Method Article
Heterotopic כליה Autotransplantation במודל חזירי: פרוטוקול צעד-אחר-צעד
In This Article
Summary
Porcine models of organ transplantation provide an important platform to study mechanisms of organ preservation. This article describes a heterotopic porcine renal autotransplantation model, which allows investigating new approaches to improve the outcome of transplantation using marginal kidney grafts.
Abstract
Kidney transplantation is the treatment of choice for patients suffering from end-stage renal disease. It offers better life expectancy and higher quality of life when compared to dialysis. Although the last few decades have seen major improvements in patient outcomes following kidney transplantation, the increasing shortage of available organs represents a severe problem worldwide. To expand the donor pool, marginal kidney grafts recovered from extended criteria donors (ECD) or donated after circulatory death (DCD) are now accepted for transplantation. To further improve the postoperative outcome of these marginal grafts, research must focus on new therapeutic approaches such as alternative preservation techniques, immunomodulation, gene transfer, and stem cell administration.
Experimental studies in animal models are the final step before newly developed techniques can be translated into clinical practice. Porcine kidney transplantation is an excellent model of human transplantation and allows investigation of novel approaches. The major advantage of the porcine model is its anatomical and physiological similarity to the human body, which facilitates the rapid translation of new findings to clinical trials. This article offers a surgical step-by-step protocol for an autotransplantation model and highlights key factors to ensure experimental success. Adequate pre- and postoperative housing, attentive anesthesia, and consistent surgical techniques result in favorable postoperative outcomes. Resection of the contralateral native kidney provides the opportunity to assess post-transplant graft function. The placement of venous and urinary catheters and the use of metabolic cages allow further detailed evaluation. For long-term follow-up studies and investigation of alternative graft preservation techniques, autotransplantation models are superior to allotransplantation models, as they avoid the confounding bias posed by rejection and immunosuppressive medication.
Introduction
Kidney transplantation is the treatment of choice for patients with end-stage renal disease, due to associated lower rates of morbidity and mortality when compared to dialysis 1-3. Despite major improvements in patient outcomes following kidney transplantation, graft shortage still poses a severe challenge worldwide. The number of patients waiting for a kidney transplant by far exceeds the number of organs available 4-6. To increase the number of kidneys available for transplantation and to reduce patient waiting times, further sources of kidney grafts are needed.
Commonly, standard criteria donor (SCD) and extended criteria donor (ECD) kidney grafts from donation after brain death (DBD) as well as kidneys recovered from live donors (LDKT) are utilized. Since the 1990s, an increasing number of kidney grafts have been recovered in a donation after circulatory death (DCD) scenario, to further expand the donor pool 7,8. However, DCD and ECD kidney grafts demonstrate acceptable but decreased outcomes after transplantation, depending on different factors, such as donor age, warm and cold ischemia times, and the preservation technique used 9-11. Thus, additional research is required to improve the outcome of patients receiving marginal kidney grafts and to further increase the donor pool.
The porcine model of renal transplantation is well established and provides a clinical important scenario to investigate innovative approaches for the improvement of marginal kidney graft outcomes. In contrast to rodent and canine kidneys, which are unilobular, porcine and human kidneys are multilobular and are anatomically similar, particularly in regard to the arterial, venous, and urinary collecting systems 12,13. In addition, porcine and human kidneys demonstrate similarities in the pathophysiology of ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI), biochemistry, and immunological parameters 14. Thus, porcine renal transplantation is well-suited to investigate new organ preservation methods for marginal kidney grafts 15-17, model human IRI 18, study immunological pathways and allograft tolerance 19, provide surgical training 20-22, test new pharmacological therapies 23, implement new medical devices, and study new immunological mechanisms in xenotransplantation 24-26.
The renal porcine and human transplantation settings are not completely analogous. This article focuses on important technical details that will facilitate successful establishment of a renal autotransplantation model. Species-adapted pre- and postoperative housing, administration of anesthesia with close monitoring, and matched surgical techniques are described in the protocol and demonstrated in the video. Resection of the contralateral native kidney provides the opportunity to assess the function of the transplanted kidney. The placement of venous and urinary catheters and the use of metabolic cages allow more in-depth assessment. For studies aimed at investigating alternative graft preservation methods and mechanisms of IRI, autotransplantation models are superior to allotransplantation models, as they avoid the complications and confounding bias associated with rejection and use of immunosuppressive medications.
Protocol
כל החיות קיבלו טיפול אנושי וכל מחקרים ביצענו בהתאם למדיניות ולהנחיות של המועצה הקנדית על טיפול בבעלי חיים. כל הנהלים בוצעו תחת הפרוטוקולים Animal השתמש אושרו על ידי ועדת טיפול בבעלי חיים מוסדיים אוניברסיטת בריאות רשת.
הערה: סקירה סכמטי של פרוטוקול המחקר מוצג באיור 1.
פרוטוקול הניסוי באיור 1.. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
1. בעלי חיים
- השתמש חזירי יורקשייר זכר (30 קילו) בפרוטוקול זה.
2. כליה שתל אחזור
- נוהל לפני ניתוח
- לשכן את Yorkshir זכרחזירי דואר במתקן מחקר לפחות שבוע להתאקלם אותם. השתמש זריקה תוך שרירית של צפלוספורין דור שלישי, כגון ceftiofur, במשך 3 ימים כדי להפחית את הסיכון הפוטנציאלי של זיהומים עם סטרפטוקוקוס suis ו סלמונלה. לצום החזירים למשך תקופה מינימלית של 6 שעות לפני אינדוקציה של הרדמה כדי למנוע שאיפה.
- ליזום הרדמה של חזיר על ידי זריקה תוך שרירית של קטמין (20 מ"ג / ק"ג), אטרופין (0.04 מ"ג / ק"ג), ו midazolam (0.3 מ"ג / ק"ג). בהמשך לכך, להובלת בעלי חיים ממתקן הדיור לחדר הניתוח (OR).
- מניח את החזיר בעמדת פרקדן על שולחן הניתוח. אפשר חזיר לנשום 2 ליטר של חמצן עם 5% isoflurane ספונטני. לחשוף את מיתרי הקול עם לרינגוסקופ ולרסס אותם עם 2% פתרון מקומי לידוקאין למנוע laryngospasm הנגרמת אינטובציה. לאחר אינטובציה עם צינור 6.5 מ"מ, לחסום את השרוול עם 3-5 מ"ל של אוויר.
הערה: Capnometry מאשרת את positio הנכוןn של צינור לקנה הנשימה. - להקטין את הגז isoflurane ל -2.5%. הגדר את הנשמה כדי 14-16 נשימות / דקה ואת נפח גאות למשקל הגוף 10-15 מ"ל / ק"ג. לפקח על החזיר מקרוב. קצב פעימות לב רוויון חמצן נרשמים על ידי דופק oxymetry. אשר הרדמה תקינה על ידי קצב לב מופחת (מתחת 150 פעימות / דקה) ולחץ דם (להלן ערכים סיסטולי של 100 מ"מימ כספיים), כמו גם עדר תנועות חזיריות (לא שימוש של שרירים).
- בתנאים סטריליים, להכניס 9.5 Fr. לומן יחיד קטטר קבוע לתוך וריד הצוואר הפנימי באמצעות טכניקה Seldinger 27. בקצרה, להשתמש במחט לנקב את הווריד. לאחר הגדרת ה-החוט המדריך, להחליף את המחט עם ההיכרויות משם לקלף, ואחריו החלפת החוט עם קטטר וסקולרית. תקן את הקטטר אל העור באמצעות 3-0 משי או תפר monofilament שאינו נספג.
- נהל 500 מ"ג של metronidazole, 1 גרם של Cefazolin, ו -20 מ"ג של פנטופרזול. מוֹדָעָהראש 200 מ"ל של תמיסת של לקטט רינגר עם 5 דקסטרוז% (D5W) ו 1 מ"ל של פנטניל ציטראט לשעה לווריד במהלך הניתוח. החל משחת עיני וטרינרים על עיניים כדי למנוע יובש לאחר הרדמה.
- הליך ניתוחי
- בעקבות חיטוי וכיסוי סטרילי של שדה כירורגי, לבצע חתך קו האמצע של 25 ס"מ אורך. הכנס מפשק. מכסי מעיים גדולים וקטנים במגבת ולמקם אותם לצד שמאל הגישה אופטימלי בכליה ימנית.
- לשחרר את השופכן ואת בכליה הימנית עצמו מכל רקמה חסידה באמצעות הכווייה.
- מנתח את הווריד התקין הכליות העורקות באמצעות הכווייה עד מוצאם מן הווריד הנבוב הנח לבין אב עורקים, בהתאמה, חופשיים. כדי למנוע לווזוספזם עורק, מנהלה של 30-65 מ"ג של papaverine צריך להיחשב.
- לאחר דיסקציה כליות מלאה, עניבה (משי, 3-0) וחותכים השופכן distally. הכנהקערת קרח ea ושקית איבר סטרילי.
- ראשית, מהדק את עורק הכליה קרוב האאורטה שני, מהדק את עורק הכליה קרובה הווריד הנבוב באמצעות מהדק כלי. לאחר מכן, לכרות את השתל כליות ומיד cannulate את עורק הכליה עם צינורית עורק הכליה. השתמש 500 מ"ל של ketoglutarate טריפטופן-היסטידין קר כקרח פתרון (HTK) כדי לשטוף את הדם. אחסן את הכליה על קרח עד להשתלה.
- באתרו, לסגור את עורק הכליה הנותרים עם ליגטורה (משי, 2-0) ואת עורק הכליה עם תפר רץ (prolene, 6-0).
- לאחר בדיקת האזור הגזור לדימום, לסגור את דופן בטן עם תפר רץ (monofil, 1) ואת העור עם תפר monofilament 3-0 משי או שאינו נספג ..
- נוהל לאחר ניתוח
- תקן את תת עורי צנתר ורידי עם תפר (משי, 3-0) ואת המנהרה אותו לחלק האחורי של חזיר כדי למנוע מניפולציה בלתי רצויות. לאחר הצבת החזיר נוטה, suture (משי, 3-0) את הקטטר בחוזקה על העור.
- לגמול את החזיר ממכונת הנשמה ולתת לו להתאושש בתחום הדיור שלה לאחר האקסטובציה. נהל לקטט רינגר לווריד להרחבת נפח ולנהל 0.3 עצירות מ"ג על שיכוך כאבים. אל תשאירו חיה ללא השגחה עד שהוא שב להכרתו מספיק כדי לשמור שכיבה sternal.
3. כליות שתלו השתלה
- נוהל לפני ניתוח
- להרדים את החזיר באמצעות הזרקה תוך ורידית של propofol (1-2 מ"ג / ק"ג משקל גוף) ואחריו עירוי מתמשך של propofol בשיעור של 50-100 מ"ג / hr. Re-לצנרר החזיר כמתואר בשלב 2.1.3 ו 2.1.4 ולהגדיר את הגז isoflurane ל 3-4%.
- נהל 1 גרם של Cefazolin ו -20 מ"ג של iv פנטופרזול במהלך הניתוח, להשתמש באותו פרוטוקול הרדמה כמתואר 2.1.4.
- בעקבות חיטוי סטרילי, לעשות חתך של 4 ס"מ ליד קנה הנשימה. לנתח את tissue לחשוף את העורק הראשי. לעבור מלקחיים יתר הולט עניבת משי (2-0) סביב עורק. השתמש בטכניקה Seldinger להציג קטטר פלסטיק למדוד את לחץ הדם באופן רציף לאורך כל הניתוח. לחלופין, טכניקות מדידות לחץ דם לא פולשנית יכולות להיות מנוצלת.
- הליך ניתוחי
- לאחר חיטוי סטרילי, לפתוח מחדש את חלל הבטן על ידי חיתוך התפרים של תפרי עור fascia, לחדש מפשק הכירורגים כדי לחשוף את חלל בטן, ואת חזרת המעי לצד שמאל כדי לאפשר גישה נוחה יותר כלי infrarenal.
- השתלת שתל כליה השתמר הקצה אל צד כדי הווריד הנבוב ואבי העורקים infrarenal. לכן, לנתח וריד נבוב ואב עורקים מעל 5-8 סנטימטר מעל הסתעפות הכסל באמצעות טנדרי כווייה. במידת האפשר, נא לא להפריע את כלי הלימפה; אם לא אפשרי, לסגור אותם עם 5-0 תפרים prolene.
- לאחר שסיים את הנתיחה, לבדוק FOr הדימום ולהסיר רקמת נותרים מהכלי. ודא כי הידוק מלא של הווריד הנבוב ואב עורקים עם מלחציים Satinsky אינו ריאלי.
- לאחר מכן, לכרות נגדי כליות (משמאל). לשם כך, מקם את המעי בצד ימין; לנתח את השופכן, כליה עצם, עורק הכליה, ואת עורק הכליה מרקמות חסידות. לקשור את כלי השופכן ודם לכרות את הכליה. בדוק אם הדימום.
- מיקום מחדש של המעי שמאלה כדי לחשוף את אבי העורקים infrarenal ואת הווריד הנבוב. להזריק הפרין (100 IU / ק"ג משקל גוף) ולחכות 2 דקות לפחות.
- השקת ורידים:
- השתמש מהדק Satinsky כדי לצבוט את הווריד הנבוב לחלוטין ולעשות חתך חריץ המתאים לגודל של פתיחת עורק הכליה, באמצעות להב 11. ניתן להשתמש במספרי Pott להאריך את החריץ נוסף.
- לאחר גלישת הכליה לתוך שקית בד המכילה קרח סטרילי, להסיר אותו מן הקרח ולמקם אותו לתוך שדה הניתוח. השתמש בשתי פעמים חמושות 6-0prolene תפרים לבצע גולגולת תפר בפינת זנב.
- להיות קרוב ככל האפשר הכליות, לקשור את הפינה העליונה ולבצע תפר ריצה באמצעות 6-0 prolene, החל הקיר האחורי. לאחר שסיים 2/3, להשתמש בקצה השני של עניבה כדי להשלים התפר על הצד הקדמי. אחרי שקשרתי את תפרי הגולגולת, לקשור את התפרים בזווית הזנב.
- מקם מהדק בולדוג על עורק הכליה ולפתוח מהדק Satinsky. בדוק ההשקה לדימומים.
- השקת עורקים:
- השתמש Satinsky מהדק שוב כדי לצבוט האאורטה לחלוטין. השתמש 11 להב לעשות חתך חריץ, התאמת פתיחת עורק הכליה. השתמש אגרוף 4.0 מ"מ עגול להבטחת פתיחה נקיה.
- השתמש באחת 6-0 prolene תפר לבצע ההשקה העורקת, החל מ בצד המקבל. ודא כי האנדותל העורק הנו כלול בכל תפר למנוע לנתיחה. בינתיים, להתחיל לטפטף רציפה של 10 מ"ל norepinephrine (16 מ"ג / 250 מ"ל) מדולל 500 מ"ל של לקטט רינגר ו לכיל כדי לשמור על הלחץ הסיסטולי מעל 100 מ"מ כספית.
- להזריק verapamil תוך arterially לפני השלמת השקת העורקים ולנהל papaverine מבחינת נושא שלו מחוץ הספינה כדי למנוע לווזוספזם.
- מקם מהדק בולדוג על עורק הכליה ולפתוח מהדק Satinksy. בדוק את anastomoses לדימומים.
- לגולל את הכליה מן הבד ולהסיר את הקרח. פתח את מהדק בולדוג הוורידים הראשון, ואחריו מהדק בולדוג העורק. לאחר רה-פרפוזיה, ייצור השתן צריך להתחיל מיד.
- השתמש במטלית כדי לאבטח בעמדה חיובית עבור השתל המושתל ולתחזק reperfusion הומוגנית.
- השקה של השופכן:
- השתמש במספרי Pott לפתוח השופכן מן השתל לבין נמען על אורך אורך של 0.5 סנטימטר.
- השתמש בשתי 6.0 פוליאסטר, פולי (p-dioxanone) התפרים עבור יור מצד אל צדהשקת teral. בצע stich פינה בכל צד, ולאחר מכן להפעיל את הקיר האחורי באופן רציף הראשון, ואחריו הקיר הקדמי.
- לאחר בדיקת דימום, להסיר את הבד לעטוף חלק המעי הדק סביב הכליה להחזיק אותו בעמדה. סגור את דופן הבטן עם שני monofil 1 תפרים. סגור את העור עם 3-0 משי או תפר monofilament שאינם נספגים.
- שמירה על לחץ דם סיסטולי מעל 100 מ"מ כספית באופן רציף על ידי titrating עירוי נוראפינפרין בזהירות עד חזיר הושם לתוך אפרקדן.
- נוהל לאחר ניתוח
- לאחר סגירת הבטן כאמור, לשמור על חזיר לחמם באמצעות כרית חימום ושמיכה מחזורי-חום. הסר את קו עורקי, לסגור את החור לנקב בעורק עם סטיץ 6-0 prolene ולסגור את האתר החתך.
- סובב את החזיר על מועדי עמדה, לעצור את טפטוף נוראפינפרין לגמול את החזיר ממכונת הנשמה. אלהחזיר נמוך להתאושש בתחום הדיור שלה ולנטר אותו מקרוב כדי להבטיח התאוששות חלקה שלה מההליך. קח דגימות גז דם כל hr דרך קטטר הצוואר המושתל. ספק לקטט רינגר נפח תחליף ולנהל 0.3 עצירות מ"ג על שיכוך כאבים.
- בעקבות האקסטובציה, לפקח על חזיר מקרוב עד שהוא מסוגל לשתות באופן ספונטני. אל תשאירו חיה ללא השגחה עד שהוא שב להכרתו מספיק כדי לשמור שכיבה sternal. אל תחזור בעל חיים אשר עבר ניתוח לחברה של בעלי חיים אחרים עד התאושש לחלוטין.
4. לאחר הניתוח ומעקב
- נהל iv עצירות 0.3 מ"ג כל 8 שעות לפחות ניתוח 2 ימים לאחר או יותר במידת הצורך. באופן שיגרתי לנהל מנת מניעתי אחת של אנטיביוטיקה במהלך הניתוח. במקרה של סימני זיהום, לנהל iv Cefazolin 1 גרם פעמיים לכל iv יום ו metronidazole פעם ביום עדשיפור קליני מתרחש. נהל לקטט רינגר עד החזיר שותה מספיק מים. ניתן להשתמש 1,000 הפרין IU לנעול את הקטטר כדי למנוע קרישה.
- לאסוף דגימות דם ורידים באמצעות קטטר צוואר דגימות שתן כדי להעריך את מצבו והתפקוד כלייתי של החזיר.
- המתת חסד, להשרות הרדמה של חזיר עם iv propofol (5-10 מ"ל) ולתחזק אותו עם 5% isoflurane. לצנרר החזיר כמתואר לעיל. לאחר relaparatomy אוסף מדגם ברקמת הכליה, לגרום דום לב על ידי הזרקה תוך ורידית של 40 KCl mval.
תוצאות
בחלק הבא, את התוצאות של הניסויים autotransplantation כליות (n = 4) הם הפגינו. לאחר יחזור שתל הראשוני, החזירים התאוששו בתחום הדיור שלהם. בינתיים, שתל הכליות אוחסנו על קרח למשך זמן ממוצע של 7 שעות 35 דקות (± 18 דקות). לאחר reinduction של הרדמת laparotomy חוזר, הכליות הנגדיות היו כריתה ואת שתלי הקר מאוחסנת מושתלי heterotopically כמתואר. לאחר גמילה ממכונת ההנשמה, החזירים היו התאוששו מניתוח והיה במעקב במשך 10 ימים (ראו איור 1). יומי (יום שלאחר הניתוח 1-4; תרמיל) או כל יום שני (6-10 pod) דגימות דם נאספו לבצע סקר גז דם מנתח; כדי להעריך את תפקוד הכליות, חנקן קריאטינין ודם בסרום אוריאה ערכים (BUN) נאמדו. לשם השוואה, את התוצאות של שתל כליה אחת allotransplanted מוצגים. עבור דיכוי חיסוני, חזיר זה קיבל ציקלוספורין 100 מ"ג PO ושיתוףrtisone 250 מ"ג ivbid הטכניקה הכירורגית של ריטלין היה זהה בפרוטוקול autotransplant; לא חם איסכמיה זמן יושם.
כל החזירים היו במצב קליני טובים בתקופת המעקב. ערכי קריאטינין ו BUN בסרום חשפו את העלייה הגדולה ביותר ביום אחד לאחר הניתוח (Crea 2.8 ± 0.7 מ"ג / ד"ל, BUN 25.3 ± 7 מ"ג / ד"ל) והירידה עד 10 תרמיל (Crea 1.7 ± 0.4 מ"ג / ד"ל, BUN 10.7 ± 4 מ"ג / ד"ל) קרוב ערכי הבסיס הראשוני. שתל כליה allotransplanted הפגינו ערכי קריאטינין ו BUN גבוה לאחר פונקציה שתל ראשונית טובה, כשמשווים את autografts, ככל הנראה בשל דחייה (איור 2 ו -3). המוסטאסיס חומצה-בסיס (איור 4) ורמות אלקטרוליטים (איור 5) היו יציבה ללא התערבות. בדיקה היסטולוגית הראה נשמר tubulointerstitium בכליות autotransplanted (Figur דואר 6), מפוזר דלקת אינטרסטיציאלית tubulitis, ו glomerulitis בכליות allotransplanted (איור 7).
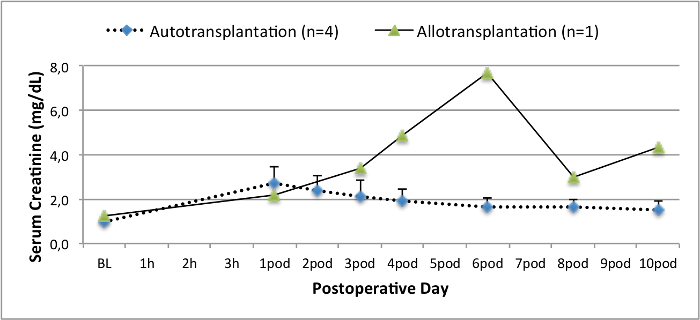
איור 2. ערכי קריאטינין בסרום. ערכי קריאטינין בסרום (ממוצע וסטיית תקן) עבור מחקר ולאחר 10 לאחר ניתוח. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
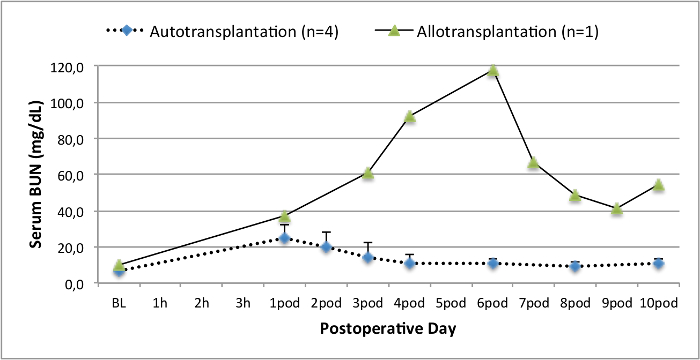
איור 3. ערכי BUN סרום. ערכי BUN סרום (ממוצע וסטיית תקן) עבור המחקר ולאחר 10 ימים לאחר הניתוח. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
"Jove_content" FO: keep-together.within-page = "1"> 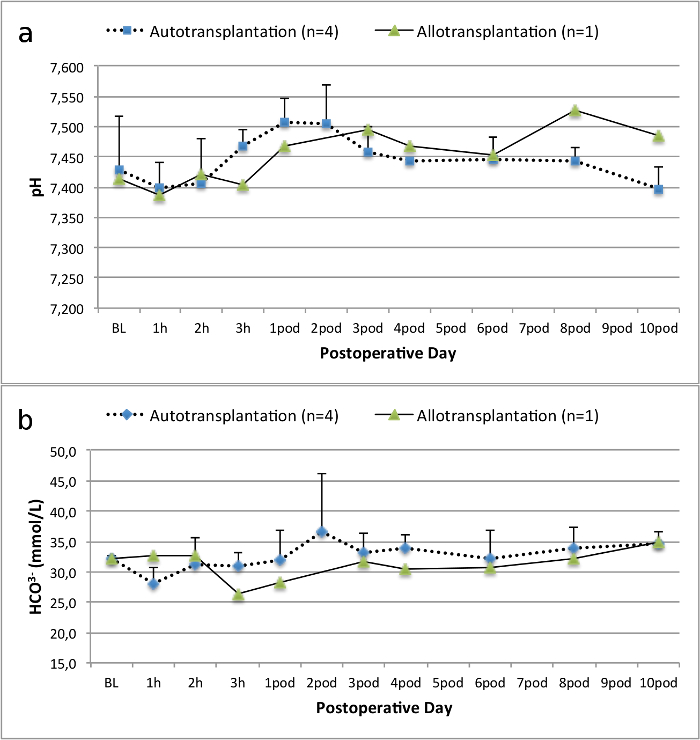
איור 4. המוסטאסיס חומצה-בסיס. המוסטאסיס חומצה-בסיס (ממוצע וסטיית תקן) עבור המחקר ולאחר 10 ימים לאחר הניתוח. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
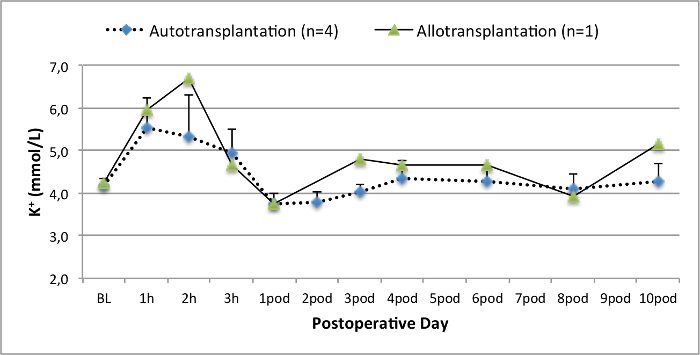
רמות איור 5. אלקטרוליט. רמות אלקטרוליטים (ממוצע וסטיית תקן) עבור המחקר ולאחר 10 ימים לאחר הניתוח. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
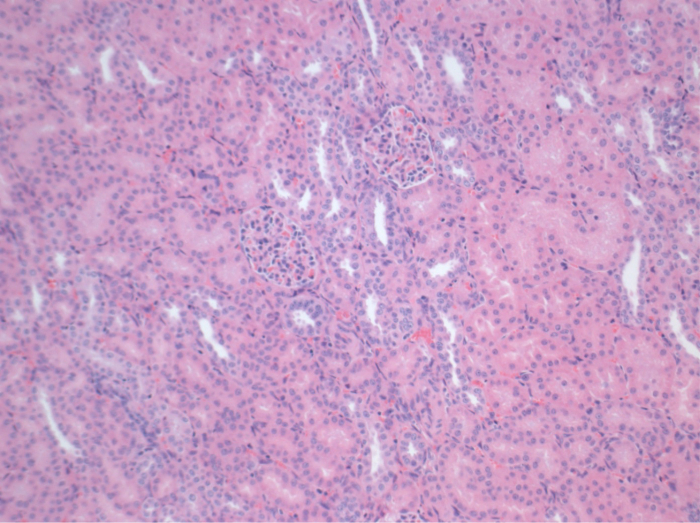
איור 6. היסטולוגיה (H &# 38;.. E), הגדלה 100X tubulointerstitium רגילה בכליות autotransplanted 10 ימים לאחר הניתוח אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
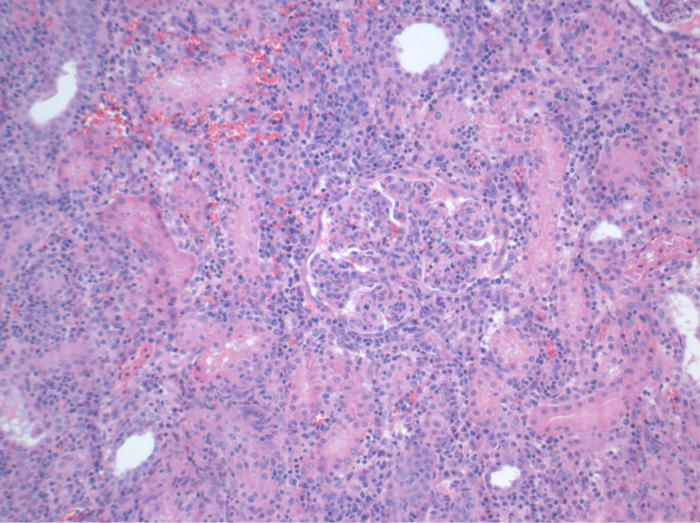
איור 7. היסטולוגיה (H & E), בהגדלה 100x. דלקת אינטרסטיציאלית נרחב, tubulitis, ו glomerulitis, עולה בקנה אחד עם דחייה, בכליות allotransplanted 10 ימים לאחר הניתוח. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
Discussion
המודל של השתלת כליה חזירית מספק הזדמנות ייחודית לקדם בתחום השתלת אדם בשל דמיון בהיבטים כירורגית, פיזיולוגיה, ביוכימיה, ואימונולוגיה 14.
בהתאם מטרת המחקר הניסיוני, המודל של autotransplantation כליות יש מספר יתרונות בהשוואה לדגם אלוגרפט. למרות מספר קבוצות לדווח פונקציה שתל כליה טובה אחרי אלוגרפט 28, דיכוי חיסוני בחזירים הוא מאתגר, במיוחד השתלת כליה. דגימת דם לפני ניתוח מנתח כדי להבטיח תאימות עבור אנטיגן לויקוציטים חזירים (SLA) הם ריאליים, אבל יקרים ולא מעשי 14. לאחר ניתוח, סוכנים אימונוסופרסיבי מוצעים כגון tacrolimus ו ציקלוספורין (מעכבי calcineurin, CNI) הם אוראליים או IV 28. אוראלי אינו מעשי, כמו חזירים בדרך כלל מסרבים לבלוע מדיקה אוראליtion. יתר על כן, חסימות מעיים עלולות לייתר קליטה מספקת של תרופות מדכאות חיסון ותחזוקה של רמות תרופה טיפוליות. העירוי המתמשך של iv של CNI בחי פעילה הן תובעני מבחינה טכני. הרביעי מנהלת בולוס מוביל ערכי שיא גבוה, אשר לגרום לרעילות. כך, החקירה של טכניקות שימור חדשות, המודל של autotransplantation כליות יש מספר יתרונות. בתוצאות הנציג של שתל כליות allotransplantated שהוצג לעיל, לשיא מתעכב וגדילה של קריאטינין ו BUN ולציין דחייה, אשר באה לידי ביטוי על ידי ערכה היסטולוגית.
המודל החזירי של autotransplantation כבר השתמש בעבר כדי לחקור טכניקות שימור חדשות 14,18,29. עם זאת, ערכי קריאטינין ו BUN לאחר ניתוח בסרום המדווח של חזירי autotransplanted בתרחיש פועם לב להשתנות במידה ניכרת על המערכת הניסיונית 22,30 . הפרוטוקול התורם פועם הלב אנו מציגים כאן תוצאה הוא שיא קריאטינין בדם נמוך לאחר ניתוח של 2.8 מ"ג / ד"ל (± 0.7) ו BUN שיא של 25.3 מ"ג / ד"ל (± 7.4). תוצאות אלו ניתנים להשוואה עם ערכי השיא הנמוכים שהציגו Hanto ועמיתיו 28 ו Snoeijs ועמיתיו 31.
כדי להבטיח תוצאה מוצלחת לאחר השתלת כליה במודל autotransplantation חזירי, זיהינו כמה גורמים טכניים מפתח למזער את שיעור הסיבוכים מסוים. השימוש פתרון היסטידין-טריפטופן-ketoglutarate (HTK) מפחיתה את הסיכון לווזוספזם בשל תוכנו נמוך של אשלגן בהשוואה אוניברסיטת ויסקונסין (UW) פתרון. כדי להמשיך להקטין את הסיכון של לווזוספזם בנקודת reperfusion, verapamil ניתן להזריק לתוך עורק הכליה, ו papaverine יכול להינתן מקומי במהלך אחזור ואחרי reperfusion. בנוסף, טפטוף מתמיד של נוראפינפרין טיטרציה לשמורלחץ הדם הסיסטולי מעל 100 מ"מ כספית מבטיח reperfusion הומוגנית. זה שימושי כדי לשמור על לחץ דם זה לפחות עד חזיר ממוצבת נוטה. יתר על כן, את המיקום של שתל המושתל חשוב למנוע מסתלסל של כלי דם anastomosed החדש. לכן, כדאי לכרות את הכליה הנגדית עזב לפני לתפירת anastomoses של שתל כדי למנוע מניפולציה מכאנית נרחבת. לאחר סיום ההשקה של השופכן, גלישת מעי דק סביב שתל המושתלים מאבטח עמדתה לאחר סגירת דופן הבטן. סיבוכים כגון חסימות מעיים עקב מסתלסל של המעי הם נצפו לעתים נדירות, אבל יכול לגרום לסיבוכים חמורים, כולל ileus, ניקוב המעי, ומוות. בסך הכל, טכניקה כירורגית מדויקת, הרדמה קשוב מעקב צמוד במהלך מעקב להבטיח תפקוד תוצאה ואת השתל קליני טוב.
ניתן perfo anastomoses עורקי ורידיrmed שימוש בטכניקות שונות. מיקום Orthotopic של השתל מאפשר anastomoses מקצה לקצה של העורק עורק הכליה. במקרה של השתלת heterotopic, השתל יכול להיות ממוקם שקע הכליות הנגדי עבור anastomoses מקצה לקצה, על כלי הכסל, או אב העורקים דיסטלי ישירות. השתלת heterotopic עם anastomoses כדי האאורטה קאווה ישירות טכניקה מקצה בצד עדיפה במודל זה כפי שהוא יכול להפחית את הסיכון של פקק לווזוספזם 32. וריאציות אנטומיות עם bifurcations ורידים מאוד מוקדם עשויות להוביל את הצורך בתפירת שני anastomoses ורידים נפרד. אם העורק או הווריד הם קצרים יחסית, השתל ניתן להפעיל 180 ° להגדיל את האורך של הכלי. השופכן מצד אל צד השקה יכול להשיג תוצאות ניסוי טובה בלי מסבכת חומרות או דליפת שתן.
באופן כללי, המודל החזירי של השתלת כליה מציע יתרונות לעומת במודלים של בעלי חיים אחרים. כמו דescribed לעיל, דמיון מסוים קיים בין החזירי ואת המערכת האנושית, המאפשר תרגום מהיר היחסי של טכניקות חדשות לתוך פרקטיקה קלינית. הטכניקה של השתלה מהבחינה טכנית קלה יותר בהשוואה לדגמים מכרסמת. בנוסף, על פי ההצעה של צנתרים ורידיים, דגימות דם היקפיות ניתן לאסוף בקלות ומעובד לחקירה נוספת. האוסף של שתן מאפשר הערכה נוספת של פגיעה בכליות פונקציה. כדי לאסוף דגימות שתן, קטטר מלעורית יכול להיות מוכנס לתוך שלפוחית השתן. כדי למנוע מניפולציה של חזיר, בקצה הדיסטלי יש מנהרה תת עורית לחלק האחורי של החיה. אפשרות נוספת לאיסוף שתן היא שימוש בכלובים מטבולית, המאפשרים תקופות גבייה ארוכות טווח כדי להעריך את הפינוי קריאטינין וריכוז ביומרקרים נוספים בשתן. תמונות sonography, סריקות CT, ו- MRI אפשריות. תרומה לאחר פרוטוקולי מות דם ניתן חיקה ידי ההחלה חמהאיסכמיה לפני אחזור. יתר על כן, חזירים קלים יחסית לטפל אם מסורס להגביל ההתנהגות התוקפנית שלהם.
חסרונות כולל את העלויות הגבוהות של רכישת בעלי חיים, דיור, ציוד רפואי כירורגי אחר, וכוח אדם. גורמים אלה אומרים שזה לא ריאלי לכלול מספר רב של בעלי חיים בכל קבוצה לימוד. יתר על כן, לעומת במודלים של מכרסמים, מספר המצומצם של אזכור זמין בספרות נתונים ביולוגיים נורמטיביים חזיר. כחלופה להערכה של טכניקות מפותחות חדשים, כגון דרכי שימור הרומן, קבוצות אחרות תיארו את reperfusion vivo לשעבר normothermic כחלופה השתלת כליה 33,34. טכניקה זו היא קלה יותר לביצוע ופחות יקר. עם זאת, השתלת שתל כליה טופל מספקת מודל דומה יותר בפרקטיקה הקלינית ומאפשר עוד מעקב תקופות. לכן, היא משמשת עבור שתל מציאותי יותר להעריךment.
לסיכום, המודל החזירי של autotransplantation כליות heterotopic מספק תרחיש חשוב קליני לחקור גישות חדשות חדשניות לשיפור תוצאות שתלו כליה. בפרט, פרוטוקול זה כולל פרטים טכניים חשובים שייאפשרו הקמה מוצלחת של מודל autotransplantation כליות ומאפשר תרגום המהיר של ממצאים חדשים על ניסויים קליניים.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Sorin Group (Milano, Italy), XVIVO Perfusion Inc. (Goteborg, Sweden), and Braun AG (Melsungen, Germany) for their support. We highly appreciate the support of the John David and Signy Eaton Foundation.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Anesthesia Equipment | |||
| Anesthesia Machine, Optimax | Moduflex Anesthesia Equipment | SN5180 | |
| Infusion Pump 3,000 | SIMS Graseby LTD. | SN300050447 | |
| Infusion Pump Line | Smith Medical ASD Inc. | 21-0442-25 | |
| Intravenous permanent catheter (9.5 Fr) | Cook Medical Company | G01865 | |
| Isoflurane Vapor 19.1 | Draeger Medical Canada Inc. | N/A | |
| Mallinckrodt, Tracheal Tube, 6.5 mm | Covidien Canada | 86449 | |
| Temperature Therapy Pad | Gaymar Industries Inc | TP26E | |
| Ventilator, AV 800 | DRE Medical Equipment | 40800AVV | |
| Warm Touch, Patient Warming System | Nellcor/ Covidien Canada | 5015300A | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Surgical Equipment | |||
| Abdominal Retractor | Medite GmbH | 07-0001-00 | |
| Aorta/vein punch 4.0 mm, round | Scanlan International Inc. | 1001-602 | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Peripheral, Clamp | Aesculap Inc. | FB463R | |
| De Bakey-Beck, Atraumatic Vena Cava, Clamp | Aesculap Inc. | FB519R | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Mini-Bulldog, Straight | Aesculap Inc. | FB422R | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Mini-Bulldog, Curved | Aesculap Inc. | FB423R | |
| De Bakey, Atraumatic Coarctation Clamp, Angled | Aesculap Inc. | FB453R | |
| Dissection Blade #11 | Feather Safety Razor Co. | 089165B | |
| Connector (1/4") with male luer lock | Sorin Group Inc. | AB1452 | |
| Liver Admin Set (flush line) | CardioMed Supplies Inc | 17175 | |
| Maxon, 1 | Covidien Canada | 606173 | |
| Med-Rx Suction Connecting Tube | Benlan Inc. | 70-8120 | |
| Organ Bag | CardioMed Supplies Inc | 2990 | |
| Potts – De Martel, Scissors | Aesculap Inc. | BC648R | |
| Renal artery cannula, 1.6" | Sorin Group Inc. | VC-11000 | |
| Sofsilk, 2-0 | Covidien Canada | S405 | |
| Sofsilk, 3-0 | Covidien Canada | S404 | |
| Satinsky, Suprahepatic Cava Clamp | Aesculap Inc. | FB605R | |
| Suction Tip | Tyco Healthcare Group LP | 8888501023 | |
| Surgipro II, 6-0 | Covidien Canada | VP733X | |
| Valleylab, Cautery Pencil | Covidien Canada | E2515H | |
| Valleylab, Force Tx | Valleylab Inc. | 216151480 | |
| Valleylab, Patient Return Electrode | Covidien Canada | E7507 | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Medication | |||
| Atropine Sulfate 15 mg/30 ml | Rafter 8 Products | 238481 | |
| Buprenorphine 0.3 mg/ml | RB Pharmaceuticals LDT | N/A | |
| Ceftiofur 3 mg/ml | Pfizer Canada Inc. | 11103 | |
| Cefazolin 1 g | Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada Inc. | 2237138 | |
| Fentanyl Citrate 0.25 mg/5 ml | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 2240434 | |
| Heparin 10,000 iU/10 ml | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 10750 | |
| Histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate (HTK) solution | Methapharm | CU001LBG | |
| Isoflurane 99.9%, 250 ml | Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada Inc. | 2231929 | |
| Ketamine Hydrochloride 5,000 mg/50 ml | Bimeda-MTC Animal Health Inc. | 612316 | |
| Lactated Ringer’s + 5% Dextrose 1 L | Baxter Corporation | JB1064 | |
| Lactated Ringer’s 1 L | Baxter Corporation | JB2324 | |
| Metronidazole 500 mg/100 ml | Baxter Corporation | 870420 | |
| Midazolam 50 mg/10 ml | Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada Inc. | 2242905 | |
| Norepinephrine 16 mg/250 ml Dextrose 5% | Baxter Corporation | N/A | |
| Pantoprazole 40 mg | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 2306727 | |
| Papaverine 65 mg/2 ml | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 9881 | |
| Propofol 1,000 mg/100 ml | Pharmascience Inc. | 2244379 | |
| Saline 0.9%, 1 L | Baxter Corporation | 60208 | |
| Solu-Medrol 500 mg | Pfizer Canada Inc. | 2367963 | |
| Verapamil | Sandoz Canada Inc. | 2166739 | |
| Xylocaine Endotracheal 10 mg/50 ml | AstraZeneca | 2003767 |
References
- Wolfe, R. A., Ashby, V. B., et al. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med. 341 (23), 1725-1730 (1999).
- Ingsathit, A., Kamanamool, N., Thakkinstian, A., Sumethkul, V. Survival advantage of kidney transplantation over dialysis in patients with hepatitis C: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transplantation. 95 (7), 943-948 (2013).
- Tonelli, M., Wiebe, N., et al. Systematic review: kidney transplantation compared with dialysis in clinically relevant outcomes. Am J Transplant. 11 (10), 2093-2109 (2011).
- Matas, A. J., et al. OPTN/SRTR Annual Data Report 2012: Kidney. Am J Transplant. 14, (2014).
- . Annual Report 2013 - Eurotransplant International Foundation. Available from: https://www.eurotransplant.org/cms/mediaobject.php?file=AR20135.pdf (2013)
- Morrissey, P. E., Monaco, A. P. Donation after circulatory death: current practices, ongoing challenges, and potential improvements. Transplantation. 97 (3), 258-264 (2014).
- Maggiore, U., Oberbauer, R., et al. Strategies to increase the donor pool and access to kidney transplantation: an international perspective. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 30 (2), 217-222 (2014).
- Summers, D. M., Johnson, R. J., Hudson, A., Collett, D., Watson, C. J., Bradley, J. A. Effect of donor age and cold storage time on outcome in recipients of kidneys donated after circulatory death in the UK: a cohort study. Lancet. 381 (9868), 727-734 (2013).
- Wadei, H. M., Heckman, M. G., et al. Comparison of kidney function between donation after cardiac death and donation after brain death kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 96 (3), 274-281 (2013).
- Moers, C., Smits, J. M., et al. Machine perfusion or cold storage in deceased-donor kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 360 (1), 7-19 (2009).
- Pereira-Sampaio, M. A., Favorito, L. A., Sampaio, F. J. B. Pig kidney: anatomical relationships between the intrarenal arteries and the kidney collecting system. Applied study for urological research and surgical training. J Urol. 172 (5 Pt 1), 2077-2081 (2004).
- Bagetti Filho, H. J. S., Pereira-Sampaio, M. A., Favorito, L. A., Sampaio, F. J. B. Pig kidney: anatomical relationships between the renal venous arrangement and the kidney collecting system. J Urol. 179 (4), 1627-1630 (2008).
- Giraud, S., Favreau, F., Chatauret, N., Thuillier, R., Maiga, S., Hauet, T. Contribution of large pig for renal ischemia-reperfusion and transplantation studies: the preclinical model. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011 (21), 532127 (2011).
- Gallinat, A., Paul, A., et al. Role of oxygenation in hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys from heart beating donors. Transplantation. 94 (8), 809-813 (2012).
- Thuillier, R., Allain, G., et al. Benefits of active oxygenation during hypothermic machine perfusion of kidneys in a preclinical model of deceased after cardiac death donors. J Surg Res. 184 (2), 1174-1181 (2013).
- Hosgood, S. A., Barlow, A. D., Yates, P. J., Snoeijs, M. G. J., van Heurn, E. L. W., Nicholson, M. L. A pilot study assessing the feasibility of a short period of normothermic preservation in an experimental model of non heart beating donor kidneys. J Surg Res. 171 (1), 283-290 (2011).
- Delpech, P. O., Thuillier, R., et al. Effects of warm ischaemia combined with cold preservation on the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α pathway in an experimental renal autotransplantation model. Br J Surg. 101 (13), 1739-1750 (2014).
- Kirk, A. D. Crossing the bridge: large animal models in translational transplantation research. Immunol Rev. 196, 176-196 (2003).
- Golriz, M., Hafezi, M., et al. Do we need animal hands-on courses for transplantation surgery. Clin Transplant. 27, 6-15 (2013).
- He, B., Musk, G. C., Mou, L., Waneck, G. L., Delriviere, L. Laparoscopic surgery for kidney orthotopic transplant in the pig model. JSLS. 17 (1), 126-131 (2013).
- Faure, A., Maurin, C., et al. An experimental porcine model of heterotopic renal autotransplantation. Transplant Proc. 45 (2), 672-676 (2013).
- Hosgood, S. A., Yates, P. J., Nicholson, M. L. 1400W reduces ischemia reperfusion injury in an ex-vivo porcine model of the donation after circulatory death kidney donor. World J Transplant. 4 (4), 299-305 (2014).
- Ghanekar, A., Mendicino, M., et al. Endothelial induction of fgl2 contributes to thrombosis during acute vascular xenograft rejection. J Immunol. 172 (9), 5693-5701 (2004).
- Ghanekar, A., Lajoie, G., et al. Improvement in rejection of human decay accelerating factor transgenic pig-to-primate renal xenografts with administration of rabbit antithymocyte serum. Transplantation. 74 (1), 28-35 (2002).
- Cowan, P. J., Cooper, D. K. C., d'Apice, A. J. F. Kidney xenotransplantation. Kidney Int. 85 (2), 265-275 (2014).
- Seldinger, S. I. Catheter replacement of the needle in percutaneous arteriography; a new technique. Acta radiol. 39 (5), 368-376 (1953).
- Hanto, D. W., Maki, T., et al. Intraoperative administration of inhaled carbon monoxide reduces delayed graft function in kidney allografts in Swine. Am J Transplant. 10 (11), 2421-2430 (2010).
- Maathuis, M. -. H. J., Manekeller, S., et al. Improved kidney graft function after preservation using a novel hypothermic machine perfusion device. Ann Surg. 246 (6), 982-991 (2007).
- Gallinat, A., Paul, A., et al. Hypothermic reconditioning of porcine kidney grafts by short-term preimplantation machine perfusion. Transplantation. 93 (8), 787-793 (2012).
- Snoeijs, M. G., Matthijsen, R. A., et al. Autologous transplantation of ischemically injured kidneys in pigs. J Surg Res. 171 (2), 844-850 (2011).
- Golriz, M., Fonouni, H., Nickkholgh, A., Hafezi, M., Garoussi, C., Mehrabi, A. Pig kidney transplantation: an up-to-date guideline. Eur Surg Res. 49 (3-4), 121-129 (2012).
- Hosgood, S. A., Bagul, A., Yang, B., Nicholson, M. L. The relative effects of warm and cold ischemic injury in an experimental model of nonheartbeating donor kidneys. Transplantation. 85 (1), 88-92 (2008).
- Hoyer, D. P., Gallinat, A., et al. Influence of oxygen concentration during hypothermic machine perfusion on porcine kidneys from donation after circulatory death. Transplantation. 98 (9), 944-950 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved