마그네틱 부품 특성
Overview
출처: 알리 바지, 코네티컷 대학교 전기 공학학과, 스토스, CT.
이 실험의 목적은 설계 및 재료 관점에서 다른 자기 구성 요소로 실습 경험을 달성하는 것입니다. 이 실험은 알 수 없는 설계 요소를 식별하여 자기 물질 및 인덕터 설계의 B-H 곡선을 다룹니다. 인덕터 나 변압기와 같은 자기 요소의 B-H 곡선은 권선이 감싸는 코어를 형성하는 자기 물질의 특성입니다. 이러한 특성은 코어가 권선에서 흐르는 전류에 대해 처리할 수 있는 자기 플럭스 밀도에 대한 정보를 제공합니다. 또한 코어가 자기 포화되기 전에 한계에 대한 정보를 제공하며, 즉 코일을 통해 더 많은 전류를 밀어붙일 때 더 이상 자기 플럭스 흐름이 되지 않습니다.
Procedure
1. 상대적 투과성 식별
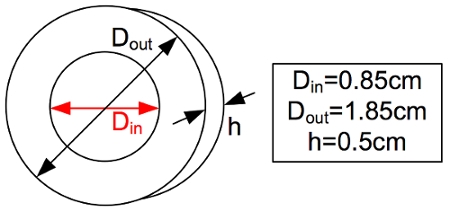
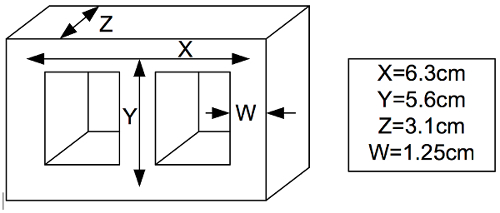
절차를 따라 작은 인덕터 (노란색 / 흰색 페릿 코어)의 상대적 투과성을 찾습니다. 코어 치수는 도 2에 표시되며 회전 수는 N=75입니다.
- LCR 미터를 사용하여 120Hz와 1000Hz 모두에서 인덕터의 유도를 측정합니다.
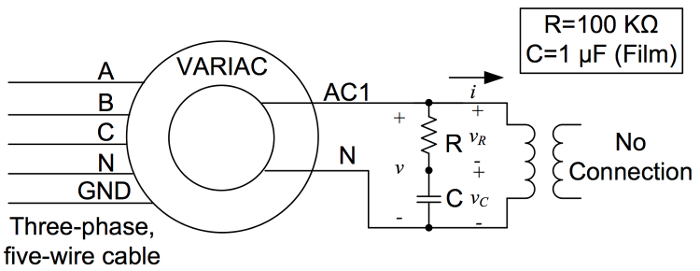
- 프로토 보드에서 도 1에서 회로를 구축하지만, 프로토 보드에서 분리 기능 생성기 출력을 유지합니다.
- 채널 1에 연결된 전류 프로브와 채널 2에 연결된 전압 프로브를 통해 오프셋이 없는 차동 전압 프로브와 전류 프로브를 확인합니다.
- 프로브 자체및 범위에 대한 차동 프로브의 배율 조정 계수에 유의하십시오. 더 나은 해상도를 위해 차동 프로브를 1/20으로 설정합니다.
- 프로브 자체에 현재 프로브를 100mV/A로 설정하고 범위에서 1X로 설정합니다. 계산을 수행할 때 이러한 배율 조정 요소를 사용해야 합니다.
- 기능
Results
Application and Summary
인덕터 및 기타 전자기장치(예:변압기)는 많은 전기, 전자 및 기계 시스템에서 매우 일반적이지만 특정 응용 분야에 대한 인덕터를 구입하는 것은 사소한 일이 아닙니다. 인덕터를 구입하더라도 데이터 시트 정보는 실제 자료, 회전 수 및 기타 세부 정보에 대한 모호성을 가질 수 있습니다. 이 실험의 테스트는 자신의 인덕터를 구축하거나 기성 용 인덕터를 구성하려는 엔지니어와 기술자에...
건너뛰기...
이 컬렉션의 비디오:

Now Playing
마그네틱 부품 특성
Electrical Engineering
15.1K Views

전기 안전 주의사항 및 기본 장비
Electrical Engineering
144.7K Views

파워 폴 보드 소개
Electrical Engineering
12.5K Views

DC/DC 부스트 컨버터
Electrical Engineering
57.1K Views

DC/DC 벅 컨버터
Electrical Engineering
21.2K Views

플라이백 컨버터
Electrical Engineering
13.3K Views

단상 변압기
Electrical Engineering
20.2K Views

단상 정류기
Electrical Engineering
23.5K Views

사이리스터 정류기
Electrical Engineering
17.6K Views

단상 인버터
Electrical Engineering
18.0K Views

DC 모터
Electrical Engineering
23.4K Views

AC 인덕션 모터 특성
Electrical Engineering
11.7K Views

VFD 공급 AC 유도 장치
Electrical Engineering
7.0K Views

AC 동기식 장치 동기화
Electrical Engineering
21.6K Views

AC 동기식 장치 특성
Electrical Engineering
14.3K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유
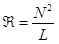 (7)
(7)