A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Standardized Preparation of Single-Cell Suspensions from Mouse Lung Tissue using the gentleMACS Dissociator
In This Article
Summary
Dissociating cells from specific tissue types requires specific parameters for tissue agitation to obtain a high volume of viable, culturable cells. The Miltenyi gentleMACS dissociator optimizes this task with a simple, practical protocol. In this publication the use of this apparatus on lung tissue is explained.
Abstract
Protocol
To work under sterile conditions, it is recommended to perform all steps in a laminar flow hood.
1. Materials
- HEPES buffer: 10 mM HEPES-NaOH pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1.8 mM CaCl2)
- Collagenase D solution: Collagenase D: 100 mg/mL (Collagenase D > 0.15 U/mg), in HEPES buffer
- DNase I solution: 20,000 U/mL DNase I
- PBS buffer at pH 7.2
- PEB buffer: 1 part BSA Stock Solution in 20 parts autoMACS Rinsing Solution
- Tissue: lung derived from 6/7 week old adult female BALB/C mouse, free of adjoining organs.
- Optional: CD11c MicroBeads, MACS MS Columns, MACS Separator for the isolation of dendritic cells from mouse lung single-cell suspension
2. Dissociating the lung tissue
- Rinse tissue in a Petri dish containing PBS to remove erythrocytes.
- Transfer a maximum of 450 mg lung tissue to a gentleMACS C Tube containing 4.9 mL HEPES buffer.
- Add 100 μL Collagenase D solution to a final concentration of 2 mg/ml Collagenase D.
- Add 10 μL DNase I solution for up to 150 mg tissue (final concentration of 40 U/ml DNase I) or 20 μL DNase I for 150-450 mg lung tissue (final concentration of 80 U/mL DNase I).
- Tightly close the C Tube and attach it onto the gentleMACS Dissociator. Then run the program "m_lung_01".
- Incubate for 30 min at 37°C with automated rotation or manually turning every 5 min.
- Return sample to the gentleMACS Dissociator and run the program "m_lung_02".
3. Filtration
- Prepare a 50 mL tube for collecting filtered cells by replacing the cap with a 70 μm mesh cell strainer.
- Once the second gentleMACS Program ends, depending on the distribution of sample material in the tube, you may centrifuge the tube briefly to collect the sample material at the bottom of the tube.
- Remove the cells through the septum sealed cap of the C Tube using a suitable 1000 μl pipette tip and apply them to the cell strainer.
- Wash the cell strainer with 5 ml HEPES buffer at RT.
- Centrifuge the cells to a pellet in a 50 mL tube at 300xg for 10 min.
- Aspirate the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in your desired volume of PEB buffer.
Part 4: Representative Results:
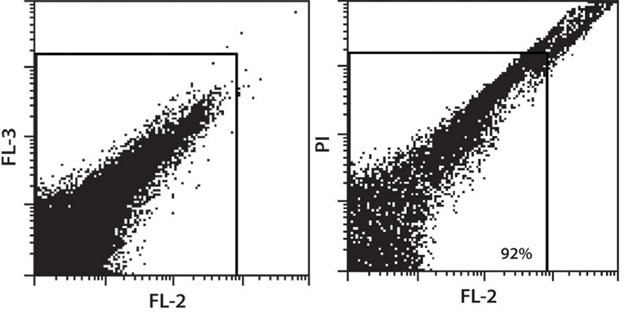
Figure 1. Lung dissociation with the gentleMACS™ Dissociator resulted in 92% viable cells. Dead cells were fluorescently stained with propidium iodide (PI) ( right dot plot; left dot plot: no PI staining).
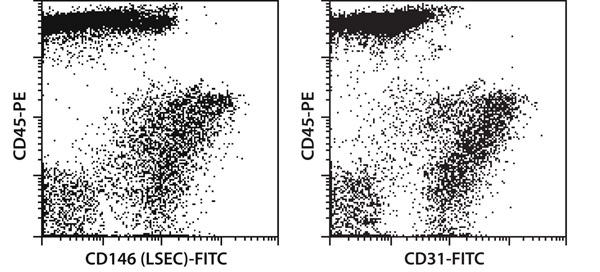
Figure 2. Dissociation of mouse lung tissue using the gentleMACS Dissociator results in a high percentage of viable leukocytes and endothelial cells. The derived single-cell suspensions were stained with CD45-PE and CD146-FITC or CD31-FITC and analyzed by flow cytometry.

Figure 3. Single-cell suspension derived from mouse lung tissue was stained with CD11c-FITC and Anti-mPDCA-1-APC to detect mouse CD11clow m-PDCA-1+ plasmacytoid DCs as well as CD11chigh cells.

Figure 4. Enrichment of dendritic cells using CD11c MicroBeads, a MiniMACS Separator and two MS Columns.
Discussion
In this video, we introduce a new method for the dissociation of mouse lung tissue. We show that a combination of mechanical and enzymatic treatment of lung tissue yielded a high percentage of viable leukocytes and endothelial cells. Specifically, the mechanical disintegration of the tissue was achieved by the gentleMACS Dissociator. The gentleMACS C Tubes include a rotor - stator system, which dissociates tissue in a gentle way. The procedure is controlled by the program settings of the instrument. The settings were opt...
Disclosures
The authors are employees of Miltenyi Biotec GmbH who make the instrument used in this article.
Acknowledgements
The authors are employees of Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, Germany.
Materials
References
- Swanson, K. Flt3-Ligand, IL-4, GM-CSF, and Adherence-Mediated Isolation of Murine Lung Dendritic Cells: Assessment of Isolation Technique on Phenotype and Function. J. Immunol. 173, 4875-4881 (2004).
- Vermaelen, K., Pauwels, R. Accurate and simple discrimination of mouse pulmonary dendritic cell and macrophage populations by flow cytometry: Methodology and new insights. Cytometry Part A. 61A, 170-177 (2004).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved