Nose, Sinuses, Oral Cavity and Pharynx Exam
Обзор
Source: Richard Glickman-Simon, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Public Health and Community Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, MA
This video provides an overview of sinus, nose, and throat examinations. The demonstration begins with a brief overview of the anatomy of the region. The upper third of the nose is bony, and the bottom two-thirds are cartilaginous. Air entering the nares passes through the nasal vestibules and into the narrow passageway between the nasal septum medially and the bony turbinates laterally. Beneath each curving turbinate is a groove or meatus. The nasolacrimal duct and most of the air-filled paranasal sinuses drain into the inferior and middle meatuses, respectively. Of the three sets of paranasal sinuses, only the maxillary and frontal can be readily examined. A continuous, highly vascular mucosa lines the entire nasal cavity and sinuses.
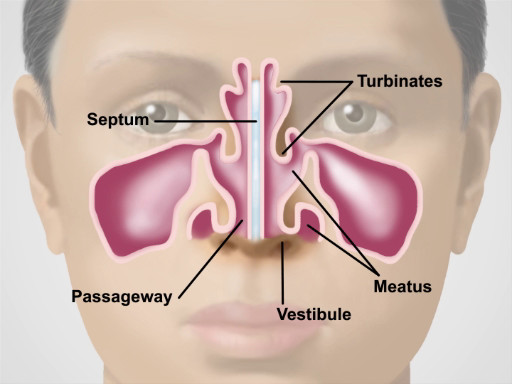
Figure 1. Anatomy of the Nose.
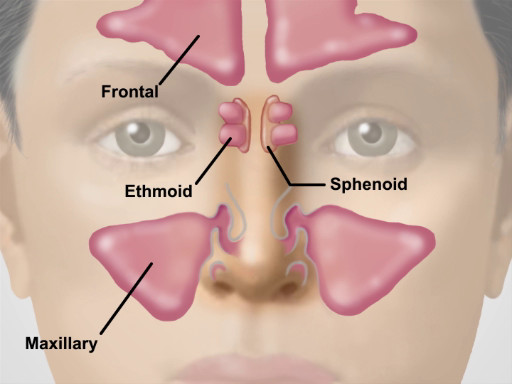
Figure 2. Location of the Major Sinuses.
Muscular folds of the lips mark the entrance to the oral cavity. The pinkish gingiva, or gums, attach firmly to the teeth and adjacent bone into which the teeth embed. The buccal mucosa lines the inner cheeks, where the Stensen duct drains the parotid glands into small papillae near the upper second molars. Small, red papillae cover the dorsal surface of the tongue along with a whitish coat of varying thickness. The midline lingual frenulum connects the undersurface of the tongue to the floor of the mouth, where the Wharton duct drains the submandibular glands into papillae on either side. Arching over the tongue are the anterior and posterior pillars of the soft palate and midline uvula. If present, the tonsils can be seen protruding bilaterally between the pillars. The bony hard palate rises anteriorly above the soft palate. The pharynx lies posteriorly behind the soft palate and tongue.

Figure 3. Anatomy of the Oral Cavity.
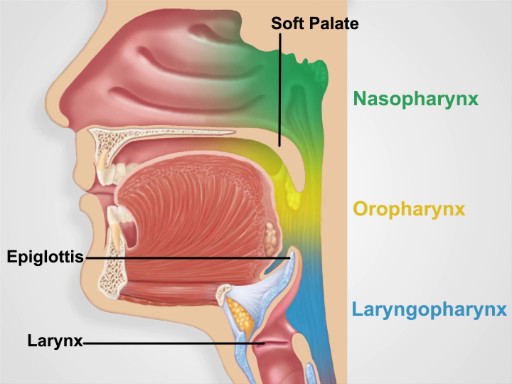
Figure 4. Pharyngeal Regions.
Процедура
1. Nose and Sinus Exam
- Inspect the nose for skin changes, nodules, and deformities. Slight deviation of the septum is common, and benign if it does not cause airflow obstruction.
- Press gently on the tip of the nose to widen the nares, and inspect the vestibule with the aid of a pen light.
- Conduct the nose cavity exam with an otoscope.
- Using the largest ear speculum available, inspect the nasal cavity with the otoscope.
- Tilt the patient's head back slightly, and h
Заявка и Краткое содержание
Because of their constant exposure to the environment, the nose, sinuses, oral cavity, and pharynx often suffer from infections and other inflammatory conditions. Viral and allergic rhinitis are by far the most common nasal disorders. Both can produce copious watery discharge, but viral infections tend to produce a deep red mucosa, while allergies produce a pale, bluish one. Other common conditions found on nasal examination include epistaxis, septal deviation, and nasal polyps. Tenderness over the paranasal sinuses sugg
Теги
Перейти к...
Видео из этой коллекции:

Now Playing
Nose, Sinuses, Oral Cavity and Pharynx Exam
Physical Examinations II
65.8K Просмотры

Eye Exam
Physical Examinations II
77.2K Просмотры

Ophthalmoscopic Examination
Physical Examinations II
68.0K Просмотры

Ear Exam
Physical Examinations II
55.1K Просмотры

Thyroid Exam
Physical Examinations II
105.0K Просмотры

Lymph Node Exam
Physical Examinations II
387.4K Просмотры

Abdominal Exam I: Inspection and Auscultation
Physical Examinations II
202.6K Просмотры

Abdominal Exam II: Percussion
Physical Examinations II
248.2K Просмотры

Abdominal Exam III: Palpation
Physical Examinations II
138.5K Просмотры

Abdominal Exam IV: Acute Abdominal Pain Assessment
Physical Examinations II
67.3K Просмотры

Male Rectal Exam
Physical Examinations II
114.5K Просмотры

Comprehensive Breast Exam
Physical Examinations II
87.6K Просмотры

Pelvic Exam I: Assessment of the External Genitalia
Physical Examinations II
307.1K Просмотры

Pelvic Exam II: Speculum Exam
Physical Examinations II
150.4K Просмотры

Pelvic Exam III: Bimanual and Rectovaginal Exam
Physical Examinations II
147.7K Просмотры
Авторские права © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Все права защищены