A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Methods Article
Decomposing the Variance in Reading Comprehension to Reveal the Unique and Common Effects of Language and Decoding
In This Article
Summary
Here we present a protocol for decomposing the variance in reading comprehension into the unique and common effects of language and decoding.
Abstract
The Simple View of Reading is a popular model of reading that claims that reading is the product of decoding and language, with each component uniquely predicting reading comprehension. Although researchers have argued whether the sum rather than the product of the components is the better predictor, no researchers have partitioned the variance explained to examine the extent to which the components share variance in predicting reading. To decompose the variance, we subtract the R2 for the language-only model from the full model to obtain the unique R2 for decoding. Second, we subtract the R2 for the decoding-only model from the full model to obtain the unique R2 for language. Third, to obtain the common variance explained by language and decoding, we subtract the sum of the two unique R2 from the R2 for the full model. The method is demonstrated in a regression approach with data from students in grades 1 (n = 372), 6 (n = 309), and 10 (n = 122) using an observed measure of language (receptive vocabulary), decoding (timed word reading), and reading comprehension (standardized test). Results reveal a relatively large amount of variance in reading comprehension explained in grade 1 by the common variance in decoding and language. By grade 10, however, it is the unique effect of language and the common effect of language and decoding that explained the majority of variance in reading comprehension. Results are discussed in the context of an expanded version of the Simple View of Reading that considers unique and shared effects of language and decoding in predicting reading comprehension.
Introduction
The Simple View of Reading1 (SVR) continues as a popular model of reading because of its simplicity-reading (R) is the product of decoding (D) and language (L)-and because SVR tends to explain, on average, approximately 60% of explained variance in reading comprehension2. SVR predicts that correlations between D and R will decline over time and that correlations between L and R will increase over time. Studies generally support this prediction3,4,5. There are disagreements, however, about the functional form of SVR, with additive models (D + L = R) explaining significantly more variance in reading comprehension than product models (D × L = R)6,7,8, and a combination of sum and product [R = D + L + (D × L) explaining the largest amount of variance in reading comprehension3,9.
Recently the SVR model has expanded beyond regressions based on observed variables to latent variable modeling using confirmatory factory analysis and structural equation modeling. D is typically measured with untimed or timed reading of real words and/or nonwords and R is usually measured by a standardized reading test that includes literacy and informational passages followed by multiple-choice questions. L is typically measured by tests of expressive and receptive vocabulary and, especially in the primary grades, by measures of expressive and receptive syntax and listening comprehension. Most longitudinal studies report that L is unidimensional10,11,12,13. However, another longitudinal study14 reports a two-factor structure for L in the primary grades and a unidimensional structure in grades 4 and 8. Recent cross-sectional studies report that a bifactor model best fits the data and predicts R15,16,17,18. For example, Foorman et al.16 compared unidimensional, three-factor, four-factor, and bifactor models of SVR in data from students in grades 4-10 and found that a bifactor model fit best and explained 72% to 99% of the variance in R. A general L factor explained variance in all seven grades and vocabulary and syntax uniquely explained variance only in one grade each. Although the D factor was moderately correlated with L and R in all grades (0.40-0.60 and 0.47-0.74, respectively), it was not uniquely correlated with R in the presence of the general L factor.
Even though latent variable modeling has expanded SVR by shedding light on the dimensionality of L and the unique role that L plays in predicting R beyond the primary grades, no studies of SVR except one by Foorman et al.19 have partitioned the variance in reading comprehension into what is due uniquely to D and L and what is shared in common. This is a big omission in the literature. Conceptually it makes sense that D and L would share variance in predicting written language because word recognition entails the linguistic skills of phonology, semantics, and discourse at the sentence and text levels20. Similarly, linguistic comprehension must be connected to orthographic representations of phonemes, morphemes, words, sentences, and discourse if text is to be understood21. Multiplying D by L does not yield the knowledge shared by these components. Only decomposition of the variance into what is unique and what is shared by D and L in predicting R will reveal the integrated knowledge crucial to the success of educational interventions.
The one study by Foorman et al.19 that decomposed the variance of reading comprehension into what is unique and what is shared in common by D and L employed a latent variable modeling approach. The following protocol demonstrates the technique with data from students in grades 1, 7, and 10 based on single observed variables for D (timed decoding), L (receptive vocabulary), and R (standardized reading comprehension test) to make the decomposition process easy to understand. The data represent a subset of the data from Foorman et al.19.
Protocol
Note: The steps below describe decomposing total variance in a dependent variable (Y) into unique variance, common variance, and unexplained variance components based on two selected independent variables (called 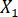 and
and 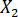 for this example) using software with a graphical user interface and data management software (see Table of Materials).
for this example) using software with a graphical user interface and data management software (see Table of Materials).
1. Reading Data into Software with a Graphical User Interface
- Click on File.
- Hover the mouse over Open.
- Click on Data.
- Locate the relevant data file on the computer.
- If the file type is not consistent with the software with a graphical user interface, click on Files of Type and select the appropriate file format.
- Click on Open.
2. Estimate the Variance Explained in the Dependent Variable (Y)
- Total Variance Explained based on Two Independent Variables — Total R2.
Note: An R2 value is known as the coefficient of determination and represents the proportion of variance for a dependent variable that is explained by a set of independent variables.- Click on Analyze and hover the mouse over Regression and select Linear.
- Click on the dependent variable in the variable list. Then click on the arrow next to Dependent.
- Click on the two independent variables (X1 and X2) in the variable list. Then click on the arrow next to Independent(s).
- Click OK.
- Click on the viewer window of the software.
- Use the mouse to scroll to the section called Model Summary. Record the value under the column R Square and label this value Total R2.
- Total Variance Explained based on

- Repeat steps 2.1.1 through 2.1.4 using only
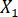 in the independent variable list.
in the independent variable list. - Click on the viewer window of the software.
- Use the mouse to scroll to the section called Model Summary. Record the value under the column R Square and label this value
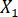 R2.
R2.
- Use the mouse to scroll to the section called Model Summary. Record the value under the column R Square and label this value
- Repeat steps 2.1.1 through 2.1.4 using only
- Total Variance Explained based on
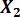
- Repeat steps 2.1.1 through 2.1.4 using only
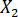 in the independent variable list.
in the independent variable list. - Click on the viewer window of the software.
- Use the mouse to scroll to the section called Model Summary. Record the value under the column R Square and label this value
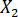 R2.
R2.
- Use the mouse to scroll to the section called Model Summary. Record the value under the column R Square and label this value
- Repeat steps 2.1.1 through 2.1.4 using only
3. Computing the Unique, Common, and Unexplained Variance Components
- Open the data management software.
- Enter the labels Total R2,
 R2, and
R2, and 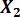 R2 in cells A1, B1, and C1, respectively.
R2 in cells A1, B1, and C1, respectively. - Enter the Total R2 value from step 2.1.5.1 in cell A2.
- Enter the
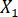 R2 value from step 2.2.2.1 in cell B2.
R2 value from step 2.2.2.1 in cell B2. - Enter the
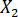 R2 value from step 2.3.2.1 in cell C2.
R2 value from step 2.3.2.1 in cell C2. - Calculate the Unique Variance of Variable 1 (U
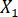 R2) in the data management software.
R2) in the data management software.
- In Cell D2 type: “=A2-C2” (i.e., Total R2 minus
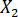 R2). In Cell D1 label this value U
R2). In Cell D1 label this value U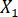 R2.
R2.
- In Cell D2 type: “=A2-C2” (i.e., Total R2 minus
- Calculate the Unique Variance of Variable 2 (U
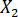 R2) in the data management software.
R2) in the data management software.
- In Cell E2 type: “=A2-B2” (i.e., Total R2 minus
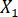 R2). In Cell E1 label this value U
R2). In Cell E1 label this value U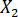 R2.
R2.
- In Cell E2 type: “=A2-B2” (i.e., Total R2 minus
- Calculate the Common Variance between Variables 1 and 2 (C
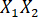 R2) in the data management software.
R2) in the data management software.
- In Cell F2 type: “=A2-D2-E2” (i.e., Total R2 minus U
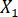 R2 minus U
R2 minus U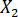 R2). In Cell F1 label this value C
R2). In Cell F1 label this value C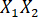 R2.
R2.
- In Cell F2 type: “=A2-D2-E2” (i.e., Total R2 minus U
- Calculate the Unexplained Variance (e) in the data management software.
- In Cell G2 type: “=1-A2” (i.e., 1-Total R2). In Cell G1 label this value e.
4. Plot the UX1R2, UX2R2, CX1X2R2, and e values
Note: Values in cells D2, E2, F2, and G2 are plotted.
- Click and drag the mouse over Cells D2, E2, F2, and G2 to highlight the data.
- Click on Insert on the ribbon of the data management software.
- Click on Charts | Pie Chart | 2-D Pie Chart.
Results
The objective of this study was to investigate the contributions of unique and common variance of language (L) and decoding (D) to predicting reading comprehension (R) in grades 1, 7, and 10 in Florida, a state whose demographics are representative of the nation as a whole. There were two hypotheses regarding predictions of the variance explained in reading comprehension. First, after the primary grades, the unique contribution of D will significantly decrease, and the unique contribution...
Discussion
There are three critical steps in the protocol for decomposing the variance in R into unique and common variance due to L and D. First, subtract the R2 in the L-only model from the full model to obtain the unique R2 for D. Second, subtract the R2 for the D-only model from the full model to obtain the unique R2 for L. Third, to obtain the common variance explained by L and D, subtract the sum of the two unique R2 from the R2 for the full model.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgements
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through a subaward to Florida State University from Grant R305F100005 to the Educational Testing Service as part of the Reading for Understanding Initiative. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute, the U.S. Department of Education, the Educational Testing Service, or Florida State University.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| IBM SPSS Statistics Software | IBM | ||
| Microsoft Office Excel | Microsoft |
References
- Gough, P., Tunmer, W. Decoding, reading, and reading disability. Remedial and Special Education. 7, 6-10 (1986).
- Quinn, J. M., Wagner, R. K. Using meta-analytic structural equation modeling to study developmental change in relations between language and literacy. Child Development. , (2018).
- Chen, R. S., Vellutino, F. Prediction of reading ability: A cross-validation study of the simple view of reading. Journal of Literacy Research. 29 (1), 1-24 (1997).
- Catts, H., Hogan, T., Adlof, S., Catts, H., Kamhi, A. Developmental changes in reading and reading disabilities. Connections between language and reading disabilities. , (2005).
- Gough, P., Hoover, W., Peterson, C., Cornoldi, C., Oakhill, J. Some observations on the simple view of reading. Reading comprehension difficulties. , (1996).
- Dreyer, L., Katz, L. An examination of "The Simple View of Reading.". Haskins Laboratories Status Report on Speech Research. SR-111/112. , 161-166 (1992).
- Neuhaus, G., Roldan, L., Boulware-Gooden, R., Swank, P. Parsimonious reading models: Identifying teachable subskills. Reading Psychology. 27, 37-58 (2006).
- Kershaw, S., Schatschneider, C. A latent variable approach to the simple view of reading. Reading and Writing. 25, 433-464 (2012).
- Hoover, W., Gough, P. The simple view of reading. Reading and Writing. 2, 127-160 (1990).
- Adlof, S., Catts, H., Little, T. Should the simple view of reading include a fluency component?. Reading & Writing. 19, 933-958 (2006).
- Anthony, J., Davis, C., Williams, J., Anthony, T. Preschoolers' oral language abilities: A multilevel examination of dimensionality. Learning and Individual Differences. 35, 56-61 (2014).
- Bornstein, M., Hahn, C., Putnick, D., Suwalsky, J. Stability of core language skill from early childhood to adolescence: A latent variable approach. Child Development. 85, 1346-1356 (2014).
- Protopapas, A., Simos, P., Sideridis, G., Mouzaki, A. The components of the simple view of reading: A confirmatory factor analysis. Reading Psychology. 33, 217-240 (2012).
- Tomblin, J. B., Zhang, X. The dimensionality of language ability in school-age children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 49, 1193-1208 (2006).
- Foorman, B., Herrera, S., Petscher, Y., Mitchell, A., Truckenmiller, A. The Structure of Oral Language and Reading and Their Relation to Comprehension in grades kindergarten through grade 2. Reading and Writing. 28 (5), 655-681 (2015).
- Foorman, B., Koon, S., Petscher, Y., Mitchell, A., Truckenmiller, A. Examining General and Specific Factors in the Dimensionality of Oral Language and Reading in 4th-10th Grades. Journal of Educational Psychology. 107 (3), 884-899 (2015).
- Kieffer, M., Petscher, Y., Proctor, C. P., Silverman, R. Is the whole greater than the sum of its parts? Modeling the contributions of language comprehension skills to reading comprehension in the upper elementary grades. Scientific Studies of Reading. 20 (6), 436-454 (2016).
- Kim, Y. S. G., Park, C., Park, Y. Dimensions of discourse level oral language skills and their relation to reading comprehension and written composition: an exploratory study. Reading and Writing. 28, 633-654 (2015).
- Foorman, B., Petscher, Y., Herrera, S. Unique and common effects of decoding and language factors in predicting reading comprehension in grades 1-10. Learning and Individual Differences. 63, 12-23 (2018).
- Perfetti, C. Reading ability: Lexical quality to comprehension. Scientific Studies of Reading. 11 (4), 357-383 (2007).
- Perfetti, C., Stafura, J. Word knowledge in a theory of reading comprehension. Scientific Studies of Reading. 18 (4), 22-37 (2014).
- Torgesen, J., Wagner, R., Rashotte, C. . Test of Word Reading Efficiency. , (2012).
- Dunn, L., Dunn, D. . Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test-4. , (2007).
- MacGinitie, W., MacGinitie, R., Maria, K., Dreyer, L. . Gates-MacGinitie Reading Tests. , (2000).
- Wanzek, J., Wexler, J., Vaughn, S., Ciullo, S. Reading interventions for struggling readers in the upper elementary grades: a synthesis of 20 years of research. Reading & Writing. 23, 889-912 (2010).
- Foorman, B., Petscher, Y., Stanley, C., Herrera, S. Latent profiles of reading and language and their association with standardized reading outcomes in kindergarten through tenth grade. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness. 10 (3), 619-645 (2017).
- Lesaux, N. K., Kieffer, M. J., Kelley, J. G., Harris, J. Effects of academic vocabulary instruction for linguistically diverse adolescents: Evidence from a randomized field trial. American Educational Research Journal. 51 (6), 1159-1194 (2014).
- Lawrence, J., Crosson, A., Paré-Blagoev, E., Snow, C. Word generation randomized trial: Discussion mediates the impact of program treatment on academic word learning. American Educational Research Journal. 52 (4), 750-786 (2015).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved