Method Article
Measuring Electrical Conductivity to Study the Formation of Brines Under Martian Conditions
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
The objective of the protocol is to monitor the hydration of salts and the brine formation process. Electrical conductivity is used as the measurement technique. The experiments are performed in a simulated Martian environment of temperature, relative humidity and carbon-dioxide atmosphere.
Abstract
This paper describes a protocol to design experiments to study the formation of brines under Martian conditions and monitor the process with electrical conductivity measurements. We used the Engineering Qualification Model (EQM) of Habitability: Brines, Irradiation, and Temperature (HABIT)/ExoMars 2022 instrument for the experiment setup but we provide a brief account of constructing a simple and inexpensive electrical conductivity measurement setup. The protocol serves to calibrate the electrical conductivity measurements of the salt deliquescence into brine in a simulated Martian environment. The Martian conditions of temperature (-70 °C to 20 °C), relative humidity (0% to 100%) and pressure (7 - 8 mbar) with carbon-dioxide atmosphere were simulated in the SpaceQ Mars simulation chamber, a facility at the Luleå University of Technology, Sweden. The hydrate form of the known amount of salt accommodated between a pair of electrodes and thus the electrical conductivity measured depends predominantly on its water content and the temperature and relative humidity of the system. Electrical conductivity measurements were carried out at 1 Hz while exposing salts to a continuously increasing relative humidity (to force transitioning through various hydrates) at different Martian temperatures. For demonstration, a day-night cycle at Oxia Planum, Mars (the landing site of ExoMars 2022 mission) was recreated.
Introduction
One of the main research topics of planetary exploration is the water cycle, but it is difficult to design a general, robust and scalable procedure, that allows to monitor the interaction of the atmosphere with the ground. Laboratory simulations can recreate the planetary atmospheres, surfaces and the interactions within. However, it comes with a challenge, from procuring necessary equipment to training personnel. This paper describes a protocol to design experiments to study the formation of brines under Martian conditions of temperature, relative humidity and carbon-dioxide atmosphere, and monitors the process with electrical conductivity measurements. We also provide a brief account of constructing a simple and inexpensive electrical conductivity measurement setup. The protocol may be adapted to design similar experiments in vacuum or other planetary atmospheres.
Importance of brine formation studies
Hygroscopic salts can absorb atmospheric water vapor to form liquid solutions in a process called deliquescence. This process creates brine under favorable conditions on the surface of Earth and Mars that is likely to exist in certain times and places. The reverse process called efflorescence is also possible when the brines dehydrate under unfavorable conditions. The plausible existence of brines on the surface or subsurface of Mars has several implications on the current terrestrial and Martian studies. Additionally, salts can hydrate, hold and release water molecules, which also affects the water cycle and the properties of the regolith.
There is an increasing international interest on determining the temperature, relative humidity and pressure conditions that are favorable for the formation of brines due to deliquescence of salts and salt mixtures, both for Earth and Mars. Field observations of the dark steep-sloped water tracks near Don Juan Pond (DJP) watershed and the formation of wet patches in the McMurdo Dry Valleys in Antarctica have been attributed to the brine formation in the calcium-chloride rich sediments1.
These results have also been validated with laboratory experiments simulating the low temperatures between -30 °C and 15 °C and a relative humidity between 20% and 40%2. Chloride-bearing evaporites in the Yungay region in the hyper-arid core of the Atacama Desert, Chile can absorb water and harbor microbial life3. The processes occurring in the DJP and the driest places on Earth such as the Atacama Desert may be analogous to several of the Martian studies suggesting that similar processes could be happening on the present-day Mars1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16. Recent remote sensing observations of the Salar de Uyuni (Bolivian Altiplano) have described a similar process to what is observed on Mars from orbit17. Despite harsh conditions, the deliquescence-driven brine formation process can sustain liquid water in quantities large enough to allow colonies of bacteria to thrive deep within the salt nodules3. This is of interest to astrobiologists and planetary scientists.
Diurnal absorption and desorption of the atmospheric moisture by the deliquescent salts in the Martian regolith has been reported4,5. The brine formation process of perchlorates existing on Mars have already been studied, observing the changes in phase or hydration state of individual salt particles1,9,18.Different brine related studies have also been performed under Mars-relevant conditions to determine the relative humidity values at which Mars relevant salts and salt mixtures will undergo deliquescence and efflorescence19,20,21. Others have used these experiment conditions to study the evaporation rates of brines at Martian temperature, relative humidity and carbon-dioxide atmosphere22.
Methods of brine formation detection and monitoring
Several methods exist to monitor the brine formation process. Visual observation and images in the visible wavelengths are the simplest. Weighing the salts to monitor the increase in mass could well be used23. Usually the environmental parameters such as temperature, relative humidity and pressure are monitored to properly interpret the observations. Some studies used a hygrometer. The hygroscopic properties of the salts can also be measured with differential mobility analyzers or electrodynamic balances, but their operation is not accurate enough beyond a relative humidity of90%24. In recent studies, transmission and scanning electron microscopes (TEM and SEM) have been widely utilized. Both these microscopes have environmental cells that enable studying the interaction of water with individual salt particles24. The phase changes and transitions in individual salt particles are generally detected with optical, infrared (IR) or Raman spectroscopy incorporated in the experimental setup8,13,19,20,25. Existing spectroscopic methods offer good observation limits and a clear detection of phase changes, but they are not compatible to monitor bulk salt samples and for the continuous monitoring of the brine formation process through the intermediate stages of phase transitions. Furthermore, the laser-based microscopic devices such as the 'Raman microscope' are expensive and may require a complex experimental setup.
We use electrical conductivity as the measurement technique. Measurements to determine the relative humidity at which the salts undergo deliquescence have been performed using electrical conductivity where the derived values were in good agreement with those determined using a standard hygrometer26. The time series of the brine formation process of the deliquescent salts has been studied using electrical conductivity earlier by Heinz et al.27. Here, they used a mixture of JSC Mars-1a simulant and perchlorates or chlorides. The electrical conductivity technique has also been used to detect liquid or frozen water in soils28,29. The advantage of this method is that, it can be applied both to small and medium-sized samples, as long as they are contained in the space between the two electrodes.
This protocol could be useful to design similar experiments that involves controlling the temperature and relative humidity in vacuum or simulating the extraterrestrial atmospheres such as Mars and others.

Figure 1: Construction of the experiment setup. A block diagram showing a simple electrical conductivity measurement setup comprising of the main components such as electrodes, measuring circuits and an Arduino. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Electrical conductivity of brines can be measured with a simple inexpensive setup as shown in Figure 1. The specific products to construct the setup is given in Table of Materials. The setup primarily consists of a pair of metal electrodes of same dimensions separated by a known distance within which the salt or salt mixtures for the study are accommodated. A PT1000 resistance temperature detector can be used to measure the temperature of the salts. One of the flat ends of the electrodes can be soldered to each terminal of a shielded coaxial cable. Similarly, the two terminals of the sensor can be soldered to another shielded coaxial cable. The other ends of each of these coaxial cables can be connected to the circuits to measure electrical conductivity and temperature, respectively. An Arduino board and a simple serial data monitor can be used to retrieve the data and store it.
In the context of this experiment, we use the Engineering Qualification Model (EQM) of the HABIT/ExoMars 2022 instrument, the closest replica of the Flight Model (FM) that will be flown to Mars in 2022. HABIT stands for HabitAbility: Brines, Irradiation, and Temperature. It is one of the two European payloads in the ExoMars 2022 Surface Platform Kazachok and has the objective to study the habitability conditions at the landing site, Oxia planum, Mars. The Brine Observation Transition To Liquid Experiment (BOTTLE) is one of the components of HABIT instrument with a purpose to demonstrate the liquid water stability on Mars31. The protocol described here serves to calibrate the electrical conductivity measurements as a function of brine formation under Martian conditions of temperature, relative humidity and carbon-dioxide atmosphere31. This is applied to retrieve the calibrated electrical conductivity measurements of BOTTLE that aids with the detection of liquid brine formation process on Mars, which is one of its primary mission objectives18. By calibration, here we refer to experiment-level calibration. Instrument-level calibration is performed with determining the geometrical cell constants of each electrode pair and with calibration standards of known electrical conductivity31.
Protocol
1. Construction of the experiment setup for measuring electrical conductivity
- Choose the dimensions of the electrodes and the distance between the electrode pair. The dimensions of the electrodes depend on the dimensions of the sample container and thereby the amount of salts used. The dimensions of the HABIT BOTTLE container dimensions mentioned below can be taken as reference for the sample container and the amount of salts can be referred from Step 2.1. The geometrical cell constant can be derived from equation (1).
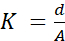 (1)
(1)
where, d - distance between the electrode pair, and
A - Area of the electrodes (= Length x Breadth).
The geometrical cell constant, K decides the electrical conductivity range to which the measurement setup is sensitive. For example, K = 1 cm-1 can measure in 5 - 200, 000 µScm-1 range while K = 10 cm-1 can measure in 10 µScm-1 - 1 Scm-1 range. There may be various levels of electrode pairs. The choice of material could be from copper, platinum, gold, etc. Several long-term experiments at Omnisys Instrument AB, Sweden facility with gold and platinum electrodes, passing direct current (DC) in brine medium has shown that gold electrodes are preferred in terms of better corrosion resistance for this operation.
NOTE: HABIT has a total of 16 electrode pairs with a possibility to study six different salts at three levels (two corner cells measure only with low and mid electrode pairs) separated within a container of dimensions 25 mm x 15 mm x 15 mm (L x W x H). BOTTLE uses three levels of electrode pairs of dimensions: Low: 1.6 x 0.4, Mid: 1.6 x 0.2, High: 1.6 x 0.2, separated at 2.5 cm producing a cell constant of 3,9062 cm-1 and 7.8125 cm-1. The measurements were performed using an optical measurement system (e.g., Mitutoyo MF 176). - Prepare a container with flat surfaces to hold the salts to study as shown in Figure 1. The container size can be chosen depending on the geometrical dimensions of the electrodes and the distance between the electrode pair where the salts are accommodated. Multiple containers configuration may be adapted. The containers may be 3D printed in PLA or preferably milled with aluminum or other metal, they should be protected against water loss as vapor or liquid leakage through the walls.
- Prepare the epoxy 2216 resin coating and apply it on the walls of the container(s). Leave it for an hour for it to set and cure the coated container(s) at 66 °C for 2 hours.
NOTE: The epoxy coating can be dissolved in a solvent and sprayed for best results. - Accommodate the electrode pair on the opposite walls of the container(s) and glue them with the epoxy 2216 resin that was already applied.
- Use a long shielded coaxial cable and solder the ends on one side to the contact point of each of the electrode in a pair.
- Connect the other end of the shielded coaxial cable to the two terminals of the electrical conductivity measuring circuit.
NOTE: A simple electrical conductivity measuring circuit can be built with one terminal to an AC voltage source to generate electric pulses at a specified frequency and the other terminal to a voltage divider circuit to read the voltage drop across the electrode pair. The digital output pins of Arduino can be used in Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) mode to generate the required AC voltage. AC voltage is used to prevent corrosion of the electrodes. The voltage drop across the electrode pair can also be measured with the analog input pins of the Arduino with its in-built 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Other commercial circuits are also available. - Similarly, use thermal paste to glue the PT1000 Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) on one of the walls of the container(s).
- Use another long shielded coaxial cable to connect the one side to the two terminals of the PT1000 sensor and the other side to a temperature measuring circuit.
NOTE: A simple temperature measuring circuit can be built with one terminal to an DC voltage source and the other terminal to a voltage divider circuit to read the voltage drop across the PT1000 sensor which can be measured with the analog input pins of the Arduino with its in-built 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Other commercial circuits are also available.- To prepare the HABIT instrument for the experimental setup, separate the cable connection between the BOTTLE component and the Electronics Unit (EU). Then, unscrew the 8x M3 bolts of the BOTTLE, to remove the top lid and the HEPA filter holder in order to expose the six open cells. Before feeding in the salts to study, clean the cells and electrodes of the BOTTLE, preferably using an electrode cleaning solution and a sterile cotton swab to free of any particles or liquids.
- Carry out calibration of the electrical conductivity measurements of the setup prior to feeding in the salts, using a set of calibration standards with known electrical conductivity values to determine the calibration function coefficients for each electrode pair. Use the electrical conductivity measurement of 0.0364 µScm-1 (as zero or dry point) when BOTTLE was subjected to vacuum conditions in a thermal vacuum chamber and maintained at 25 °C as the absolute zero electrical conductivity of the system. Further, use two calibration standards: 84 µScm-1 and 1413 µScm-1 to derive a two-point calibration function as shown in equation (2).
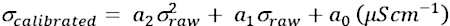 (2)
(2)
where, σcalibrated - Calibrated actual electrical conductivity,
σmeasured - Raw measured electrical conductivity, and
a2,a1,a0 - Polynomial constants - Fit the raw electrical conductivity measured by the setup into the derived calibration function to achieve a true electrical conductivity measurement.
NOTE: The initial calibration is achieved while maintaining the temperature of the system at 25 °C. However, as the temperature changes during the experiment, the electrical conductivity values change. As it gets complex to derive temperature vs electrical conductivity functions at different temperatures, we use temperature data only to determine the phase state of the brine. Nazarious et al.31 has discussed this aspect in detail.
2. Manipulation of the deliquescent salt samples
- Weigh a specific amount of salt or sample that is considered for the study. We weighed 1.5 g each of four different salts: calcium-chloride CaCl2, ferric-sulphate Fe2(SO4)3, magnesium-perchlorate Mg(ClO4)2, and sodium-perchlorate NaClO4in individual containers.
CAUTION: Some salts particularly perchlorates are corrosive and therefore any contact with skin or eye must be avoided.- Use proper chemical garments, goggles and nitrile gloves while handling the salts. In case of contact with skin or eye, immediately rinse with plenty of water and consult a doctor.
NOTE: In addition to the salts, we added 0.75 g of sodium salt of alginic acid (Super Absorbent Polymer, SAP) into each of the four containers with salt and mixed thoroughly to obtain a uniform salt-SAP mixture. We used SAP as a solidifying agent as a safety measure to avoid the brine to rise by capillarity and run off from the flight model instrument. While the salts absorb gaseous water from the atmospheric environment, the SAP absorbs water from a liquid state, from the liquid brine of salts once it is in contact with it. Adding SAP was purely due to the engineering limitations for storing the salts in Earth conditions (prior to ExoMars launch in 2022) and has less meaning for the experiment itself. Consequently, the electrical conductivity measurement is a result from the mixture of salt+SAP+water which is expected. Since the goal of this experiment is to monitor the absorption of water in the whole system, the changes in electrical conductivity from the dry state of salt+SAP to the hydrated states is deemed relevant for interpretation. The calibration procedure was also carried out for the same salt+SAP combination. - Use the same salt and SAP mixtures and weights that were used for the flight model of BOTTLE component of the HABIT/ExoMars instrument.
- Use proper chemical garments, goggles and nitrile gloves while handling the salts. In case of contact with skin or eye, immediately rinse with plenty of water and consult a doctor.
3. Feeding the salt samples in the experiment setup
- Carefully transfer the entirety of the previously weighed salt in step 2 into the experiment container(s).
NOTE: The previously weighed salt-SAP mixture was carefully transferred into the four cells of BOTTLE in the following order: Cell-2: calcium-chloride CaCl2, Cell-3: ferric-sulphate Fe2(SO4)3, Cell-4: magnesium-perchlorate Mg(ClO4)4, Cell-5: sodium-perchlorate NaClO4. Cell-1 and Cell-6 were left empty.- Follow the same order in the flight model of BOTTLE, so this configuration and experiment is targeted towards the calibration and interpretation of its operation on Mars.
- Level the top surface of the salts such that they cover the electrodes. Choose the amount of salts to achieve this criterion.
NOTE: Each salt-SAP mixture of BOTTLE weighed 2.25 g in total and covered the low electrode in each cell. This amount was chosen so that the brine formed will not overflow. - Use a HEPA filter to cover the top of the container(s). This will allow interaction of salts with the ambient relative humidity of the simulated environment.
NOTE: A nylon based HEPA filter with a holder frame was used to cover the salt-SAP mixtures in BOTTLE and the top lid of BOTTLE was secured with 8x M3 bolts.
4. Installation of the experiment setup in the simulation chamber
- Place the experiment container(s) in the simulation chamber32. Make sure of a good thermal contact between the working table of the chamber and the container(s).
- Place the electrical conductivity and temperature measurement circuit outside the chamber. This will avoid any temperature induced noises in the circuits that might compromise the measurements.
- Make the power and data connection between the measuring circuits and the container(s) through an intermediate connector of the simulation chamber.
NOTE: BOTTLE uses a dedicated split cable for its 2x DB-9 connectors of the EU to the interior DB-25 connector of the chamber. The split cable is a customized power and data connection cable specific for this purpose. From the exterior of the DB-25 connector of the chamber, another split cable with the power connections was plugged to a DC power supply and the 2x USB data connections to a laptop with the HABIT EQM LabView software installed.
5. Controls of the simulation chamber
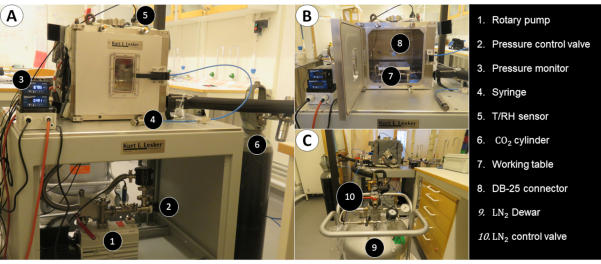
Figure 2: Controls of the simulation chamber32. Representation of the Mars simulation chamber with its various systems for controlling temperature, relative humidity, and carbon-dioxide pressure. Power and data connection outlets are also shown. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Maintaining the temperature of the working table between 20 °C and -30 °C
NOTE: The temperature of the working table is regulated using the liquid nitrogen (LN2) feedthrough system as per the protocol shown in Figure 2. Initially the chamber is maintained at the laboratory ambient temperature.- Open the valve for the flow of LN2. The temperature will start to decrease.
- Set the desired temperature on the feedback controller. The PT100 temperature sensor fitted on the working table acts as a feedback loop.
- Once the desired temperature is reached, close the valve to shut the flow of LN2.
- Maintaining the carbon-dioxide pressure
- Turn ON the vacuum pump until the pressure inside the chamber reads vacuum.
- Once the chamber is in vacuum, turn the vacuum pump OFF, and inject the chamber with CO2 gas until it reaches the pressure of 7-8 mbar.
- Maintaining the relative humidity
- Inject the water in increments of 0.5 mLusing a stainless-steel Swagelok syringe fitted on to the chamber. This will increase the relative humidity gradually.
NOTE: The syringe is in turn connected to a ball valve so the syringe can be used to inject water multiple times. - Ensure the pressure is within the limits. Otherwise, release the pressure by adjusting the valve.
- Inject the water in increments of 0.5 mLusing a stainless-steel Swagelok syringe fitted on to the chamber. This will increase the relative humidity gradually.
6. Electrical conductivity vs relative humidity experiment
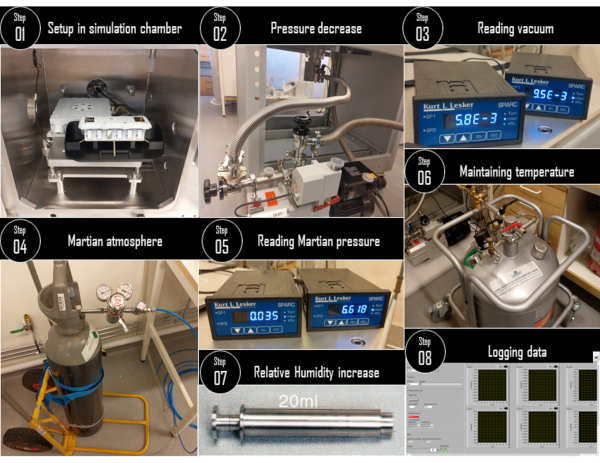

Figure 3: Electrical conductivity vs relative humidity experiment. Steps of the experiment protocol for performing the calibration experiment to derive the relationship of electrical conductivity as a function of relative humidity. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Turn the rotary vacuum pump ON to flush out all the air from inside the chamber. The pressure inside the chamber will reduce to an order of 10-3 mbar.
NOTE: The relative humidity will be close to zero. The ambient temperature of the working table of the chamber is around 20 °C. There may be an increase in the electrical conductivity and the BOTTLE temperature (deliquescence is an exothermic reaction) as the pressure is reduced. - Carefully inject the carbon-dioxide atmosphere from the gas cylinder to maintain a pressure between 7 and 8 mbar.
- Set the working table temperature to a certain value such that the PT1000 measuring the container temperature will record 20 °C.
- Wait for about 5 minutes at 20 °C to achieve equilibrium and begin the data acquisition following step 7.
- Slowly inject water inside the chamber using the syringe system and maintain the relative humidity at 10% and wait for 5 minutes to achieve equilibrium. If the pressure rises when increasing the relative humidity, adjust the rotary vacuum pump valve to remove the extra atmosphere.
- Slowing increase the relative humidity to 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90% and 100%. At every relative humidity value, maintain it for about 5 minutes to achieve equilibrium and begin data acquisition following step 7.
NOTE: This concludes one set of the calibration experiments as per the protocol shown in Figure 3. - The salt sample may have formed the brine by now. Discard the salt samples from the container(s).
- Renew the salt samples for the next experiment following step 8.
- Similarly, reduce the working table temperature to maintain the container temperature at 15 °C, 10 °C, 5 °C, 0°C, -5 °C, -10 °C, -15 °C, -20 °C, -25 °C, and -30 °C. At each stop, repeat steps 6.5 to 6.8 to make the measurement of the electrical conductivity of the salt samples.
NOTE: As a safety feature, below -33 °C, the BOTTLE heater will kick in to maintain a temperature between -30 °C and -33 °C. Therefore, we ran experiments until -30 °C. But one may choose to go for lower temperatures. - Rising to the ambient temperature from the coldest temperature of -30 °C could be achieved by shutting down the experiment, releasing the vacuum and opening the front door of the chamber allowing the laboratory ambient air to mix and naturally increase the container temperature. For additional data, one can choose to allow the temperature to naturally increase inside the chamber. It will be a very slow process though and may take in orders of 7-10 hours.
7. Logging and saving the data
- Use the in-built serial monitor of Arduino or a third-party serial monitor software (e.g,m Teraterm, Realterm, etc.).
- Configure the Arduino to read from the measurement circuits at a frequency of 1 Hz for one continuous hour followed by the first 5 minutes of every hour. This may be applicable for Marian day-night simulation described in step 9.
- Set the DC power supply voltage as specified for the measuring circuits.
NOTE: The power cable of HABIT is connected to a DC power supply of 28 V and the 2x USB data connections to a laptop with the HABIT EQM LabView software installed. The software has only Windows 10 support. - Enter the serial COM port for the data connection and execute the Arduino program.
NOTE: Refer to Device Manager to identify the correct COM ports. - Acquire data for the first 100 seconds and stop the data acquisition by closing the serial monitor. Remember to copy the data from the Arduino serial monitor window.
- Open a text editor and paste the copied data to save as .txt or .csv data file format for easier post-processing using MATLAB or Python.
NOTE: Third-party software may have auto saving function. - Name the data file to match the experiment description.
- For the next set of data acquisition, first power cycle the experiment setup by switching OFF and ON the DC power supply and repeat the steps 7.3 to 7.7.
- For the HABIT EQM LabView software: In the Main tab, enter the two COM ports COM Port 1 and COM Port 2, each corresponding to one of the USB data connections. Click Connect and then Start for data acquisition at a frequency of 1 Hz. Record the data for the first 100 seconds.
- View the acquired data by clicking the Debug tab and Open on Real-time data view. This will open a new window with multiple tabs each corresponding to different measurements of the HABIT instrument. For this experiment we are concerned about tabs: "Cell 2", "Cell 3", "Cell 4", "Cell 5", "EU Temperature" and "CU Temperature". The data will be saved as "Log.txt" in HEX format in the "C:\LABVIEW\Data" folder of the laptop. Re-run of the software will replace the existing data in the "Log.txt" file.
8. Renewing the salt samples
NOTE: This step is followed to introduce dry salt samples for each new experiment.
- Stop the experiment and carefully disconnect the cables and unload the experiment container(s) off the simulation chamber.
- Carefully remove the HEPA filter and the salt samples from the container(s) and put them in separate bio-hazard sealed bags.
NOTE: The perchlorates and the other salts are not safe for disposal in the sink with running water or at general waste disposal. Care must be taken to pack them in bio-hazard sealed bags and disposed as per the chemical waste disposal norms. If other samples are studied, such as regolith samples, or polymers etc., then the waste products can be handled as recommended by the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) of those products. - Gently clean and reset the container(s) for the next experiment.
- Follow the steps 2 to 4 to fill the salt samples in the container(s) and place it back inside the simulation chamber.
9. Simulation of a day-night cycle on Mars
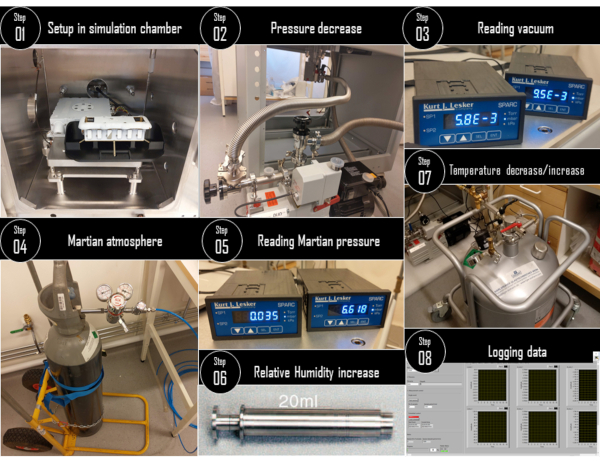

Figure 4: Simulation of a day-night cycle on Mars. Steps of the experiment protocol for performing the Mars Sol simulation. Please note that the steps 6 and 7 are switched from figure 3 since for the Martian day-night simulation, the relative humidity is set initially over 80% before the temperature decrease (day-night transition). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Follow the steps 2 to 4 to setup the demonstration experiment.
- Follow the step 7 to setup the data-logging of the experiment and acquire continuous data for the first hour and for the first 5 minutes of data every hour, at a frequency of 1 Hz.
NOTE: HABIT uses this kind of schedule to monitor at a good frequency and prevent over-exposing the electrodes to alternating current. - Simulating the environmental conditions at Oxia Planum, Mars in the chamber
NOTE: We used the SpaceQ Mars simulation chamber, a facility at the Luleå University of Technology, Sweden for this demonstration as shown in Figure 4.
NOTE: Oxia Planum is the planned landing site of ExoMars 2022 at Mars.- Turn the rotary vacuum pump ON to flush out all the air from inside the chamber. The pressure inside will reduce to an order of 10-3 mbar.
NOTE: The relative humidity will be close to zero. The ambient temperature of the working table of the chamber is around 20 °C. There may be an increase in the electrical conductivity and container temperature (deliquescence is an exothermic reaction) as the pressure is reduced. - Carefully inject the carbon-dioxide atmosphere from the gas cylinder to maintain a pressure between 7 and 8 mbar.
- Slowly inject water inside the chamber using the Swagelok syringe to gradually increase the relative humidity. Be careful to adjust the rotary vacuum pump valve to remove the extra atmosphere if the pressure increases beyond the required limits.
- Maintain the carbon-dioxide atmospheric pressure of about 7-8 mbar at about 80% relative humidity.
- Slowly open the LN2 feedthrough system value to reduce the working table temperature to simulate the Martian day-night transition. Observe the possible difference in working table temperature and the container temperature.
NOTE: The rate of temperature decrease can be controlled by adjusting the LN2 flow rate. - Allow the temperature to drop until the container temperature reads -30 °C (working table temperature of -70 °C), and then shut off the LN2 flow.
NOTE: As a safety feature, below -33 °C, the BOTTLE heater will kick in to maintain a temperature between -30°C and -33 °C. Therefore, we ran the experiment until -30 °C. But one may choose to go for lower temperatures. - The working table and the container(s) will slowly warm up to ambient laboratory temperature (night-day transition). The relative humidity will also likely increase and so does the pressure. Remember to operate the rotary vacuum pump valve to remove excess pressure.
NOTE: Here, with relative humidity, we mean to correlate the amount of water vapor in the air. Since the relative humidity sensor is measuring the air, it is reasonable to say that, higher the moisture content, higher the relative humidity. Initially, when the working table is frozen to -30 °C the water vapor is condensed and frozen on the table, and when the temperature increases this condensed water evaporate at Martian pressures and are sensed as moisture in the air by the relative humidity sensor. The changes in the ambient air relative humidity are thus due to a change in the state of water, and a release of frost from the working table to the air as vapor when the temperature increases. - When the container temperature reaches 20 °C (similar to working table temperature), shut down the experiment, releasing the vacuum and opening the front door of the chamber to remove the experiment setup.
- Turn the rotary vacuum pump ON to flush out all the air from inside the chamber. The pressure inside will reduce to an order of 10-3 mbar.
Results
The data acquired in HABIT are in HEX format and are converted to ASCII format before analyzing. The calibration experiments established a relationship between the electrical conductivity values corresponding to the hydrate forms of the four different salt-SAP mixtures at various Martian temperatures and relative humidity conditions. The relationship at 25 °C is shown in Figure 5A for air and Figures 5B-5E for the four different salt-SAP mixtures, calcium-chloride CaCl2- SAP, ferric-sulphate Fe2(SO4)3 - SAP, magnesium-perchlorate Mg(ClO4)2 - SAP, and sodium-perchlorate NaClO4- SAP, respectively. We observed and cataloged: i) the variability in electrical conductivity measurements as a function of temperature, and ii) the ranges of electrical conductivity of the air and the salt-SAP mixtures as a function of relative humidity. This information will be pivotal in interpreting the hydration level of the salt-SAP mixtures from the BOTTLE operation on Mars, considering the retrieved electrical conductivity, temperature and relative humidity conditions.
In Figure 5A, we observed a direct correlation of electrical conductivity and relative humidity for air. As the relative humidity inside the chamber was increased by injecting water in 0.5 mL increments, the air increased its relative humidity as it happens at Mars conditions. The electrical conductivity increased significantly. The lower electrode is presumably colder because of its proximity to the refrigerated table, this leads in turn to higher RH and higher EC. For the given combination of temperature and relative humidity at Martian pressures during this experiment, we also recorded a maximum electrical conductivity (not temperature-compensated) of air at a relative humidity of 59%. Figures 5B-5E show that all the four salt-SAP mixtures captured water to different extents. A gradual increase in electrical conductivity from RH=0% was observed for Calcium Chloride and Sodium Perchlorate, and an increase around RH=40-50% in case of Ferric sulphate and Magnesium Perchlorate. All the salt-SAP mixtures had the maximum value at 85%, the maximum we achieved inside the chamber.
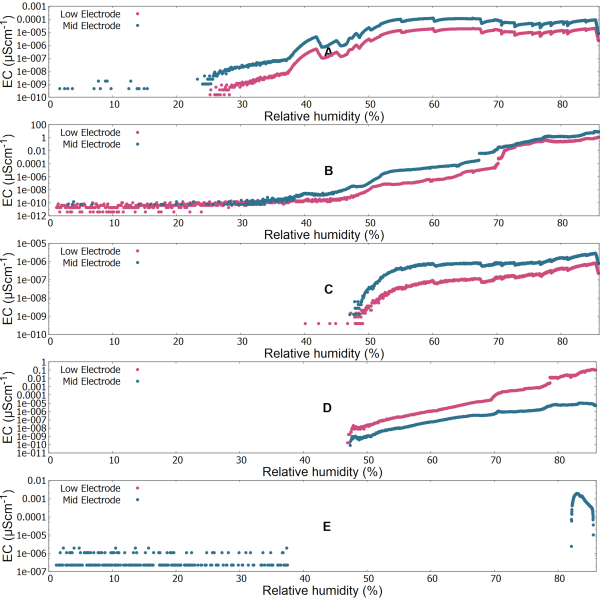
Figure 5: Electrical conductivity as a function of relative humidity (1% - 85%) at 25 °C. (A) Air, (B) calcium-chloride, (C) ferric sulphate, (D) magnesium-perchlorate, (E) sodium-perchlorate electrical conductivities are shown in log scale with base 10. Electronics Unit (EU) recorded a mean temperature of 25.27 °C (Min: 24.12 °C, Max: 25.95 °C), Container Unit (CU) recorded a temperature increase from 19.6 °C to 32.91 °C as a result of the exothermicity of water capture. The mean working table temperature was 19.11 °C and the mean air temperature was 19.16 °C. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Electrical conductivity of a salt depends on a variety of factors. At the end of the experiment, we noticed that ferric sulphate was the least hydrated (see Figure 7) showing electrical conductivity values lower than the air. The electrical conductivity between the electrodes is also sensitive to the area of contact with the salt+SAP mixture. Some of the granular material, including SAP, may be a better isolator than moisturized air. The air in the empty container had sufficient moisture content that moved freely resulting in a higher electrical conductivity (see Figure 5A) than the ferric sulphate which had no contribution in terms of enough water absorbed to show a significant electrical conductivity signal (see Figure 5C). We also observed water drops in the empty containers at the end of the experiments showing that the air in between the electrodes was at some point saturated and allowed for fog formation and some of it condensed on the sides, as seen in Figure 5A. The absence of low electrode conductivity could mean that the salt particles in contact with the lower electrode was completely frozen (coldest at the bottom of the instrument because of its direct contact with the working table of the chamber) showing no electrical conductivity.
As a demonstration practice of HABIT operation on Mars following a successful landing in early 2021, we simulated one Sol of the environment conditions at Oxia Planum, the planned landing site of the ExoMars 2022 mission. The obtained results mimic the day-night cycle of the BOTTLE operation on Mars and provides a first-hand data in relevant conditions. Figure 6 shows that during the simulation of the Martian day-night cycle, deliquescence has been observed in all the salt-SAP mixtures. Figures 6C-6F show the electrical conductivity values of the four different salt-SAP mixtures, calcium-chloride CaCl2- SAP, ferric-sulphate Fe2(SO4)3 - SAP, magnesium-perchlorate Mg(ClO4)2 - SAP, and sodium-perchlorate NaClO4- SAP, respectively.
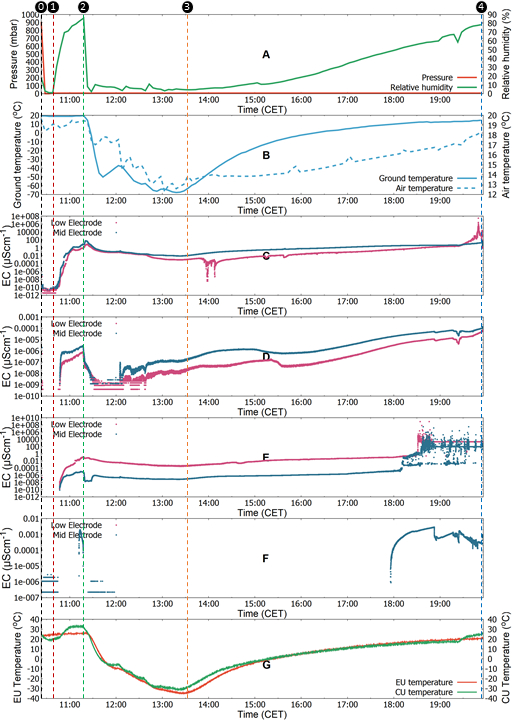
Figure 6: Calibrated electrical conductivity measurements of the Mars Sol simulation. (A) Pressure and relative humidity, (B) ground and air temperature, (C) calcium-chloride, (D) ferric sulphate, (E) magnesium-perchlorate, (F) sodium-perchlorate electrical conductivities (in log scale with base 10), and (G) Electronics Unit (EU) and Container Unit (CU) or BOTTLE temperatures are shown. Vertical lines with circled numbers indicate various phases of the simulation. 0-1: Pumping out air to attain vacuum and carbon-dioxide injection to maintain a 7-8 mbar pressure at constant temperature, 1-2: water injection to increase the relative humidity at constant temperature, 2-3: working table cooling ON to decrease the temperature (day-night transition), accompanied by a relative humidity decrease, and 3-4: working table cooling OFF to increase the temperature (night-day transition), accompanied by a relative humidity increase. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The initial ramp in the electrical conductivity may be attributed to the rapid pressure decrease while relative humidity remained high, accelerating the process of water capture followed by outgassing of the remaining water in the mixture. This was also consistent with the exothermicity of water capture process by the salts. The temperature increase in the Electronics Unit (EU) and BOTTLE may be a combination of a rapid depressurization (under constant volume) and the exothermic behavior of salt-water interaction. The pressure dip observed around 13:00 could be associated with reaching the lowest temperature in the working table, which is also coincident with a small uptick in the RH. At colder temperatures, the working table behaved as a water sink freezing the water droplets and hence the relative humidity of the air was low. During this phase of Martian day-night transition, there were less significant signs in the electrical conductivity curves. But, during the night-day transition, when the temperature increased and so did the relative humidity, the salt-SAP mixture began capturing water steadily as indicated by the increase in electrical conductivity in the later part of the experiment also mirrored by the sudden increase in the BOTTLE temperature. The final electrical conductivity values indicated the extent of water capture by each of the four salt-SAP mixtures as shown in Figure 7. All the salt-SAP mixtures captured water and particularly, calcium-chloride salt-SAP mixture produced liquid brine. The maximum electrical conductivity value of the CaCl2 brine of ̴100 µScm-1 is coherent with the literature31.
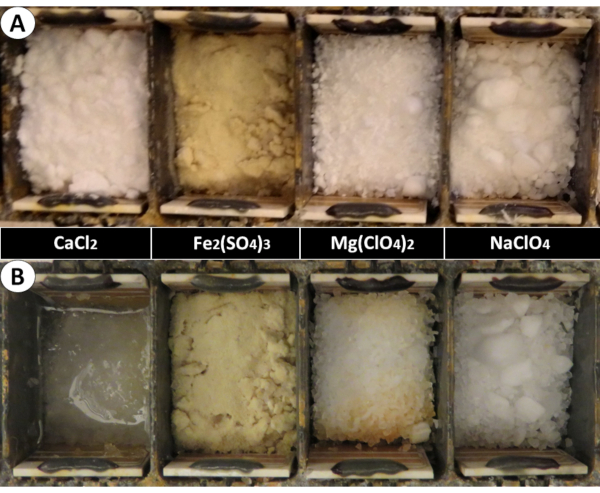

Figure 7: Images of the salt-SAP mixtures. (A) before and (B) after the Mars Sol simulation. Left to right: Initial conditions of 1.5 g each of calcium-chloride, ferric sulphate, magnesium-perchlorate, sodium-perchlorate with 0.75 g SAP in each salt. Calcium-chloride in the left corner produced liquid brine also showing relevant electrical conductivity values of ̴100 µScm-1. All other salt-SAP mixtures also captured considerable amounts of water as appearing wet in the images. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
This is the maiden attempt to characterize the electrical conductivity of the brine formation process in vacuum or Martian pressure conditions. The key element of this experiment is to simulate the Martian day-night cycle with the Mars simulation chamber to study the salts. The results of the salt deliquescence are shown as a representative result while the focus is more on achieving the required conditions to simulate Martian environment. With this first experiment, we now understand the process and the limitations of the chamber as mentioned in the discussion section of the manuscript. In the future experiments, we will follow this protocol for various science experiments that is relevant to process on Mars. Earlier studies have carried out the electrical conductivity measurements in ambient laboratory pressures27,28,29. Measuring in lower pressures poses a challenge and thus demanded a modification to the protocol used for the Earth pressure conditions. During a previous calibration campaign in a climate chamber under ambient pressures, different hydrates were prepared by adding defined amounts of salt and water, prior to each set of the experiments to derive the relationship between the electrical conductivity and the salt hydrate form at different Martian temperatures31. But, with Martian pressures, the added water used to form hydrates will eventually outgas when reducing the pressure, thus we started off every experiment with a dry salt-SAP mixture and regulated the relative humidity to transition through various hydrate forms.
Past studies monitoring the brine formation process using Raman spectroscopic methods, generally were performed with an individual granule of the salt particle in an environmental cell and observing the phase transitions in the O-H stretching region of the Raman spectra1,9,18. The electrical conductivity characterization of the brine formation process deemed to be more sensitive to intermediate phase transitions than the existing Raman spectroscopy and provided a continuous time series of the brine formation process27. From our experiments, we also demonstrated electrical conductivity as a viable measurement option for bulk salt samples with good precision.
During the design of the electrical conductivity measurement system for the HABIT instrument, we had challenges to solve. Selection of the electrode material was based on its resistance to corrosion and the surface smoothness to avoid sporadic glitches in the electrical conductivity measurements. The hygroscopic salts sometimes climb up along the walls of the container by capillarity and hence a choice of hydrophobic coating is essential. We used a coating based on an epoxy resin composition that prevented the brine from capillary rise. Also, the electrical characteristics such as the voltage of the electric pulse, its frequency and the current sense reference resistor were crucial for the design. BOTTLE uses a ±2.048 V bias voltage with an electric pulse of ±70 mV and ±700 V for low and high conductance modes. The electric pulses at 1 kHz passes through a gold electrode, and via the salt samples to study, and are read-out at a gold electrode on the other side with 10 k-ohm and 100-ohm reference resistors for low and high conductance modes respectively.
Since each of the experiments to characterize the electrical conductivity as a function of relative humidity, required a constant and stable temperature, the protocol is designed to accommodate within the temperature stability limits of the Mars simulation chamber. There is an observable difference in the working table temperature (regulated by the LN2 feedthrough system of the chamber) and the BOTTLE temperature due to the thermal isolation. This means that the working table temperature is not always identical with the BOTTLE temperature and the difference must be considered for an optimal experiment condition.
Future experiments in the Mars simulation chamber will include deriving a relationship between the air electrical conductivity and the relative humidity at different temperatures. During the Mars Sol simulation, we observed a possible correlation between the relative humidity of the air and its electrical conductivity. This may be relevant for calibrating the two empty cells at the two ends of BOTTLE and incorporate it with the calibration of the salt-SAP mixtures for more precise interpretation of their hydration level. To carry out this experiment, empty experiment container(s) can be adapted without any salt samples following the same experiment protocol.
The described experiment protocol provides a simpler, easily adaptable alternative way to monitor the brine formation process which can also be applied to other samples that may interact with atmospheric moisture. It could be complimentary for studies on understanding the physical and chemical properties of the brines formed by sea-salt mixtures that will be applicable to define conditions under which brines may react with cannister surfaces generally used to store nuclear fuel and nuclear wastes33,34. The corrosive properties of brines for different materials can be studied under different environment conditions by adapting the protocol. We applied this protocol to study the deliquescent properties of four mixtures of salt and SAP that we carry to Mars onboard the HABIT instrument. However, the hygroscopic properties of salt or salt mixtures in any form, for example, smoke particles can be analyzed for their cloud-nucleating potential24. The experiment protocol could also be applied to simulate various atmosphere-surface related phenomenon on Mars and elsewhere inside a laboratory.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The HABIT Engineering Qualification Model (EQM) that was used for the experiments was fabricated by Omnisys, Sweden, as part of the HABIT project development, under the supervision of MPZ and JMT, and funded by the Swedish National Space Agency (SNSA). HABIT and BOTTLE are the original ideas of MPZ and JMT. SpaceQ Mars simulation chamber is a Luleå University of Technology facility situated in Luleå, Sweden. The Kempe Foundation funded the design and fabrication of the SpaceQ chamber. The SpaceQ chamber was manufactured by Kurt J. Lesker Company, U.K., under the supervision of MPZ. MPZ has been partially funded by the Spanish State Research Agency (AEI) Project No. MDM-2017-0737 Unidad de Excelencia “María de Maeztu”- Centro de Astrobiología (INTA-CSIC) and by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (PID2019-104205GB-C21). AVR and JMT acknowledge support from the Wallenberg Foundation.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 84 µS/cm and 1413 µS/cm conductivity calibration standard | Atlas Scienific | CHEM-EC-0.1 | |
| Arduino Uno | Arduino | 8058333490090 | |
| Calcium Chloride | Sigma Aldrich | CAS Number: 10043-52-4 | Anhydrous, free-flowing, ≥96% |
| Carbon Dioxide gas cylinder | AGA Gas | ||
| Experiment container | 3D printed in PLA or milled in aluminum/other metal | ||
| EZO Conductivity circuit | Atlas Scienific | EZO-EC | |
| EZO RTD circuit | Atlas Scienific | EZO-RTD | |
| Ferric Sulphate | Sigma Aldrich | CAS Number: 15244-10-7 | 97% |
| Gold electrodes | Custom designed | ||
| HEPA filter | Nitto | NTF9317-H02 | |
| Liquid Nitrogen tank | AGA Gas | ||
| Magnesium Perchlorate | Sigma Aldrich | CAS Number: 10034-81-8 | Free-flowing, ≥99.0% |
| Pressure gauge | Pirani | CCPG−H2−1 | 1x10-9 to 1000 mbar |
| PT100 sensor | |||
| PT1000 sensor | |||
| Scotch-Weld Epoxy Adhesive | 3M | EC-2216 B/A | |
| Sodium Perchlorate | Sigma Aldrich | CAS Number: 7601-89-0 | Free-flowing, ≥98.0% |
| Sodium salt of alginic acid (SAP) | Sigma Aldrich | CAS Number: 9005-38-3 | Powder |
| Sterile water | VWR Chemicals BDH | CAS Number: 7732-18-5 VWR: 75881-014 | Water ASTM Type II, Reagent Grade |
| Swagelok syringe | Fischer scientific | KD Scientific 780812 | |
| T/RH probe | Vaisala | HMT 334 | (-70 to + 180C) and (0 to 100 % RH) |
| Teraterm | |||
| Whitebox Labs Tentacle Shield | Atlas Scienific | TEN-SH |
References
- Gough, R. V., et al. Brine formation via deliquescence by salts found near Don Juan Pond, Antarctica: laboratory experiments and field observational results. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 476, 189-198 (2017).
- Gough, R. V., Chevrier, V. F., Tolbert, M. A. Formation of liquid water at low temperatures via the deliquescence of calcium chloride: implications for Antarctica and Mars. Planetary and Space Science. 131, 79-87 (2016).
- Farris, H. N., Davila, A. Deliquescence-driven brine formation in the Atacama Desert, Chile: Implications for liquid water at the Martian surface. 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference. , (2016).
- Martín-Torres, J., Zorzano, M. -. P. Should We Invest in Martian Brine Research to Reduce Mars Exploration Costs. Astrobiology. 17 (1), 3-7 (2017).
- Martín-Torres, J., et al. Transient liquid water and water activity at Gale crater on Mars. Nature Geoscience. 8, 357-361 (2015).
- Zorzano, M. -. P., Mateo-Martí, E., Prieto-Ballesteros, O., Osuna, S., Renno, N. Stability of liquid saline water on present day Mars. Geophysical Research Letters. 36, 20201 (2009).
- Chevrier, V. F., Hanley, J., Altheide, T. Stability of perchlorate hydrates and their liquid solutions at the Phoenix landing site, Mars. Geophysical Research Letters. 36, 10202 (2009).
- Gough, R. V., Chevrier, V. F., Baustian, K. J., Wise, M. E., Tolbert, M. A. Laboratory studies of perchlorate phase transitions: support for metastable aqueous perchlorate solutions on Mars. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 312 (3-4), 371-377 (2011).
- Gough, R. V., Chevrier, V. F., Tolbert, M. A. Formation of aqueous solutions on Mars via deliquescence of chloride-perchlorate binary mixtures. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 393, 73-82 (2014).
- Fischer, E., Martínez, G. M., Elliott, H. M., Rennó, N. O. Experimental evidence for the formation of liquid saline water on Mars. Geophysical Research Letters. 41, 4456-4462 (2014).
- Nuding, D. L., Rivera-Valentin, E. G., Davis, R. D., Gough, R. V., Chevrier, V. F., Tolbert, M. A. Deliquescence and efflorescence of calcium perchlorate: an investigation of stable aqueous solutions relevant to Mars. Icarus. 243, 420-428 (2014).
- Nuding, D. L., Davis, R. D., Gough, R. V., Tolbert, M. A. The aqueous stability of a Mars salt analog: instant Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 120, 588-598 (2015).
- Nikolakakos, G., Whiteway, J. A. Laboratory investigation of perchlorate deliquescence at the surface of Mars with a Raman scattering lidar. Geophysical Research Letters. 42, 7899-7906 (2015).
- Chojnacki, M., McEwen, A., Dundas, C., Ojha, L., Urso, A., Sutton, S. Geologic context of recurring slope lineae in melas and coprates chasmata, Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 121, 1204-1231 (2016).
- Pál, B., Kereszturi, &. #. 1. 9. 3. ;. Possibility of microscopic liquid water formation at landing sites on Mars and their observational potential. Icarus. 282, 84-92 (2017).
- Rivera-Valentín, E. G., et al. Constraining the potential liquid water environment at Gale Crater, Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 123 (5), 1156-1167 (2018).
- Bhardwaj, A., et al. UAV Imaging of a Martian Brine Analogue Environment in a Fluvio-Aeolian Setting. Remote Sensing. 11 (18), 2104 (2019).
- Martin, S. T. Phase transitions of aqueous atmospheric particles. Chemical Reviews. 100 (9), 3403-3454 (2000).
- Primm, K. M. Freezing of perchlorate and chloride brines under Mars-relevant conditions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 212, 211-220 (2017).
- Primm, K. M. The effect of mars-relevant soil analogs on the water uptake of magnesium perchlorate and implications for the near-surface of Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 123 (8), 2076-2088 (2018).
- Toner, J. D. The formation of supercooled brines, viscous liquids, and low-temperature perchlorate glasses in aqueous solutions relevant to Mars. Icarus. 233, 36-47 (2014).
- Altheide, T., et al. Experimental investigation of the stability and evaporation of sulfate and chloride brines on Mars. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 282 (1-4), 69-78 (2009).
- Slank, R. A., Chevrier, V. F. Experimental simulation of deliquescence and implications for brine formation at the Martian surface. Mars Workshop on Amazonian Climate. , (2018).
- Freney, E. J., Martin, S. T., Buseck, P. R. Deliquescence Measurements of Potassium Salts. American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting. , (2007).
- Baustian, J., Wise, M. E., Tolbert, M. A. Depositional ice nucleation on solid ammonium sulfate and glutaric acid particles. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. 10 (5), 2307-2317 (2010).
- Yang, L., Pabalan, R. T., Juckett, M. R. Deliquescence Relative Humidity Measurements Using an Electrical Conductivity Method. Journal of Solution Chemistry. 35 (4), 583-604 (2006).
- Heinz, J., Schulze-Makuch, D., Kounaves, S. P. Deliquescence induced wetting and RSL-like darkening of a Mars analogue soil containing various perchlorate and chloride salts. Geophysical Research Letters. 43, 4880-4884 (2016).
- McKay, C. P., Friedmann, E. I., Gómez-Silva, B., Cáceres-Villanueva, L., Andersen, D. T., Landheim, R. Temperature and moisture conditions for life in the extreme arid region of the Atacama desert: Four years of observations including the El Niño of 1997-1998. Astrobiology. 3 (2), 393-406 (2003).
- Davis, W. L., de Pater, I., McKay, C. P. Rain infiltration and crust formation in the extreme arid zone of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Planetary and Space Science. 58 (4), 616-622 (2010).
- Martín-Torres, J., et al. The HABIT (HabitAbility: Brine Irradiation and Temperature) environmental instrument for the ExoMars 2022 Surface Platform. Planetary and Space Science. 190, (2020).
- Nazarious, M. I., Vakkada Ramachandran, A., Zorzano, M. -. P., Martin-Torres, J. Calibration and preliminary tests of the Brine Observation Transition To Liquid Experiment on HABIT/ExoMars 2020 for demonstration of liquid water stability on Mars. Acta Astronautica. 162, 497-510 (2019).
- Vakkada Ramachandran, A., Nazarious, M. I., Mathanlal, T., Zorzano, M. P., Martín-Torres, J. Space Environmental Chamber for Planetary Studies. Sensors. 20 (14), 3996 (2020).
- Carroll, S., Rard, J., Alai, M., Staggs, K. Technical Report: Brines formed by multi-salt deliquescence. Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL). , (2005).
- Bryan, C. R., Schindelholz, E. J. Properties of Brines formed by Deliquescence of Sea-Salt Aerosols. Sandia National Laboratories. , (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved