A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Photogeneration of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Application in Photoinduced Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization
In This Article
Summary
We describe a protocol to photogenerate N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) by UV irradiation of a 2-isopropylthioxanthone/imidazolium tetraphenylborate salt system. Methods to characterize the photoreleased NHC and elucidate the photochemical mechanism are proposed. The protocols for ring-opening metathesis photopolymerization in solution and miniemulsion illustrate the potential of this 2-component NHC photogenerating system.
Abstract
We report a method to generate the N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) 1,3-dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene (IMes) under UV-irradiation at 365 nm to characterize IMes and determine the corresponding photochemical mechanism. Then, we describe a protocol to perform ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) in solution and in miniemulsion using this NHC-photogenerating system. To photogenerate IMes, a system comprising 2-isopropylthioxanthone (ITX) as the sensitizer and 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (IMesH+BPh4-) as the protected form of NHC is employed. IMesH+BPh4- can be obtained in a single step by anion exchange between 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride and sodium tetraphenylborate. A real-time steady-state photolysis setup is described, which hints that the photochemical reaction proceeds in two consecutive steps: 1) ITX triplet is photo-reduced by the borate anion and 2) subsequent proton transfer takes place from the imidazolium cation to produce the expected NHC IMes. Two separate characterization protocols are implemented. Firstly, CS2 is added to the reaction media to evidence the photogeneration of NHC through formation of the IMes-CS2 adduct. Secondly, the amount of NHC released in situ is quantified using acid-base titration. The use of this NHC photo-generating system for the ROMP of norbornene is also discussed. In solution, a photopolymerization experiment is conducted by mixing ITX, IMesH+BPh4-, [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 and norbornene in CH2Cl2, then irradiating the solution in a UV reactor. In a dispersed medium, a monomer miniemulsion is first formed then irradiated inside an annular reactor to produce a stable poly(norbornene) latex.
Introduction
In chemistry, N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) species fulfill the twofold role of ligand and organocatalyst1. In the former case, the introduction of NHCs has resulted in the design of metal transition catalysts with improved activity and stability2. In the latter case, NHCs have proved to be superior catalysts for manifold organic reactions3,4. Despite this versatility, handling bare NHCs is still a significant challenge5, and producing these highly reactive compounds so they are released in situ and "on demand" is a very attractive goal. Consequently, several strategies have been developed to release NHC in the reaction media which mostly rely on the use of thermolabile progenitors6,7,8. Surprisingly, while this could unleash a novel generation of photoinitiated reactions useful for macromolecular synthesis or preparative organic chemistry6, generation using light as stimulus has been scarcely explored. Recently, a first photo-generating system able to produce NHC has been unveiled9. It consists of 2 components: 2-isopropylthioxanthone (ITX) as photosensitive species and 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (IMesH+BPh4-) as the NHC protected form. Consequently, in the following paragraphs, we report a method to generate the NHC 1,3-dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene (IMes) under UV-irradiation at 365 nm, characterize it, and determine the photochemical mechanism. Then, we describe a protocol to perform ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) in solution and in miniemulsion using this NHC photogenerating system.
In the first portion, we report a synthesis protocol to produce IMesH+BPh4-. This protocol is based on anion metathesis between the corresponding imidazolium chloride (IMesH+Cl-) and sodium tetraphenylborate (NaBPh4). Then, to demonstrate the in situ formation of NHC, two protocols involving the irradiation at 365 nm of a IMesH+BPh4-/ITX solution in a photoreactor are described. The first consists of monitoring the deprotonation of the imidazolium cation IMesH+ through 1H NMR spectroscopy. Direct evidence for formation of the desired NHC (IMes) is provided in a second method, where the adduct IMes-CS2 is successfully isolated, purified, and characterized.
The second section describes two protocols that shed light on the photochemical mechanism involving the NHC two-component photogenerating system IMesH+BPh4-/ITX. Firstly, an original real-time steady state photolysis experiment reveals that electron transfer is induced by photo-excitation of ITX in the presence of tetraphenylborate. Electron donor properties of this borate anion10 drives a photoreduction of 3ITX* triplet excited-state into ITX●- radical anion through a so-called photo-sensitized reaction. The formation of NHC confirms that ITX●- species may further abstract a proton from IMesH+ to produce the desired NHC. Based on acid/base titration using phenol red pH indicator as titrant, a second original protocol is implemented that allows the determination of the yield of released NHC.
In the third section, we describe a protocol in which the above-mentioned photogenerated IMes can be exploited in photopolymerization. Of primary interest is ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP), because this reaction is still at a preliminary stage of development with regard to photoinitiation11,12. Initially limited to ill-defined and highly sensitive tungsten complexes, photoinduced ROMP (photoROMP) has been extended to more stable complexes based on W, Ru, and Os transition metals. Despite the variety of precatalysts, almost all photoROMP processes rely on the direct excitation of a single photoactive precatalyst13. By contrast, we use radiation to create the NHC imidazolidene ligand (IMes), which can react subsequently with a non-photoactive Ru precatalyst [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 dimer9. In this method, the photogeneration of NHC ligand drives the in situ formation of a highly active ruthenium-arene NHC complex known as RuCl2(p-cymene)(IMes) (Noels' catalyst)14,15. Using this indirect methodology, two distinct photoROMP experiments of norbornene (Nb) are performed: 1) in solution (dichloromethane) and 2) in aqueous dispersed system from a monomer miniemulsion16.
Protocol
1. NHC Photogenerating System: Synthesis and Reactivity
- Synthesis of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (IMesH+BPh4-)
- Preparation of the solution of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride (IMesH+Cl-) in ethanol.
- Add 1.00 g (2.93 mmol) of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride to a 50 mL round bottom flask equipped with a stir bar.
- Dissolve the 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride in 30 mL of ethanol.
- Preparation of the solution of sodium tetraphenylborate (NaBPh4) in ethanol.
- Add 1.35 g (3.92 mmol) of sodium tetraphenylborate to a 50 mL round bottom flask equipped with a stir bar.
- Dissolve the sodium tetraphenylborate in 30 mL of ethanol.
- Generation of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (IMesH+BPh4-)
- Add (dropwise) the solution of sodium tetraphenylborate into the solution of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride under stirring.
- Stir the reaction mixture for 10 min at room temperature.
- Remove the stir bar and filter the white precipitate using a vacuum and fritted glass filter of pore size 3.
- Wash the precipitate with 30 mL of ethanol and filter it (fritted glass filter with pore size 3). Wash the precipitate with 30 mL of deionized water and filter it (fritted glass filter with pore size 3).
- Dry the white precipitate at 60 °C for 15 h. Analyze the product by 1H and 13C NMR in DMSO-d6 according to previously reported procedures9.
- Preparation of the solution of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride (IMesH+Cl-) in ethanol.
- Photogeneration of NHC 1,3-dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene, also known as IMes, by UV irradiation of the dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate in the presence of isopropylthioxanthone (ITX)
- Add 39 mg (0.062 mmol, 2 equiv.) of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate, 7.8 mg (0.031 mmol, 1 equiv.) of ITX, and 0.5 mL of deuterated THF (previously stored over 3 Å molecular sieves) in an NMR tube.
- Place the NMR tube inside the photochemical reactor equipped with a circular array of 16 fluorescent tubes emitting a monochromatic radiation at 365 nm and irradiate for 10 min.
- Monitoring of deprotonation of IMesH+BPh4- by 1H NMR spectroscopy
- Analyze the deprotonation of IMesH+ into IMes by 1H NMR.
NOTE: 1H NMR spectra were recorded at 25 °C on a NMR spectrometer operating at 400 MHz. TMS was used as internal standards for calibrating the chemical shifts in 1H NMR.- Calibrate the integration parameters so that in the 1H NMR spectra the CH3 singlet of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (δ = 2.0 ppm) corresponds to six.
- Determine the integration value of the N-CH-N signal area (δ = 8.4-9.4 ppm) in order to evaluate the degree of IMesH+ deprotonation. The integration value should vary from 1 (when no deprotonation occurred, before irradiation) to 0 (when complete deprotonation of IMesH+ has been performed).
- Analyze the deprotonation of IMesH+ into IMes by 1H NMR.
- Formation, isolation, and characterization of the 1,3-dimesitylimidazoliumdithio-carboxylate adduct (IMes-CS2)
- Add 0.02 mL of carbon disulfide in the as-irradiated NMR tube. The reaction media changes in color from orange/brown to dark red, indicating the formation of the IMes-CS2 adduct.
- Let it react for 12 h. A red precipitate forms assigned to the IMes-CS2 adduct.
- Filter the red precipitate (fritted glass filter with pore size 3) and dry it under air at room temperature for 12 h.
- Solubilize the red solid in 0.5 mL of deuterated DMSO. Confirm the chemical structure by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy.
CAUTION: Carbon disulfide is highly toxic and should be handled with care under a fume hood.
2. Photochemical Mechanism
- Real-time photobleaching of IMesH+BPh4-/ITX
- Prepare a stock solution of ITX by adding 0.76 mg (3 x 10-3 mmol) of ITX to 15 mL of dry acetonitrile (previously stored over 3Å molecular sieves).
- Transfer 3 mL of ITX solution into a UV quartz cell covered with a rubber stopper containing 1.10 mg of IMesH+BPh4- (1.8 x 10-3 mmol) and a stirring micromagnet. The molar ratio ITX:IMesH+BPh4- is 1:3.
- Degas the solution by bubbling nitrogen for 10 min, then irradiate the solution at 365 nm with a medium-pressure Hg-Xe lamp under continuous stirring (63 mW cm-2, power of 75 mW).
- Monitor the change of UV-absorbance at 365 nm during irradiation by using a spectrometer after passing a transmitted actinide beam.
- Apply the same procedure (steps 2.1.1-2.1.4) for other experiments but replace IMesH+BPh4- with other quenchers: IMesH+Cl- (0.61 mg, 1.8 x 10-3 mmol) or NaBPh4 (0.62 mg, 1.8 x 10-3 mmol).
- Quantification of photogenerated NHC by spectrophotometric titration
- Add 1.85 mg of dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (3 x 10-4 mmol, 3 equiv.) and 0.25 mg of ITX (10-4 mmol, 1 equiv.) to 10 mL of dry acetonitrile.
- Transfer 2 mL of this freshly prepared solution into a conventional spectroscopic quartz cell capped with a rubber septum.
- Purge the colorless mixture with nitrogen before exposing the cuvette to a 365 nm LED spotlight (power of 65 mW) for 1 min.
- After each irradiation time, add gradually 0.1 mL portions of phenol red (PR) solution (2 x 10-4 M in dry acetonitrile) into the cuvette. This latter titrating solution was prepared in advance.
- Record a UV-vis spectrum after each 0.1 mL addition of PR solution until reaching 1 mL.
NOTE: The indicator solution is initially transparent and contains the bis-protonated form H2PR. After its addition, acid/base reaction with NHC causes the formation of the pink bivalent anion PR2- with a maximum absorption at 580 nm. Plotting the absorbance at 580 nm as a function of the titrant volume gives two intersecting straight lines, indicative of the titration endpoint. - Repeat the same procedure (steps 2.2.1-2.2.5) with the same ITX/IMesH+BPh4- solution irradiated for longer times: 2 min, 5 min, and 10 min. For each time, a new IMesH+PH4-/ITX sample must be prepared.
NOTE: At the equivalence point in the acid-base titration:
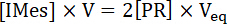 (1)
(1)
Where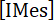 is the concentration of photogenerated IMes released in the UV cuvette, V is the initial volume of IMesH+BPh4-/ITX solution, [PR] is the concentration of PR, and Veq is the total volume of PR added into the UV cuvette at the titration end-point. Therefore, the yield of IMes released upon irradiation of IMesH+BPh4-/ITX solution is obtained from equation (2):
is the concentration of photogenerated IMes released in the UV cuvette, V is the initial volume of IMesH+BPh4-/ITX solution, [PR] is the concentration of PR, and Veq is the total volume of PR added into the UV cuvette at the titration end-point. Therefore, the yield of IMes released upon irradiation of IMesH+BPh4-/ITX solution is obtained from equation (2):
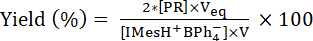 (2)
(2)
Where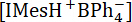 is the initial concentration of IMesH+BPh4-.
is the initial concentration of IMesH+BPh4-.
The validity of the method is checked by titrating a free IMes solution (1 x 10-4 M in acetonitrile) using a similar acetonitrile PR solution as a titrant (2 x 10-4 M).
3. Photoinduced Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization
- PhotoROMP of Nb in solution
- Add 1 g (11 mmol, 540 equiv.) of Nb, 120 mg (0.196 mmol, 10 equiv.) of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate, 12 mg (19.6 mmol, 1 equiv.) of dichloro(para-cymene)ruthenium dimer, and 25 mg (0.098 mmol, 5 equiv.) of ITX in a 20 mL test tube equipped with a stir bar.
- Dissolve the solids in 10 mL of dichloromethane and cap the tube with a rubber septum.
- Purge the mixture by bubbling nitrogen gas through a syringe needle for 15 min.
- Place the tube inside the photochemical reactor equipped with a circular array of 16 fluorescent lamps (emitting at 365 nm) and irradiate for 10 min. The solution becomes viscous, indicating that high-molecular weight polyNb is formed.
- Precipitate the polymer by pouring the solution into 300 mL of methanol.
- Filter the polymer (fritted glass filter with pore size 3) and dry it at 60 °C for 8 h.
- Analyze the polymer by 1H NMR according to reported procedures9 by dissolving about 10 mg of polymer in 0.5 mL of CD2Cl2.
- Analyze the polymer by size exclusion chromatography according to reported procedures9, using THF as eluent and dissolving 10 mg of polymer in 1 mL of THF.
- PhotoROMP of Nb in miniemulsion
- Preparation of Nb miniemulsion.
- Dissolve 15.0 g of neutral surfactant polyoxyethylene (100) stearyl ether in 150 mL of milliQ water
- Introduce the aqueous phase in the annular LED photoreactor closed with rubber septum and place the reactor under the airtight sonication probe.
- Degas the solution by bubbling nitrogen during 1 h.
- Mix 4.94 g of Nb (5.2 x 10-2 mol; 510 equiv.; 25 w%), 2.85 mL of hexadecane (10 w%), and 6 mL of dichloroethane (32.5 w%) in a 50 mL round bottom flask closed with a rotaflo. Degas the solution with a freeze-pump-thaw cycle.
- Add 6 mL of dichloroethane (32.5 w%) in a second 50 mL round-bottom flask closed with a rotaflo. Degas the solution by freeze-pump-thaw. Add 162 mg of 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (2.6 x 10-4 mol, 5 equiv.), 33 mg of ITX (1.3 10-4 mol, 2.5 equiv.), and 30 mg of dichloro(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) dimer (4.9 x 10-5 mol, 1 equiv.) under inert atmosphere (glovebox) to the flask.
- Mix the two organic solutions containing the monomer and the catalytic mixture under a nitrogen flux, and introduce 15 g of the final organic solution inside the photoreactor, containing the aqueous phase under stirring.
- Stir the two phases during 1 h to form a rough macroemulsion. Sonicate during 10 min (power 50%; pulse on-time: 5 s, off-time: 5 s) to form the miniemulsion.
- Photopolymerization of NB miniemulsion.
- Replace the airtight sonication probe by the LED lamp equipped with a water cooling system and protected by a cladding tube under a nitrogen flux.
- Place the closed reactor inside the photocabinet to prevent exposure to UV radiation.
- Irradiate the monomer miniemulsion for 100 min to obtain polymer latex. During irradiation, particle size and monomer conversion can be determined as explained below.
- Determination of particle size, conversion and molecular weight.
- Collect 4 mL of miniemulsion sample during irradiation process.
- Add 20 µL of miniemulsion in a glass cuvette containing 5 mL water to prepare a 250x diluted sample for particle size analysis by dynamic light scattering (DLS).
- Dissolve 100 µL of miniemulsion in 500 µL of THF to measure the Nb conversion by gas chromatography (GC), with hexadecane as internal standard (GC retention times: tGCNb = 1.77 min; tGCdodecane = 13.25 min).
- Precipitate the rest of the sample in 20 mL of acetone. Filter the polymer. Dry the polymer under a vacuum and measure the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) [SEC in tetrahydrofuran (THF) (1 mL min-1) with trichlorobenzene as the flow marker, using both refractometric and UV detectors].
CAUTION (Part 1-3): Possibly hazardous sources of light emitting in the UV and visible range are used in the described experiments. These lamps can present a reasonably foreseeable risk of harming the eyes and skin of lab members. Consequently, all measures possible should be put in place by the experimenter to reduce the risks to as low as is reasonably practicable. A list of common measures includes the isolation of the light source inside a protective casing (photocabinet, for example), training of all workers, placing the hazardous sources of light in well-designated laboratories or fume hoods with restricted access, providing suitable safety gears (safety goggles blocking UVA irradiation are sufficient for all described protocols), and displaying appropriate warning and safety signs.
- Preparation of Nb miniemulsion.
Results
Step 1.1 describes the efficient anion metathesis between 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride (IMesH+Cl-) and sodium tetraphenylborate (NaBPh4) to yield 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium tetraphenylborate (IMesH+BPh4-). The desired photolatent NHC is obtained in excellent yield (98%). Figure 1 shows 1H and 13C NMR spectra, both testifying that a pure product exhibiting the correct st...
Discussion
Reported here is an easy and versatile protocol for the in-situ generation of NHC upon UV-irradiation at 365 nm. The anion exchange reaction between 1,3-dimesitylimidazolium chloride and sodium tetraphenylborate provides straightforward access to the NHC protected from IMesH+BPh4- in quantitative yield. Nevertheless, if using another starting imidazolium salt, the solvent employed to perform the metathesis reaction should be chosen with care so that it allows the solubilization of both st...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Financial support by the French National Research Agency (ANR program: DS0304 2016, contract number: ANR-16-CE07-0016) and the French Ministry of Research (doctoral grant of Emeline Placet) are gratefully acknowledged.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Material | |||
| Dimesitylimidazolium chloride, 97% | ABCR | AB130859 | |
| Sodium tetraphenylborate, 99% | ABCR | AB118843 | |
| Dichloro(p-cymene) ruthenium dimer, 98% | ABCR | AB113524 | |
| Norbornene, 99% | ABCR | AB171849 | |
| Isopropythioxanthone, 97% | Sigma Aldrich | 406317 | |
| Carbon disulfide, 99.9% | Sigma Aldrich | 335266 | |
| Dichloromethane | Sigma Aldrich | 270997 | |
| Ethanol | VWR | 20821.31 | |
| Deuterated DMSO | Eurisotop | D010FE | |
| Deuterated THF | Eurisotop | D149CB | |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane | Sigma Aldrich | 284505 | |
| Brij S 100 | Sigma Aldrich | 466387 | |
| Hexadecane | Sigma Aldrich | H6703 | |
| Phenol red, 98% | Sigma Aldrich | P4633 | |
| Acetonitrile | VWR | 83639.290 | |
| 1,3-Bis(mesityl)imidazol-2-ylidene, 97% | Sigma Aldrich | 696188 | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Equipment | |||
| Rayonet photochemical reactor | Southern New England Ultraviolet Company | RPR-200 | |
| UV lamps for photochemical reactor | Southern New England Ultraviolet Company | RPR-3500A | |
| 1H and 13C NMR spectrometer | Bruker | Avance III HD spectrometer | |
| Sonication probe | BioBlock | Vibra-cell | |
| Gas chromatography | Varian | GC3900 | |
| LED Lamp and Photo-cabinet | Peschl ultraviolet | novaLIGHT TLED100-365 | |
| Dynamic Light Scattering | Malvern | zetasizer Nano ZS | |
| 365 nm UV-LED light source coupled with a flexible light-guide | Hamamastu | LC-L1V3 | |
| UV/vis spectrometer | Perkin Elmer | Lambda 35 | |
| Hg- Xe lamp with filter centred at 365 nm | Hamamastu | LC-9588/01A | |
| Radiometer | Ocean Optics | USB4000 | |
References
- . . N-Heterocyclic carbenes: from laboratory curiosities to efficient synthetic tools. , (2017).
- Díez-González, S., Marion, N., Nolan, S. P. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Late Transition Metal Catalysis. Chemical Reviews. 109 (8), 3612-3676 (2009).
- Fevre, M., Pinaud, J., Gnanou, Y., Vignolle, J., Taton, D. N-Heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) as organocatalysts and structural components in metal-free polymer synthesis. Chemical Society Review. 42 (5), 2142-2172 (2013).
- Naumann, S., Dove, A. P. N-Heterocyclic carbenes as organocatalysts for polymerizations: trends and frontiers. Polymer Chemistry. 6 (17), 3185-3200 (2015).
- Naumann, S., Buchmeiser, M. R. Liberation of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) from thermally labile progenitors: protected NHCs as versatile tools in organo- and polymerization catalysis. Catalysis Science Technology. 4 (8), 2466-2479 (2014).
- Naumann, S., Buchmeiser, M. R. Latent and Delayed Action Polymerization Systems. Macromolecular Rapid Communication. 35 (7), 682-701 (2014).
- Neilson, B. M., Bielawski, C. W. Photoswitchable NHC-promoted ring-opening polymerizations. Chemical Communication. 49 (48), 5453-5455 (2013).
- Teator, A. J., Tian, Y., Chen, M., Lee, J. K., Bielawski, C. W. An Isolable, Photoswitchable N-Heterocyclic Carbene: On-Demand Reversible Ammonia Activation. Angewandt Chemie International Edition. 54 (39), 11559-11563 (2015).
- Pinaud, J., et al. In Situ Generated Ruthenium-Arene Catalyst for Photoactivated Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization through Photolatent N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligand. Chemistry - A European Journal. 24 (2), 337-341 (2018).
- Konishi, T., Sasaki, Y., Fujitsuka, M., Toba, Y., Moriyama, H., Ito, O. Persistent C60 anion-radical formation via photoinduced electron transfer from tetraphenylborate and triphenylbutylborate. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions. 2 (3), 551-556 (1999).
- Ogawa, K. A., Goetz, A. E., Boydston, A. J. Developments in Externally Regulated Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization. Synletter. 27 (2), 203-214 (2016).
- Eivgia, O., Lemcoff, N. G. Turning the Light On: Recent Developments in Photoinduced Olefin Metathesis. Synthesis. 50 (1), 49-63 (2018).
- Monsaert, S., Vila, A. L., Drozdzak, R., Van Der Voort, P., Verpoort, F. Latent olefin metathesis catalysts. Chemical Society Review. 38 (12), 3360-3372 (2009).
- Delaude, L., Demonceau, A., Noels, A. F. Synthesis and Application of New N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ruthenium Complexes in Catalysis: A Case Study. Current Organic Chemistry. 10 (2), 203-215 (2006).
- Delaude, L., Demonceau, A. Retracing the evolution of monometallic ruthenium-arene catalysts for C-C bond formation. Dalton Transaction. 41 (31), 9257-9268 (2012).
- Asua, J. M. Miniemulsion polymerization. Progress in Polymer Science. 27 (7), 1283-1346 (2002).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved