15.14 : Forced Oscillations
When an oscillator is forced with a periodic driving force, the motion may seem chaotic. The motions of such oscillators are known as transients. After the transients die out, the oscillator reaches a steady state, where the motion is periodic, and the displacement is determined.

Using the equations of force and motion, the amplitude of the driven oscillator is obtained. It depends on the natural and driving frequency.
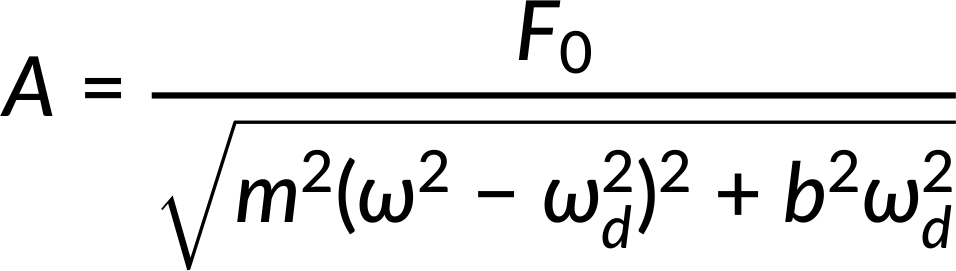
In the equation for amplitude, when the driving frequency is much smaller (or much larger) than the natural frequency, the square of the difference of the two angular frequencies is positive and large, resulting in a small amplitude for the oscillations of the mass. As the frequency of the driving force approaches the natural frequency of the system, the amplitude of the oscillations increases. When the frequency of the driving force equals the natural frequency of the system, this results in maximum amplitude.
Let's consider a real-life example. Most of us have played with toys involving an object supported on an elastic band, like a paddle ball suspended from a finger. At first, when the finger is held steady, the ball bounces up and down with a small amount of damping. If the finger is moved up and down slowly, the ball follows along without bouncing much on its own. As the frequency at which the finger moves up and down increases, the ball responds by oscillating with increasing amplitude. When the ball is driven at its natural frequency, the ball’s oscillations increase in amplitude with each oscillation for as long as it is driven.
The phenomenon of driving a system with a frequency equal to its natural frequency is called resonance. A system that is being driven at its natural frequency is said to resonate. As the driving frequency gets progressively higher than the resonant or natural frequency, the amplitude of the oscillations becomes smaller until the oscillations nearly disappear and the finger simply moves up and down with little effect on the ball.
This text is adapted from Openstax, College Physics, Section 16.8: Forced Oscillations and Resonance and Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 15.5: Forced Oscillations.
장에서 15:

Now Playing
15.14 : Forced Oscillations
Oscillations
6.5K Views

15.1 : 단순 조화 운동
Oscillations
9.2K Views

15.2 : Simple Harmonic Motion의 특성
Oscillations
12.4K Views

15.3 : Equilibrium Position에 대한 진동
Oscillations
5.2K Views

15.4 : 단순 조화 운동의 에너지
Oscillations
8.7K Views

15.5 : Spring-Mass System의 주파수
Oscillations
5.3K Views

15.6 : 단순 조화 운동(Simple Harmonic Motion)과 균일한 원운동(Uniform Circular Motion)
Oscillations
4.1K Views

15.7 : 문제 해결: 단순 조화 운동의 에너지
Oscillations
1.2K Views

15.8 : 단순 진자
Oscillations
4.5K Views

15.9 : 비틀림 진자
Oscillations
5.2K Views

15.10 : 물리적 진자
Oscillations
1.6K Views

15.11 : 중력으로 인한 가속도 측정
Oscillations
496 Views

15.12 : 감쇠 진동
Oscillations
5.6K Views

15.13 : 댐핑의 종류
Oscillations
6.3K Views

15.15 : 공명의 개념과 그 특성
Oscillations
5.0K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유