Method Article
태아 알코올 스펙트럼 장애의 쥐 모델에서 Hippocampal 기능 장애를 평가 하기 위해 추적 Eyeblink 클래식 컨디셔닝의 사용
요약
추적 eyeblink 클래식 컨디셔닝 (ECC) 평가 하는 데 사용 되었다 hippocampal 종속 연관 학습 했다 성인 쥐에 투여 초기 신생아 두뇌 개발 하는 동안 알코올의 높은 농도 (11.9 %v / v). 일반적으로, ECC 절차는 많은 심리적, 생물 의학 설정을 통해 뇌 기능 장애를 탐지 하기 위한 사운드 진단 도구입니다.
초록
신생아 쥐 관리 되었다 4-9, 산 후 시절 에틸 알코올 (11.9 %v / v)의 상대적으로 높은 농도 태아 뇌 조직의 급속 한 변화를 겪 습 비슷합니다 시간 가속 인간의 세 번째 임신 기간 중 발생 하는 뇌 변경. 태아 알코올 스펙트럼 장애 (FASDs)의이 모델 생산 양과-술자리 일부 임산부 알콜에 나타나는 패턴을 흉내 낸 심각한 뇌 손상. 우리 추적 eyeblink 클래식 컨디셔닝 (ECC), 일반적으로 알코올 노출 성인 자손에 본 장기 hippocampal 기능 장애를 평가 하기 위해 연관 학습의 더 높은 순서 이체를 사용 하 여를 설명 합니다. 나이의 90 일, 설치류 수술 기록 준비 되었고 자극 전극 측정 시 (EMG) 왼쪽된 눈 꺼 풀 근육에서 활동을 깜박 하 고 가벼운 충격 후부 왼쪽된 눈에 각각 전달. 5 일 복구 기간 후, 그들은 추적 연관 학습의 차이점 알코올 노출와 쥐 제어를 결정 하는 ECC의 6 회를 받았다. 추적 ECC 수정할 수 있는 쉽게 같은 장비 및 소프트웨어를 사용 하 여 서로 다른 신경 시스템 평가 될 수 있다 그래야 많은 가능한 ECC 절차 중 하나입니다. ECC 절차 일반적으로 서로 다른 뇌 시스템 및 두뇌를 모욕 하는 다른 조건에 신경 병리학을 탐지 하기 위한 진단 도구로 사용할 수 있습니다.
서문
It is quite hard to imagine that in today's day and age with better health care and access to health services, alcohol abuse remains a major global health concern. Unfortunately, it has been shown that an expectant mother who drinks a high amount of alcohol can have a child with severe brain damage and neurodevelopmental disorders that last a lifetime, as evident in those afflicted with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)1,2,3. In women with some confirmed history of maternal alcohol use, the developing fetus is also susceptible to small amounts of alcohol or different patterns of alcohol consumption that produce varying differences in blood alcohol concentrations. In this latter case, while the children may not exhibit the severe morphological or neurobehavioral disruptions as those with FAS, they may still exhibit lifelong cognitive disabilities and emotional disturbances that range from mild to severe3,4. Altogether, FAS and less severe forms of prenatal alcohol-mediated disruptions constitute a collection of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs). It is no surprise that FASDs are completely preventable, but astonishingly estimates show that in populations where alcohol abuse is quite common, they remain the primary non-genetic cause of neural and cognitive disability, affecting about 2% to 5% of young US children and those in European countries such as France and Sweden. With respect to the incidence of FAS alone within the US, the prevalence is 2 to 7 per 1,000 live births5, implying that the overall incidence of FASDs to be much higher than that for FAS.
Neuroimaging studies conducted in children with FASDs have shown that they display brain abnormalities, such as a thinner corpus callosum6, smaller anterior cerebellar vermis7, and smaller hippocampus8. These brain abnormalities underlie some of the long-term neurocognitive disruptions observed in children with FASDs. The exact links that tie variations in maternal alcohol-mediated brain changes and variations in the profile (i.e., type, extent) of particular neurocognitive impairments have yet to be clearly determined. But as a starting point, the hippocampus is an excellent candidate for determining its susceptibility to prenatal alcohol effects. Indeed, children with FASDs exhibit deficits in hippocampal-mediated behaviors such as place learning9,10 and delayed object recall11.
Rodent models of FASDs have proven to be invaluable in elucidating the mechanisms leading to neurocognitive disruptions seen in children with FASDs. A well-established binge-exposure model that we have adopted involves delivering alcohol to rats during postnatal days 4-912,13, a period when the brain undergoes rapid synapse and dendritic contact formation, comparable to human fetal week 24 and extending into the 3rd trimester14,15,16,17. This particular model induces significant loss of hippocampal neurons18,19 and neurons in many other brain regions such as the cerebellum12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23, accompanied by severe impairments in cognitive functions spanning different domains21,24,25. Cognitive disruption from early alcohol exposure in rats may be assessed in different ways, particularly with eyeblink classical conditioning (ECC). ECC is a paradigm that has been utilized for more than a century to scientifically investigate the fundamental basis of learning26,27 and as such, provides a useful method to better understanding the adverse neurocognitive consequences resulting from fetal alcohol exposure. It is a very flexible paradigm that allows investigators to use a variety of different ECC procedures, any of which can be examined across many mammalian species ascending the phylogenetic scale (from mice to humans) and over different courses of brain development28,29,30,31. Furthermore, the fundamental neural circuits that mediate associative learning in this paradigm are supported by experimental and neuropsychological reports in these same species26,32,33,34,35,36,37.
One form of ECC, trace ECC is demonstrated in this paper (Figure 1). To provide context, it is compared against the more traditional form - delay ECC. The ECC paradigm was modeled after classical conditioning using dogs, first carried out by the Nobel-Prize winning physiologist, Ivan Pavlov. Pavlov discovered that certain stimuli such as tones do not naturally elicit salivation, but when it precedes and overlaps with the delivery of food, the salivary response can be strengthened from repeated presentations of the two, provided that this tone-food contingency is maintained. This is an example of delay ECC, with the notion that associative strength is mediated by immediate temporal contiguity between the two stimuli, thus making learning conditions optimal for an animal. He also tested other variations of the tone-food contingency, such as turning the tone off and leaving a "trace" period before delivering the food. When these two stimuli were discontiguous enough, it became much harder for the dogs to emit salivation responses prior to the delivery of the food. The discontiguity between the tone being turned off and the delivery of the food is thus an example of trace ECC. As rodents do not naturally salivate to the presence of food, more species-relevant stimuli such as mild shock are used instead; they also do not naturally emit defensive eyeblink responses to tones. With this backdrop, rodent ECC procedures involve presenting a tone at a given decibel level and pairing it in some fashion with mild shock to either the eyelid muscle (orbicularis oculi) or the temporalis muscle to elicit an eyeblink response. The tone is considered a conditioned stimulus (CS) while the shock is considered an unconditioned stimulus (US). In delay ECC, the CS is presented first; this stimulus remains on for a given duration. Afterwards, the US is delivered. These two stimuli overlap for a given duration, and then both terminate simultaneously; the resultant eyeblink response emitted due to the US is considered an unconditioned response (UR). In this procedure, rodents learn to emit eyeblink responses sometime after the CS is presented, but just before the US, in order to anticipate this aversive stimulus. The learned eyeblink response is referred to as a conditioned response (CR). For trace ECC, the CS and US are separated by a period of time that is void of stimuli known as a trace interval; they do not overlap in time as in delay ECC. During this interval, the animal is tasked to resolve the associational requirements between stimuli. Similar to delay ECC, learning occurs when the animal consistently emits a blink response after the CS turns off, but immediately before delivery of the US. Over some amount of acquisition training (CS paired with US), learning curves (i.e., based on different CR measurements) develop. Lesion and neuroimaging studies show that successful learning in delay ECC is dependent on having intact cerebellar-brain stem neuro-circuitry38,39,40, whereas trace ECC is a higher-order procedure that requires additional neural engagement from the hippocampus41,42,43,44 and other cortical structures45,46. Because of the timing-related requirements needed in order to acquire trace CRs successfully, this task is also more difficult to learn (even for normal subjects).
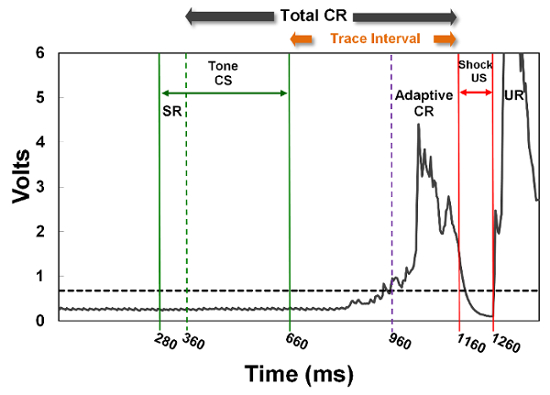
Figure 1: Trace eyeblink classical conditioning. An actual waveform is shown that is representative of an adult rat in the unintubated-control (UC) group. The tone CS (85 dB, 2.8 kHz) is first presented for 380 ms. A trace interval of 500 ms ensues, where no stimuli are present. Afterwards a shock US (1.6 mA) is delivered for 100 ms. Successful learning in this task occurs when the frequency (%) or amplitude (in volts) of eyeblinks during the conditioned response (CR) time window (Total CR period) increases over many sessions of training. In particular, rodents with an intact hippocampus will usually emit more well-timed CRs (Adaptive CRs) just prior to the onset of the shock US (within a 200-ms window). Startle responses (SRs) during the first 80 ms after tone CS onset and unconditioned responses (URs) are also measured. Non-associative SRs are typically low or nonexistent in well-trained rodents, while URs are expected to be high in frequency and amplitude. This task requires that the rodent learn to bridge the association between the CS offset and US onset (during the trace interval), therefore making it inherently more difficult to acquire compared to delay ECC. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Here we demonstrate the adverse functional consequences of neonatal alcohol exposure that is delivered in a binge-like manner, as assessed by a trace ECC procedure that delivers an 85 dB tone CS (2.8 kHz) which remains on for 380 ms, followed by a 1.6 mA shock US which remains on for 100 ms, and these stimuli are separated by a trace period of 500 ms. We have reported on the utility of this behavioral assay in previous studies examining choline intervention and iron supplementation in mitigating the effects of neonatal alcohol exposure18,47. Indeed, trace ECC can be used as a diagnostic tool to assess neonatal alcohol-induced hippocampal pathology. The advantage it has over delay ECC is that it is more sensitive to detecting disturbances in hippocampal function, which is compromised in humans with FASDs.
Demonstration of ECC extends far outside the fetal alcohol field. Many variants of ECC (e.g., delay, trace, compound, reversal) can be used to elucidate ontogenetic differences in learning across development, the neurobiological basis of associative learning in normal mammals, as well as the vulnerabilities of different brain systems to many challenges, including (but not limited to) teratogens, environmental toxins, traumatic brain injury, neurodegenerative diseases, and psychiatric conditions.
프로토콜
NOTE: All procedures were approved and carried out in accordance with the policies set forth by the East Carolina University IACUC. Long-Evans rats were generated from females mated with male breeders. Pups from all three treatment groups (see 1.1) were generated within a litter from the same dam. Five litters were produced and each litter was culled to 8 pups on postnatal day (PD) 3. The remaining two pups from each litter were assigned to separate experiments. Both male and female offspring (one per exposure group) were included in the study. A total of N = 27 adult offspring were examined in this study; 3 rats were excluded due to broken 3T wire leads (see 3.1.1) which were irreparable on Day 1 of ECC training.
1. Preparation of Groups, Materials, and Solutions
- On PD 3, remove pups from the dam and place them on a thermo-regulated water heating pad to keep warm. Use a random selection procedure to place rat pups into one of three groups: (1) alcohol-intubated (AI); (2) sham-intubated control (SI); or (3) unintubated-control (UC). Carry out approved procedures for identification, such as [non-toxic] ink tattooing of their paws with a 30G x 1/2 in needle following a numbering scheme. Return the pups to the dam when finished with tattooing.
- Prepare an intragastric intubation tube(s) using polyethylene (PE) size 50 and 10. The overall length of this tube is user-dependent and can be adjusted accordingly.
- Use micro dissecting scissors to cut a 3 in piece of PE-50 tubing and a 6 in piece of PE-10 tubing.
- Carefully attach the PE-50 tubing to a sterile 22 G x 1 in hypodermic needle.
- Insert one end of the PE-10 tubing into the open end of the PE-50 tubing. A diagonal cut may be needed at the tip of the PE-10 tubing in order to direct it into the PE-50 tubing.
- Cut a small piece of PE-50 tubing (about 2-3 mm) and insert it on the open end of the PE-10 tube. This will serve as a visual stopper.
- Store the complete intragastric intubation tube in fresh 70% isopropyl alcohol to keep it sterile.
- Carry out aseptic procedures to prepare a stock milk solution in 50 mL bottles. The stock milk solution is based on a diet formula first established by West et al. (1984)48. Store the bottles at -18 °C until time of use. Thaw two bottles of milk using warm water prior to use.
- Draw out 7.16 mL of 95% ethyl alcohol (USP) using a sterile syringe and add it to one 50 mL milk bottle. This makes an 11.9% v/v alcohol solution that is delivered to rat pups over the first two feedings of the day (see 2.1.1); the total daily dose of alcohol is 5.25 g/kg/day. It is designed to deliver the alcohol in a volume (0.0278 mL/g per feeding) in enriched milk solution.
NOTE: This amount can be adjusted based on litter size and expected usage over 3-4 days. The amount of alcohol added must also be adjusted in order to make an 11.9% v/v solution. - Shake this bottle well and label it accordingly (i.e., 11.9% v/v Ethyl Alcohol in Milk).
- Label the second bottle of milk (without alcohol added) accordingly (e.g., Milk-Only) and use it for supplemental feedings as indicated in 2.1.1.
- Store both milk bottles in the refrigerator.
- Draw out 7.16 mL of 95% ethyl alcohol (USP) using a sterile syringe and add it to one 50 mL milk bottle. This makes an 11.9% v/v alcohol solution that is delivered to rat pups over the first two feedings of the day (see 2.1.1); the total daily dose of alcohol is 5.25 g/kg/day. It is designed to deliver the alcohol in a volume (0.0278 mL/g per feeding) in enriched milk solution.
2. Neonatal Alcohol Exposure (Postnatal Days 4-9)
- Give AI and SI pups 4 total intubations per day starting on PD 4. Separate each intubation by 2 h. Because AI pups are intubated with an actual solution, each of their intubations are considered feedings.
- Intubate the AI pups with the 11.9% v/v Ethyl Alcohol in Milk solution during the first two feedings of the day, and then intubate them with the Milk-Only solution during the last two feedings of the day to supplement their growth.
- Intubate the SI pups 4 times without any solution every two hours, ensuring the same duration of PE-10 tube exposure that AI pups endure. The UC group does not receive any intubations.
- Remove pups from the dam and place them on a thermo-regulated water heating pad to keep warm. Weigh each pup and record its body weight (in g). Refer to a pre-made feeding chart to determine the intubation volume for each AI pup and note it in a record sheet.
- Place the 11.9% v/v Ethyl Alcohol in Milk solution in a warm water bath and shake it well.
- Intragastric intubation procedure:
- Flush out the intragastric intubation tube that was stored in 70% isopropyl alcohol well with warm water.
- Extract the correct amount of solution using a sterile 1 mL syringe.
- Dip the tip of the intubation tube (PE-10 end) in fresh corn oil (this facilitates insertion).
- Measure the length of the PE-10 tube from the pup's mouth to its stomach. Adjust the PE-50 stopper to guide with the stopping point.
- Carefully insert the PE-10 tube into the pup's mouth, proceeding down its esophagus, slightly passing through the gastroesophageal sphincter, and into its stomach. Examine the pup, stabilize it, and depress the syringe plunger to deliver the solution. Do this at a slow rate.
NOTE: To avoid accidentally inserting the tube into the trachea, first direct the tube so that it curves and makes contact with the soft palate prior to proceeding forward. Use the palate as a guide, as the tube will naturally deflect off this region and be guided down the esophagus. Otherwise, any substantial deviation of the tip ventrally may cause it to enter into the trachea. It is best to remove the tube and not to proceed with the intubation if one is not certain about its entry position - reinsert the tube correctly on the next attempt. - Carefully remove the PE-10 tubing and examine the pup for backwash of solution, blood, or physical injury. Replace pup with its littermates if it is fine. The entire intubation procedure takes approximately less than 1 min for each pup and approximately 4 min total for the 4 intubation-treated pups in each litter (2 AI, 2 SI).
- Intragastric intubation procedure for SI pups: Follow the same PE-10 insertion procedure as that for AI pups, but without any solution for the same duration (1 min).
- Return all pups back to the dam immediately after completing procedures for the last pup in the litter. Return the dam to the vivarium until the next feeding session (in 2 h).
- Flush out the intragastric intubation tube with warm sterile water and replace it in 70% isopropyl alcohol for storage. Flush the tube well with water prior to each feeding session.
- Repeat 2.2 (except weighing pups) to 2.2.2.9 for the second feeding session. At the last two feedings, intubate the AI pups with the Milk-Only solution using the same intubation volumes determined in 2.2.
- Weigh the rats at regular intervals such as on PD 15 (when eyes open), PD 21 (weaning), PD 30, PD 60, and PD 90 (surgery) to obtain representative growth curves.
3. Fabrication and Modification of Electrodes
- Fabricate one electromyographic (EMG) "headstage" for each rat (Figure 2). The headstage allows for recording of eyeblink responses via the eyeblink system (Figure 4).
- Construct a headstage that consists of two size 3T polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)-coated stainless steel wires (5 cm each), one size 10T PTFE-coated stainless steel wire (5 cm), three male contact pins, and one micro strip socket insulator that is cut-down to 3 holes (see 3.1.4).
- Strip off the PTFE coating from the 10T wire by grasping the center with a serrated high precision tweezer and removing the coating in both directions with the smooth high precision tweezer. Ensure that all traces of coating have been removed from this wire.
- Crimp one end of the 10T wire to a contact pin with a serrated platform dental plier; this will serve as a ground wire. Hold a 3T wire carefully with the smooth high precision tweezer 1 to 1.5 mm from one end. Strip off the 1 to 1.5 mm PTFE coating while leaving the rest of the coating intact. Crimp a contact pin to the exposed end of the 3T wire.
- Carry out the same procedures for the second 3T wire. Both wires will serve as the positive and negative leads of the EMG recording electrodes.
- Perform tug tests on all wires to ensure that they are secured to the pins. Take caution not to bend or damage the wires.
- Cut a segment of a socket insulator strip down to 3.5 holes (cut the middle of the fourth hole) with the cutting blade of a wire stripper. Scale down this segment to just 3 full holes and sand-down both sides if necessary. This helps to ensure that 3 full holes are available. Insert pin-wire units into the three holes of the micro strip until the crimped ends are flushed with the bottom edge of the insulator segment. The 10T assembly needs to be in one outer hole of the micro strip and not in the middle.
- Modify bipolar stimulating electrodes (Figure 2).
- Give each rat one bipolar stimulating electrode. This electrode applies a small amount of electrical current via a stimulus isolator (see eyeblink system) as the shock US during ECC. The electrodes are acquired from a manufacturer in twisted form and are shielded.
- Untwist the two metal leads 2-3 times to make a V-shape (spread 5 mm) and then use the smooth high precision tweezer to straighten each "prong" as much as possible. Scrape off 1 mm of shielding from each prong's tip (all around) with a razor blade. Inspect each prong for irregularities and bends, and correct if necessary without scraping off additional shielding.
- Remove manufacturing oil and foreign debris from the EMG headstages and bipolar electrodes by washing them in 95% ethyl alcohol. Allow them to dry then autoclave.
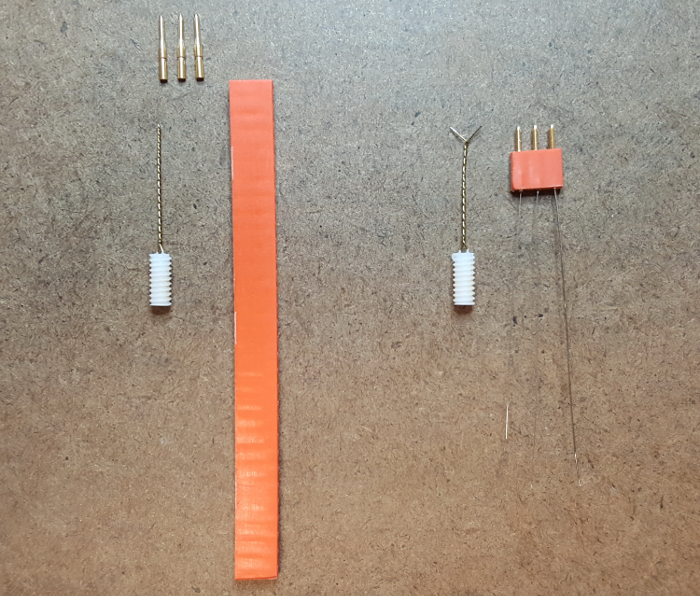
Figure 2: Electromyographic (EMG) recording electrodes and bipolar electrode. The finished EMG headstage (right, orange) is constructed from three male contact pins, two size 3T PTFE-coated wires, one size 10T PTFE-coated wire, and a modified micro strip. The three wires are approximately 5 cm each and are crimped to the contact pins. The finished bipolar electrode (right, white) is untwisted, re-straightened, and molded in a V-shape (5 mm split). Shielding is removed from the tips of the two prongs. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Eyelid Surgery Procedure (Postnatal Day 90)
- Preparation of materials (see Materials for detailed supply information), animals, surgical, and non-surgical areas:
- Autoclave surgical instruments and supplies - the number in parentheses ( ) indicates approximately how much is needed per adult rat or measurement: surgical instruments (1 set per 4 rats, as approved by the ECU IACUC), gauze pads (3-4), cotton-tipped swabs (5-6), 20 x 20 wrap (4 per/surgery session), porcelain crucible (1), stainless steel microspatula (1), 0.9% saline (1 wash bottle), Petri dish (1), and 0-80 stainless steel screws (3/rat).
- Other sterile supplies needed: surgical blade size 10 (1 per 4 rats), surgical drape (1 per rat), veterinary ophthalmic ointment, povidone-iodine (1 wash bottle), 26G x 3/8" hypodermic needle (2), nickel-plated pin vise with #55 drill bit, nickel-plated flathead jeweler's screwdriver (1.8-2 mm blade).
- Prepare a sterile holding area for all surgical tools and supplies using an approved research/medical grade disinfectant. Place materials on this space when the area is ready.
- Prepare a sterile surgical space using an approved research/medical grade disinfectant. This space contains a thermo-regulated water heating pad, stereotaxic apparatus fitted with a rat anesthesia mask, glass bead sterilizer, and isoflurane gas vaporizer (for anesthesia). The vaporizer has tubes to the anesthesia mask and to an induction chamber located on a separate space for non-sterile animal preparation procedures; each tube is controlled by its own valve.
- Scrub hands and arms thoroughly with antimicrobial soap. Without touching the inside, pre-open any items that have been packaged in sterilization pouches or wraps. Don sterile gloves using aseptic procedure and transfer all pertinent items to the surgical area. Set the drill bit at the proper depth in the pin vise (~ 2 mm) and prepare the screwdriver. Cover the sterile materials with a sterile wrap until the surgery is ready to begin.
- Prepare a non-sterile space with a weighing scale, electric fur trimmer, sterile 1 mL syringes with 26G x 3/8 in needles (1 per rat), surgery log, and buprenorphine (0.03 mg/mL concentration) administered 0.1 mL/100 grams.
CAUTION: Buprenorphine is a DEA schedule III semisynthetic opioid, and must be locked and logged appropriately. - Check the isoflurane vaporizer for appropriate gas level; add more gas if it is low. Leave the gas flow and mixture knobs off for now. Turn on the O2 tank and check that there will be enough gas for all surgeries.
- Weigh each rat and record its body weight in the surgery log. Use a buprenorphine injection chart to determine the proper injection volume.
- Turn on the vaporizer valve to the induction chamber and leave the valve to the surgery mask off. Turn the mixture to 3 and flow rate to 3 (3% isoflurane with 100% O2 as the carrier gas at a volume of 3 L/min).
- Place a rat in the induction chamber and allow it to reach proper anesthetic plane (slow breathing, lack of pedal reflex, lack of blink reflex). Remove the rat from the chamber once it has reached anesthetic plane.
- Shave its head using the fur trimmer, exposing a sufficient amount of skin for the incision site and the left eyelid. If necessary, place it back in the induction chamber to reach anesthetic plane again before resuming with the trimming.
- Disinfect the exposed skin by applying alternating rubs of isopropyl alcohol and povidone-iodine three times. If necessary, place it back in the induction chamber to reach anesthetic plane again, prior to transferring to the surgery table.
- Surgery
- Turn on the vaporizer valve to the anesthesia mask and shut off the valve to the induction chamber. Adjust the mixture to 2.5 and flow rate to 2 (2.5% isoflurane with 100% O2 as the carrier gas at a volume of 2 L/min). Transfer the rat to the stereotaxic apparatus and follow standard procedures in securing its head to the incisor bar and ear bars (see Geiger et al., 200849 for an example).
- Give the rat a pre-surgical injection of buprenorphine (SC) and carefully dispose of the needle (uncapped) in a sharps container. Place a sterile surgical drape on the rat, exposing just the surgical area and isolating it from the rest of the body.
- Don a surgical mask, surgical cap, surgical gown, goggles, and any other personal protective equipment required by the IACUC. Wash and scrub hands and arms thoroughly with antimicrobial soap. Don sterile gloves using sterile procedure.
- Apply a small amount of ophthalmic ointment to both eyes using a cotton-tipped swab to prevent them from drying.
- Proceed with the surgery when the rat exhibits proper anesthetic plane. Monitor the rat continuously throughout the surgery and check the isoflurane level periodically. Adjust the flow and mixture knobs accordingly during surgery based on the rat's response to the anesthesia.
- Make an anterior-posterior incision at the midline of the cranium with a scalpel blade. This incision should expose enough area in front of the eyes (i.e., exposing the frontal bone) and slightly behind the lambdoid suture.
- Scrape away the periosteum on top of the cranium carefully not to cause excessive bleeding. Wipe off excess connective tissue and blood with a cotton-tipped swab.
- Drill a hole using the drill bit with the aid of a pin vise, starting directly behind the coronal suture on one parietal bone. Remove any blood and bone debris with a cotton-tipped swab. Grasp a 0-80 screw by the threading with splinter forceps and fasten it to the hole with the jeweler's screwdriver; tighten-down the screw just enough without damaging cortical brain tissue (usually 3-4 full turns).
- Follow the same procedures described in 4.2.8 to fasten two more 0-80 screws to the skull, one directly behind the coronal suture of the opposite parietal bone and one directly anterior to the right lambdoid suture. It has been found that 3 screws are sufficient for anchoring the dental cement (see 4.2.18) to the cranium, as a fourth screw (anterior to the left lambdoid suture) would impede the placement of the bipolar electrode.
- Remove an EMG headstage from the Petri dish. Face the headstage so that the 10T wire is on the rat's right side. Bend the 10T wire upward, making it parallel with the bottom edge of the micro strip. Give it a slight bend to the right side so that the wire can come around the anterior and posterior 0-80 screws. Set it aside but close enough to reach.
- [Assuming one is right-handed] Place 3 in dressing forceps in the left hand and 4 in dressing forceps in the right hand. Grasp the upper skin at the incision site of its left eye with the 4 in dressing forceps and direct the 3 in dressing forceps towards the corner of this eye; grasp the skin at this corner. Maintain the grasp with the 3 in dressing forceps while releasing the 4 in dressing forceps.
- Take one 26G x 3/8 in needle and insert it through the corner of the eyelid; rotate the needle so that the beveled side is face-up. Use the micro dissecting forceps with platform to insert the middle 3T wire into the needle's hole. Push it through the hole a few centimeters without going down completely; this wire is the negative lead.
- Carry out the procedures described in 4.2.11 and 4.2.12 to insert the outside 3T wire into the middle portion of the eyelid; this wire is the positive lead.
- Grasp both needles with one hand while grasping the headstage with the other hand (or forceps). Pull the needles away from the eyelid while guiding the headstage in the same direction in one continuous movement. If necessary, rotate the headstage so that the 10T wire is towards the animal's right eye; do not allow the 3T wires to cross. Use fine tipped forceps to double-check that the positive lead is in the middle of the eyelid.
- Adjust the headstage so that it is centered between the eyes and is in an optimal position atop the frontal bone, anterior to the bilaterally-inserted screws. Hold the headstage with one hand and hold the 3 in dressing forceps with the other hand. Wrap the 10T wire around one or both screws on the 10T side.
- Place 3 in dressing forceps in one hand and 4 in dressing forceps in the other hand. Use the 3 in dressing forceps to grasp the skin at the incision site towards the left temple. Use the 4 in dressing forceps to create a small "pocket" by separating the skin (i.e., superficial fascia) from the temporalis muscle. Use the iris scissors to cut away more connective tissue, working in towards the corner of the left eye, to increase the size of this pocket. Be careful not to go in too deep or cut any blood vessels.
- Take a bipolar electrode and shape the wire leads so that they can be fitted along the curvature of the temporalis muscle, while the two prongs are situated (dorsal and ventral) posterior to the left eye (see video), and the bottom end of the bipolar electrode can be situated straight atop the cranium. Allow enough distance between the headstage and this electrode for the commutator cable plugs (Figure 3) to attach without impediment.
- Pour dental cement powder into the crucible - start with about 1/3 of the crucible, and then scale the amount as necessary. Add the liquid component until the consistency is watery, and mix these components with the spatula. When the cement's consistency becomes more viscous, apply it to the incision site - covering all edges of the skin with at least 1/8 in borders.
- Apply enough cement to fortify the headstage and bipolar electrode without preventing the rat from closing both of its eyes. Quickly wipe off any cement that drips onto unwanted areas of the rat's fur.
- Ensure that at least 4-5 threads of the bipolar electrode are left unsealed by cement so that the bipolar plug can be twisted on (Figure 3). Remove excess cement from the headstage - the top of the micro strip and the three contact pins must be clean. The cement hardens quickly and may easily prevent full coupling of any of these electrodes to the commutator cable plugs. Use splinter forceps to remove excess cement that has partly dried.
- Wait for the cement to harden; it becomes clear. Use the micro dissecting scissors to snip off excess length from the two 3T wires, leaving a few centimeters of working room.
- Grab the micro dissecting forceps with platform on the left hand while grabbing the micro dissecting forceps with fine points on the right hand. Grasp one 3T wire with the left forceps slightly in front of the eyelid. With the right forceps, push the eyelid up to expose more 3T wire and hold it there. Release the left forceps and use the left hand to grasp the headstage (ensure it is secure by now). Use the right forceps to strip off some PTFE shielding, which allows the wire to make contact with the orbicularis oculi muscle.
NOTE: Take caution not to pull too hard on a 3T wire, as it may detach from the contact pin. If a wire detaches, then it will not be possible to replace the contact pin as the hardened cement will not release freely from the cranium without causing bone breakage. - Perform the steps in 4.2.21 to strip off excess PTFE from the second 3T wire.
- Grab the two micro dissecting forceps as stated in 4.2.21 (with platform on left, fine points on right). Position the left forceps slightly in front of one 3T wire while leaving room for the right forceps to be positioned directly in front of the eyelid. Grasp the wire with both forceps.
- Create a "hook" by keeping the right forceps still and rotating the left forceps up and around towards the eyelid; do this in one motion. Carefully release the right forceps, and then the left forceps.
NOTE: Hooking the electrodes on the eyelids help to minimize the possibility of them rubbing onto the cornea. This also minimizes the possibility for wire breakage during any point in the behavioral testing phase. While hooking does not fully prevent the wire from rubbing against the cornea for all animals, they typically show no signs of eye damage as reflected by their high blink amplitudes (measured by the digital oscilloscope in 5.1.7) and from daily post-surgical health observations (excessive tearing, partial eyelid closure, lack of mobility from eye damage). If a rat shows initial signs of discomfort, it is anesthetized with isoflurane (see 4.1.10) and its electrodes are re-examined and/or re-positioned. Ophthalmic ointment is applied to prevent the cornea from drying. The rat is observed daily for any post-procedural eye complications and should they persist, then seek veterinary care. Rats that exhibit severe eye complications which cannot be corrected with electrode re-positioning or with veterinary treatment, are humanely euthanized according to the standard operating procedures of the ECU IACUC.
- Create a "hook" by keeping the right forceps still and rotating the left forceps up and around towards the eyelid; do this in one motion. Carefully release the right forceps, and then the left forceps.
- Perform the steps in 4.2.23 for the second 3T wire. Snip off excess wire using the micro dissecting scissors.
- Use one hand to release the rat from the ear bars while supporting its body with the other hand. Inspect its head for any blood or debris, clean up if necessary, and give it a post-operative injection of buprenorphine.
- Place the rat in a recovery bin that has a source of heat (such as a thermo-regulated water heating pad) to aid recovery. Mark in the surgery end time in the surgery log and any pertinent notes about the rat during surgery. Monitor the rat for proper respiration and when it exhibits sternal recumbency or moves about, it may be returned to its home cage.
- Re-sterilize the instruments (except micro dissecting forceps - as they may be damaged) using the bead sterilizer and ensure that the surgical area remains aseptic, and repeat aseptic procedures if multiple eyelid surgeries will be performed.
5. Trace Eyeblink Classical Conditioning Procedure

Figure 3: Modified operant conditioning box for eyeblink conditioning. Rats are freely-moving mammals, and therefore a rotating commutator is used for maintaining electrical signal contact from the EMG and bipolar plugs that are attached to the head. The commutator is attached to the arm of the stanchion, which is counter-weighted for alleviating pressure on the rat. A piezo tweeter (speaker) delivers a 2.8 kHz tone at 85 dB and these values are calibrated regularly. Acoustical foam assists with attenuating environmental noise. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
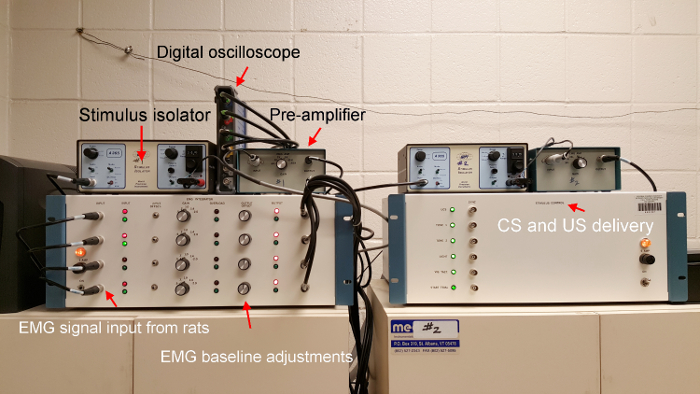
Figure 4: Eyeblink conditioning system. This custom-built system consists of an EMG Integrator unit that filters and amplifies incoming signals from the rats, a Stimulus Control unit that delivers various stimuli in addition to tones and shocks, a pre-amplifier for each operant box to increase EMG signal gain, and a stimulus isolator for each operant box; it provides varying shock levels (in mA). A digital oscilloscope (not part of the stock eyeblink system) is used for diagnostic purposes during habituation and acquisition. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Begin habituation and acquisition training 5 days after surgery. Give each rat one day of handling and habituation to the training apparatus - consisting of a modified operant conditioning box that is housed in a larger sound-attenuated chamber (Figure 3) - and follow with 6 days of acquisition training. Carry out the habituation and acquisition sessions using a custom-built eyeblink system (Figure 4).
- Create a training log file and print it out to use for daily record keeping. This log should have the squad of rats pre-assigned pseudo-randomly (or other randomization method) to their training boxes.
- Power on the eyeblink system, computer, and run the eyeblink software. This version of the software has different modules (or applications) that run independently. Run the Animal module to create a *.RAT file that contains subject information (session number, animal ID, sex, weight, and box number). A single RAT file manages up to four rats, which comprises a squad of subjects. Enter the values accordingly and save the file. Create a separate RAT file for each squad of rats to be trained.
- Transfer the rats from their vivarium to the testing room and close the door. Handle each rat for 5 min.
- Transfer a rat to its designated box and connect the EMG and bipolar plugs from the commutator cable to the corresponding EMG headstage and bipolar electrode on its head.
NOTE: On first exposure to the commutator cable, a rat may struggle and show signs of stress. Handle the rat carefully and allow breaks in between unsuccessful attachments to alleviate its stress. - Use a commutator that rotates 360° while maintaining electrical signal delivery/reception as a rat moves freely within a box. It has 5 channels (3 for the EMG electrodes, 2 for the bipolar electrodes) leading into the EMG Integrator unit, which filters and amplifies the raw signal.
- Determine that the rat is moving freely, and that it is not hindered by the weight of the commutator cable assembly or stanchion arm. Adjust the counter weight at the back of the stanchion if necessary. Check that all plugs are secure then close the box door. Perform the same connection/check procedure for all rats.
- Use an oscilloscope to observe their EMG activity for abnormal signals (e.g., high frequency and/or high amplitude electrical activity) and a video surveillance system to check their status (e.g., motor activity, sensitivity to environment, signs of pain) if available. Note any problems that are observed in the training log.
- Allow rats to habituate to their chambers for 10 min, and then return them to their homecages.
- Clean and disinfect the operant boxes, sweep the floor, and clean the table(s). Carry out these procedures after every session.
- Acquisition training occurs over 6 consecutive days (sessions).
- Day 1: Transfer a rat to its designated box and connect the EMG and bipolar plugs from the commutator cable to the corresponding EMG headstage and bipolar electrode on its head. Carry out the same procedures indicated in 5.1.6 and 5.1.7.
- Turn on the stimulus isolators and set the current to be delivered at 0.4 mA (4% of 10 mA as shown in video). The isolators deliver electrical current in alternating fashion (i.e., from trial to trial), between the dorsal and ventral prongs of the bipolar electrode. This helps reduce muscle fiber fatigue (at each muscle site) over repeated stimulus deliveries.
- Observe all eyeblink responses emitted and tolerances exhibited on each trial for all rats. After every second trial, increase the shock US intensity by 0.4 mA for each rat, until 1.6 mA is reached (on Trials 7 and 8). Double-check that all rats are responding normally in their boxes, that all amplification and gain settings are constant, and for proper electrical signals (i.e., low/little EMG noise) coming from them. Use a shock US intensity of 1.6 mA for all days of acquisition training.
NOTE: If a rat exhibits pain to a given shock level (e.g., jumping high off the floor, climbing on walls, running around), the trial is paused and it will be returned to the previous mA setting (0.4 mA below) for two trials. Afterwards, the rat will receive the higher shock value that it did not tolerate again and if tolerance is shown, it will receive increasing values until 1.6 mA is reached. If it cannot tolerate any value, then the next lower value (in 0.4 increments) at which it tolerates will be used throughout training. - Use an oscilloscope to observe their EMG activity for abnormal signals (e.g., high frequency and/or high amplitude electrical activity) and a video surveillance system to check their status (e.g., motor activity, sensitivity to environment, signs of pain).
NOTE: Explanation of Trace ECC: A representative trial epoch with captured EMG waveforms is illustrated in Figure 1 and the trace ECC procedure is explained in detail in the video. The trace conditioning training file is set to deliver 100 trials (90 paired CS-US trials and 10 CS-only trials on every 10th trial) with an average inter-trial interval of 30 sec. The entire training session lasts approximately 52 min (assuming no stoppages). All rats are naïve in Session 1 and will develop differential learning curves (as determined by the expression of CRs) as they progress through several days of training. - Start the training: Run the Blink software module. When prompted, select the correct RAT file and the training file for "trace" eyeblink conditioning.
- Write down the start time and the experimenter's name in the training log. Monitor all activity at this point: proper EMG signals, good blink responses to the shock US (i.e., high/frequent URs), health status of the animals, and proper hardware function. Write any noteworthy remarks in the training log.
- Data collection is captured automatically by the software as RAW files (one per rat, per day). The RAW files contain EMG amplitude (in volts), frequency counts, latency, and areal data for startle responses (SRs), URs, and CRs (total and adaptive). Shock artifact obscures the first 100 ms of the UR period, therefore only the last 140 ms of the UR period contain UR data.
- At the end of training, the software will automatically close. Remove all rats from their training boxes and return them to the vivarium.
- Repeat steps 5.2.5 - 5.2.6 for all subsequent training days. Before starting the Blink module on a given day, update the session number within the RAT file. This allows for creation of new RAW files for all rats that day. Each rat should have 6 RAW files, assuming that none has been removed from the training.
- Process the RAW files and create a file that has been filtered for statistical analysis.
- Run the Analysis module. Review each session for each rat on a trial-by-trial basis for problematic trials. This is carried out to screen for trials that may be compromised due to various reasons (e.g., excessive pre-CS baseline activity, excessive movement, electrode detachment, cabling/wire issues). The software has algorithms that assist the experimenter with detecting and removing "bad trials" from being part of the filtered data set.
- Import the filtered data into a spreadsheet program and perform pertinent statistical analyses.
결과
Eyeblink 소프트웨어는 다양 한 유형의 측정 데이터의 크고 포괄적인 세트를 제공 수 있습니다. 간결, 우리는이 연구에서 보고 대표 결과 학습 및 성능에 대 한 적응형 CR 비율, 적응형 CR 진폭, UR 비율 및 UR 진폭을 포함 하는 측정. 적응형 CR 기간 추적 ECC50,,5152중 해 마에서 향상 된 시 냅 스가 소성의 결과로 반복된 훈련을 통해 잘 초과 eyeblink 응답의 인수를 나타내는 선택 되었다. 통해 UR 대책 여부에 신생아 알코올 유발 학습 적자 추적 ECC 동기 또는 모터 차이 보다는 학습 치료 그룹 간의 차이 알 수 있습니다-우리 연관 학습 중단 또는 충격에 응답 중단 했다 명료 하 선정 됐다. 각 측정값에 대 한 데이터 반복 측정 요소로 세션 ANOVAs 혼합 2 (섹스) x 3 (Neonatal 그룹) x 6 (세션)을 사용 하 여 분석 되었다. 신생아 치료 위한 중요 한 주요 효과 했다 Tukey의 포스트 hoc 테스트를 사용 하 여 분석 하 고 중요 한 상호 작용은 간단한 효과 테스트를 사용 하 여 분석 되었다. 모든 통계 분석 0.05의 최소한 알파를 사용 하 여 실시 했다 및 그래프에 결과 평균 ± SEM.
적응형 CR 비율 측정부터, ANOVA 신생아 그룹, F(2,21)의 중요 한 주요 효과 표시 11.69, p = < 0.001, 하지만 섹스의 중요 한 주요 효력이 없다 (p = 0.71) 또는 이러한 요소 사이의 중요 한 상호 작용 (p = 0.20). CR 비율 적응 훈련, F(5, 105)의 6 개의 세션에 걸쳐 증가 예상 대로 81.15, p = < 0.001, 그리고 신생아 그룹 간의 차이 일정 수준의 세션, F(10, 105)에 의존 했다 4.58, p = < 0.001. 전혀 다른 중요 한 상호 작용 세션 요소를 포함 했다. 마찬가지로 적응 CR 진폭, 거기 했다 다시 신생아 그룹, F(2,21)의 중요 한 주요 효과 22.32, p = < 0.001, 하지만 섹스의 중요 한 주요 효력이 없다 (p = 0.21) 또는 이러한 요소 사이의 중요 한 상호 작용 (p = 0.48). CR 진폭 또한 훈련, F(5, 105)의 6 개의 세션에 걸쳐 크게 증가 59.27, p = < 0.001, 그리고 신생아 그룹 간의 차이 일정 수준의 세션, F(10, 105)에 의존 했다 4.31, p = < 0.001. 전반적으로, 두 CR 조치 그룹 의미와 훈련의 다른 세션에서 크게 구분이 의미 간의 중요 한 차이 보였다. 확인 하려면 그룹 크게 달랐다, Tukey의 포스트 hoc 테스트는 알코올 intubated (AI) 쥐 수행 크게 악화 (UC) unintubated-제어 및 가짜 intubated (SI) 쥐 보다 두 CR 조치에 나타났다 (p < 0.01 CR 비율; p < CR 진폭 0.001)는 서로 다를 하지 않았다 (p> 0.05). 간단한 효과 테스트 AI 쥐 CRs 세션 2에서 시작 하 고 세션 6 들고 UC와 시 쥐에 비해 인수에 더 크게 손상 되었다 확인 두 CR 조치에 대 한 상호 작용 세션 x 상당한 Neonatal 그룹에 수행 (모든 p< 0.05)는 6 개의 세션에 걸쳐 서로 다 하지 않았다. 유일한 예외는 적응형 CR 진폭 시 쥐 세션 3까지 AI 쥐에서 크게 다를 시작 하지 않았다 했다. 이러한 결과 그림 5A, 5B에 표시 됩니다.
섹스, 신생아 그룹, 또는 세션 요소와 이러한 요소의 상호 작용 통해 UR 대책에 상당한 차이가 있었다. 이러한 부정적인 결과 표시 각 그룹은 동등 하 게, 충격 eyeblink 응답 우리 방출할 수 동기 또는 모터 차이 (그림 6A, 6B) 점멸에 의해 영향을 학습 적자 AI 쥐에서 관찰 되지 않았습니다.
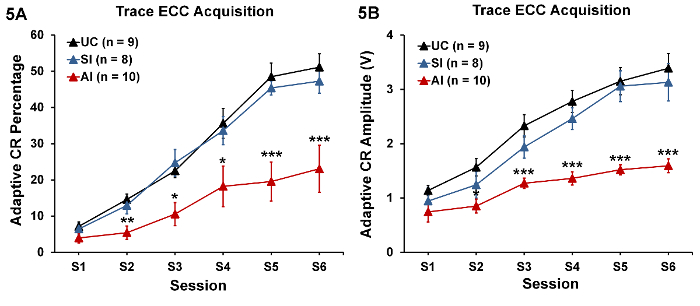
그림 5 : 추적의 인수 조건 응답 (평균 ± SEM). 초기 알콜 노출 (AI 그룹) 적합 조건 반응 (CR) 비율 (A)와 (B) 진폭의 인수를 크게 영향을 받습니다. 추적 ECC는 본질적으로 얻기 어렵다, 따라서 조치는 모든 그룹-지연 ECC에 대 한 상대적으로 낮은, 백분율 FASD21,53의 설치류 모델에서 80-85%에 도달할 수 있습니다. 그럼에도 불구 하 고, 추적 ECC 절차는 쉽습니다 알코올 효과 초기 두뇌 발달 동안에 해 마, 부담 스러운 더 많은입니다. p 를 = < 0.05, * * p = < 0.01, * * * = p < UC 및 AI 쥐; 사이 0.001 샘플 크기는 괄호에 제공 됩니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭 하십시오.
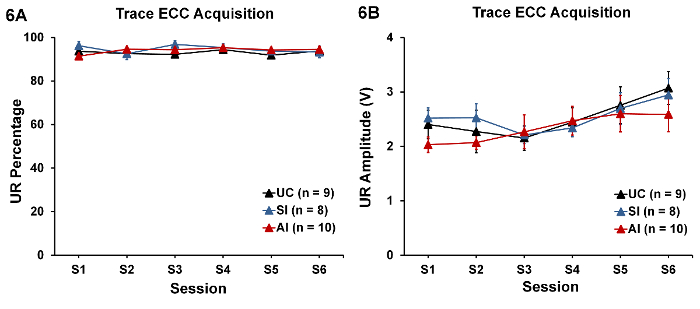
그림 6 : Unconditioned 응답 (± SEM을 의미)의 인수. Eyeblink 성능 (UR 비율과 UR 진폭) 그룹 중 크게 다른 아니었다. 차이의 부족 수집 훈련 중에 사용 하는 충격 강도 차동 AI 쥐 동기 부여를 변경 하지 않았다 또는 그들의 생산 능력을 방어 깜박 모두 제어 그룹 (UC 및 SI)에 비해 충격에 대 한 응답을 나타냅니다. 샘플 크기는 괄호에 제공 됩니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭 하십시오.
토론
출생 후 일 4-9 중 에틸 알코올을 받은 신생아 쥐 새끼 추적 eyeblink 성인에서 장애를 컨디셔닝 전시. 이러한 연구 결과 알코올 hippocampal 기능에 해로운 효과 지속으로 기형 발생 물질은 아이디어를 지원 합니다. 전반적으로, 조건 응답 추적 절차에 있던 두 컨트롤 그룹에 있는 쥐에 비해 알코올에 노출 된 쥐를 위해. 알코올에 노출 된 쥐에 연관 학습 장애 동기 또는 모터 차이 의해 영향을 받지 했다 (즉., 깜박이 충격 미국 강도 차이가).
추적 ECC elucidating 도전 유도 hippocampal neuropathology에 대 한 유용한 진단 도구입니다, 하는 동안이 메서드의 결과 적절 한 문맥에 배치 되어야 합니다. 첫째,이 데모의 핵심 절차 요소 개발 두뇌 하 시 활동의 기록을 허락 한다 충격, 위에서 언급 한 하드웨어, 그리고 관심의 인지 기능을 평가 하는 학습 패러다임을 사용 하 여 후속 동물 테스트의 외과 이식 전극 하드웨어의 제작에 대 한 취약성의 알려진된 창 동안 알코올의 대상된 배달 관련. 과정에서 각 단계에서 해야 합니다 주의 쥐 주제에 의도 하지 않은 불필요 한 피해를 발생 하지 하 고 그들의 건강 징후를 정기적으로 모니터링 합니다. 그들의 행동 결과 인지 "창"을 제공, 정확 하 게는 심리적 구조 설명 때 그들의 건강 알코올 주입, 하드웨어 결함, 또는 수술 주입을 포괄 하는 실험적인 오류에 의해 손상 되지. 따라서, 연구 과정에서 절차 상의 각 요소 간에 발견에 ECC에서 결과 추정 수 있도록 사운드 방식으로 구현 되어야 합니다. 둘째, ECC 패러다임 연관 학습의 본질에 통찰력을 제공 하지만 해야 합니다 주의 하지이 접근을 사용 하 여 결과 확장 하 고 광범위 하 게 다른 인지 도메인-작업 메모리, 단기/장기 기억, 의식-등을 돌리다 한 실험적인 디자인으로 ECC 연구 내에서이 도메인의 일부 일 면을 통합 했다 하지 않는 한. 예를 들어이 데모 추적 ECC 학습의 수집 단계를 검사 하지만 그들은 훈련을 완료 한 후 쥐에 메모리 보존을 조사 하지 않았다. 메모리는 이렇게 학습 이외에 평가 해야 하는 독립적인 심리적 프로세스입니다. 디자인, 하나 중 단기 또는 장기 메모리 능력을 평가 하기 위해 메모리 보존 간격을 통합할 수 있습니다. 셋째, 병렬 메모리 시스템54 동작을 동기, 경험, 그리고 호르몬 요인 함께 동시에 작동 하지 않을 수 있습니다 인정 (ECC) 동안 연관성은 이해 하지만 "좋은" 또는 "가난한" 학습에 대해 공개 하는 많은 프로세스 중 하나에 대 한 필수적입니다. 마지막으로, 추적 ECC 아니다 순전히 hippocampal 종속 작업, 다른 뇌 영역 크롬의 몇 가지 구성 요소를 중재할 수 있습니다. 따라서, 다른 신경 회로 및 자극 매개 변수를 연구에 활용, 의미 개별 결과에 따라 때에 고려 한다 유형 사이 상호 작용의 이해. 소 뇌, 예, 또한 추적 ECC, 어디 그것 영향 CR와 타이밍, 특히 ISI는 짧은 기간에 크롬의 지형 특성에 기여. 추적 ECC 긴 추적 간격 (1000 ms), 테스트는 인간 소 뇌 손상에 영향을 받지 않습니다 하지만 그는 짧은 추적 간격 (400 ms)34에 영향을. 또한, 마우스에 이전 대상 및 중간 agranular 영역을 대상으로 등 쪽 내측 전 두 엽 피 질 (mPFC)의 양측 병 변 비슷한 결과46를 생산 하는 토끼에서 꼬리 mPFC의 파괴 하는 동안 추적55, CRs 인수를 방지 합니다. 이러한 연구 결과 또한 고려 소 뇌-뇌 전 두 엽 기여에 종 차이 줄기 추적 ECC와 같은 구동된 연관 학습의 중요성을 강조. 성인 500 ms 추적 CRs의 PD 4-9에 부정적인 영향을 중 신생아 알코올 노출 쥐이 연구 등에서47,56, 이것은 하지 알콜 (5 g/kg)57, 알코올에 노출 된 쥐에 추적 장애 추적 간격의 기간에 따라 달라 집니다 제안의 상대적으로 높은 복용량에 도전 하는 경우에 300 ms 추적 간격을 경험 하는 신생아 알코올에 노출 된 쥐에 대 한 같은 경우.
본이 연구에서는 해 마 신경 관련 손상 장애 추적 CRs의 취득에 의해 반영 된 전시 vitally 중요 추적 ECC, 중재에 대 한 신생아 알콜 노출에 의해 도전 되 고 강조 했다. 그러나 그것은,, 소 뇌-뇌 줄기 회로, 특히 interpositus 핵, ECC, 수집, 식, ECC 작업 포함 추적 ECC36,40,55,,5859의 종류에 따라 CR의 지형 기능 등의 다양 한 측면에 대 한 필수적입니다 경고 해야 합니다. 실제로,이 신경 회로 추적 ECC60등 ECC의 더 높은 순서 형태 동안 CRs의 식 구동을 위한 해 마와 상호 작용 합니다. 여부 알코올 노출 초기 두뇌 발달 동안 구체적으로 영향을 미치는 hippocampal 기능 추적 ECC에에서 완전히 명확 하지 않습니다. 많은 다른 두뇌 지구는 mPFC, 소 뇌, 그리고 해 마18,19,23,47,,6162를 포함 하 여 초기 알코올 모욕에 취약 하 고 알코올 많은 ECC 절차에 걸쳐 이러한 구조를 다양 한 각도 변화, 하지만 기능적으로 중요 한 차이의 기능 방해 매우 높습니다. 추적 ECC 연구에서 결과의 해석에 관한 함정, 불구 추적 CRs의 성공적인 인수 표시 되었습니다 적어도 그대로 해 마에 의존 하는 동물 병 변 연구42,44,63,,6465에 의해 지원. 이 프로시저는 추적 조건 때문에, 기본 신경 회로 훨씬 더 나은 응답을 발달 알코올 노출 사이의 링크 모리스 물 미로에 장소 학습 등 다른 hippocampal 종속 작업 보다 소설 개체 인식, 이해 위한 매우 귀중 한 접근에 따라서 남아 있다 및 콘텐츠 및 컨디셔닝 공포 추적.
"시험" 인식, 행동 방법으로 ECC 발달 neuroteratology의 분야에서 광범위 한 적용을 있다. 실제로, 우리의 실험실에서 최근 연구 결과 개발 해 마는 다른 중재 전략18,47에 의해 완화 될 수 있습니다 알코올 효과에 매우 민감한 개념 지원. 여기에 주요 장점은 그 알코올 유발 추적 ECC 학습 적자의 더 나은 이해, 그들은 수 있습니다 연관 학습-외부 기반 hippocampal 기능에서 다른 문제의 예측 같은 hippocampal neurocircuitry에 의해 중재 될 것으로 알려져 특히 그입니다.
응용 프로그램 추적 ECC 및 그것의 다른 변종 (예를 들어, 지연, 반전, 차별, 복합) neurobiological 메커니즘 및 신경 시스템 연관 학습에 관련 된 명료 하의 태아 알코올 연구의 분야를 넘어 확장할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어이 패러다임에 인간의 경우 정신 분열 증66,67같은 정신 조건, 알 츠 하이 머 병68,69, 같은 신경 퇴행 성 질환의 동물 모델 및 약물 남용70,,7172의 많은 관심을 받았습니다. Neurocognitive 기능 부전을 평가 하는 연구 방법으로 그 혜택은 따라서 신경 과학을 비롯 한 많은 심리적, 생물 의학 분야에 걸쳐 분명 있습니다.
공개
저자는 공개 없다.
감사의 말
이 작품은 지원 교부 금에 의해 TDT에서는 알콜 음료 의료 연구 재단 (ABMRF).
자료
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Neonatal Alcohol Exposure | |||
| 190 Proof Ethyl Alcohol (USP) | Pharmco-AAPER | 225-36000 [ECU Medical Storeroom] | Can be substituted; should be USP; avoid using 200 proof ethyl alcohol |
| Container/Basket for Pups | Any | ||
| Corn Oil | Any | Food grade | |
| Heated Water Therapy Pump w/ Pads | Gaymar | TP-500 | To keep pups warm; can be substituted |
| Hypodermic Needles 22G x 1 in, Sterile | Any | ||
| Hypodermic Needles 30G x 1/2 in, Sterile | Any | ||
| Isopropyl Alcohol 70% | EMD Millipore | PX1840-4 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted; reagent grade www.fishersci.com |
| Long-Evans Rats (Female and Male Breeders) | Charles River Laboratories | N/A [ECU Dept. of Comparative Medicine] | Age and weight need to be specified; pricing varies by these factors www.criver.com |
| Micro Dissecting Scissors, 3.5 in, 23 mm Blades | Biomedical Research Instruments | 11-2200 | For cutting PE tubing brisurgical.com |
| Polyethylene 10 Tubing (0.011 in. I.D.; 0.024 in. O.D.) | BD Diagnostic Systems | 22-204008 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| Polyethylene 50 Tubing (0.023 in. I.D.; 0.038 in. O.D.) | BD Diagnostic Systems | 22270835 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| Regulated water heater or baby milk bottle warmer | Any | Optional; helps with warming up cold milk solutions | |
| Tuberculin Syringes, Sterile, 1.0 ml | Any | ||
| Tuberculin Syringes, Sterile, 10 ml | Any | Can be used to draw out ethyl alcohol or use appropriate size micropipet | |
| Weigh Scale | Any | Should have good resolution (in gram units) | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| EMG Headstage Fabrication and Bipolar Electrode Modification | |||
| Bipolar Electrode, 2 Channel SS Twisted | Plastics One, Inc. | MS303/2-B/SPC ELECT SS 2C TW .008" | Must specify custom length of 20 mm below pedestal www.plastics1.com |
| Centi-Loc Strip Socket Insulator (aka, Micro Strip) | ITT Cannon / ITT Interconnect Solutions | CTA4-IS-60* or CTA4-1S-60* | *Depends on vendor; see www.onlinecomponents.com or www.avnetexpress.avnet.com |
| Dental Pliers, Serrated | CMF Medicon | 390.20.05 | Can be substituted; use to crimp wires to male contact pins www.medicon.de |
| Micro Dissecting Scissors, 3.5 in, 23 mm Blades | Biomedical Research Instruments | 11-2200 | Only use to cut 3T wires; cutting 10T wires will damage the blade - use the blade of the wire stripper instead brisurgical.com |
| PTFE-Coated Stainless Steel Wire, 10T (Bare Diameter .010 in) | Sigmund Cohn-Medwire | 316SS10T | www.sigmundcohn.com |
| PTFE-Coated Stainless Steel Wire, 3T (Bare Diameter 0.003 in) | Sigmund Cohn-Medwire | 316SS3T | www.sigmundcohn.com |
| Razor Blade | Any | To strip 1 mm from prongs of bipolar electrode | |
| Relia-Tac Socket Contact Pin, Male | Cooper Interconnect | 220-P02-100 | See Allied Electronics Cat # 70144761 www.alliedelec.com |
| Tweezers, High Precision, Serrated, 4 3/4 in | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 78314-00D | To grasp 10T wire firmly while stripping PTFE with smooth tweezers www.emsdiasum.com |
| Tweezers, High Precision, Smooth, 4 3/4 in | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 78313-00B | www.emsdiasum.com |
| Tweezers, Ultra Fine Tips, 4 3/4 in | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 78510-0 | To strip 1 mm of PTFE from one end of 3T wire; grasp shielded portion with smooth tweezers www.emsdiasum.com |
| Wire Stripper, 16-26 AWG | Any | Use the blade end to cut micro strips | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Eyelid Surgery | |||
| Surgical Instruments (High Quality Stainless Steel) | |||
| 2 x Dressing Forceps, 4 in Serrated | Biomedical Research Instruments | 30-1205 | Can be substituted; extra forceps for grasping electrodes/screws outside of surgery tray brisurgical.com |
| Dressing Forceps, 3 in Serrated | Biomedical Research Instruments | 30-1200 | Can be substituted brisurgical.com |
| Instrument Tray | Biomedical Research Instruments | 24-1355 | Can be substituted brisurgical.com |
| Knife Handle No. 3, 5 in | Biomedical Research Instruments | 26-1000 | Can be substituted brisurgical.com |
| Micro Dissecting Forceps, 3.5 in, Fine Points | Biomedical Research Instruments | 10-1630 | Can be substituted brisurgical.com |
| Micro Dissecting Forceps, 3.5 in, Smooth Platform (0.3 x 5 mm) | Biomedical Research Instruments | 10-1720 | brisurgical.com |
| Micro Dissecting Scissors, 3.5 in, Extremely Delicate, 15 mm Blades | Biomedical Research Instruments | 11-2000 | Can be substituted brisurgical.com |
| Plain Splinter Forceps, 3.5 in | Biomedical Research Instruments | 30-1600 | Can be substituted brisurgical.com |
| #10 Stainless Steel Surgical Blade for #3 Handle, Sterile | Any | Can be substituted | |
| 0-80 x 0.125 in Stainless Steel Screws | Plastics One, Inc. | 0-80 x 0.125 | Can be substituted www.plastics1.com |
| Alcohol Prep Pads, Sterile | Fisher Scientific | 22-363-750 [Fisher Scientific | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| Betadine Povidone-Iodine | Purdue Frederick Co. | 6761815101 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| Betadine Povidone-Iodine Prep Pads | Moore Medical | 19-898-946 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| Cotton-Tipped Swabs, Autoclavable | Any | Typically 7.6 cm or 15.2 cm length | |
| Drill Bit for Pin Vise, #55 (0.052 in) | Any | Metal should resist rusting and corrosion | |
| Gauze Pads, 2 in x 2 in | Fisher Scientific | 22-362-178 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| General Purpose Latex/Nitrile/Vinyl Gloves | Any | ||
| Glass Bead Sterilizer | Any | Sterilize instruments between surgeries | |
| Heated Water Therapy Pump w/ Pads x 2 | Gaymar | TP-500 | Can be substituted; separate pumps are recommended - 1 for surgery, 1 for recovery |
| Hypodermic Needles 26G x 3/8 in, Sterile | Any | ||
| Isoflurane | Vedco | NDC 50989-150-12 | Manfacturer can be substituted; veterinary approval may be required |
| Isoflurane Vaporizer System, Tabletop, Non-Rebreathing | Parkland Scientific | V3000PK | Can be substituted www.parklandscientific.com |
| Jewelers Screwdriver w/ 1.8-2 mm Blade | Any | Metal should resist rusting and corrosion | |
| Ortho-Jet BCA Package (Dental Cement) | Lang Dental | B1334 | Contains powder (1 lb) and liquid www.langdental.com |
| Oxygen Tank with Pressure Regulator, Large | Local supplier | ||
| Porcelain Crucible, High-Form, Glazed, 10 ml | CoorsTek, Inc. | 07-965C [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted with Fisher FB-965-I Wide-Form Crucible www.fishersci.com |
| Puralube Veterinary Ophthalmic Ointment, Sterile | Henry Schein Company | NC0144682 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| Quatricide PV-15 | Pharmacal | PV-15 | Antimicrobial disinfectant; can be substituted www.pharmacal.com |
| Rat Gas Anesthesia Masks for Stereotaxic Surgery | Stoelting Company | 51610 | www.stoeltingco.com |
| Rat Stereotaxic Apparatus w/ Ear Bars (45 Degree) | Any | 45 degree bars are recommended to prevent damaging eardrums | |
| Roboz Surgical Instrument Milk | Roboz Surgical | NC9358575 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted; for lubricating instruments during autoclaving www.fishersci.com |
| Rodent Hair Trimmer | Any | ||
| Sodium Chloride | Fisher Scientific | S641-500 [Fisher Scientific] | To make 0.9% saline; reagent grade; USP www.fishersci.com |
| Stainless Steel Microspatula (Blade: 0.75 L x 0.18 in. W) | Fisher Scientific | 21-401-15 [Fisher Scientific] | Can be substituted www.fishersci.com |
| Starrett Pin Vise, 0.000 in - 0.055 in | Any | Nickel-plated or equivalent recommended to resist rusting and corrosion | |
| Sterile Surgical Gloves | Any | ||
| Sterilization Wraps, 20 in x 20 in, Autoclavable | Propper Manufacturing | 11-890-8C [Fisher Scientific] | Useful for wrapping autoclavable supplies and on sterile field during surgery www.fishersci.com |
| Surgical Drape, Sterile/Autoclavable | Any | May need to cut to size for rats | |
| Surgical Gown* | Any | *If required by IACUC | |
| Surgical Mask | Any | ||
| Tuberculin Syringes, Sterile, 1.0 ml | Any | ||
| Weigh Scale | Any | Should have good resolution (in gram units) | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Eyeblink System and Components (assuming 4-rodent system) | |||
| 5 Channel Commutator x 4 | Plastics One, Inc. | SL2 + 3C | www.plastics1.com |
| Bipolar Electrode Cable, Dual 305 x 4 | Plastics One, Inc. | 305-305 80CM TT2 (C) | Provides plug end to bipolar electrode on rat and to commutator; must be modified www.plastics1.com |
| Cable, 5 Channel, Shielded, 26 AWG x 4 | Any | To fabricate commutator cable; this must be made from scratch | |
| Chamber for Operant Test Box (Inside: 24 H x 23 W x 14 D in) x 4 | Med-Associates | Can be substituted; inner dimensions should fit operant test box comfortably, with room for acoustical foam; fit with fan - 55-60 dB www.med-associates.com | |
| Eyeblink System and Software | JSA Designs | N/A | Proprietary and customized for research lab |
| Heat Shrink Tubing (3/16 in, 1/4 in, 3/8 in, 1/2 in Diameters) | Any | To protect modified commutator cable soldered ends and splices | |
| Melamine Triple Peak Acoustical Foam w/Black Hypalon (24 x 48 in) | McMaster-Carr | 9162T5 | Can be substituted; cut to fit 4 housing chambers www.mcmaster.com |
| Operant Test Box (Exterior 12.5 L x 10 W x 13.5 in H), Complete x 4 | Med-Associates | ENV-007 Custom Package | With stainless steel grid floor and custom top (3 in hole in center for commutator cable) www.med-associates.com |
| Oscilloscope (Optional) | Any | Recommended minimum specs: 200 MHz analog bandwidth, 1 GS/s real-time sampling, 4 channels; see www.picotech.com /td> | |
| Piezo Tweeters (Speakers) x 4 (7 x 3 in) | MCM Electronics | 53-805 | Must match frequency range specifications for eyeblink system (2500 Hz - 25 KHz) www.mcmelectronics.com |
| Soldering Station, Solder, Flux, Tinner | Any | For soldering 26 AWG cables to female sockets (that fit male relia-tac contact pins) and bipolar plugs | |
| Stimulus Isolators x 4 | WPI International | A365 | These units run on 16-9V alkaline batteries; a suitable rechargeable version (A365R) is available www.wpiinc.com |
| Tripolar Electrode Cable for SL3C Commutator x 4 | Plastics One, Inc. | 335-335 80cm TT3 C | Provides plug end to EMG headstage on rat and to commutator; must be modified www.plastics1.com |
| USB LED Lights x 4 | Any | USB-based lights do not cause electrical "noise" with the EMG signals from the rats www.plastics1.com | |
| Webcams x 4, Surveillance Software | Any | ||
| PC Computer Running MS Windows OS | Any |
참고문헌
- Jones, K. L., Smith, D. W. Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet. 2, 999-1001 (1973).
- Stratton, K. R., Howe, C. J., Battaglia, F. C. . Fetal alcohol syndrome: Diagnosis, epidemiology, prevention, and treatment. , (1996).
- Streissguth, A. P., Barr, H. M., Martin, D. C., Herman, C. S. Effects of maternal alcohol, nicotine, and caffeine use during pregnancy on infant mental and motor development at eight months. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 4 (2), 152-164 (1980).
- Streissguth, A. P., O'Malley, K. Neuropsychiatric implications and long-term consequences of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry. 5 (3), 177-190 (2000).
- May, P. A., et al. Prevalence and epidemiologic characteristics of FASD from various research methods with an emphasis on recent in-school studies. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 15 (3), 176-192 (2009).
- Sowell, E. R., et al. Mapping callosal morphology and cognitive correlates: Effects of heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Neurology. 57 (2), 235-244 (2001).
- Sowell, E. R., et al. Abnormal development of the cerebellar vermis in children prenatally exposed to alcohol: Size reduction in lobules I-V. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 20 (1), 31-34 (1996).
- Autti-Ramo, I., et al. MRI findings in children with school problems who had been exposed prenatally to alcohol. Dev Med Child Neurol. 44 (2), 98-106 (2002).
- Hamilton, D. A., Kodituwakku, P., Sutherland, R. J., Savage, D. D. Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome are impaired at place learning but not cued-navigation in a virtual Morris water task. Behav Brain Res. 143 (1), 85-94 (2003).
- Uecker, A., Nadel, L. Spatial but not object memory impairments in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Am J Ment Retard. 103 (1), 12-18 (1998).
- Uecker, A., Nadel, L. Spatial locations gone awry: object and spatial memory deficits in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Neuropsychologia. 34 (3), 209-223 (1996).
- Goodlett, C. R., Lundahl, K. R. Temporal determinants of neonatal alcohol-induced cerebellar damage and motor performance deficits. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 55 (4), 531-540 (1996).
- Goodlett, C. R., Kelly, S. J., West, J. R. Early postnatal alcohol exposure that produces high blood alcohol levels impairs development of spatial navigation learning. Psychobiol. 15, 64-74 (1987).
- Bayer, S. A., Altman, J., Russo, R. J., Zhang, X. Timetables of neurogenesis in the human brain based on experimentally determined patterns in the rat. Neurotoxicol. 14 (1), 83-144 (1993).
- Dobbing, J., Sands, J. Quantitative growth and development of human brain. Arch Dis Child. 48 (10), 757-767 (1973).
- West, J. R. Fetal alcohol-induced brain damage and the problem of determining temporal vulnerability: A review. Alcohol Drug Res. 7 (5-6), 423-441 (1987).
- Zecevic, N., Rakic, P. Differentiation of Purkinje cells and their relationship to other components of developing cerebellar cortex in man. J Comp Neurol. 167, 27-48 (1976).
- Rufer, E. S., et al. Adequacy of maternal iron status protects against behavioral, neuroanatomical, and growth deficits in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. PLoS One. 7 (10), e47499 (2012).
- Tran, T. D., Kelly, S. J. Critical periods for ethanol-induced cell loss in the hippocampal formation. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 25 (5), 519-528 (2003).
- Pierce, D. R., Goodlett, C. R., West, J. R. Differential neuronal loss following early postnatal alcohol exposure. Teratology. 40 (2), 113-126 (1989).
- Tran, T. D., Jackson, H. J., Horn, K. H., Goodlett, C. R. Vitamin E does not protect against neonatal ethanol-induced cerebellar damage or deficits in eyeblink classical conditioning in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 29 (1), 117-129 (2005).
- Goodlett, C. R., Peterson, S. D., Lundahl, K. R., Pearlman, A. D. Binge-like alcohol exposure of neonatal rats via intragastric intubation induces both Purkinje cell loss and cortical astrogliosis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 21 (6), 1010-1017 (1997).
- Green, J. T., Tran, T. D., Steinmetz, J. E., Goodlett, C. R. Neonatal ethanol produces cerebellar deep nuclear cell loss and correlated disruption of eyeblink conditioning in adult rats. Brain Res. 956, 302-311 (2002).
- Cronise, K., Marino, M. D., Tran, T. D., Kelly, S. J. Critical periods for the effects of alcohol exposure on learning in rats. Behav Neurosci. 115 (1), 138-145 (2001).
- Tran, T. D., Cronise, K., Marino, M. D., Jenkins, W. J., Kelly, S. J. Critical periods for the effects of alcohol exposure on brain weight, body weight, activity and investigation. Behav Brain Res. 116 (1), 99-110 (2000).
- Steinmetz, J. E. Brain substrates of classical eyeblink conditioning: A highly localized but also distributed system. Behav Brain Res. 110 (1-2), 13-24 (2000).
- Thompson, R. F. The neurobiology of learning and memory. Science. 233 (4767), 941-947 (1986).
- Ivkovich, D., Eckerman, C. O., Krasnegor, N. A., Stanton, M. E., Woodruff-Pak, D. S., Steinmetz, J. E. . Eyeblink classical conditioning: Vol. 1 Applications in humans. , 119-142 (2000).
- Woodruff-Pak, D. S., Steinmetz, J. E. . Eyeblink classical conditioning: Volume I - Applications in humans. , (2000).
- Woodruff-Pak, D. S., Steinmetz, J. E. . Eyeblink classical conditioning: Volume II - Animal models. , (2000).
- Kishimoto, Y., et al. Implicit Memory in Monkeys: Development of a Delay Eyeblink Conditioning System with Parallel Electromyographic and High-Speed Video Measurements. PLoS One. 10 (6), e0129828 (2015).
- Chen, L., Bao, S., Lockard, J. M., Kim, J. K., Thompson, R. F. Impaired classical eyeblink conditioning in cerebellar-lesioned and Purkinje cell degeneration (pcd) mutant mice. J Neurosci. 16 (8), 2829-2838 (1996).
- Freeman, J. H., Carter, C. S., Stanton, M. E. Early cerebellar lesions impair eyeblink conditioning in developing rats: Differential effects of unilateral lesions on postnatal day 10 or 20. Behav Neurosci. 109 (5), 893-902 (1995).
- Gerwig, M., et al. Trace eyeblink conditioning in patients with cerebellar degeneration: Comparison of short and long trace intervals. Exp Brain Res. 187 (1), 85-96 (2008).
- LaBar, K. S., Disterhoft, J. F. Conditioning, awareness, and the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 8 (6), 620-626 (1998).
- McCormick, D. A., Steinmetz, J. E., Thompson, R. F. Lesions of the inferior olivary complex cause extinction of the classically conditioned eyeblink response. Brain Res. 359 (1-2), 120-130 (1985).
- Clark, R. E., Zola, S. Trace eyeblink classical conditioning in the monkey: a nonsurgical method and behavioral analysis. Behav Neurosci. 112 (5), 1062-1068 (1998).
- Anderson, B. J., Steinmetz, J. E. Cerebellar and brainstem circuits involved in classical eyeblink conditioning. Rev Neurosci. 5 (3), 251-273 (1994).
- Thompson, R. F., Krupa, D. J. Organization of memory traces in the mammalian brain. Annu Rev Neurosci. 17, 519-549 (1994).
- Miller, M. J., et al. fMRI of the conscious rabbit during unilateral classical eyeblink conditioning reveals bilateral cerebellar activation. J Neurosci. 23 (37), 11753-11758 (2003).
- Geinisman, Y., et al. Remodeling of hippocampal synapses after hippocampus-dependent associative learning. J Comp Neurol. 417 (1), 49-59 (2000).
- Ivkovich, D., Stanton, M. E. Effects of early hippocampal lesions on trace, delay, and long-delay eyeblink conditioning in developing rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 76 (3), 426-446 (2001).
- Moyer, J. R., Deyo, R. A., Disterhoft, J. F. Hippocampectomy disrupts trace eye-blink conditioning in rabbits. Behav Neurosci. 104 (2), 243-252 (1990).
- Solomon, P. R., Vander Schaaf, E. R., Thompson, R. F., Weisz, D. J. Hippocampus and trace conditioning of the rabbit's classically conditioned nictitating membrane response. Behav Neurosci. 100 (5), 729-744 (1986).
- Kronforst-Collins, M. A., Disterhoft, J. F. Lesions of the caudal area of rabbit medial prefrontal cortex impair trace eyeblink conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 69 (2), 147-162 (1998).
- Weible, A. P., McEchron, M. D., Disterhoft, J. F. Cortical involvement in acquisition and extinction of trace eyeblink conditioning. Behav Neurosci. 114 (6), 1058-1067 (2000).
- Thomas, J. D., Tran, T. D. Choline supplementation mitigates trace, but not delay, eyeblink conditioning deficits in rats exposed to alcohol during development. Hippocampus. 22 (3), 619-630 (2012).
- West, J. R., Hamre, K. M., Pierce, D. R. Delay in brain growth induced by alcohol in artificially reared rat pups. Alcohol. 1 (3), 213-222 (1984).
- Geiger, B. M., Frank, L. E., Caldera-Siu, A. D., Pothos, E. N. Survivable stereotaxic surgery in rodents. J Vis Exp. (20), e880 (2008).
- Christian, K. M., Thompson, R. F. Neural substrates of eyeblink conditioning: acquisition and retention. Learn Mem. 10 (6), 427-455 (2003).
- Kishimoto, Y., Nakazawa, K., Tonegawa, S., Kirino, Y., Kano, M. Hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors are crucial for adaptive timing of trace eyeblink conditioned response. J Neurosci. 26 (5), 1562-1570 (2006).
- Shors, T. J., et al. Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature. 410 (6826), 372-376 (2001).
- Tran, T. D., Stanton, M. E., Goodlett, C. R. Binge-like ethanol exposure during the early postnatal period impairs eyeblink conditioning of short and long CS-US intervals in rats. Dev Psychobiol. 49 (6), 589-605 (2007).
- Mizumori, S. J., Yeshenko, O., Gill, K. M., Davis, D. M. Parallel processing across neural systems: Implications for a multiple memory system hypothesis. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 82 (3), 278-298 (2004).
- Siegel, J. J., et al. Trace Eyeblink Conditioning in Mice Is Dependent upon the Dorsal Medial Prefrontal Cortex, Cerebellum, and Amygdala: Behavioral Characterization and Functional Circuitry(1,2,3). eNeuro. 2 (4), (2015).
- Murawski, N. J., Jablonski, S. A., Brown, K. L., Stanton, M. E. Effects of neonatal alcohol dose and exposure window on long delay and trace eyeblink conditioning in juvenile rats. Behav Brain Res. 236 (1), 307-318 (2013).
- Lindquist, D. H. Hippocampal-dependent Pavlovian conditioning in adult rats exposed to binge-like doses of ethanol as neonates. Behav Brain Res. 242, 191-199 (2013).
- Ivarsson, M., Svensson, P. Conditioned eyeblink response consists of two distinct components. J Neurophysiol. 83 (2), 796-807 (2000).
- Woodruff-Pak, D. S., Lavond, D. G., Thompson, R. F. Trace conditioning: abolished by cerebellar nuclear lesions but not lateral cerebellar cortex aspirations. Brain Res. 348 (2), 249-260 (1985).
- Takehara-Nishiuchi, K. The Anatomy and Physiology of Eyeblink Classical Conditioning. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. , (2016).
- Mattson, S. N., Schoenfeld, A. M., Riley, E. P. Teratogenic effects of alcohol on brain and behavior. Alcohol Res Health. 25 (3), 185-191 (2001).
- Goodfellow, M. J., Abdulla, K. A., Lindquist, D. H. Neonatal Ethanol Exposure Impairs Trace Fear Conditioning and Alters NMDA Receptor Subunit Expression in Adult Male and Female Rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 40 (2), 309-318 (2016).
- Beylin, A. V., et al. The role of the hippocampus in trace conditioning: Temporal discontinuity or task difficulty?. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 76 (3), 447-461 (2001).
- Port, R. L., Romano, A. G., Steinmetz, J. E., Mikhail, A. A., Patterson, M. M. Retention and acquisition of classical trace conditioned responses by rabbits with hippocampal lesions. Behav Neurosci. 100 (5), 745-752 (1986).
- Weiss, C., Bouwmeester, H., Power, J. M., Disterhoft, J. F. Hippocampal lesions prevent trace eyeblink conditioning in the freely moving rat. Behav Brain Res. 99 (2), 123-132 (1999).
- Brown, S. M., et al. Eyeblink conditioning deficits indicate timing and cerebellar abnormalities in schizophrenia. Brain Cogn. 58 (1), 94-108 (2005).
- Sears, L. L., Steinmetz, J. E. Effects of haloperidol on sensory processing in the hippocampus during classical eyeblink conditioning. Psychopharmacology. 130 (3), 254-260 (1997).
- Kronforst-Collins, M. A., Moriearty, P. L., Schmidt, B., Disterhoft, J. F. Metrifonate improves associative learning and retention in aging rabbits. Behav Neurosci. 111 (5), 1031-1040 (1997).
- Woodruff-Pak, D. S., Finkbiner, R. G., Sasse, D. K. Eyeblink conditioning discriminates Alzheimer's patients from non-demented aged. Neuroreport. 1 (1), 45-48 (1990).
- Oristaglio, J., Romano, A. G., Harvey, J. A. Amphetamine influences conditioned response timing and laterality of anterior cingulate cortex activity during rabbit delay eyeblink conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 92 (1), 1-18 (2009).
- Scavio, M. J., Clift, P. S., Wills, J. C. Posttraining effects of amphetamine, chlorpromazine, ketamine, and scopolamine on the acquisition and extinction of the rabbit's conditioned nictitating membrane response. Behav Neurosci. 106 (6), 900-908 (1992).
- Fortier, C. B., et al. Delay discrimination and reversal eyeblink classical conditioning in abstinent chronic alcoholics. Neuropsychology. 22 (2), 196-208 (2008).
재인쇄 및 허가
JoVE'article의 텍스트 или 그림을 다시 사용하시려면 허가 살펴보기
허가 살펴보기더 많은 기사 탐색
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유