Method Article
Correlative Light Electron Microscopy (CLEM) for Tracking and Imaging Viral Protein Associated Structures in Cryo-immobilized Cells
In This Article
Summary
A correlative light electron microscopy (CLEM) method is applied to image virus-induced intracellular structures via electron microscopy (EM) in cells that are previously selected by light microscopy (LM). LM and EM are combined as a hybrid imaging approach to achieve an integrated view of virus-host interactions.
Abstract
Due to its high resolution, electron microscopy (EM) is an indispensable tool for virologists. However, one of the main difficulties when analyzing virus-infected or transfected cells via EM are the low efficiencies of infection or transfection, hindering the examination of these cells. In order to overcome this difficulty, light microscopy (LM) can be performed first to allocate the subpopulation of infected or transfected cells. Thus, taking advantage of the use of fluorescent proteins (FPs) fused to viral proteins, LM is used here to record the positions of the "positive-transfected" cells, expressing a FP and growing on a support with an alphanumeric pattern. Subsequently, cells are further processed for EM via high pressure freezing (HPF), freeze substitution (FS) and resin embedding. The ultra-rapid freezing step ensures excellent membrane preservation of the selected cells that can then be analyzed at the ultrastructural level by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Here, a step-by-step correlative light electron microscopy (CLEM) workflow is provided, describing sample preparation, imaging and correlation in detail. The experimental design can be also applied to address many cell biology questions.
Introduction
The idea of combining two microscopy modalities to obtain a better picture of a specific biological process is rather old. Thus, the very first study about viruses using "correlative microscopy" was published in 1960 as two separate publications1,2. In that study, the authors analyzed the changes in the morphology of the nucleus induced by adenoviruses by means of two microscopy techniques. In the first publication, electron microscopy (EM) observations describing the morphological details associated with adenovirus infection were reported1. In a second publication, the different structures observed by EM were correlated with light microscopy (LM) images of histochemical staining patterns, to define the nature of the structures previously observed by EM2.
In these early studies, however, their observations were performed using different infected cells prepared as independent experiments. The "correlation" was, indeed, meant as the combination of information coming from two imaging modalities to understand a certain phenomenon, comparing all the findings that have been obtained with different assays in order to understand a given biological process.
Nowadays, the term correlative microscopy, also known as correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM), is applied to an increasing number of methods (reviewed in references3,4,5), with the commonality that both imaging techniques (LM and EM) are carried out on the very same sample. The combination of both methods results, thereby, in a multi-modal, multi-scale and multi-dimensional analysis of that sample3. The advantages are that LM can provide a broad overview of many different cells, enabling the identification of cell subpopulations expressing a protein or proteins of interest within a heterogeneous cell population. EM overcomes the resolution limit of LM, providing a higher resolution image of a particular intracellular event. Furthermore, EM enables the visualization of the non-fluorescent subcellular context, including all membrane bound organelles, large macromolecular complexes (e.g., ribosomes, centrioles, etc.) and cytoskeletal elements, thereby providing additional spatial information, the so-called "reference space"6, and giving context to the fluorescent spot detected by LM.
During the last few years, CLEM has become a powerful tool not only for cell biologists5, but also for virologists (reviewed in reference7) willing to understand the complex virus-cell interactions that lead to a successful virus propagation. Thus, understanding how viruses modify cell membranes and organelles to their own benefit is essential to develop antiviral drugs to eradicate pathogenic viruses.
Here, a CLEM method is described that allows the detection by LM of cells expressing viral proteins fused to a fluorescent protein (FP). These cells are subsequently cryo-immobilized and further prepared for ultrastructural analysis via transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to gain new insights into how the expression of these proteins rearrange intracellular membranes (Figure 1). CLEM has been performed with chemically fixed cells in most of the virology studies published to date8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19. This is mainly due to the need of inactivating infectious material for biosafety reasons in biosafety level-2 and -3 (BSL-2 and BSL-3) laboratories, where cryo-immobilization of cells is usually not possible. For those questions requiring an optimal preservation of the cell membranes, vitrification via high pressure freezing (HPF) is, however, highly recommended20. In these cases, the CLEM protocol described here can be applied. Interestingly, especially when working with infectious specimens, HPF can be performed on samples that have been previously chemically inactivated, for example in BSL-2 and BSL-3 laboratories. The combination of chemical fixation followed by HPF is a possibility to profit at least partially from the advantages of cryo-preservation methods21,22.
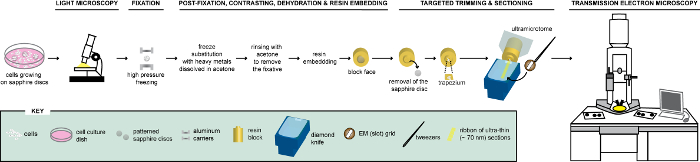
Figure 1: Schematic representation of the workflow for the analysis of cells via CLEM. Cells growing on patterned sapphire discs are first analyzed by LM to localize cells expressing FPs before their processing for EM. Once located, cells are immediately fixed by HPF and FS to be subsequently embedded in resin. Upon polymerization of the resin, the support where cells were growing (=sapphire discs) must be removed from the resin block. The block containing the embedded cells is trimmed to a small trapezium from which the remaining cells, expressing FPs, are sectioned with a diamond knife. Ultrathin sections are collected on slot grids and further examined by TEM to obtain ultrastructural information of these cells. This figure is adapted and modified with permission from reference29. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
1. Preparation of Patterned Sapphire Discs for Cell Culture
- Transfer the patterned sapphire discs (see Table of Materials), with an alphanumeric pattern etched onto one of their surfaces, into a 15 mL conical centrifugation tube.
NOTE: Alternatively, conventional 0.05 mm thick sapphire discs without alphanumeric pattern can be used in which a reference pattern is created by carbon coating them with a finder grid on top. To this aim, they should be cleaned with ethanol before the carbon pattern is applied. - Wash them thoroughly with ethanol. Spread them out in a Petri dish with filter paper and let them dry. Place them on a glass slide separate from each other using slim long tweezers.
- Check with an inverted microscope (4X magnification) whether the pattern of coordinates is readable on every sapphire disc.
NOTE: If this is not the case, flip the sapphire discs with the help of the tweezers. - Store the sapphire discs in a Petri dish.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here.
2. Cell Culture with Patterned Sapphire Discs
- Sterilize the patterned sapphire discs with an ultraviolet (UV) crosslinker for 5 min.
- Take the sapphire discs to the cell culture biosafety cabinet. Sterilize the long tweezers with ethanol in the biosafety cabinet.
- Add half of the cell culture medium (see Table of Materials) to a cell culture dish. Transfer the sapphire discs carefully with the long tweezers into the cell culture dish.
- Seed 1 x 105 Huh7-Lunet cells, stably expressing the T7 polymerase resuspended in the other half of the cell culture medium, onto the culture dish.
NOTE: Calculate the number of cells to be seeded in such a way that at the end point of the experiment the cell confluency should be not over 20–30%. High cell density will hinder the relocation of the cells at later stages by EM. Furthermore, over-confluency might result in the detachment of cells from the sapphire discs. - Check that the sapphire discs remain at the bottom of the culture dish and that the alphanumeric coordinates are still readable with the inverted microscope.
NOTE: If the discs float in the cell culture medium, use the long tweezers to push the discs to the bottom and eventually to flip them back to the correct orientation. - Transfect the cells the next day as previously reported in references21,23 following the transfection agent's manufacturer instructions.
3. LM Imaging of Cells Growing on Patterned Sapphire Discs
- Transfer the sapphire discs at the end point of the experiment to a metal imaging plate containing 30–50 µL/ position of pH indicator-free medium to reduce nonspecific background fluorescence.
NOTE: The metal plate described here (Figure 2) has been designed at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) workshop. In the absence of this plate or a similar one, glass-bottom cell culture dishes could be also used instead for LM. It is important to change the normal cell culture medium for medium without pH indicator. Note also that long exposure times should be avoided because they might cause photobleaching, leading to reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and physiological damage of the cells24,25. - Image the cells under an inverted widefield fluorescence microscope.
NOTE: When using a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged protein, as shown in the representative results, 450–490 nm and 500–550 nm excitation and emission filters, respectively, should be used. - Acquire first a low magnification image (10–20X) of the cells to allocate cells expressing FPs. Record the coordinates of the patterned sapphire discs where the cells of interest are located by using differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy.
NOTE: Stitching several areas might help to have a better overview of the location of the cell/cells of interest. Note also that phase-contrast microscopy could be optionally used here. - Acquire high magnification (fluorescence and DIC) images (63–100X, oil-immersion objectives) of the same cell/cells to better discern the subcellular localization of the protein of interest within the intracellular space.
NOTE: DIC images provide contextual information. This information is often critical to correlate LM images with EM micrographs later on, because the final correlation is more precise with "anatomical" landmarks of the cell. As some sapphire discs might break during cryo-immobilization, it is highly recommended to prepare triplicates per condition. Furthermore, some cells detach from the discs during HPF and the subsequent steps of this protocol, while the ultrastructure of other cells might contain artifacts as a consequence of freezing damage. Therefore, at least two areas of the discs should be imaged via LM to ensure that in the end there will be enough cells to be analyzed. Importantly, these two areas should be on opposite sides of the disc. In this manner the resin block where the cells are embedded can be cut into two halves and sections of these areas can be obtained.
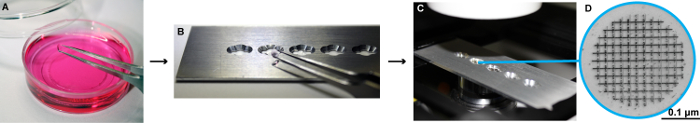
Figure 2: Schema for the LM imaging of cells growing on patterned sapphire discs. (A) The sapphire discs are transferred with help of fine tweezers to an imaging plate. (B-C) This plate has been specially designed at the EMBL workshop in Heidelberg to fit into the light microscope, where the sapphire discs can be imaged with cell culture medium without pH indicator. It consists of a metal slide, 75 mm x 25 mm x 1 mm, with four-five holes milled into it with a 3 mm drill bit to fit the size of the sapphire discs. In addition, small grooves were milled on each side of the holes at a 90° angle. These holes make it easier to access the discs with forceps when manipulating them. To allow for optimal imaging conditions glass coverslips No. 0 (0.085 to 0.13 mm thick) were glued below the holes with UV glue and placed under UV light to harden. (D) High magnification image of the patterned sapphire disc depicting the alphanumeric coordinates that are etched on its surface. The patterned sapphire discs are commercially available (see Table of Materials). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Cryo-Immobilization of Cells Growing on Patterned Sapphire Discs via HPF
- Place the "A" and "B" aluminum carriers for HPF (see Table of Materials) in a Petri dish with filter paper soaked with 1-hexadecene. Immerse the patterned sapphire discs containing the cells in a Petri dish with 1-hexadecene.
NOTE: Move the discs a bit to wash the cell culture medium away. - Assemble the sapphire discs between an "A" and a "B" aluminum carrier in the HPF holder as follows (Figure 3B). On the bottom, place a "B" carrier with its flat side facing upwards. Place the sapphire discs on this flat side with the cells facing upwards. Add an "A" carrier with its 0.1-mm depth facing the cells.
NOTE: Because the patterned sapphire discs are thicker than the conventional sapphire discs, the commercially available "A" carrier (designed to be used with non-patterned 0.05-mm sapphire discs) had to be cut down to 0.05 mm at this 0.2 mm depth side at the EMBL workshop in order to fit into the HPF holder (Figure 3A). To this aim, the "A" carrier is inserted into the end of a metal tube so that its 0.2 mm side is exposed and remains still while cutting it down. The cut down side is then sanded so that it is flat. Alternatively, a special aluminum carrier can be used on top of the patterned sapphire disc (commercially available, see Table of Materials), being in this case the HPF "sandwich" composed only of the sapphire disc and this carrier. - Close the holder of the HPF machine and freeze the cells.
NOTE: This protocol is specific for a particular HPF machine. Other HPF machines could be alternatively used6,26. In any case, please be aware of the existence of new generation machines from the suppliers.
CAUTION: Use safety goggles and hearing protection headset. - Place the frozen "sandwich" in a polystyrene box with liquid nitrogen for temporary storage.
CAUTION: Use goggles and get in contact with the local safety officers to be informed about the potential dangers when handling liquid nitrogen.- To avoid confusion, place each "sandwich" in a separate 0.5 mL microcentrifuge tube (inside the polystyrene box) marked with a number.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here. If freeze substitution (FS) cannot be immediately performed, the samples can be stored in cryo-tubes (with a hole punched in the top) inside boxes, that are held in a rack in a cryogenic liquid nitrogen dewar (see Table of Materials). This liquid nitrogen container should be located in a room with oxygen gas sensors, to avoid suffocation in case of an oxygen deficiency.
CAUTION: All the procedures described below (steps 5 and 6) must be carried out in a biosafety cabinet. Furthermore, most of the reagents used are hazardous. Before using them, it is mandatory to read carefully the Material Safety Data Sheets provided by the manufacturers, as well as ask the safety officers about the local rules to ensure safe handling. For the correct disposal of these used materials, as well as for the proper use of the equipment described below, it is also required to consult the local institute’s health and safety procedures.
- To avoid confusion, place each "sandwich" in a separate 0.5 mL microcentrifuge tube (inside the polystyrene box) marked with a number.
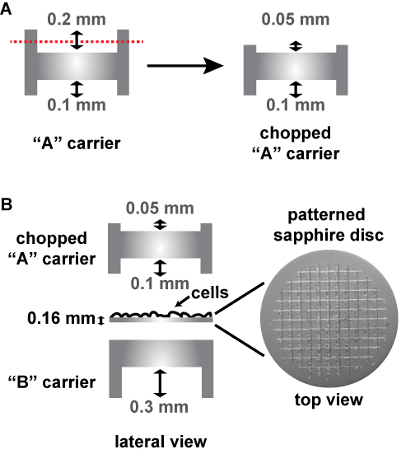
Figure 3: Schema of the assembly of patterned sapphire discs between two aluminum carriers for HPF. (A) Cut-away views of a conventional "A" carrier, that has to be cut on its deeper side from 0.2 mm to 0.05 mm. (B) The 0.16 mm thick sapphire disc with the alphanumeric pattern etched on the surface is assembled into two aluminum carriers for HPF, as follows: The sapphire disc is placed on the flat side of a "B" carrier with the cells facing upwards. A chopped "A" carrier with its 0.1-mm depth facing the cells is placed on top to close the "HPF sandwich". The aluminum carriers and the patterned sapphire discs are commercially available (see Table of Materials). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. FS of Cryo-Fixed Cells
- Fill up the FS machine (see Table of Materials) with liquid nitrogen. Set the temperature to -90 °C and wait until the machine reaches this temperature.
- Prepare the FS medium containing 0.2% osmium tetroxide (OsO4) (v/v), 0.1% uranyl acetate (UA) (w/v) in glass-distilled acetone while the FS machine is cooling down.
NOTE: To prepare, (for instance) 12 mL of FS medium, mix 600 µL of 4% OsO4with 0.012 g of UA in a small glass container. Dissolve this mixture in an ultrasonic bath device for 5 min. Add 11.4 mL of glass-distilled acetone with a pipette and mix well. - Fill up 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes with 200-500 µL of FS medium, close the lid and transfer them to the FS machine. Wait 10 min for the FS medium to cool down.
- Transfer the frozen "sandwiches" containing the sapphire discs with cells in liquid nitrogen using cooled long tweezers to the tubes containing the FS medium.
CAUTION: Use cryo-protective gloves and goggles.
NOTE: The HPF "sandwiches" could be disassembled spontaneously during their handling. In this case, make sure that the frozen sapphires discs are transferred to the microcentrifuge tubes. The aluminum carriers can be discarded. - Run the FS as follows until the next day27: from -90 °C to -80 °C for 8 h; from -80 °C to -50 °C for 8 h; from -50 °C to -20 °C for 2 h; from -20 °C to 0 °C for 2 h.
6. Resin Embedding of Freeze Substituted Samples
CAUTION: All the procedures described below must be carried out in a biosafety cabinet. Furthermore, most of the reagents used are hazardous. Before using them, it is mandatory to read carefully the Material Safety Data Sheets provided by the manufacturers, as well as ask the safety officers about the local rules to ensure safe handling. For the correct disposal of these used materials, as well as for the proper use of the equipment described below, it is also required to consult the local institute's health and safety procedures.
- Take out the substituted specimens from the FS machine and place them on ice for 20 min.
- Keep the samples at room temperature for 20 min and wash them thoroughly (3 times, 10 min each) with glass-distilled acetone. Discard the aluminum carriers with long tweezers if they are still in the microcentrifuge tubes after the FS.
- Infiltrate the cells (on the remaining sapphire discs) in a four-step epoxy resin series using 1 h incubations in 25%, 50%, and 75% resin in glass-distilled acetone, followed by overnight incubation with 100% resin. Exchange the 100% resin the next day for 1h.
- Carefully place the sapphire discs into flow-through rings mounted in reagent baths filled with 100% resin. These rings are used as polymerization molds for 10 sapphire discs.
NOTE: The sapphire discs must be completely pushed to the bottom with the coordinates facing upwards in a readable manner. This could be checked with help of a binocular attached to a fume extractor. Alternatively, a binocular inside a biosafety cabinet could be used instead. Importantly, there are numbers (1-10) engraved on the bottom of the reagents that help to identify the samples. In addition, for identification of the samples a paper tag could be included in the resin block. - Polymerize the samples in the oven at 60 °C for 48 h.
7. Removal of Patterned Sapphire Discs from the Polymerized Resin Blocks
- Remove the hard resin blocks containing the cells from the oven.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here. If not, let the blocks cool down to room temperature before cutting them. - Cut the embedding molds with a razor blade to have access to the resin blocks. Remove the cylindrical resin blocks using tweezers.
NOTE: If a paper tag has not been included in the resin block before polymerization, number the blocks with a permanent marker and store them in 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes. The protocol can be paused here. - Immerse the tip of the resin block containing the sapphire disc in a polystyrene box containing liquid nitrogen until it stops "bubbling". Then, immerse the tip of the resin block in boiling H2O.
- Repeat the two previous steps as many times as needed until the sapphire disc falls off of the resin block.
CAUTION: Use goggles and cryo-protective gloves.
NOTE: If this does not work, use a razor blade to remove a bit of the polymerized resin around the discs before trying again. The protocol can be paused here.
8. Targeted Trimming and Ultrathin Sectioning for TEM
- Identify the area on the resin block face where the cells of interest are present by examining the block face with the binocular of an ultramicrotome.
NOTE: The negative imprint of the coordinate pattern from the patterned sapphire discs is retained on the block face. This allows the identification of the area where the cells of interest are located for targeted trimming. The LM images must be flipped vertically in order to facilitate the finding of the same position of the block face. - Trim the embedded cell monolayer containing the cell/cells of interest to a small flat pyramid with the shape of a trapezium (~ 200 µm × 250 µm average size) with a clean razor blade.
- Obtain 70-nm ultrathin sections of the embedded cells with a 35° diamond knife.
- Place the sections on EM slot grids with help of ultra-fine tweezers.
NOTE:: The use of mesh grids should be avoided because the sections could be masked by the grid bars. - Store the grids in a grid box.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here.
9. TEM Analysis of Ultrathin Sections
- Place the slot grid into the holder of the transmission electron microscope. Acquire low magnification (overview) images, where the complete cell profile of the cell of interest is visible.
NOTE:: The cell/cells of interest can be found back by using the cell profiles and the locations of the cells to one another as references, comparing to the DIC views acquired before by LM. - Acquire high magnification images of the cell/cells of interest, to try and find, at the ultrastructural level, features that correspond to the fluorescent signals observed previously by LM.
NOTE: Montage images can be obtained at high magnification to have an overview at high resolution of the cell/cells of interest. Furthermore, it is often necessary to acquire images of the same cell in consecutive serial sections to be able to reconstruct the cell in 3D before comparing to the fluorescence images.
Results
Using the procedure presented here (Figure 1), Huh7-Lunet cells stably expressing the T7-RNA polymerase were seeded on patterned sapphires discs and subsequently transfected with a plasmid expressing two domains of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural protein NS5A, tagged with GFP (pTM_AH-D1-GFP) (Figure 4). The following day, the patterned sapphire discs, where the cells were growing, were taken out of the cell culture dishes and imaged by means of LM (Figure 4, Figure 2). Those cells expressing the AH-D1-GFP were identified by the presence of green fluorescence in the cytosol and recorded to save their positions within the coordinate-pattern of the sapphire discs (Figures 5A, 5B). Immediately following their LM examination, the sapphire discs containing the cells of interest were assembled between two aluminum carriers (Figure 3) and subjected to cryo-immobilization by HPF. Cells were then freeze substituted and subsequently embedded in an epoxy resin.
Upon removal of the sapphire discs from the polymerized resin blocks, the imprint of the alphanumeric pattern was visible on the block face, which allowed retrieving the areas where the cells of interest were located. The rest of the resin block was trimmed away to generate a small trapezium harboring the cells of interest. Serial ultrathin sections were obtained from this trapezium, collected on EM slot grids and further analyzed by TEM (Figure 5C). Note that obtaining manually serial consecutive sections although feasible28 is labor intensive and requires well-trained and skilled personnel. It is also important that the cells have a low confluency when subjected to this CLEM protocol (Figure 5A) in order to guarantee a quick recognition of the same cell previously identified by LM. Otherwise, having higher cell confluency might dramatically slow down the successful locating of cells at the EM level.
TEM analysis of several ultrathin sections of the cell of interest (Figures 5D, 5E), expressing the AH-D1-GFP, revealed the presence in its intracellular space of large accumulations of vesicles of variable morphology delimited from the surrounding cytosol by a single lipid bilayer (Figure 5E).
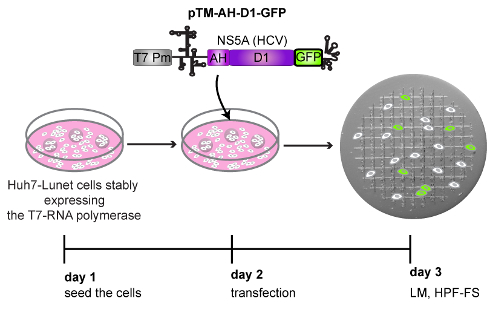
Figure 4: Schematic representation of the workflow followed to perform the CLEM example depicted in Figure 5. Huh7-Lunet cells stably expressing the T7-RNA polymerase were transfected with a DNA plasmid encoding the amphipathic helix (AH) and the domain 1 (D1) of HCV NS5A protein, tagged at its C-terminal with GFP (pTM_AH-D1-GFP). The expression of this part of the NS5A protein is controlled transcriptionally by a T7 promoter (T7 Pm) and translationally by an encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) IRES (internal ribosome entry site) element, indicated by a secondary structure. Twenty-four h post-transfection (24 hpt) cells growing on patterned sapphire discs and expressing the AH-D1-GFP were detected by LM and immediately subjected to HPF-FS. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
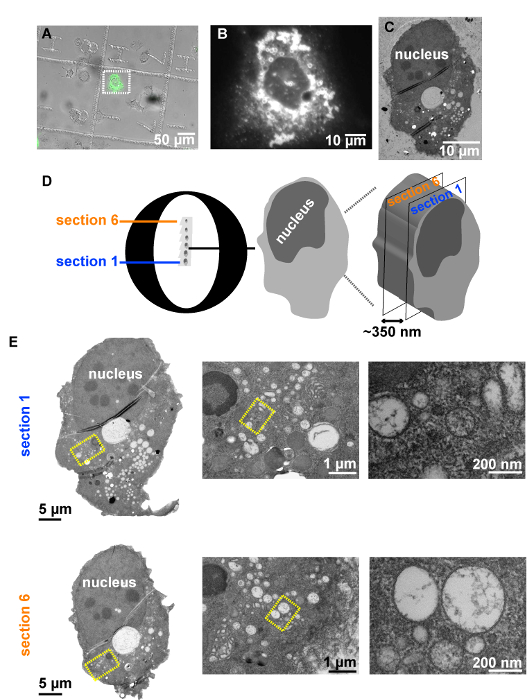
Figure 5: Example of a CLEM procedure. (A) Huh7-Lunet cells stably expressing the T7 polymerase analyzed by fluorescence microscopy to allocate GFP-positive cells grown on patterned sapphire discs, 24 h after transfection with the plasmid pTM_AH-D1-GFP. (B) Higher magnification image of a single cell selected within the white dashed rectangle to be analyzed by CLEM. (C) TEM image of an ultrathin section of the same cell after HPF, FS and resin embedding. (D) Schematic representation of serial 70-nm ultrathin sections on a slot EM grid containing the cell of interest. (E) On the left: TEM overviews of two sections of the cell of interest. On the right: High magnification TEM images of the intracellular areas selected in yellow rectangles on the left, revealing high numbers of vesicles delimited from the cytosol via a single membrane. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
The CLEM methodology presented here to study the impact of a viral protein expression on cell membranes has been successfully used before to elucidate the HCV replication-associated structures, mainly double membrane vesicles (DMVs)21, as well as to determine the critical building blocks required to form these HCV-induced structures23. Note that in our first work using CLEM to study HCV replication21, a slightly modified version of the protocol described here was applied. In that study, conventional 0.05 mm thick sapphire discs, without alphanumeric pattern, were used in which a reference pattern was created by carbon coating them with a finder grid on top (see Table of Materials). This version of the current protocol can be eventually applied, with the advantage that the "A" carrier for HPF can be used directly, without the need of cutting it down as in Figure 3A. Alternatively, as mentioned in the protocol, a thicker "A" carrier can be utilized (see Table of Materials) with patterned sapphire discs, without the need of a "B" carrier.
Interestingly, this protocol can be applied not only to study BSL-1 samples, such as cells transfected with viral proteins as described here and elsewhere19,23, but also to study virus-infected cells. Although working with human pathogens is usually restricted to BSL-2 and BSL-3 laboratories, in some countries it is still possible to perform cryo-immobilization under these biosafety conditions. In those BSL-2 and BSL-3 laboratories where vitrification is not possible, due to the local regulations or the absence of an HPF machine, virus-infected cells can be still prepared using this method if chemical fixation with aldehydes is carried out in advance, namely before leaving the BSL-2 or BSL-3 facilities. Furthermore, aldehydes need to be quenched immediately after fixation to keep the fluorescence, while the rest of the protocol is identical to the one described here. This technique can be considered redundant because the cells are fixed twice, chemically and via vitrification. However, this double fixation protocol leads indeed to a much better preservation of the HCV-induced DMVs in comparison to the DMVs found in cells subjected to chemical fixation alone21.
For further modifications and troubleshooting the reader is referred to the notes throughout the protocol part of this manuscript. These notes describe pitfalls to avoid, as well as alternatives to overcome putative difficulties that might arise when performing this method.
The main requisite for applying this technique is an HPF machine. When cryo-immobilizing the cells via HPF is not feasible (due to the absence of an HPF machine) or not required (when the membrane preservation does not need to be optimal), cells can be chemically fixed and subsequently prepared and analyzed by EM8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19. This option does not require the use of sapphire discs, but cell culture dishes with gridded patterns for relocating cells or cell clusters. The main advantage of the use of these dishes is their larger diameter in comparison to sapphire discs, allowing the screening of larger surface areas. Thus, the application of this CLEM protocol has been successfully applied to study the effect of an antiviral compound against HCV15 or to visualize the membrane rearrangements induced by the nonstructural proteins of noroviruses19. Another issue that can limit the performance of this method is the absence of a commercial FS device. In this case, basic homemade FS systems can be utilized instead. Although automatic FS devices might reduce handling mishaps, homemade devices are used successfully for instance at Kent McDonald's30 and Paul Walther's labs.
With respect to chemical fixation, the protocol described here ensures an optimal preservation of the intracellular structures20. Therefore, in case the above-mentioned HPF and FS devices are available, vitrifying the cells of interest would be preferred.
Future alternatives to this CLEM approach include the possibility of using this method not only to acquire 2D information at the ultrastructural level, but also to gain 3D information about the architecture of membrane and organelle alterations caused by viruses. The 3D-EM methods, including electron tomography (ET) and focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) (extensively described in29), could be also applied to cells that have been prepared following this current protocol21,31. In addition, 3D information could be also obtained at the LM level, when using a confocal microscope, which allows the acquisition of z-stacks. In fact, this option is highly recommended when a precise correlation between LM and EM datasets is desired (see for example17). The information included in 3D z-stacks aids to improve the correlation with the 2D TEM images. Thus, in such a scenario, the best fitting LM and EM images can be selected and then subjected to one of the correlation software available, such as the ec-CLEM plugin of ICY (http://icy.bioimageanalysis.org/)32 or the Landmark Correspondences plugin of Image J (http://imagej.net/Landmark_Correspondences), resulting in the generation of overlapping LM-EM images.
When temporal information is needed to understand the kinetics of a certain event, time-lapse imaging can be used to monitor dynamics of living cells in combination with EM. During the event of interest, cells are fixed immediately, generating a "frozen snapshot" that can be subsequently analyzed via EM, providing detailed ultrastructural information about that particular moment at the time of immobilization. In order to obtain that "frozen snapshot", after the observation in real time, cells can be either chemically fixed33 or cryo-immobilized6. Since many cellular processes occur faster than the diffusion processes of chemical fixation, if possible, ultra-rapid freezing should be performed. However, it is important to take into account that the HPF machines differ in their effective time resolution34.
Furthermore, although this protocol has been designed for the embedding of cells in an epoxy resin, cells can be also embedded in low viscosity resins, such as Lowicryls, LR White or LR Gold. The use of these embedding media enables to preserve the antigenicity35,36, as well as fluorescence37,38 and, therefore, are mostly used for post-embedding on-section immunolabeling39,40 and on-section CLEM41,42,43,44, where the LM is done after the embedding. Both approaches (immuno-EM and on-section CLEM) must be crucial for those experiments in which non-characteristic structures can be easily found via TEM and/or as a control against miscorrelation between LM and EM signals. Likewise, labeling with antibodies that can be visualized by both imaging modalities (LM and EM) can be carried out45 in order to, for example, identify transfected cells in LM (pre-embedding stage) and achieve a much more accurate localization of the GFP signal via its specific labeling by immuno-EM (post-embedding stage). It must be taken into account, however, that permeabilization is conducted before LM to permit the access of the antibodies to the intracellular space, which might result in a sub-optimal preservation of the cell architecture at the EM level. Interestingly, this protocol is also well suited for multi-color experiments that can be achieved with the use of other fluorescent tags, other than GFP (as shown here). In conclusion, there are many putative possibilities of adapting this protocol, both on the LM and/or on the EM sides, depending on the questions that are being addressed. For a comprehensive description of other alternative protocols the reader is referred to5,46. Regardless of how the microscopy modalities are combined, together the result is a gain of information, allowing us to better understand how viruses and their proteins interact with their hosts in real life.
The most critical step within this method is the collection of serial sections from the cells of interest. As highlighted in the representative results section, this requires expert staff, as well as a lot of patience. Importantly, this step is essential to find the cells back at the EM level for two reasons. First, in this sort of CLEM protocol using pre-embedding LM, the coordinates are only visible at the LM level and on the resin block face after the embedding. However, they will not be visible on the sections by TEM. Therefore, targeted trimming on the block face down to the regions of interest (ROIs) must be accomplished carefully with a razor blade to ensure that the sections that are subsequently obtained contain the cells expressing a given FP. Second, "scanning" several sections is necessary to find the best overlay between the LM and the EM acquisitions. In contrast to methods where LM is performed at the post-embedding stage, in this case the LM-EM overlay is not so precise. The low overlay accuracy is due to differences in axial resolution between LM and EM, shrinkage during sample processing of EM, and compression during sectioning42. Nevertheless, efficient tracking methods, such as the use of landmarks, help to find the cells back. This includes the position of one cell to another, as well as the shape of the cells and their nucleus. In this regard, as explained in the protocol, DIC images provide "anatomical" information of the cells that are critical to improve the correlation. Alternatively, the nuclei or other well-recognizable cell organelles (such as mitochondria or lipid droplets) can be stained before LM and used as landmarks.
Finally, it is noteworthy to mention that although this manuscript is focused on the use of this technique for virology studies, the scope of this experimental design can be expanded to address more general biological questions.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the staff members of the Electron Microscopy Core Facilities (EMCF) at EMBL (Heidelberg) and at the University of Heidelberg. We also would like to thank Ulrike Herian, Stephanie Kallis and Andrea Hellwig (Heidelberg University), as well as Eberhardt Schmidt and Renate Kunz (University of Ulm) for expert technical assistance. Work by R.B. and his team (U.H. and I.R.-B.) was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, SFB1129, TP11 and TRR83, TP13.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| UV Crosslinker | Stratagene | 400072 | Stratalinker 1800, 230 Vac, equipped with 254-nm UV light bulbs, 8 Watts/each. |
| Patterned sapphire discs | Engineering Office M. Wohlwend, Sennwald, Switzerland | 627 | They have a 0.3 mm diameter and are 0.16 mm thick, as well as an an etched alphanumeric pattern to allow for re-location of the cells. They can be only ordered per e-mail: martin-wohlwend@bluewin.ch. |
| Slim and long tweezers | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA | 72919-SS | "Style SS", for handling sapphire discs. |
| Cell culture medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | 41965-062 | Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, nonessential amino acids, 100 units penicillin per ml, 100 µg streptomycin per ml and 10% fetal calf serum (DMEM complete, see below). Package containing 10 bottles, 500 mL/each. |
| L-glutamine | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | 25030-123 | Package containing 20 bottles of 100 mL/each. |
| Nonessential amino acids | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | 11140-068 | Package containing 20 bottles of 100 mL/each. |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | 15140-163 | Package containing 20 bottles of 100 mL/each. |
| Fetal calf serum | Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA | F7524 | Bottle of 50 mL |
| Inverted microscope | Olympus Deutschland, Hamburg, Germany | CKX41 | It is an inverted microscope with trinocular head options and fluorescence upgrade capability. |
| Huh7-Lunet cells stably expressing the T7 RNA-polymerase | Avaliable at Prof. Dr. Ralf Bartenschlager laboratory | Not available | Contact Prof. Bartenschlager at: ralf.bartenschlager@med.uni-heidelberg.de. |
| Mirus TransIT-LT1 Transfection Reagent | Mirus Bio LLC, Madison, USA | MIR 2304 | Broad spectrum, low toxicity, DNA transfection reagent. Vial of 0.4 mL |
| Inverted widefield fluorescence microscope | Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Germany | Zeiss Observer.Z1 | Inverted fluorescence microscope for experiments involving living cell cultures. |
| 1-hexadecene | Merck, Darmstadt, Germany | 8220640100 | Bottle of 100 mL |
| "A" aluminium holders for high pressure frezing (HPF) | Engineering Office M. Wohlwend, Sennwald, Switzerland | 241 | This is the holder that has been used for this protocol and has 2 different depths of 0.1 and 0.2 mm. It can be only ordered per e-mail: martin-wohlwend@bluewin.ch. |
| "B" aluminium holders for HPF | Engineering Office M. Wohlwend, Sennwald, Switzerland | 242 | This is the holder that has been used for this protocol.It is 0.3 mm thick.They can be only ordered per e-mail: martin-wohlwend@bluewin.ch. |
| "A" aluminium holder for HPF (special for working with patterned sapphire discs) | Engineering Office M. Wohlwend, Sennwald, Switzerland | 737 | This is the holder than can be used alone with the patterned sapphire disc (as an alternative to the current protocol), without the need of a "B" holder or the edition of the "A" holder. It is 0.84 mm thick. It can be only ordered per e-mail: martin-wohlwend@bluewin.ch. |
| Sapphire discs | Engineering Office M. Wohlwend, Sennwald, Switzerland | 405 | These sapphires discs are the "conventional" one, with a 0.3 mm diameter and a thickness of 0.05 mm . They can be also used for CLEM as an alternative instead of patterned sapphire discs. |
| Finder grids | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, Philadelphia, USA | LF135-Cu | These 135 mesh grids are used to create an alphanumeric pattern on "conventional" sapphire discs (described above) via carbon coating, so that they can be used for CLEM. 100 grids/vial. |
| HPF machine | ABRA Fluid AG, Widnau, Switzerland | HPM 010 | This HPF machine has been used for this protocol. |
| HPF machine | Leica Microsystems, Vienna, Austria | EMPACT 2 | "EMPACT 2", as an alternative to the use of the HPM machine that it has been used in this protocol (described above). |
| Cryo-tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | Z763667-500EA | For long term-storage of cryo-immobilized samples in liquid nitrogen. Package containing 500 cryovials. |
| Liquid nitrogen dewar | Cole-Parmer GmbH, Wertheim, Germany | GZ-05094-60 | For long term-storage of cryo-immobilized samples in liquid nitrogen, equipped with cryo-racks with a capacity of 1600 cryo-tubes. |
| Automatic freeze substitution (AFS) machine | Leica Microsystems, Vienna, Austria | EM AFS2 | This machine performs freeze substitution and progressive lowering of temperature (PLT) techniques and allows low temperature embedding and polymerization of resins. |
| Osmium tetroxide (OsO4) | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA | 19150 | 4% aqueous solution, one box containing 10 x 2 mL ampules. |
| Uranyl-Acetate (UA) | Serva, Heidelberg, Germany | 77879.01 | Bottle containing 25 grs of (UA)-2 H2O. |
| Sonicator | Bandelin Electronic, Berlin, Germany | 329 | "Sonorex Super RK 31" is a high-power ultrasonic cleaning bath for aqueous cleaning solution that is used in this protocol to mix OsO4 and Ua when preparing the FS medium. |
| Glass-distilled acetone | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA | 10015 | Bottle of 100 mL |
| Stereomicroscope | Leica Microsystems, Vienna, Austria | Leica M80 | Routine stereomicroscope for daily inspections, equipped with a camera for capturing images. |
| Epoxy resin | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA | 14120 | Embed 812 is a kit containing several components that must be mix together in the proportions given by the manufacturers. |
| Flow through rings | Leica Microsystems, Vienna, Austria | 16707157 | Package containing 100 pieces. |
| Reagent baths | Leica Microsystems, Vienna, Austria | 16707154 | Package containing 100 pieces. |
| Ultramicrotome | Leica Microsystems, Vienna, Austria | Leica EM UC7 | Ultramicrotome for preparation of semi- and ultrathin sections at room temperature. |
| Ultra 35 ° diamond knife | Diatome Ltd., Nidau Switzerland | AGG339-735 | This knife have an edge length of 3 mm. |
| Ultra fine tweezers | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA | E78318 | "Style 3X", for handling EM grids. |
| EM slot grids | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA | G2010-Cu | 100 grids/vial. |
| EM grid storage box | Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA | 71155 | It has capacity for 100 grids. |
References
- Morgan, C., Godman, G. C., Breitenfeld, P. M., Rose, H. M. A correlative study by electron and light microscopy of the development of type 5 adenovirus. I. Electron microscopy. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 112, 373-382 (1960).
- Godman, G. C., Morgan, C., Breitenfeld, P. M., Rose, H. M. A correlative study by electron and light microscopy of the development of type 5 adenovirus. II. Light microscopy. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 112, 383-402 (1960).
- Caplan, J., Niethammer, M., Taylor, R. M., Czymmek, K. J. The power of correlative microscopy: multi-modal, multi-scale, multi-dimensional. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 21, 686-693 (2011).
- de Boer, P., Hoogenboom, J. P., Giepmans, B. N. Correlated light and electron microscopy: ultrastructure lights up. Nature Methods. 12, 503-513 (2015).
- Müller-Reichert, T., Verkade, P. Correlative light and electron microscopy III, First edition. , Elsevier/Academic Press. Cambridge, MA. (2017).
- Brown, E., Mantell, J., Carter, D., Tilly, G., Verkade, P. Studying intracellular transport using high-pressure freezing and Correlative Light Electron Microscopy. Seminars in Cell and Developmental Biology. 20, 910-919 (2009).
- Bykov, Y. S., Cortese, M., Briggs, J. A., Bartenschlager, R. Correlative light and electron microscopy methods for the study of virus-cell interactions. FEBS Letters. , (2016).
- Spuul, P., et al. Assembly of alphavirus replication complexes from RNA and protein components in a novel trans-replication system in mammalian cells. Journal of Virology. 85, 4739-4751 (2011).
- Nagel, C. H., Dohner, K., Binz, A., Bauerfeind, R., Sodeik, B. Improper tagging of the non-essential small capsid protein VP26 impairs nuclear capsid egress of herpes simplex virus. PLoS One. 7, 44177(2012).
- Sharma, M., Kamil, J. P., Coughlin, M., Reim, N. I., Coen, D. M. Human cytomegalovirus UL50 and UL53 recruit viral protein kinase UL97, not protein kinase C, for disruption of nuclear lamina and nuclear egress in infected cells. Journal of Virology. 88, 249-262 (2014).
- Kallio, K., et al. Template RNA length determines the size of replication complex spherules for Semliki Forest virus. Journal of Virology. 87, 9125-9134 (2013).
- Martinez, M. G., Snapp, E. L., Perumal, G. S., Macaluso, F. P., Kielian, M. Imaging the alphavirus exit pathway. Journal of Virology. 88, 6922-6933 (2014).
- Lebrun, M., et al. Varicella-zoster virus induces the formation of dynamic nuclear capsid aggregates. Virology. 454-455, 311-327 (2014).
- Madela, K., et al. A simple procedure to analyze positions of interest in infectious cell cultures by correlative light and electron microscopy. Methods in Cell Biology. 124, 93-110 (2014).
- Berger, C., et al. Daclatasvir-like inhibitors of NS5A block early biogenesis of hepatitis C virus-induced membranous replication factories, independent of RNA replication. Gastroenterology. 147, 1094-1105 (2014).
- van der Schaar, H. M., et al. Illuminating the Sites of Enterovirus Replication in Living Cells by Using a Split-GFP-Tagged Viral Protein. mSphere. 1, (2016).
- Vale-Costa, S., et al. Influenza A virus ribonucleoproteins modulate host recycling by competing with Rab11 effectors. Journal of Cell Science. 129, 1697-1710 (2016).
- Wang, L., et al. Visualization of HIV T Cell Virological Synapses and Virus-Containing Compartments by Three-Dimensional Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy. Journal of Virology. 91, (2017).
- Doerflinger, S. Y., et al. Membrane alterations induced by nonstructural proteins of human norovirus. PLOS Pathogens. 13, 1006705(2017).
- Dahl, R., Staehelin, L. A. High-pressure freezing for the preservation of biological structure: theory and practice. Journal of Electron Microscopy Technique. 13, 165-174 (1989).
- Romero-Brey, I., et al. Three-dimensional architecture and biogenesis of membrane structures associated with hepatitis C virus replication. PLOS Pathogens. 8, 1003056(2012).
- Sosinsky, G. E., et al. The combination of chemical fixation procedures with high pressure freezing and freeze substitution preserves highly labile tissue ultrastructure for electron tomography applications. Journal of Structural Biology. 161, 359-371 (2008).
- Romero-Brey, I., et al. NS5A Domain 1 and Polyprotein Cleavage Kinetics Are Critical for Induction of Double-Membrane Vesicles Associated with Hepatitis C Virus Replication. MBio. 6, 00759(2015).
- Dixit, R., Cyr, R. Cell damage and reactive oxygen species production induced by fluorescence microscopy: effect on mitosis and guidelines for non-invasive fluorescence microscopy. The Plant Journal. 36, 280-290 (2003).
- Jou, M. J., Jou, S. B., Guo, M. J., Wu, H. Y., Peng, T. I. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation and calcium increase induced by visible light in astrocytes. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1011, 45-56 (2004).
- McDonald, K. L., Morphew, M., Verkade, P., Muller-Reichert, T. Recent advances in high-pressure freezing: equipment- and specimen-loading methods. Methods in Molecular Biology. 369, 143-173 (2007).
- Walther, P., Ziegler, A. Freeze substitution of high-pressure frozen samples: the visibility of biological membranes is improved when the substitution medium contains water. Journal of Microscopy. 208, 3-10 (2002).
- White, J. G., Southgate, E., Thomson, J. N., Brenner, S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 314, 1-340 (1986).
- Romero-Brey, I., Bartenschlager, R. Viral Infection at High Magnification: 3D Electron Microscopy Methods to Analyze the Architecture of Infected Cells. Viruses. 7, 6316-6345 (2015).
- McDonald, K. L., Webb, R. I. Freeze substitution in 3 hours or less. Journal of Microscopy. 243, 227-233 (2011).
- Villinger, C., Neusser, G., Kranz, C., Walther, P., Mertens, T. 3D Analysis of HCMV Induced-Nuclear Membrane Structures by FIB/SEM Tomography: Insight into an Unprecedented Membrane Morphology. Viruses. 7, 5686-5704 (2015).
- Paul-Gilloteaux, P., et al. eC-CLEM: flexible multidimensional registration software for correlative microscopies. Nature Methods. 14, 102-103 (2017).
- Polishchuk, R. S., Mironov, A. A. Correlative video light/electron microscopy. Current Protocols in Cell Biology Supplement. , Chapter 4, Unit 4 8(2001).
- McDonald, K. L. A review of high-pressure freezing preparation techniques for correlative light and electron microscopy of the same cells and tissues. Journal of Microscopy. 235, 273-281 (2009).
- Newman, G. R., Jasani, B., Williams, E. D. A simple post-embedding system for the rapid demonstration of tissue antigens under the electron microscope. The Histochemical Journal. 15, 543-555 (1983).
- Schwarz, H., Humbel, B. M. Influence of fixatives and embedding media on immunolabelling of freeze-substituted cells. Scanning Microscopy. 3, Supplement. Discussion 63-54 57-63 (1989).
- Luby-Phelps, K., Ning, G., Fogerty, J., Besharse, J. C. Visualization of identified GFP-expressing cells by light and electron microscopy. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 51, 271-274 (2003).
- Nixon, S. J., et al. A single method for cryofixation and correlative light, electron microscopy and tomography of zebrafish embryos. Traffic. 10, 131-136 (2009).
- McDonald, K. L. Rapid embedding methods into epoxy and LR White resins for morphological and immunological analysis of cryofixed biological specimens. Microscopy and Microanalysis. 20, 152-163 (2014).
- Webster, P., Schwarz, H., Griffiths, G. Preparation of cells and tissues for immuno EM. Methods in Cell Biology. 88, 45-58 (2008).
- Kukulski, W., et al. Correlated fluorescence and 3D electron microscopy with high sensitivity and spatial precision. Journal of Cell Biology. 192, 111-119 (2011).
- Peddie, C. J., et al. Correlative and integrated light and electron microscopy of in-resin GFP fluorescence, used to localise diacylglycerol in mammalian cells. Ultramicroscopy. 143, 3-14 (2014).
- Hampoelz, B., et al. Pre-assembled Nuclear Pores Insert into the Nuclear Envelope during Early Development. Cell. 166, 664-678 (2016).
- Lemercier, N., et al. Microtome-integrated microscope system for high sensitivity tracking of in-resin fluorescence in blocks and ultrathin sections for correlative microscopy. Scientific Reports. 7, 13583(2017).
- Takizawa, T., Powell, R. D., Hainfeld, J. F., Robinson, J. M. FluoroNanogold: an important probe for correlative microscopy. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 8, 129-142 (2015).
- Romero-Brey, I. 3D electron microscopy (EM) and correlative light electron microscopy (CLEM) methods to study virus-host interactions. Methods in Molecular Biology: Influenza Virus Methods & Protocols. Yamauchi, Y. , Springer. (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved