Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Application and Methodology of the Non-destructive 19F Time-domain NMR Technique to Measure the Content in Fluorine-containing Drug Products
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
A simple and non-destructive technique that measures the average content of drug substances in formulated drug products containing fluorine using low-field fluorine-19 (19F) time-domain (TD) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is presented here. The technique can be applied to the development and manufacturing of drugs in the pharmaceutical industry.
Streszczenie
Here, we describe a protocol developed by our group that uses low-field fluorine-19 (19F) time-domain (TD) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to measure the average content of fluorinated drugs in their formulated drug product forms: tablets or capsules. This method is specific to fluorinated drugs because it detects only the content of fluorine, avoiding interference from the excipients that lack fluorine. The advantages of measuring the active content of fluorinated drugs using low-field 19F TD-NMR versus high-field 19F solid-state (SS) NMR are the simplicity of the method; the low cost; and the non-destructive nature of the technique, with all samples recoverable in intact forms (e.g., powders, tablets, and capsules), making this technique affordable for any laboratory.
We have tested the method with three fluorinated drug products available on the market - cinacalcet, lansoprazole, and ciprofloxacin - with doses ranging from 15 to 500 mg. The results of the analyses, measured by low-field 19F TD-NMR, supported the reported label claims for the average drug content.
Based on the simplicity and reproducibility of the analysis, we envision this methodology being implemented in any laboratory, including manufacturing plants, as a process analytical technology (PAT) tool in the pharmaceutical industry.
Wprowadzenie
In the pharmaceutical industry, the content of drug substances in their unit-of-dosage forms (e.g., tablets and capsules) must be within the range on the label claim to meet quality control and performance guidelines. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is the conventional analytical technique used to measure the content uniformity of drugs in their formulated forms. However, the method is lengthy and destructive, requiring the dissolution of the drug into its formulated form using the appropriate solvents prior to analysis. Even with automation, the process can take 1 - 3 h per sample, depending on the development of the appropriate analytical method1,2,3. In addition to HPLC, near-infrared (NIR) has been used for the same purpose and as a PAT tool, with the caveat of requiring the chemometric analysis of the data, making its implementation lengthy and more complex4. Both techniques are destructive, with the formulated drug discarded after analysis.
In this manuscript, we describe the step-by-step protocol of a methodology previously published by our group5 to measure the average content of fluorinated drugs in their dosage forms (e.g., tablets and capsules) using low-field 19F NMR. Over the years, the percentage of fluorinated drugs on the market approved by worldwide regulatory agencies as formulated drug products has increased from 2% in 1970 to 25% in 20136. Therefore, we believe that there is a demand to develop a simpler but more specific method than the currently available methods for the quality control of the content of fluorinated drugs in their formulated forms.
Drugs containing fluorine-19 (19F) in their structures have the advantage of being easily detected by 19F NMR due to its 100% abundance and 83% sensitivity compared to protons7. Direct measurement by 1H TD-NMR is not useful because both excipients and API have protons, and the total proton signal comes from all the components of the drug product, making it impractical to measure the API content in drug products using 1H TD-NMR. Therefore, measuring the drug content of fluorinated drug products using 19F TD-NMR has the advantage of no interference with excipients due to the lack of fluorine. To demonstrate our methodology of measuring the average drug content of fluorinated drug products, we selected three commercially formulated drug products containing fluorine in different dose ranges. Figure 1 depicts the structures of the drugs selected, where two of them - cinacalcet HCl8 and lansoprazole9-have a trifluoromethyl (CF3) group in their structures, with doses ranging from 15 to 90 mg, and the third one - ciprofloxacin HCl monohydrate10 - contains one fluorine atom attached to an aromatic ring, with a 500-mg dose.
Here, we demonstrate the methodology we have developed5 to quantitate the average drug content of fluorinated drug products using a low-field benchtop TD-NMR instrument (23.4 MHz for 1H and 22.0 MHz for 19F). We also compare two software packages (RI Calibration and Mnova software) that can be used to report the results.
Protokół
Caution: Please consult all relevant material safety data sheets (MSDS) before using any chemicals. Drug substances in general are toxic and should be handled with the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE; e.g., gloves, safety glasses, lab coat, full-length pants, and closed-toe shoes), with special caution when weighing powder materials. It is recommended to use a balance placed in a hood with good air flow to minimize the powder from solid materials disseminating out of the area surrounding the balance.
NOTE: The software instructions are specific for RINMR, RI Calibration, and Mnova. For other TD-NMR vendor instruments and software packages, the instructions will vary.
1. Preparation of Samples Prior to the 19F TD-NMR Measurement
- Weigh the samples for calibration (powder drug substance or active pharmaceutical ingredient (API)) in the appropriate NMR tubes (2.5-, 3-, 5-, 10-, 18-, and 25-mm OD NMR tubes) until the marking line (height of the coil for the NMR probe), or around 30 mm in height. Notice that the height may depend on the probe.
NOTE: Cinacalcet HCl is an example of an API to use for calibration to determine the drug content in cinacalcet commercial tablets. The weight will depend on the density of the powder. In the case of cinacalcet HCl, the weights of the API are around 7.2 , 3.5 , 1.0 , 0.3 , 0.1 , and 0.07 g when filling the height of the coil for the 25-, 18-, 10-, 5-, 3-, and 2.5-mm NMR tubes, respectively. - Weigh the formulated drug product samples (tablets or capsules) in the appropriate NMR tubes until the marking line (height of the coil for the NMR probe), or around 30 mm in height, as indicated above.
NOTE: 25- or 18-mm tubes are appropriate for large-sized tablets/capsules or when enough formulated drug product is available. For smaller tablets/capsule or when not enough formulated drug product is available but the signal-to-noise ratio may still be sufficient for measurement, use 10-mm tubes. Measure the tablets directly, or crush if desired. No observation of variations in their measurements have been observed here, as mentioned in the Discussion.- When preparing commercial tablets of cinacalcet, weigh around fifteen 90-mg tablets in the 25-mm NMR tube (around 9.2 g), fifty 30-mg tablets in the 25-mm NMR tube (around 9.6 g), twenty-two 30-mg tablets in the 18-mm NMR tube (around 4.2 g), and twenty-three 60-mg tablets in the 25-mm NMR tube (around 8.8 g).
2. Preparation of the NMR Instrument for Measurement
- Tuning the NMR instrument to 19F
- Carry out all measurements at the temperature of the permanent magnet in the NMR instrument. Here, use 40 °C; no temperature control is available for the 26-mm 19F NMR probe used here. Carry out all measurements at a frequency of 22.0 MHz for 19F using the 23-MHz (for 1H) NMR instrument.
- Place the Teflon standard sample inside a 25- or 26-mm NMR tube and place it into the probe inside the magnet. Allow for equilibration for around 5-10 min and tune the instrument to 19F. Select "Auto O1" under the "Commands" menu in the RINMR software. Repeat the measurement at least 3 times and take the last value of the O1 parameter (frequency offset).
- Calibration of the 19F 90-degree pulse
- Calibrate the 90-degree pulse for F-19 with the standard Teflon sample using the standard automated calibration sequence available in the instrument. Select "Auto P90" under the "Commands" menu in the RINMR software.
NOTE: Normally, the 90-degree pulse does not need to be measured frequently unless the instrument is not performing or the probe has not been used for some time. The 90-degree value obtained for Teflon with the 26-mm 19F NMR probe used here was 7.05 µs.
- Calibrate the 90-degree pulse for F-19 with the standard Teflon sample using the standard automated calibration sequence available in the instrument. Select "Auto P90" under the "Commands" menu in the RINMR software.
3. Measurement of the T1 or Longitudinal Relaxation Time for Standard Pure API Samples
- For a better signal-to-noise ratio, place the API sample prepared in the 25-mm NMR tube inside the F-19 probe installed in the magnet and let it equilibrate for at least 10 min.
- Measure the T1 relaxation time, following the instructions of the instrument manual, for each API sample using a standard experiment for inversion-recovery from the RINMR software.
NOTE: The recommended experimental parameters are 16 scans collected with a 0.1-µs dwell time; 8 data points; a 90-degree pulse, as mentioned above; and a dead time of 10 µs for the F-19 26-mm probe. An array of delays from 100 µs to 8 s (e.g., 100 µs, 500 µs, 10 ms, 100 ms, 300 ms, 700 ms, 1 s, 2 s, 5 s, and 8 s) for drugs with CF3 and delays from 100 µs to 20 s (e.g., 100 µs, 500 µs, 1 ms, 100 ms, 500 ms, 1 s, 5 s, 10 s, 15 s, and 20 s) for drugs with one fluorine group attached to the aromatic ring are recommended.- In the RINMR software, load the "invrec.exe" pulse sequence by selecting "Load" under "Sequence" and clicking "Open." Check that the basic parameters have the correct values by clicking "A" or selecting "Acquisition" under the "Parameters" menu.
- Select "Scripts" under the "Tools" menu; a window will pop up. Select the "T1.ris" tab and click the green arrow; a window will pop up. Select the delay list file with appropriate delays or create the list after clicking "Open." Once the delay list is satisfactory, click "OK."
NOTE: A window will display a prompt for the creation of a file for all spectra that will be collected in order to calculate the T1 value. The location and names of the folders and files are up to the user. - Click on "Save" for the instrument to start acquiring the data and automatically saving the files for the delays in the selected folder.
NOTE: The RIMNR software will create the T1 relaxation curves and calculate the T1 relaxation times for each case. A window will pop up with the T1 relaxation curve and the time constant or T1 value. Here, the value of T1 for cinacalcet HCl was 2.4 s.
4. Measuring Calibration Samples with Pure API
- Measuring the API samples to build the calibration curve
- Place one calibration sample in the magnet for a particular API. Equilibrate the samples for a minimum of 5 min for the smaller tubes and 10 min for the larger tubes.
- Acquire a free induction decay (FID) or SOLID (90x-90y FID) experiment with the appropriate parameters following the instructions in the instrument manual. In the RINMR software, load the "solid.exe" (or "fid.exe") pulse sequence by selecting "Load" under "Sequence" and clicking "Open."
NOTE: The recommended experiment is SOLID for solid materials that are fast-relaxing with short T2s (transversal relaxation time). The recommended experimental parameters are 128 scans collected, with a 0.1 µs dwell time, 1,024 data points, a 90-degree pulse (7.05 µs in this case, calibrated using Teflon), and a dead time of 10 µs for the 19F 26-mm probe. A recycle delay of 7.5 s for drugs with the CF3 group and 20 s for drugs with the F group attached to an aromatic (due to longer T1 relaxation times) have been used for the cases presented here, based on their T1 measurements. - Measure all samples prepared for each API after they are equilibrated to the temperature of the magnet for 5 - 10 min to generate the calibration curves of every API sample. Save the data in a folder, giving a distinct name to every experimental run.
- Calculate the weight percentage of the samples based on the amount in each tube and considering the purity of the API sample in the largest tube.
5. Measurement of the drug product samples as tablets
- Place the already prepared formulated drug product samples (tablets or capsules) in the magnet to measure them one at a time. Equilibrate the sample for 5 min for small NMR tubes or for 10 min for the samples in the larger NMR tubes.
- Acquire the same NMR experiment (i.e., SOLID) with the same conditions as for the calibrated samples for each particular API.
6. Generation of the calibration curves with pure API samples and adding the data from drug product samples as tablets in the calibration curves
- In these cases, select the region of the SOLID experiment from 5 to 300 points to create the calibration curves. The data can be analyzed in three different ways, as outlined below.
- Open the RI Calibration software. Recall all the SOLID data by clicking on the clip symbol to open the FID or SOLID files from a particular API. For all the samples measured, enter the weight percentages under the “Conc” column and the weights under the “Mass” column. Select the appropriate region (5-300 points) using the average method to build the calibration curve (open the icon of “Display NMR data” to select the range of points for the calculation). Save the calibration curve.
Note: The Cal column will provide the percentage of drug in the samples measured. - In the RI Calibration software with the same selected region (5-300 points), use the fit method to build the calibration curve. Save the calibration curve. Follow the same instructions as in step 4.2.2.
- Open the software (e.g., Mnova). Drag all the SOLID data from a particular API and enter the weight percentages of the standard samples; manual instructions can be found by clicking “Content” under the “Help” menu. In the “Advanced” menu, select “Time Domain” and then “Quantitation;” a window will pop up. Click on the blue plus sign to select the integration area. Integrate the appropriate region (5-300 points) using the magnitude mode to build the calibration curve.
- Save the calibration curve. In the table, enter the percentages of drugs per sample only for the standards under the “Concentration (x)” column and the weights for all the samples under the “Mass (m)” column; calibration samples should be in red (checked). Make sure that the “Signal Function” is “y=s/m” (to normalize to signal/mass).
- For reproducibility and repeatability, measure each sample 3 times on different days and build the calibration curve in both software packages. Save the calibration curve files.
7. Calculation of the Fluorinated API Drug Weight in the Formulated Drug Product Using the Calibration Curves
- Calculation of the weight percentage and average dosage amount per tablet/capsule of fluorinated API drug in the formulated drug product
- Use the file for the calibration curve from the RI Calibration software and the average method. Read the NMR data from the measured tablets (or capsules) and enter their weights to determine the weight percentage of fluorinated API in the formulated tablets or capsules from the calibration curve.
Note: The “Cal” column will provide the percentage of drug in the measured samples (calibration and commercial tablets or unknowns). Notice that the O1 parameter must be the same for the calibration samples and the tablets or capsules for the RI Calibration software. - Use the file for the calibration curve from the RI Calibration software with the fit method. Read the NMR data from the tablets (or capsules) measured and enter their weights to determine the weight percentage of fluorinated API in the formulated tablets or capsules from the calibration curve. Follow the same instructions as in step 5.2.1. Notice that the O1 parameter must be the same for the calibration samples and the tablets or capsules for the RI Calibration software.
- Use the Mnova file and drag the acquired NMR data for the formulated API (or measure them all on the same day). Follow the instructions in step 4.2.4. Enter the weights to determine the weight percentage of the fluorinated API in the formulated tablets or capsules from the calibration curve.
Note: In the table, the calibration samples will be in red (checked) and the unknown or commercial tablets/capsules in blue (unchecked). The “Concentration (x)” column will show the calculated values for the commercial tablets of unknown samples in blue based on the values of the calibration samples in red. Notice that the software does not require the use of the same O1 parameter to calculate the weight percentage. - Calculate the amount of fluorinated drug per tablet or capsule as the average value from the equation below (D = dose of API in mg, WNMR = weight percentage of API obtained from the calibration curve, w = total weight of formulated product from the weight of the formulated drug coming from the measured tablets or capsules, and N = number of formulated tablets or capsules used for the measurement) and compare with the values calculated by the software based on the calibration curves:
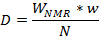
- Use the file for the calibration curve from the RI Calibration software and the average method. Read the NMR data from the measured tablets (or capsules) and enter their weights to determine the weight percentage of fluorinated API in the formulated tablets or capsules from the calibration curve.
Wyniki
We have tested low-field 19F TD-NMR with three commercial drug products (cinacalcet, lansoprazole, and ciprofloxacin) to measure the average drug content of the fluorinated drug products. Figure 1 shows the structures of the tested drugs, displaying the locations of the fluorine atoms.
We tested several lots and dosage forms (i.e., 30, 60, and 90 mg) of cinacalcet tablets, one do...
Dyskusje
As more fluorinated drugs are becoming available in the market, we have developed a specific and simple methodology to measure the average drug content of fluorinated drug products using low-field 19F TD-NMR5. We tested this method on three commercial drug products: tablets containing cinacalcet HCl, capsules containing lansoprazole, and tablets containing ciprofloxacin HCl monohydrate. The advantages of this method are its specificity due to the lack of fluorine in the excipients and i...
Ujawnienia
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Podziękowania
This manuscript is based on a previously published article5. Reprinted from5, copyright 2015, with permission from John Wiley & Sons.
We are grateful to our management, Dr. Janet Cheetham, Dr. Francisco Alvarez, Dr. Arwinder Nagi, and Dr. David Semin, for their support, interest, and encouragement to perform this research project, and to Dr. Minhui Ma and Mr. Robert Munger, for providing us with cinacalcet HCl, its formulated tablets, and information about the drug. We also want to thank Dr. Michael Bernstein, Dr. Manuel Perez, and Dr. Santiago Dominguez for their constructive support and discussions on the development of the currently commercial version of the Mnova software as it applies to the quantitation of TD-NMR data. In addition, a special thank you to Mr. Regnar L. Madarang F.N.P. for providing us with generic cipro tablets to conduct our studies.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| MQC-23 | Oxford Instruments | 52-AM4044 | 23.4 MHz for 1H and 22.0 MHz for 19F |
| 26 mm Probe (19F) | Oxford Instruments | 52-AM4061 | 19F NMR probe |
| Cinacalcet HCl | Amgen | Lot 005002 M | Purity 99.8% |
| Cinacalcet commercial tablets | Amgen | Lot 0010021308 | 30 mg tablets |
| Cinacalcet commercial tablets | Amgen | Lot D1026396 | 30 mg tablets |
| Cinacalcet commercial tablets | Amgen | Lot D118714 | 30 mg tablets |
| Cinacalcet commercial tablets | Amgen | Lot D061829 | 60 mg tablets |
| Cinacalcet commercial tablets | Amgen | Lot 00100213 | 90 mg tablets |
| Cinacalcet commercial tablets | Amgen | Lot D064074 | 90 mg tablets |
| Cinacalcet commercial tablets | Amgen | Lot 1026356 | 90 mg tablets |
| Lansoprazole | Fluka | Lot LRAA1897 | Purity 99.7% |
| Brand name Lansoprazole | Novartis | Lot DV1891 | 15 mg capsules |
| Lansoprazole generic | SUPERVALUE INC | Lot 2GE2027 | 15 mg capsules |
| Ciprofloxacin free base | Fluka | Lot BCBM7969V | 99.9% purity |
| Ciprofloxacin HCl monohydrate | Fluka | Lot P500044 | 94% purity as HCl salt |
| Cipro generic | Pack Pharmaceuticals | Lot PUB3033 | 500 mg tablets |
| 25 mm NMR tube | New Era Enterprises | NE-25TD-200-FB | |
| 18 mm NMR tube | New Era Enterprises | NE-18TD-200-FB | |
| 10 mm NMR tube | New Era Enterprises | NE-10TD-200-FB | |
| 5 mm NMR tube | New Era Enterprises | NE-HL5-7 | |
| 3 mm NMR tube | New Era Enterprises | NE-H3-7 | |
| 2.5 mm NMR tube | New Era Enterprises | NE-H5/2.5 |
Odniesienia
- El-Yazigi, A., Wahab, F. A., Afrane, B. Stability Study and Content Uniformity of Prochloroperazine in Pharmaceutical Preparations by Liquid Chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 690, 71-76 (1995).
- Takeuchi, Y., Yoshida, M., Ito, A., Sunada, H. Uniformity of Drug Content During Pharmaceutical Dry Granulation by Roller Compaction and Tableting Processes. J Drug Del Sci Tech. 19 (2), 119-124 (2009).
- Toro, I., Dulsat, J. F., Fábregas, J. L., Claramunt, J. Development and Validation of a Fully Automated method of the Chromatographic Determination of Content Uniformity of Drug Tablets. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 36, 57-63 (2004).
- Shi, Z., Hermiller, J. G., Gunter, T. Z., Zhang, X., Reed, D. E. A Novel Sample Selection Strategy by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy-Based High Throughput Tablet Tester for Content Uniformity in Early-Phae Pharmaceutical Product Development. J Pharm Sci. 101 (7), 2502-2511 (2012).
- Silva Elipe, M. V., et al. Applications of 19F Time-Domain NMR to Measure Content in Fluorine-Containing Drug Products. Magn Reson Chem. 54 (6), 531-538 (2015).
- Wang, J., et al. Fluorine in Pharmaceutical Industry: Fluorine-Containing Drugs Introduced to the Market in the Last Decade (2001-2011). Chem Rev. 114, 2432-2506 (2014).
- Dolbier, W. R. . Guide to Fluorine NMR for Organic Chemists. , (2009).
- Barman, J. A., Scott, L. J. Cinacalcet Hydrochloride. Drugs. 65 (2), 271-282 (2005).
- Horn, J. The Proton-Pump Inhibitors: Similarities and Differences. Clin Ther. 22 (3), 266-280 (2000).
- LeBel, M. Ciprofloxacin: Chemistry, Mechanism of Action, Resistance, Antimicrobial Spectrum, Pharmacokinetics, Clinical Trials, and Adverse Reactions. Pharmacotherapy. 8 (1), 3-30 (1988).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone