このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
炎症性プラークの赤外蛍光(NIRF)血管内分子イメージング、マルチモーダルアプローチの近くin vivoでの動脈硬化のイメージングに
要約
プラークの生物学の2次元血管内分子イメージングのための我々は詳細に新しい近赤外蛍光(NIRF)カテーテルを in vivoで。 NIRFのカテーテルは、プラーク熱心な起動可能とターゲット近赤外蛍光色素の存在に報告することによって、炎症など主要な生物学的プロセスを可視化することができます。カテーテルは臨床工学と電力要件を利用し、ヒトの冠状動脈のアプリケーションを対象としています。以下の調査研究では、小説を利用したマルチモーダルイメージング戦略を説明 in vivoで血管内NIRFイメージにカテーテルとタンパク質分解アクティブ炎症ウサギatheromataにおける炎症性プラークを定量化する。
要約
The vascular response to injury is a well-orchestrated inflammatory response triggered by the accumulation of macrophages within the vessel wall leading to an accumulation of lipid-laden intra-luminal plaque, smooth muscle cell proliferation and progressive narrowing of the vessel lumen. The formation of such vulnerable plaques prone to rupture underlies the majority of cases of acute myocardial infarction. The complex molecular and cellular inflammatory cascade is orchestrated by the recruitment of T lymphocytes and macrophages and their paracrine effects on endothelial and smooth muscle cells.1
Molecular imaging in atherosclerosis has evolved into an important clinical and research tool that allows in vivo visualization of inflammation and other biological processes. Several recent examples demonstrate the ability to detect high-risk plaques in patients, and assess the effects of pharmacotherapeutics in atherosclerosis.4 While a number of molecular imaging approaches (in particular MRI and PET) can image biological aspects of large vessels such as the carotid arteries, scant options exist for imaging of coronary arteries.2 The advent of high-resolution optical imaging strategies, in particular near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF), coupled with activatable fluorescent probes, have enhanced sensitivity and led to the development of new intravascular strategies to improve biological imaging of human coronary atherosclerosis.
Near infrared fluorescence (NIRF) molecular imaging utilizes excitation light with a defined band width (650-900 nm) as a source of photons that, when delivered to an optical contrast agent or fluorescent probe, emits fluorescence in the NIR window that can be detected using an appropriate emission filter and a high sensitivity charge-coupled camera. As opposed to visible light, NIR light penetrates deeply into tissue, is markedly less attenuated by endogenous photon absorbers such as hemoglobin, lipid and water, and enables high target-to-background ratios due to reduced autofluorescence in the NIR window. Imaging within the NIR 'window' can substantially improve the potential for in vivo imaging.2,5
Inflammatory cysteine proteases have been well studied using activatable NIRF probes10, and play important roles in atherogenesis. Via degradation of the extracellular matrix, cysteine proteases contribute importantly to the progression and complications of atherosclerosis8. In particular, the cysteine protease, cathepsin B, is highly expressed and colocalizes with macrophages in experimental murine, rabbit, and human atheromata.3,6,7 In addition, cathepsin B activity in plaques can be sensed in vivo utilizing a previously described 1-D intravascular near-infrared fluorescence technology6, in conjunction with an injectable nanosensor agent that consists of a poly-lysine polymer backbone derivatized with multiple NIR fluorochromes (VM110/Prosense750, ex/em 750/780nm, VisEn Medical, Woburn, MA) that results in strong intramolecular quenching at baseline.10 Following targeted enzymatic cleavage by cysteine proteases such as cathepsin B (known to colocalize with plaque macrophages), the fluorochromes separate, resulting in substantial amplification of the NIRF signal. Intravascular detection of NIR fluorescence signal by the utilized novel 2D intravascular NIRF catheter now enables high-resolution, geometrically accurate in vivo detection of cathepsin B activity in inflamed plaque.
In vivo molecular imaging of atherosclerosis using catheter-based 2D NIRF imaging, as opposed to a prior 1-D spectroscopic approach,6 is a novel and promising tool that utilizes augmented protease activity in macrophage-rich plaque to detect vascular inflammation.11,12 The following research protocol describes the use of an intravascular 2-dimensional NIRF catheter to image and characterize plaque structure utilizing key aspects of plaque biology. It is a translatable platform that when integrated with existing clinical imaging technologies including angiography and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), offers a unique and novel integrated multimodal molecular imaging technique that distinguishes inflammatory atheromata, and allows detection of intravascular NIRF signals in human-sized coronary arteries.
プロトコル
実験的大動脈腸骨動脈のアテローム性動脈硬化症の発生:in vivo動物モデルで
1)ベースライン血管造影およびバルーンの削剥
- ベースライン血管造影およびバルーンの削剥を取得する前に、ニュージーランドホワイトウサギは1週間のための高コレステロール血症(1%)食を供給されます。この動物は、ウサギの大動脈iliacs血管がヒト冠状動脈(2.5〜3.5ミリメートル)と同じ口径であり、2)高脂血症、バルーン傷害モデルが同じような炎症細胞(マクロファージが付いた炎症を起こしてアテローム性動脈硬化症を生成する1)などの翻訳関連性のために利用されている人間のアテローム性動脈硬化症のように)と分子(カテプシン)。
- コレステロール摂食に続いて、動物は、プロポフォールとケタミンで麻酔です。 1インチの腹側正中の首の切開は、サイズ15メス刃を用いて使用して行われます。鈍的切開の技術を使用して、気管の右側にある筋膜の下にある筋肉が露出している。左sternocephalicusの筋肉は、その結合組織の接合に沿って分離され、右総頸動脈を露出している。動脈は、迷走神経から分離されている。近位および遠位縫合糸ループは、撤回し、閉塞を可能にするために動脈に配置されます。 2mm厚1は動脈切開をベベル5フランス語(1.67ミリメートル外径が)血管シースを挿入し、ヘパリン(1000μ/mL、〜150units/kg)シースを介して動脈内に投与されているを介して行われます。
- 造影剤(Ultravistが)その後、遠位大動脈と両方腸骨動脈の制御の血管造影を得るために2秒の期間にわたって(1〜2mLの)注入されます。
- 腸骨大腿動脈と大動脈は、内皮削剥によって負傷している。標準的なX線透視法を用いて、3FRフォガティの塞栓摘除カテーテルは、遠位腸骨大腿動脈内に配置し、0.3から0.5コントラストのCC(50%contrast/50%生理食塩水)または空気で膨らませている。カテーテルは、その膨張した状態で近位に左腎動脈の離陸までの右腸骨と遠位大動脈に沿った距離を引き出される。バルーンの削剥に続いて、血管造影は、血管の開存性を文書化するために繰り返されます。血管造影に続いて、すべてのカテーテル及びシースが削除され、近右総頸動脈を結紮され、筋肉や筋膜が4 / 0吸収性縫合糸で縫合し、皮膚切開は4 / 0、非吸収性縫合糸で閉じられます。
- 動物は、1用量の抗生物質(Cephazolin、0.5グラムIM)の投与で回復するために許可されています。は0.01 mg / kgのブプレノルフィンIM(必要に応じて日に二回)を含む鎮痛薬。動物は、その後4週間後のバルーンの削剥のための1%のコレステロールを続けています。週5で、動物は、0.3%コレステロール食に移行されています。
ウサギAtheromataの統合されたマルチモーダルイメージング
2)注射ナノセンサーを使用してタンパク質分解アクティブ炎症プラークの標識、血管造影、血管内超音波(IVUS)、およびウサギアテロームのin vivoで血管内NIRFイメージングで
- バルーン損傷およびイメージングの前に24時間以下の8週間は、ウサギは耳静脈を経由して静脈内500ナノモル/ kgのProsense/VM110(パーキンエルマー)を注入されています。
- 注入24時間後、動物を麻酔し、動脈のアクセスは左総頸動脈(ステップ1.2参照)を介して取得されています。動脈内ヘパリン(150単位/ kg)に投与される。ベースライン血管造影は、上記のように得られる。
- IVUSカテーテルは臨床的冠動脈できる0.014インチワイヤーにロードされ、シースに挿入されます。透視を使って、線の放射線不透過性の先端は右腸骨動脈内に遠位方向に配置されている。 IVUSカテーテルは、標準的な臨床モノレールの技術を使用して近位腸骨動脈内に進めています。
- 100mmのプルバックが開始され、画像が記録されます。容器の長手方向の再建が得られ、内腔のプラークが識別されます。
- 右腸骨動脈内に遠位方向に配置されているNIRFカテーテル11,12は、0.014インチワイヤー(モノレールシステム)にロードされ、カテーテルを慎重にシースとイメージングヘッドに挿入されます。
- 複数の自動pullbacks(1 mm /秒縦引き戻し、毎分30発)が行われ、アテローム性動脈硬化症のゾーン内の蛍光シグナルが記載されています。画像が記録され、信号の範囲に基づいて適切なスケーリングと窓とのさらなる処理が実現されます。
3)安楽死および ex vivo大動脈腸骨組織の分離
- 安楽死は安楽死剤の1cc(390mgペントバルビタールナトリウムと50mgのフェニトインナトリウムの溶液)を、静脈内、単回注入で実現されます。
- 下大静脈は、血液の透明になるまで動脈樹を、0.9%生理食塩水で灌流される。アテローム性動脈硬化大動脈および腸骨動脈を同定し、周囲の組織からフリー解剖されています。 liのほかに、小型の2 × 2 cmの断片バージョン、腎臓、脾臓、心臓も得られる。
- 血管内NIRFイメージングカテーテルとex vivoで NIRFイメージングは、この段階で行うことができます。イメージングヘッドは右腸骨動脈または分岐部に配置されるまで、近位大動脈に血管が引き伸ばされているとNIRFカテーテルを再挿入されます。複数の自動pullbacksは(2.6参照)上記のように実行されます。
解離した大動脈および腸骨動脈の4) エクスビボ蛍光反射イメージング(金)
- 解剖組織は、生理食塩水の10-20 CCに置かれ、金の分析(コダックイメージステーション4000MMプロ、ケアストリームヘルス社)のために輸送される。
- 大動脈、腸骨血管が近似リアルタイムの長さやイメージに引き延ばされている複数の波長で得られる[白色光、緑色蛍光チャンネル(EX 495nmの、全角515 nm)を、Cy5の(元565 nmの、全角670 nm)およびCy7(EX波長650nm、全角760 nm)に]チャンネル。露光時間のシリーズは、各波長のために利用されている(0.1 - 30秒)と取得された画像は、DICOMや、さらなる分析のための16ビットスケーリングされていないTIFFファイルとしてエクスポートされます。陽性および陰性対照として、臓器(肝臓、脾臓、腎臓および心臓が)同じようなチャンネルと露光時間で撮像する。
- 近赤外チャンネルの増加信号(780nm +)の領域は、アテローム性動脈硬化動脈に記載されています。
セクショニングと免疫組織化学的分析のため5)組織の埋め込み
- 正常の領域(非損傷した組織、つまり、左腸骨動脈)とプラークの領域が識別され、組織の小5〜10ミリメートルのリングは、OCT(最適切断温度)メディアに埋め込まれています。ブロックは切片まで-80℃で保存されています。
- 切片と免疫組織化学的分析のための標準的な技術が実行されます。ヘマトキシリンおよびエオシン染色、ラム- 11およびカテプシンBの染色が行われている。
マルチモーダル画像の分析と統合(血管造影、IVUS、NIRFとFRI)
NIRFと金のイメージ6)の処理
- NIRFと金(赤外線780nmのチャネル付近で撮影)pullbacksから画像データを含むDICOMファイルはそれぞれ、MATLABとOsiriXはソフトウェアを使用して処理されます。信号強度の全範囲を表示するために適切なウィンドウが達成されます。最後の画像は、TIFFファイルとしてエクスポートされます。
- ファイルは、標準的な画像処理ソフトウェア(基調講演を使用することができる)にインポートされます。画像は、基準点(血管造影、腸骨の分岐、および腎動脈上すなわち椎骨)に基づいて整列されます。正常な血管とプラークの領域が識別されます。
- 興味(ROI)の領域は手動で追跡(プラークの正常組織や地域のため)と信号強度が金とNIRF画像の両方に対して、それぞれ、OsiriXは、MATLABを用いて取得されていることを意味している。適切なトレースを導くために、容器の長手方向のIVUS画像が使用され、正常な血管とプラークの同定が容易に識別されます。
- ターゲットへのバックグラウンド(TBR)の比率は、プラークのゾーンに対して計算されます。
代表的な結果:
上記のプロトコルの完了時に、我々は、識別することができますし、大動脈および腸骨血管内で炎症性プラークの拡張カテプシンプロテアーゼ活性の領域を特徴づける。起動可能なナノセンサー(Prosense/VM110)の注入は、私たちはタンパク質分解アクティブなプラークを識別することができます。これらは、近赤外チャンネル(750 nm)で金を用いて画像のように明るいまたは信号激しいゾーンで表示されます。 NIRFのpullbacksはNIRF信号の解剖学的に登録を許可IVUSと金とのアライメントによって増加信号強度と相関する。計算されたプラークのTBRは、金とNIRFから入手している(図3を参照してください:NIRF TBR 4.2意味、金TBR 2.9意味)と同様であった。明るいプラークの免疫組織化学的分析は、RAM - 11とプラークの領域(データは示さず)のカテプシンB活性の強い存在を確認。
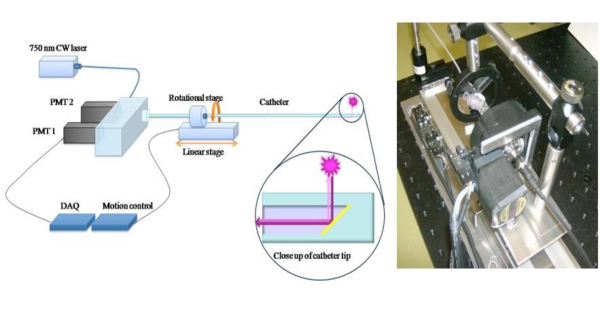
図1。 1D NIRFセンシングアプローチ6の臨床的可能性を拡張するには、2D NIRFカテーテルの概略 、我々は新たな血管内イメージングのための2次元NIRF -カテーテルを構築した。11,12特注のカテーテルは、光ファイバ(125ミクロンの直径に収納で構成されていますポリエチレンチューブで:2.9F)それは、750 nmのレーザー励起源を使用して点灯します。レーザー光が繊維軸に対して90度の角度で放出される。システムは真の2次元画像を得るために付随する360度のイメージングと長手方向の引き戻しを有効にするには2つの自動化されたモータ(回転と並進)を利用しています。画像はあくまで参考11から許可を得て使用。
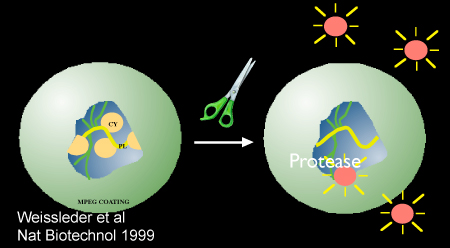
図2。ナノセンサーの回路図を実証プロテアーゼを介した活性化、Prosense/VM110。参考文献10より許可を得て使用されるイメージ。

図3。 生体とex vivoでのプラークTBRs(バックグラウンド比ターゲットへ) の
ディスカッション
炎症を起こして高リスクまたは脆弱なプラークは、心筋梗塞の大多数の可能性が高い責任があります。症状の発症に先立ってこのようなプラークの同定は、両方の結果を予測し、薬物療法を導く臨床的に重要な意味を持っています。このようなX線血管造影などの従来の冠状動脈の画像診断法は、通常、内腔の狭窄の特性評価ではなく、ハイリスク、通常は非狭窄病変の基礎となる生物学的プ...
開示事項
水産庁 - 元コンサルタント、VisEn医療、謝礼、ボストンサイエンティフィック
謝辞
この作品のサポートは、健康補助金の国民の協会によって提供されていました#R01 HL 108229、米国心臓協会サイエンティスト開発グラント#0830352N、ハワードヒューズ医学研究所のキャリア開発賞、ブロードビューベンチャーズ、欧州共同体の第七次フレームワーク計画(助成金の下でFP7/2007-2013契約#235689)、およびMGHウィリアムシュライヤーフェローシップ。
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Prosense 750 | Visen Medical | VM110 | 500 nmol/kg IV injection |
| Heparin Sodium | APP Pharmaceuticals | 401586D | |
| Cephazolin | NovaPlus | 46015683 | |
| Lidocaine HCL 2% | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-4277-01 | |
| Buprenorphine | Bedford Laboratories | NDC 55390-100-10 | |
| Ketamine | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-2051-05 | |
| High Cholesterol Diet 1% | Research Diets | C30293 | |
| HIgh Cholesterol Diet 0.3% | Research Diets | C30255 |
参考文献
- Andersson, J., Libby, P. Adaptive immunity and atherosclerosis. Clin Immunol. 134, 33-46 (2010).
- Calfon, M. A., Vinegoni, C. Intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of atherosclerosis: toward coronary arterial visualization of biologically high-risk plaques. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 15, 011107-011107 (2010).
- Chen, J., Tung, C. -. H. In Vivo Imaging of Proteolytic Activity in Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105, 2766-2771 (2002).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Molecular Imaging of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 116, 1052-1061 (2007).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Optical and Multimodality Molecular Imaging: Insights Into Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29, 1017-1024 (2009).
- Jaffer, F. A., Vinegoni, C. Real-Time Catheter Molecular Sensing of Inflammation in Proteolytically Active Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 118, 1802-1809 (2008).
- Kim, D. -. E., Kim, J. -. Y. Protease Imaging of Human Atheromata Captures Molecular Information of Atherosclerosis, Complementing Anatomic Imaging. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30, 449-456 (2010).
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 420, 868-874 (2002).
- Naghavi, M., Libby, P. From Vulnerable Plaque to Vulnerable Patient: A Call for New Definitions and Risk Assessment Strategies: Part I. Circulation. 108, 1664-1672 (2003).
- Weissleder, R., Tung, C. -. H. In vivo imaging of tumors with protease-activated near-infrared fluorescent probes. Nat Biotech. 17, 375-375 (1999).
- Razansky, R. N., Rosenthal, A. Near-infrared fluorescence catheter system for two-dimensional intravascular imaging in vivo. Optics Express. 18, 11372-11381 (2010).
- Jaffer, F. A., Calfon, M. A. Two-Dimensional Intravascular Near-Infrared Fluorescence Molecular Imaging of Inflammation in Atherosclerosis and Stent-Induced Vascular Injury. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 57, 2516-2526 (2011).
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved