Method Article
Isolation and Culture of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Human Mandible
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
The present protocol describes an efficient procedure for isolating and culturing of human mandibular bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells using the whole bone marrow adherence method. The cultured cells were identified by cell proliferation assays, flow cytometry, and multilineage differentiation induction.
Abstract
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) have shown great potential in bone regeneration, immune modulation, and treating refractory chronic diseases. Various origins have been found to obtain hMSCs recently, while bone marrow was still considered the main source. Bone marrow-derived MSCs (BMSCs) from different donor bone sites have distinct characteristics due to microenvironmental factors. Studies have shown that BMSCs from maxillofacial bone may have greater proliferative and osteogenic capacities than BMSCs from long bones or the iliac crest. And maxillofacial BMSCs were considered more suitable for stem cell therapy in the maxillofacial tissues. The mandible, especially the ascending ramal area with sufficient marrow, was a feasible donor site for harvesting BMSCs. This study described a protocol for harvesting, isolating, and culturing human mandibular bone marrow-derived MSCs (hmBMSCs). Furthermore, immunophenotyping of hmBMSCs, proliferation assays, and in vitro induction of osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic differentiation was performed to identify the cultured cells. Applying this protocol can help the researchers successfully obtain enough high-quality hmBMSCs, which is necessary for further studies of the biological function, microenvironmental effects, and clinical applications.
Introduction
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) are multipotent cells that can be differentiated into various cell types, such as osteocytes, adipocytes, and chondrocytes from mesodermal lineage, hepatocytes, and pancreocytes from endodermal lineage, and neurocytes from ectodermal lineage1. Thus, hMSCs have shown great potential in tissue regeneration. Furthermore, hMSCs are powerful immunomodulators that can regulate the microenvironment in the host tissues and effectively treat chronic refractory diseases2. Therefore, hMSCs have been widely used in cell therapy of clinical studies. Consequently, it is important to obtain sufficient hMSCs with high-quality in a convenient way successfully.
Since hMSCs were first reported in the bone marrow, many alternative MSCs sources have been found, such as adipose tissue, synovium fluid, skeletal muscle, amniotic fluid, endometrium, dental tissues, and umbilical cord1,3. However, bone marrow remains the principal source of hMSCs for most preclinical and clinical studies, and bone marrow-derived MSCs (BMSCs) are taken as a standard for comparing MSCs from other sources4. For years, the iliac crest or long bones (the tibia and femur) have been the most popular anatomic locations for obtaining bone marrow1,5. However, the iliac crest or long bones have different embryonic origins and development patterns compared with the maxillofacial bones5,6. Many clinical, laboratory and developmental studies proved that BMSCs from different origins showed site-specific properties, and the grafted BMSCs retain the properties of the donor site after implantation at the recipient site5,6,7,8,9. From the perspective of developmental origin, the maxillofacial tissues, such as the maxilla, mandible, dentin, alveolar bone, pulp, and periodontal ligament, arise exclusively from neural crest cells. In contrast, the iliac crest and long bones are formed by mesoderm. In addition, mandibles are created by intramembranous ossification, while axial and appendicular skeletons undergo endochondral ossification. Moreover, compared to the iliac crest and long bones, some clinical studies have shown that maxillofacial bone marrow-derived hMSCs had better cellular proliferative activity and differentiation capability6,8. Therefore, BMSCs from the maxillofacial areas are expected to be a better choice for maxillofacial tissue regeneration and maxillofacial chronic refractory diseases therapy.
The mandible is composed of two-layer thick cortical bones with cancellous bone marrow in between so that it can load the power of chewing. Therefore, the mandible, especially the ascending ramal area, is usually used as a donor site to obtain autologous bone grafts in craniomaxillofacial surgeries10. And in surgeries such as mandibular sagittal split ramus osteotomy and mandibular angle reduction plasty, parts of mandibular cortical and cancellous bone have to be removed to achieve a pleasing facial contour. Those discarded cancellous bones could be a potential resource for hMSCs. However, few published studies described the protocol to isolate rapidly and culture high-quality human mandibular bone marrow-derived MSCs (hmBMSCs).
The present study uses a modified whole bone marrow adherence method to introduce a reliable and reproducible protocol for the isolation and culture of hmBMSCs. And the stem cells were identified by flow cytometric immunophenotyping of MSCs, proliferation assays, and multilineage differentiation induction. Applying this standard procedure may help the researchers obtain high-quality human mandibular bone marrow-derived MSCs, which is important in further studies of the biological function, microenvironmental effects, and clinical applications.
Protocol
The procedure for harvesting human mandibular bone specimens was approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Stomatology, the Fourth Military Medical University. The study followed the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. All donors for the present study were informed of the possible risks and the study objectives. The age of the donors ranged between 18-40 years, and there was no gender bias. Written consent was obtained from all the human participants.
1. Surgery preparation
- Select the appropriate donor.
- Select the patients as donors who plan to undergo surgeries such as mandibular setback following sagittal split ramus osteotomy and mandibular angle reduction plasty.
- Prepare the preservation solution.
- Supplement 30 mL of phosphate buffer saline (1x PBS) with 1% penicillin and streptomycin in a sterile and enzyme-free 50 mL centrifuge tube on the day before surgery. Store it in a refrigerator at 4 °C.
- On the day of surgery, put the centrifuge tube with preservation solution in an icebox and keep it in the operating room 1 h before the surgery.
- Sterilize the instruments to isolate the bone marrow on the day before surgery, including scissors, tweezers, and knives at 120 °C and 0.27 MPa pressure for 20 min.
- Prepare α-MEM culture medium by mixing minimum essential medium alpha (α-MEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin and streptomycin.
- Prepare an osteogenic differentiation medium by mixing α-MEM culture medium with 50 mM ascorbic acid, 10 mM β-glycerol phosphate, and 0.1 mM dexamethasone (see Table of Materials).
- Prepare adipogenic differentiation medium A by mixing α-MEM culture medium with 1 mM dexamethasone, 0.2 mM indomethacin, 10 µg/mL of insulin, and 0.5 mM 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) (see Table of Materials).
- Prepare adipogenic differentiation medium B by mixing α-MEM culture medium with 10 µg/mL of insulin.
- Prepare chondrogenic differentiation medium by mixing Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium with high glucose (HG-DMEM) and 100 nM of dexamethasone, 100 g/mL of sodium pyruvate, 25 mg/mL of vitamin C, 40 mg/mL of proline, 10 ng/mL of TGF-β3, and 1% of ITS (see Table of Materials).
NOTE: The osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic differentiation medium can be prepared in-house, as mentioned above. However, commercially available kits for the same were used (see Table of Materials) in the present study.
2. Harvesting human mandibular bone specimen
- Before surgery, carefully study the three-dimensional computerized tomographic scan images and surgical simulation planning of the donors (Figure 1).
- Select the mandibular site that the donor plans to remove in surgery and is rich in cancellous bone with bone marrow as the donor site.
- Disinfect and drape the patient before operating.
- Resect the selected donor site of the mandible using the ultrasonic osteotome blade (see Table of Materials), avoiding inferior alveolar nerve injury and donor bone impairment.
- Put the mandibular bone specimens into the preservation solution (step 1.2) as soon as possible.
- Place the preservation solution with bone specimens in an icebox until the isolation of MSCs starts in the laboratory.
NOTE: The isolation of MSCs needs to be started as soon as possible after harvesting to preserve the viability of the cells. If the isolation of MSCs cannot be conducted immediately, the preservation solution with bone specimens can be stored in an icebox or refrigerated at 4 °C for a maximum of 2 h.
3. Isolation and cultivation of human mBMSCs
- Get the bone specimens out of the preservation solution and dip them in 1x PBS with 1% penicillin and streptomycin for 5 min on a clean bench of the laminar flow cabinet.
NOTE: This step aims to wash away the blood clot and residual oral fluids and further eliminate the microorganism because the mouth is not a completely sterile environment. Before cell isolation and cultivation, wash and disinfect hands with alcohol and wear disposable sterile gloves and masks. - Clean the adherent soft tissue and blood blot on the bone surface using sterile wet gauze.
- Fill a 6 cm sterile culture dish with 5 mL of α-MEM culture medium.
- Put the bone into the sterile culture dish and cut it into small pieces (almost 2-3 mm3 volume) with a sterilized knife or scissor.
NOTE: Hold the bone specimens with tweezers to avoid a finger cut. - Aspirate α-MEM culture medium in the culture dish with a 1 mL disposable sterile syringe.
- Insert the syringe needle with α-MEM culture medium deep into the bone marrow cavity of the cancellous bone specimen pieces.
- Flush the bone marrow into the culture dish with the syringe from all sides of the bone specimen pieces, at least 5-10 times per side.
- Repeat steps 3.5-3.7 until all the bone specimen pieces turn pure white to ensure that as much bone marrow is flushed into the culture medium.
NOTE: The total operation time of the above steps from 3.1-3.8 needs to be controlled within 30 min on ice. - Remove and discard all the bone specimen pieces with tweezers. Remove other small fragments using a cell filter with 70 µm pore size.
- Shake the culture dish softly to make the flushed cells evenly distributed.
- Place the culture dish into a cell incubator and culture the cells at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2.
- On the third day of culture, check the cell morphology and growth status under a light microscope. Remove half of the culture medium with no adherent cells and tissue fragment; add 3 mL of fresh α-MEM culture medium.
- At culture day 7, remove all the culture medium and add 5 mL of fresh α-MEM culture medium.
- Then, refresh the α-MEM culture medium every 3 days.
- Check the cell morphology and growth every day.
NOTE: When the primary cell cultures (P0) reach 70%-80% confluence after 7-10 days of culture, carry out the cell passage.
4. Cell passage
- At 70%-80% confluence, remove all the culture medium of P0 cells. Wash the culture dish gently with 1x PBS twice to clean the residual culture medium.
- Add 1 mL of 0.25% trypsin with 0.02% EDTA to the culture dish to digest the cells. Shake the culture dish softly to ensure that the trypsin is evenly distributed. Place the culture dish at 37 °C for 3 min.
- Check the cells under the microscope. When 70%-80% of the cells get contracted and rounded, add 2 mL of α-MEM culture medium to stop the digestive reaction.
- Gently blow the dish surface several times with a pipette to blow down the cells.
- Transfer the cell suspension into a 15 mL centrifuge tube. Centrifuge the cell suspension at 200 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cells with α-MEM culture medium. Seed P0 cells in culture flasks (25 cm) for expansion with a 1:2 splitting ratio. The first passage cells were called P1 cells.
- When the P1 cells reach 70%-80% confluence, repeat the cell passage following steps from 4.1-4.6. The second-generation cells were called P2 cells.
- Change the expansion splitting ratio to 1:3 after the third generation cell passage.
- Use P3 to P5 cells to conduct identification experiments.
5. Flow cytometric analysis
- Digest P3 to P5 MSCs using 0.25% trypsin with 0.02% EDTA, following steps 4.1-4.5.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cells in 1x PBS at a 1 x 106 cells/mL concentration.
- Transfer the cells into microcentrifuge tubes with 100 µL of the cell suspension per tube.
- Add immunolabeled mouse monoclonal anti-human antibodies into the microcentrifuge tubes.
NOTE: For the present study, Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated antibody against CD45, fluorescein-isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated antibody against CD90, CD34, and CD44 were used4,11 (see Table of Materials), and the dilutions of the antibodies were all 1:100. The dilutions of antibodies need to follow the manufacturer's instructions. PBS will be served as control. - Incubate the antibodies and PBS control at room temperature in the dark for 30 min.
- Centrifuge the tubes at 800 x g for 5 min at room temperature. Discard the suspension and resuspend the cells in 0.5 mL of 1x PBS. Repeat this step twice.
- Load the tubes into the flow cytometer (see Table of Materials). Count the fluorescence-labeled cell numbers using a flow cytometer with a minimum of 10,000 events.
NOTE: It is better to start the flow cytometer cell count process immediately after the immunofluorescence labeling procedure. If not, the cells need to be fixed in 1% paraformaldehyde, stored at 4 °C in the dark, and finish the process within 24 h.
6. Cell proliferation assay
- Use P3 cells to perform the cell proliferation assay. Digest P3 MSCs with 0.25% trypsin, following steps 4.1-4.5.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cells with α-MEM culture medium.
- Count the cell number with a hemocytometer, and seed the cells on 96-well culture plates at a density of 3 x 103 cells per well, a total of 35 wells, 5 wells for each counting day (at day 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7). Refresh the culture medium of cells every 3 days.
- At each counting day, discard α-MEM culture medium of the certain five wells for the certain counting day, and then add 100 µL of culture medium and 10 µL of CCK-8 solution (see Table of Materials). Incubate at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Place the culture plates in a microplate spectrophotometer (see Table of Materials) and measure the optical density value of five wells for each counting day (a total 7 counting days) at a wavelength of 450 nm. Use five wells of the culture medium without cells as blanks.
- Record the optical density value of every well, calculate the average value and standard deviation of five wells for each counting day, and plot the cell growth curve5,12.
7. Multilineage differentiation
- Perform osteogenic differentiation induction following the steps below.
- Digest the P3 cells with trypsin following steps 4.1-4.5. Seed the cells at 2 x 105 cells/cm2 in a 6-well plate. Add 2.5 mL of α-MEM culture medium per well.
- When the cells reach 60%-70% confluence, change the culture medium into the osteogenic induction medium (step 1.5). Then, change the induction medium every 3 days.
- Check the cells under a microscope every 3 days after induction. Observe the cell morphology and seek for obvious mineralization nodes.
- After 7 days of induction, perform the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining to evaluate the calcification of cells.
- Use 1x PBS to wash the cells twice gently. Add 4% paraformaldehyde to fix the cells at room temperature for 30 min. Then, use 1x PBS to wash the cells twice.
- Add ALP staining solution (see Table of Materials) and incubate at room temperature for 10 min.
NOTE: Different kinds of ALP staining solution can stain the cells with different colors, such as dark gray, red, and blue. In this protocol, the cells were stained blue. The incubation time can be prolonged if the staining color is not obvious. Some ALP solution staining kits may be poisonous; read the instructions carefully before use, wear gloves and a mask during the experiment, and wash hands carefully after use. - Wash the cells with water to stop the ALP staining reaction. Observe blue pigmented granules in the cells under a light microscope and capture the photos. Use the Image J software to quantitatively analyze the staining degree.
- Perform alizarin red staining (see Table of Materials) to evaluate the mineralization capacity of the cells.
NOTE: Obvious mineralization nodes formation of the differentiated cells usually can be seen after 21 days of induction. - Use 1x PBS to wash the cells twice gently. Then, add 4% paraformaldehyde to fix the cells at room temperature for 30 min.
- Wash the cells with 1x PBS twice, add 0.1% alizarin red staining solution (see Table of Materials) and incubate for 20 min. Again, wash the cells with 1x PBS twice.
- Observe the red nodules among fixed cells under a light microscope, indicating calcium deposits of osteogenic differentiation of cultured cells, and capture the photos.
- To quantify the amount of alizarin red, add 10% cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC, see Table of Materials) to the alizarin red-stained cells and incubate at room temperature for 30 min.
- Aspirate 50 µL of the CPC solution and measure the optical density (OD) at a wavelength of 540 nm using a microplate spectrophotometer.
- Perform adipogenic differentiation induction.
- Seed the P3 cells in a 6-well plate using the procedure described above (step 7.1).
- When the cells get 80%-90% confluence, change the culture medium into adipogenic differentiation medium A (step 1.6).
- Incubate the cells with adipogenic differentiation medium A at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 for 3 days.
- Change the induction medium to adipogenic differentiation medium B (step 1.7), and incubate for 1 day.
- Change the medium back to adipogenic differentiation medium A and incubate for 3 days. Then, replace with medium B for 1 day. Repeat this cycle 3-5 times until lipid droplets can be seen under the microscope.
NOTE: The lipid droplets can be seen approximately 21 days after induction. - Use the adipogenic differentiation medium B to culture the cells for an additional 7 days; then, big and round lipid droplets can be seen under the microscope. Refresh the medium B every 3 days.
- Remove the induction medium and use 1x PBS to wash the cells gently. Then, add 4% paraformaldehyde to fix the cells at room temperature for 10 min.
- Wash the cells with 1x PBS twice; then, incubate the cells with oil red O staining solution (1 mL per well, see Table of Materials) for 15 min. Again, wash the cells with 1x PBS twice.
- Place the cells under a microscope, and observe the red lipid droplets to evaluate the adipogenesis of differentiated cells.
- Perform chondrogenic differentiation induction.
- Digest and transfer the P3 cells into a 15 mL centrifuge tube with cell numbers of 5 x 105.
- Centrifuge the tube at 250 x g for 4 min at room temperature. Discard the supernatant by carefully decanting the top solution.
- Add 0.5 mL of chondrogenic differentiation medium (step 1.8) into the tube to resuspend the cells, and centrifuge the tube again at 150 x g for 5 min at room temperature. Repeat this step twice.
- Loosen the centrifuge tube cap to facilitate air exchange. Place the tube into the incubator and induce the cells with 0.5 mL of chondrogenic differentiation medium at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2.
- Keep the centrifuge tube stable without removing or shaking it within 24 or 48 h, until the cells start pelleting. Flick the centrifuge tube bottom to suspend the cell pellet in the differentiation medium (step 1.5).
- Renew the chondrogenic differentiation medium with a pipette every 3 days. Avoid aspirating away the cell pellet.
- Induce the cells at least for 21 days until the pellet accretes to a 2 mm diameter.
- Wash the pellet with 1x PBS, and fix it with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min. After dehydration and paraffin embedding13, section the pellet with a thickness of 3 µm using a microtome (see Table of Materials).
- Put the sections on glass slides. Stain the slides with Alcian blue solution (see Table of Materials) for 1 h at 37 °C. Wash the stained slides with water. Place the slides under a light microscope and capture photos of the blue-stained acid mucopolysaccharide indicating cartilage tissues.
Results
A mandibular bone specimen was successfully collected from the patient. And the time from cutting with the ultrasonic osteotome blade to placing the bone fragment into the centrifuge tube is about 5 min. None of the potential complications happened in and after the resection procedure, including damage of the inferior alveolar nerve or dental root, infection, vascular rupture and bleeding, mucosal injury, accidental bone fracture, etc. The hmBMSCs were successfully cultured, passaged, and differentiated without contamination.
In the present study, many adhered cells were seen under the microscope on the third day after the initial culture. On the seventh day, most of the adherent cells were already attached to the culture dish. Normally, the cultured cells reached 70%-80% confluence after 7-9 days of initial culture. After passage, the P3 cells were usually thought to be purified MSCs, which showed spindle-shaped, plastic-adherent, and fibroblast-like morphology (Figure 2). And the identification experiments were conducted in P3 to P5 cells. Cell proliferation assay, the cells growth rate increased rapidly from the third day of culture, and the increased rate slowed down on day 6 (Figure 2).
According to the definition given by the International Society for Cellular Therapy, MSCs have a positive and negative expression of particular surface molecules. In this study, the flow cytometric analysis of culture cells showed positive expression of CD44, CD90, and negative expression of CD45, CD34, which is consistent with the definition4,11 (Figure 3). In the Multilineage differentiation ability experiments, the cultured cells showed strong osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic differentiation capability. After 7 days of osteogenic induction, the extracellular matrix calcium deposition emerged under the microscope. After 21 days of osteogenic induction, the cultured cells showed obvious mineralization nodes, and the nodes were stained red with alizarin red staining (Figure 4). For adipogenesis, lots of accumulated round lipid droplets stained red by Oil-red-O staining were seen in the cytoplasm after 21 days of adipogenic induction (Figure 4). After 21 days of chondrogenic differentiation induction, the cell pellet slides showing cartilage-like tissue with cartilage lacuna can be stained blue (Figure 4).
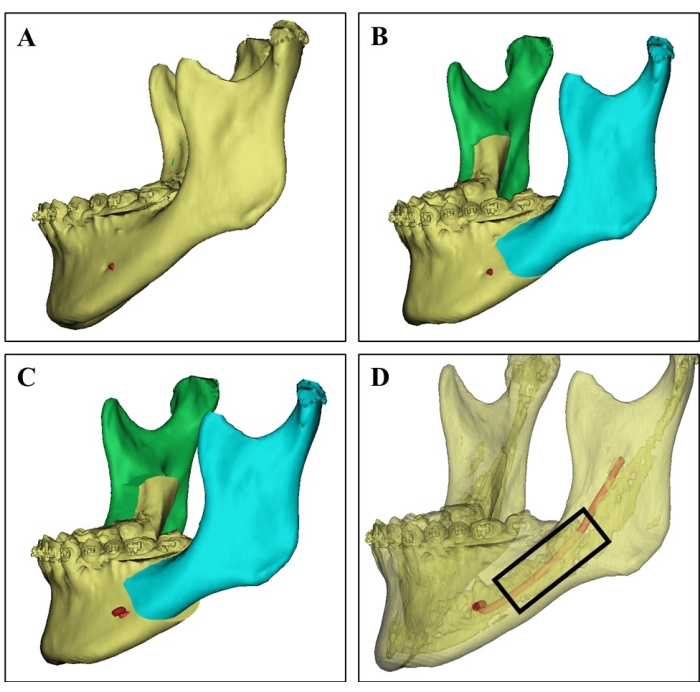
Figure 1: Donor site selection on 3D CT image. (A) 3D CT image of the donor mandible from a 21-year-old female patient. (B) Surgical simulation of the bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy of the mandible. (C) Surgical planning shows the setback of a split mandible. (D) 3D CT image showing the cortical bone (the translucent part), the cancellous bone rich in bone marrow, and the inferior alveolar nerve (red) based on different CT values, which can guide the surgeons to select the donor site and avoid nerve injury. Cancellous bone chips were harvested from the region in the black rectangle. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
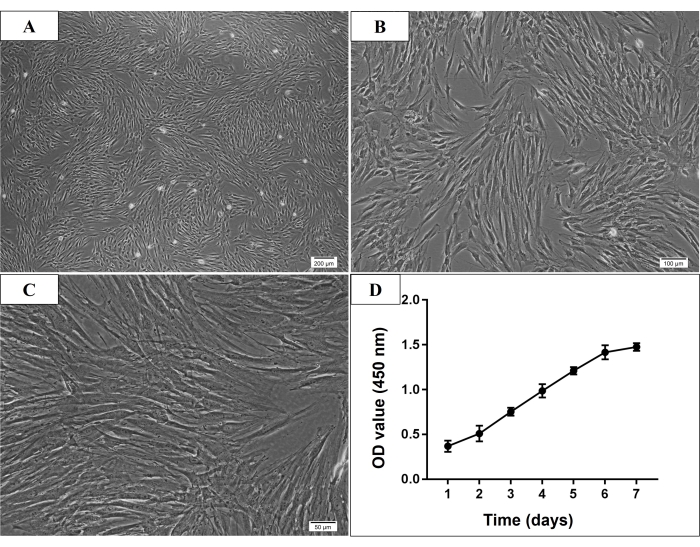
Figure 2: Microscopic morphology and growth curve of P3 human mandible-derived bone marrow stem cells (hmBMSCs). (A-C) Spindle-shaped, plastic-adherent, and fibroblast-like morphology of P3 hmBMSCs (Scale bar = 200 µm, 100 µm, 50 µm for A, B, C, respectively). (D) The cell growth curve showed that the growth rate of hmBMSCs increased rapidly from the third day of culture and the increase rate slowed down on the sixth day of culture. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
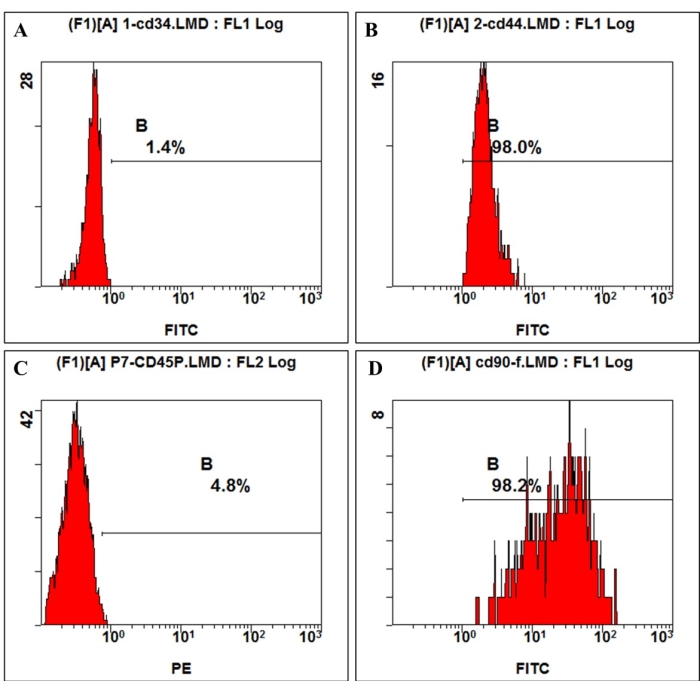
Figure 3: Cell surface antigen expression on hmBMSCs was detected by flow cytometry. Flow cytometry analysis showed that hmBMSCs were negative for CD45 (A) and CD44 (C), positive for CD44 (B), and CD90 (D). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
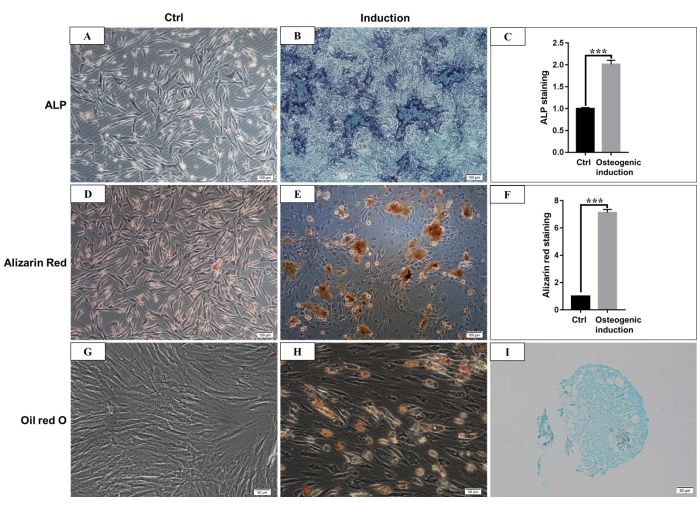
Figure 4: Osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic differentiation of hmBMSCs. (A) ALP staining of hmBMSCs after 7 days of culture without osteogenic differentiation induction (Scale bar = 100 µm). (B) ALP staining of hmBMSCs after 7 days of osteogenic differentiation induction (Scale bar = 100 µm). (C) Quantitative results of ALP staining positive area (***P < 0.001). (D) Alizarin red staining of hmBMSCs without osteogenic differentiation (Scale bar = 100 µm). (E) The formation of obvious mineralization nodes can be seen after 21 days of osteogenic differentiation of hmBMSCs, and it can be stained red with alizarin red staining (Scale bar = 100 µm). (F) Quantitative results of alizarin red staining (***P < 0.001). (G) Oil red O staining of hmBMSCs without adipogenic differentiation (Scale bar = 50 µm); (H) Round lipid droplets were seen after 21 days of adipogenic differentiation of hmBMSCs, and the lipid droplets were stained red with oil red O staining (Scale bar = 50 µm). (I) Alcian blue staining was positive after 21 days of chondrogenic differentiation induction (Scale bar = 50 µm). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
Recently, the hMSCs therapy has shown great promise in tissue regeneration and the treatment of many refractory diseases, such as immune dysfunction diseases, systemic hematological diseases, cancers, or trauma, in numerous clinical trials1,14,15,16,17. Among various sources of MSCs, bone marrow remains the most widely used and easily accessed source. We used human mandibular cancellous bone chips to successfully culture BMSCs using the whole bone marrow adherence method described in the present protocol. To date, there are four main approaches to isolate stem cells from bone marrow, including the whole bone marrow adherence method, density gradient centrifugation method, fluorescent cell sorting method, and magnetic-activated cell sorting method10. The whole bone marrow adherence method is simple, easy to operate, cheap, and can get large amounts of adherent cells. However, the limitation of this method was the low purity of primary cultured BMSCs, which were mixed with hematopoietic cells and fibroblasts. After refreshing the culture medium of primary cells regularly, the non-adherent hematopoietic cells were discarded along with the discarded medium. Also, the fibroblasts can be cleared through cell passage, and P3 cells were highly purified BMSCs. So P0 to P2 cells cannot be used for cell therapy, which means extra time was needed to purify the stem cells. Using fluorescent cell sorting and magnetic-activated cell sorting methods, one can get more purified BMSCs, while the two methods are expensive, and a long selection time can impair cell viability11. To prove that the cultured cells were MSCs, we referred to the definition of human MSCs proposed by the Mesenchymal and Tissue Stem Cell Committee of the International Society for Cellular Therapy, which included plastic adherent character, positive and negative expression of certain phenotypes, such as CD45, CD90 and so on, and multilineage differentiation ability18.
In most studies, femurs and iliac crest were the main sources of BMSCs, compared to maxillofacial bones, such as the mandible and maxilla9,16. However, the site-specific characteristic theory of hBMSCs in recent studies showed that hBMSCs from different bones had different characters in differentiation ability, proliferative activity, osteogenesis, and immunity6,8. The site-specific difference may be related to different embryological origins, adaptation to functional demands at each skeletal site, microenvironment, local vascular supply, hormonal effects, etc. Furthermore, studies showed that grafted iliac bone exhibited more rapid vertical loss than the jawbone within 6 months after the bone graft8. Otherwise, studies have found that the proliferative activity of MSCs from mandibular marrow was superior to those from iliac marrow5,8,19,20. And this proliferative activity difference was attributed to the characters that the mandible had more blood supply and a faster bone turnover rate than the ilium5,6,8. Studies also revealed that BMSCs from the mandible expressed a higher level of Runx-2 and OCN than those from femurs, and the osteogenic ability of BMSCs from the mandible was equal to or higher than those from femurs and ilium5,19,21. The adherence to titanium ability of hmBMSCs was also found stronger than BMSCs from femurs, which suggested hmBMSCs were more appropriate to be used in oral implantology5. In addition, a 3-year clinical study to reconstruct the alveolar defect found that the regenerated bone of MSCs from the dental pulp was composed of a fully compact bone with a higher matrix density, while the hm BMSCs regenerated spongy bone similar to normal human alveolar bone struct22. In conclusion, hmBMSCs were ideal therapeutic stem cells for maxillofacial regeneration and other diseases due to the same embryological origin and their superior characteristics.
However, the mandible has less bone marrow than femurs and ilium, so it is important to obtain enough bone marrow and BMSCs from the mandible for clinical use. Human iliac aspirates can obtain large amounts of bone marrow to isolate MSCs. Researchers also used the mandibular aspirates to obtain MSCs, while the initial yield of the MSCs from mandibular aspirates was three times lower than that of iliac aspirates21. Additional incisions were needed to collect enough mandible marrow aspirates, adding additional surgical trauma. Furthermore, studies have shown that the proliferative potential of the MSCs from mandible bone chips may be superior to those from mandible marrow aspirates8,21. Therefore, in this study, the discarded mandible cancellous bone chips were used to isolate MSCs. Because both sides of the mandible were included in sagittal split ramus osteotomy or mandibular angle reduction plasty, we can get enough mandible marrow from the patients without any extra harm. Recently, computer-assisted technology has been widely used in oral and maxillofacial surgery to improve the surgical effect and reduce surgical complications23. To avoid injury of the mandible and nerve during mandible bone marrow harvesting, the 3D CT image of the donors' mandible was obtained, and surgical planning of the donors was analyzed to decide the donor sites and to implement surgical simulation in the study; thus, none of the surgical complications happened. The ultrasonic osteotome blade, a tissue-specific device allowing surgeons to make precise osteotomies while protecting adjacent soft tissue24, was also used to avoid soft tissue injury and preserve the obtained bone marrow activity.
In summary, this study described a reliable, simple, safe, and cheap protocol to isolate and culture adequate human mandibular MSCs, which can be used in cell therapies of dental and maxillofacial tissues.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No.81903249) and the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi province (No.2019JQ-701, No.2022JZ-50).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 4% Paraformaldehyde | PlantChemMed | PC-00005 | |
| Adipogenic differentiation medium | OriCell, Cyagen Biosciences | HUXMX-90031 | |
| Alcian blue solution | OriCell, Cyagen Biosciences | ALCB-10001 | |
| Alcohol | Macklin | e809056 | |
| Alizarin red staining solution | Solarbio | G1452 | |
| ALP staining solution | Beijing ComWin Biotech Co.,Ltd. | CW0051S | |
| Autoclave | ALP Co., Ltd., Japan | CL-40L | |
| CCK-8 solution | Yeasen Biotech Co., Ltd. | 40203ES80 | |
| Cell filter (70 μm pore size) | BD Biosciences | 352350 | |
| Cell incubator | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 41334177 | |
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5805ZP761456 | |
| Centrifuge tube (50 mL, 15 mL) | Sangon Biotech | F600888-9001 | |
| Cetylpyridinium chloride | Aladdin | H108696 | |
| Chondrogenesis differentiation medium | OriCell, Cyagen Biosciences | HUXMX-90041 | |
| Clean bench/Laminar flow cabinet | BIOBASE | BBS-DDS00030 | |
| Culture dish (6 cm) | Thermo | 150462 | |
| Culture flasks (25 cm) | Thermo | 156367 | |
| Culture plates (96-well, 6-well) | Corning-Costar | 352350 | |
| Disposable sterile gloves and masks | Sangon Biotech | F516018-9001;F516038-9001 | |
| Disposable sterile syringe (1 mL) | Shaanxi longkangxin Medical Instrument Co., Ltd | 1.00009E+11 | |
| Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium with high glucose (HG-DMEM) | Hyclone | SH30022.01B | |
| EDTA | Solarbio | E8040-500g | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | PlantChemMed | PC-00001 | |
| Flow cytometer | Beckman Coulter | EPICS XL | |
| Fluorescein-isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated mouse monoclonal anti-human antibody against CD34 | Biolegend | 343503 | |
| Fluorescein-isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated mouse monoclonal anti-human antibody against CD44 | Biolegend | 338804 | |
| Fluorescein-isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated mouse monoclonal anti-human antibody against CD90 | Biolegend | 328108 | |
| Hemocytometer | Koraba | 30119480698 | |
| Icebox | Sangon Biotech | F615002-0001 | |
| Image J software | National Institute of Mental Health | ||
| Light microscope | OLYMPUS | IX71-2L20944 | |
| Microcentrifuge tubes | Sangon Biotech | F601620-0010 | |
| Microplate spectrophotometer | BioTek-EPOCH | 259091 | |
| Microtome | Feica | 1003001 | |
| Mimics software | Materialise | ||
| Minimum essential medium alpha (α-MEM) | Hyclone | SH30265.01 | |
| Oil red O staining solution | Solarbio | G1261 | |
| Osteogenic differentiation medium | OriCell, Cyagen Biosciences | HUXMA-90021 | |
| Penicillin and streptomycin | PlantChemMed | PC-86115 | |
| Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) | PlantChemMed | PC-00003 | |
| Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated mouse monoclonal anti-human antibody against CD45 | Biolegend | 304008 | |
| Pipette | SORFA | 320511 | |
| ProPlan CMF 3.0 | Materialise | ||
| Scissors, tweezers and knives | Shanghai Jinzhong Surgical instrument Co., Ltd | ZJA030,YAA110,J11010 | |
| Sterile wet gauze | HENAN PIAOAN GROUP Co., Ltd | ||
| Trypsin | Gibco | 17075029 | |
| Ultrasonic osteotome blade | Stryker Instruments | 5450-815-107 |
References
- Ullah, I., Subbarao, R. B., Rho, G. J. Human mesenchymal stem cells - current trends and future prospective. Bioscience Reports. 35 (2), 1-8 (2015).
- Brown, C., et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Cell therapy and regeneration potential. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 13 (9), 1738-1755 (2019).
- Trohatou, O., Maria, G. R. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regenerative medicine: Past, present, and future. Cellular Reprogramming. 19 (4), 217-224 (2017).
- Heo, J. S., Choi, Y., Kim, H. S., Kim, H. O. Comparison of molecular profiles of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta and adipose tissue. International Journal of Molecular Medicine. 37 (1), 115-125 (2016).
- Li, C. J., Wang, F. F., Zhang, R., Qiao, P. Y., Liu, H. C. Comparison of proliferation and osteogenic differentiation potential of rat mandibular and femoral bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Stem Cells and Development. 29 (11), 728-736 (2020).
- Lloyd, B., et al. Similarities and differences between porcine mandibular and limb bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Archives of Oral Biology. 77 (5), 1-11 (2017).
- Yamaza, T., et al. Mouse mandible contains distinctive mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Dental Research. 90 (3), 317-324 (2011).
- Akintoye, S. O., et al. Skeletal site-specific characterization of orofacial and iliac crest human bone marrow stromal cells in same individuals. Bone. 38 (6), 758-768 (2006).
- Mendi, A., Ulutürk, H., Ataç, M. S., Stem Yılmaz, D. cells for the oromaxillofacial area: Could they be a promising source for regeneration in dentistry. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 11 (44), 101-121 (2019).
- Hong, Y. Y., et al. Isolation and cultivation of mandibular bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (162), e61532 (2020).
- Chu, D. T., et al. An update on the progress of isolation, culture, storage, and clinical application of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 21 (3), 708 (2020).
- Yu, Y. J., et al. Activation of mesenchymal stem cells promotes new bone formation within dentigerous cyst. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 11 (1), 476 (2020).
- Sadeghipour, A., Babaheidarian, P. Making formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded blocks. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1897, 253-268 (2019).
- Mathiasen, A. B., et al. marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment in patients with ischaemic heart failure: final 4-year follow-up of the MSC-HF trial. European Journal of Heart Failure. 22 (5), 884-892 (2020).
- Maqsood, M., et al. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: Sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine. Life Sciences. 01 (256), 118002 (2020).
- Reinders, M. J., et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell therapy with early tacrolimus withdrawal: The randomized prospective, single-center, open-label TRITON study. American Journal of Transplantation: Official Journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 21 (9), 3055-3065 (2021).
- Shi, H. Y., et al. marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer progression by secreting thrombospondin-2. Cell Proliferation. 54 (10), 13114 (2021).
- Dominici, M., et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8 (4), 315-317 (2006).
- Aghaloo, T. L., et al. Osteogenic potential of mandibular vs. long-bone marrow stromal cells. Journal of Dental Research. 89 (11), 1293-1298 (2010).
- Dong, W. J., et al. Phenotypic characterization of craniofacial bone marrow stromal cells: unique properties of enhanced osteogenesis, cell recruitment, autophagy, and apoptosis resistance. Cell and Tissue Research. 358 (1), 165-175 (2014).
- Lee, B. K., Choi, S. J., Mack, D., Oh, S. H. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from the mandibular marrow aspirates. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontics. 112 (6), 86-93 (2011).
- Giuliani, A., et al. Three years after transplants in human mandibles, histological and in-line holotomography revealed that stem cells regenerated a compact rather than a spongy bone: biological and clinical implications. Stem Cells Translational Medicine. 2 (4), 316-324 (2013).
- Chen, Y. W., et al. Computer-assisted surgery in medical and dental applications. Expert Review of Medical Devices. 18 (7), 669-696 (2021).
- Gilles, R., Couvreur, T., Dammous, S. Ultrasonic orthognathic surgery: enhancements to established osteotomies. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 42 (8), 981-987 (2013).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved