原子吸光分光法による土壌の鉛の分析
概要
マーガレット職人とキンバリー ・ フライ - デュポール大学のソース: 研究所
鉛は自然に発生する土壌、レベル 10 50 ppm に至る。しかし、業界によって塗料や汚染に加えてガソリン中の鉛の普及と都市土壌頻繁背景レベル-いくつかの場所で最大 10,000 ppm より大幅の鉛の濃度があります。継続的な問題は、鉛は生物分解しない代わりに土壌に残るという事実から生じる。
深刻な健康上のリスクは、子供が特に危険で、鉛中毒に関連付けられます。米国の子供たちの何百万人は、鉛を含む土壌に公開されます。この暴露は、子供の発達や行動の問題を可能性があります。これらの問題は、学習障害、不注意、遅延の成長、脳の損傷に含まれます。環境保護庁が遊び場と非遊び場の 1,200 ppm 400 ppm の濃度で土壌の鉛のための標準を設定します。
鉛は土壌、懸念も園芸のため使用するときです。植物は土壌から鉛を取る。したがって、野菜やハーブの栽培、土することができますリードする鉛中毒を汚染しました。さらに、汚染土壌粒子をガーデニングしながら息または衣類及び履物の家にできます。園芸のために鉛濃度 400 ppm を超えると土壌を使用しないことをお勧めします。鉛は葉で格納できるので 100 と 400 ppm の鉛濃度と土壌は緑豊かな野菜やハーブに使用されないことをさらにお勧めします。同様の注意根野菜べきであるないで成長させるこの土鉛も植物の根に蓄積されるので。
手順
1. 土壌の収集と準備
- 妨げられていないエリアの土の上の 1-2 インチから土壌を収集します。菜園をサンプリングする場合は、6 インチ深いサンプルを収集します。サンプル エリアから直径 1 インチの土壌コアを収集するのに土壌オーガーを使用します。
- 2 分を揺することによってサンプルを徹底的にミックスし、USS #10 フルイを使ってふるい。
- 24 h の 40 ° C のオーブンで土壌を乾燥させます。
2. サンプル消化
- 分析用天秤を使用すると、土壌サンプルの 1 g を量り、消化管の場所します。小数点以下 4 桁にサンプルの重量を記録します。
- フードの消化管に 5 mL の水を追加します。
- 消化管に 5 mL の濃縮苛性3を追加します。
- スラリーを攪拌棒に混ぜてください。ティア ドロップ ガラス栓の消化管をカバーしてください。
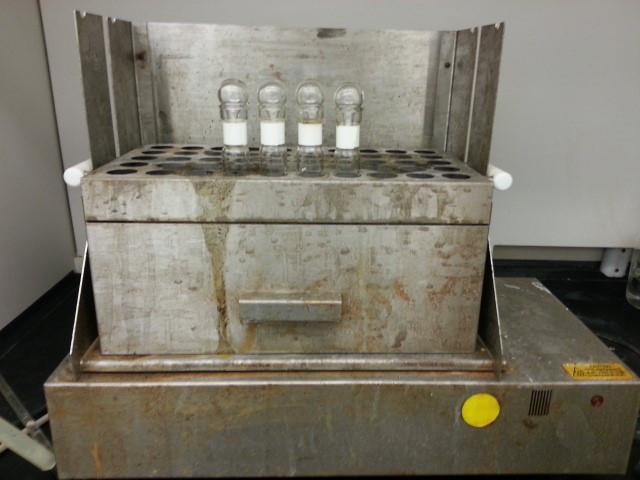
- ブロック消化に消化管を入れ (図 1
結果
申請書と概要
参考文献
- Robinson, J.W., Skelly Frame, E.M., Frame II, G.M. Undergraduate Instrumental Analysis. 6th Ed. Marcel Dekker, New York (2005).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. “Lead based paint poisoning prevention in certain residential structures.” CFR 40 Part 745. http://www.ecfr.gov. (2015).
スキップ先...
このコレクションのビデオ:

Now Playing
原子吸光分光法による土壌の鉛の分析
Environmental Science
125.8K 閲覧数

樹木: 二分のキーを使用するには、方法
Environmental Science
81.4K 閲覧数

点を中心とした樹木の調査: 四半期サンプリング
Environmental Science
49.5K 閲覧数

GIS を用いた都市林業を調査
Environmental Science
12.7K 閲覧数

プロトン交換膜燃料電池
Environmental Science
22.2K 閲覧数

バイオ燃料: セルロースからのエタノールの生産
Environmental Science
53.4K 閲覧数

組み換え食品の遺伝子検査
Environmental Science
90.1K 閲覧数

濁度と地表水の全固形物
Environmental Science
35.9K 閲覧数

水中の酸素を溶存
Environmental Science
56.0K 閲覧数

水生生物の生態系の栄養素
Environmental Science
39.0K 閲覧数

対流圏オゾンを測定
Environmental Science
26.5K 閲覧数

紫外可視分光法を用いた自動車の排気ガスのないxの定量
Environmental Science
30.3K 閲覧数

炭素・窒素環境試料の分析
Environmental Science
29.6K 閲覧数

土壌養分分析: 窒素、リンおよびカリウム
Environmental Science
216.2K 閲覧数

土壌にミミズ個体数の解析
Environmental Science
16.6K 閲覧数
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved