. Brain Research. 1210, 142-147 (2008).
- Dai, T. H., Liu, J. Z., Sahgal, V., Brown, R. W., Yue, G. W. Relationship between muscle output and functional MRI-measured brain activation. Experimental brain research. 140 (3), 290-300 (2001).
- Cabibel, V., Hordacre, B., Perrey, S. Implication of the ipsilateral motor network in unilateral voluntary muscle contraction: the cross-activation phenomenon. Journal of Neurophysiology. 123 (5), 2090-2098 (2020).
- Akselrod, M., Martuzzi, R., Serino, A., vander Zwaag, W., Gassert, R., Blanke, O. Anatomical and functional properties of the foot and leg representation in areas 3b, 1 and 2 of primary somatosensory cortex in humans: A 7T fMRI study. NeuroImage. 159, 473-487 (2017).
- Brigadoi, S., Cooper, R. J. How short is short? Optimum source-detector distance for short-separation channels in functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Neurophotonics. 2 (2), 025005 (2015).
- Funahashi, S. Prefrontal contribution to decision-making under free-choice conditions. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 11, 431 (2017).
- Simon, S. R., Meunier, M., Piettre, L., Berardi, A. M., Segebarth, C. M., Boussaoud, D. Spatial attention and memory versus motor preparation: premotor cortex involvement as revealed by fMRI. Journal of Neurophysiology. 88 (4), 2047-2057 (2002).
- Desmurget, M., Sirigu, A. A parietal-premotor network for movement intention and motor awareness. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 13 (10), 411-419 (2009).
- Nachev, P., Kennard, C., Husain, M. Functional role of the supplementary and pre-supplementary motor areas. Nature reviews. Neuroscience. 9 (11), 856-869 (2008).
- Thoenissen, D., Zilles, K., Toni, I. Differential involvement of parietal and precentral regions in movement preparation and motor intention. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 22 (20), 9024-9034 (2002).
- Al-Quraishi, M. S., Elamvazuthi, I., Tang, T. B., Al-Qurishi, M., Adil, S. H., Ebrahim, M. Bimodal data fusion of simultaneous measurements of EEG and fNIRS during lower limb movements. Brain Sciences. 11 (6), 713 (2021).
- Bishnoi, A., Holtzer, R., Hernandez, M. E. Brain Activation Changes While Walking in Adults with and without Neurological Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Studies. Brain sciences. 11 (3), 291 (2021).
- Oh, S., Song, M., Kim, J. Validating attentive locomotion training using interactive treadmill: an fNIRS study. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation. 15 (1), 122 (2018).
Réimpressions et Autorisations
Demande d’autorisation pour utiliser le texte ou les figures de cet article JoVE
Demande d’autorisationExplorer plus d’articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon