Method Article
A Polymer-based Piezoelectric Vibration Energy Harvester with a 3D Meshed-Core Structure
In This Article
Summary
In this study, we fabricated a flexible 3D mesh structure and applied it to the elastic layer of a bimorph cantilever-type vibration energy harvester for the purpose of lowering resonance frequency and increasing output power.
Abstract
In this study, we fabricated a flexible 3D mesh structure with periodic voids by using a 3D lithography method and applying it to a vibration energy harvester to lower resonance frequency and increase output power. The fabrication process is mainly divided into two parts: three-dimensional photolithography for processing a 3D mesh structure, and a bonding process of piezoelectric films and the mesh structure. With the fabricated flexible mesh structure, we achieved the reduction of resonance frequency and improvement of output power, simultaneously. From the results of the vibration tests, the meshed-core-type vibration energy harvester (VEH) exhibited 42.6% higher output voltage than the solid-core-type VEH. In addition, the meshed-core-type VEH yielded 18.7 Hz of resonance frequency, 15.8% lower than the solid-core-type VEH, and 24.6 μW of output power, 68.5% higher than the solid-core-type VEH. The advantage of the proposed method is that a complex and flexible structure with voids in three dimensions can be relatively easily fabricated in a short time by the inclined exposure method. As it is possible to lower the resonance frequency of the VEH by the mesh structure, use in low-frequency applications, such as wearable devices and house appliances, can be expected in the future.
Introduction
In recent years, VEHs have drawn much attention as an electric power supply of sensor nodes for implementing wireless sensor networks and Internet of Things (IoT) applications1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8. Among several types of energy conversion in VEHs, piezoelectric-type conversion presents high output voltage. This type of conversion is also suitable for miniaturization because of its high affinity with micromachining technology. Because of these attractive features, many piezoelectric VEHs have been developed using piezoelectric ceramic materials and organic polymer materials9,10,11,12,13.
In ceramic VEHs, cantilever-type VEHs using high-performance piezoelectric material PZT (lead titanate zirconate) are widely reported14,15,16,17,18, and the VEHs often use resonance to obtain high-efficiency power generation. In general, as the resonance frequency increases with the miniaturization of the device size, it is difficult to achieve miniaturization and low-resonance frequency simultaneously. Thus, although PZT has high-power-generation performance, it is difficult to develop small-sized PZT-based devices that work in a low-frequency band without special processing, such as nanoribbon assemblies19,20, because PZT is a high-rigidity material. Unfortunately, our surrounding vibrations such as household appliances, human motion, buildings, and bridges are mainly at low frequencies, less than 30 Hz21,22,23. Therefore, VEHs with its high-power-generation efficiency at low frequencies and small size are ideal for the low-frequency applications.
The easiest way to lower the resonance frequency is to increase the mass weight of the tip of the cantilever. As attaching a high-density material to the tip is all that is required, the fabrication is simple and easy. However, the heavier the mass is, the more fragile the device becomes. Another way of lowering the frequency is to lengthen the cantilever24,25. In the method, the distance from the fixed end to the free end is extended by a two-dimensional meandered shape. The silicon substrate is etched using a semiconductor manufacturing technique to fabricate a meandered structure. Although the method is effective for lowering resonance frequency, the area of the piezoelectric material decreases and, thus, the obtainable output power decreases. In addition, there is a disadvantage that the vicinity of the fixed end is fragile. Regarding some polymer devices, such as the low-frequency VEH, flexible piezoelectric polymer PVDF is often used. As PVDF is usually coated by a spin-coating method and the film is thin, the resonance frequency can be reduced because of the low rigidity26,27. Although the film thickness is controllable in the range of sub-micron to several microns, the attainable output power is small because of the thin thickness. Therefore, even if the frequency can be reduced, we cannot obtain sufficient power generation, and so, practical application is difficult.
Here, we propose a bimorph-type piezoelectric cantilever (consisting of two layers of piezoelectric layers and one layer of elastic layer) with two flexible piezoelectric polymer sheets, which have already been subjected to stretching treatment for improvement of piezoelectric characteristics. Furthermore, we adopt a flexible 3D mesh structure in the elastic layer of the bimorph cantilever to reduce the resonance frequency and improve the power simultaneously. We fabricate the 3D mesh structure by utilizing the backside inclined exposure method28,29 because it is possible to fabricate fine patterns with high precision in a short time. Although 3D printing is also a candidate to fabricate 3D mesh structure, the throughput is low, and the 3D printer is inferior to photolithography in machining accuracy30,31. Therefore, in this study, the backside inclined exposure method is adopted as the method for micromachining the 3D mesh structure.
Protocol
1. Fabrication of the 3D mesh structure
- Cleaning of the glass substrate
- Prepare 30 mm x 40 mm glass substrates.
- Prepare the piranha solution by pouring 150 mL of sulfuric acid (concentration: 96%) into the glass beaker. Then gently add 50 mL of hydrogen peroxide solution (concentration: 30%). Ensure that the volume ratio of sulfuric acid:hydrogen peroxide water is 3:1.
- Wear protective glasses and clothing for safety while pouring the solutions.
- Set a glass substrate in a Teflon jig for cleaning. Then immerse it in piranha solution for 1 min.
- After a 1 min immersion in piranha solution, rinse the washed glass substrate 2-3 times with pure water (overflow 2-3 times).
- Remove the water drops on the glass substrate with air blow.
- Patterning of the Cr mask pattern for backside exposure on a glass substrate
- Set the glass substrate in a chamber of a RF (Radio-Frequency) magnetron sputtering machine. Set the RF power to 250 W, the flow rate of Ar gas to 12 SCCM, the chamber pressure to 0.5 Pa, and the sputtering time to 11 min. Then form 100-200 nm of chromium film on the glass substrate by RF magnetron sputtering.
NOTE: The thickness is controlled by the sputtering time, taking into account the sputtering rate condition. - Set the substrate on a fixing stage in a spin-coater chamber. Drop a positive photoresist S1813 on the chromium film and coat the 1-2 μm thin film by spin coating at 4,000 rpm for 30 s.
- Bake the photoresist-coated substrate at 115 °C for 1 min on a hot plate to dry the resist.
- Contact a photomask and a photoresist-coated substrate. Expose UV light vertically to the photomask. Ensure that the exposure dose is 80 mJ/cm2, and the wavelength is 405 nm. Use the photomask shown in Figure 1.
- Prepare two 500 mL beakers. Then pour 150 mL of TMAH (Tetramethylammonium hydroxide: 2.38%, solvent: water) solution into one beaker and pour 150 mL of chromium etchant (Ammonium Cerium(IV) Nitrate: 16%, nitric acid: 8%) into the other beaker.
- Immerse the substrate in 150 mL of TMAH solution and develop the photoresist for 30 s to 1 min.
- Rinse the substrate with pure water.
- Immerse the substrate in the 150 mL of chromium etching solution and etch chromium for about 1 to 2 min.
- Rinse the substrate with pure water and remove water droplets with air blow.
- Prepare piranha solution by pouring 150 mL of sulfuric acid (concentration: 96%) into the glass beaker. Then gently add 50 mL of hydrogen peroxide solution (concentration: 30%). Ensure that the volume ratio of sulfuric acid:hydrogen peroxide water is 3:1.
NOTE: Wear protective glasses, clothing, and gloves for safety while pouring the solutions. Piranha solution will lose activity after a while, so prepare each time. - Place a glass substrate on a Teflon jig for cleaning. Then, immerse it in the piranha solution for 15-30 s to remove the photoresist.
- Set the glass substrate in a chamber of a RF (Radio-Frequency) magnetron sputtering machine. Set the RF power to 250 W, the flow rate of Ar gas to 12 SCCM, the chamber pressure to 0.5 Pa, and the sputtering time to 11 min. Then form 100-200 nm of chromium film on the glass substrate by RF magnetron sputtering.
- Preparation for SU-8 coating
- Set the substrate on the fixing stage in the spin-coater chamber. Drop approximately 1 mL of acrylic resin solution (concentration: 10%, solvent: toluene) on the chromium pattern side of the substrate to release a fabricated structure as a sacrificial layer. Then, form a thin film by spin coating at 2,000 rpm for 30 s.
- Bake at 100 °C for 10 min.
- SU-8 spray coating
- Launch the spray coater and pour acetone solution into the syringe for cleaning.
- Clean and remove residues inside the spray nozzle by spraying acetone solution.
NOTE: If the cleaning is insufficient, it leads to clogging at the time of spraying. Repeat this step twice to carefully clean. - Set the substrate on an attached plate in a spray coater.
- Cover the substrate with an edge cover to prevent edge bead.
- Pour the negative photoresist SU-8 3005 into the syringe.
- Set the nozzle diameter to 5 mm, the nozzle movement speed to 120 mm/s, the atomization pressure to 150 kPa, the fluid pressure to 60 kPa, the distance between the nozzle and substrate to 40 mm, the pitch distance to 3 mm, and the interval time for each layer to 45 s. Spray SU-8 multilayers on the substrate. Repeat the coating 10 times in the same way.
- Leave the substrate to stand for 5 min after coating 10 times.
NOTE: During the standing time, the SU-8 film is uniformly flattened, and the air bubbles mixed during spray coating are released. - Bake on a hot plate at 95 °C for 60 min.
- Measure the thickness of 10 layers by micrometer. Then, calculate the thickness per layer.
- Determine the remaining number of repetitions for spray coating from the calculated film thickness per layer. Then spray the multilayer to form a thick film to achieve the target film thickness. In this research, 40 layers are applied for a 200 μm thickness.
- Let the substrate stand for 5 min after the multilayer spray coating.
- Bake on a hot plate at 95 °C for 240 min.
- Leave the SU-8 coated substrate on a hot plate for 60 min and then cool it slowly to room temperature.
- 3D mesh structure forming
- Place the substrate on an angle adjustment table by flipping the substrate over (i.e., the SU-8 film is facing down) as shown in Figure 2.
- Fix the edge of the substrate with tape.
- Tilt the angle of the adjustment table to 45°.
NOTE: 0° means the substrate is in the horizontal state. The angle at this time is determined by Snell's law, calculated from the refractive index of the photoresist, the refractive index of air. By irradiating at an incident angle of 45°, a mesh structure with a structure angle of 64° is fabricated. - Place the angle adjustment table under the UV light source.
- Apply UV light vertically to the substrate at an exposure dose of 150 mJ/cm2 and a wavelength of 365 nm. After the exposure, return the angle of adjustment table to 0° and tilt it to 45° in the opposite direction. Apply UV light vertically in the same way.
NOTE: Illustrations are shown in Figure 3a,b. - Place the substrate on a hot plate and set the temperature to 95 °C for PEB (post-exposure bake). Bake the substrate for 8 min after the temperature becomes 95 °C.
- Turn off the power of the hot plate. Wait until the temperature of the hot plate drops to approximately 40 °C.
- Pour 150 mL of SU-8 developer into a 500 mL glass beaker. Set the substrate in a Teflon jig for developing.
- Pour 150 mL of isopropanol (IPA) into another 500 mL glass beaker.
- Develop for approximately 20 to 30 min. Ensure that if the developing time is not enough, it leads to insufficient opening of the mesh voids.
- Immerse the substrate with jig in IPA and rinse for 2 min.
NOTE: If the surface of SU-8 is apparently white and muddy, it indicates that development is insufficient. In that case, repeat development and rinsing again. After complete development, a mesh structure is formed, as shown in Figure 3c.
- Structure release from the glass substrate
- Pour 150 mL of toluene solution into a 500-mL glass beaker. Cover the beaker with aluminum foil because toluene is easy to evaporate at room temperature.
- Immerse the substrate in toluene solution for approximately 3-4 h. Ensure that the sacrificial layer of acrylic resin is etched, and the SU-8 structure with the mesh structure is released from the substrate, as shown in Figure 3d.
- Blow air to the substrate and remove moisture. Store it in a desiccator until it is used in step 4.3.
2. Preparation of piezoelectric film
- Prepare a PVDF sheet. Also, prepare a cutter knife with a stainless steel blade and cutting mat.
- Cut out the PVDF sheet to the device shape with a 360 mm2 sheet (10 mm x 30 mm for cantilever and 6 mm x 10 mm for electrical connection), as shown in Figure 3a.
- Place the cut PVDF films on a Petri dish with a cellulose wiper. Store them in a desiccator.
3. Preparation of substrate for bonding mesh structure and piezoelectric film
- Pour 10 mL of the main agent of PDMS and 1 mL of curing agent into a centrifuge tube (i.e., the approximate volume ratio is 10:1).
- Set the centrifuge tube in a planetary stirring and defoaming machine and mix both solutions for 1 min.
- Prepare two 30 mm x 40 mm glass substrates.
- Set the glass substrate on a fixing stage in the spin-coater chamber. Drop PDMS solution onto the glass substrate. Then, form the PDMS film by spin coating at 4,000 rpm, as shown in Figure 3e.
- Bake the substrate on a hot plate at 100 °C for 60 min to dry the PDMS film.
- Turn off the power of the hot plate. Wait until the temperature of the hot plate drops to approximately 40 °C.
4. Fabrication of bimorph vibration energy harvester
- Place the cut PVDF films one by one onto two different PDMS substrates, as shown in Figure 3f. Ensure that just by placing PVDF films on the surface of PDMS, they adhere to each other. If wrinkles are seen on the PVDF films, extend them with a roller.
NOTE: These two PVDF films are called PVDF flm1 and PVDF flm2, and the two PDMS substrates are PDMS sbs1 and PDMS sbs2, for the sake of clarity. - Drop SU-8 3005 onto the PVDF flm1 placed on PDMS sbs1. Then, form the SU-8 thin film by spin coating at 4,000 rpm as shown in Figure 3g.
NOTE: This SU-8 thin film becomes an adhesion layer between the mesh structure and the PVDF flm1. The place where the SU-8 3005 was not dropped is used for wiring to acquire electric power. - Place the SU-8 mesh structure on the PVDF flm1 and bond them as shown in Figure 3h.
- Drop SU-8 3005 onto the PVDF flm2 placed on PDMS sbs2. Then, form the SU-8 thin film by spin coating at 4,000 rpm in the same way as step 4.2.
- Peel off PVDF flm2 from PDMS sbs2 and then place on top of the SU-8 mesh structure placed on PVDF flm1, adhering them as shown in Figure 3i,j. Store the device with the bonded state in a container with low humidity such as desiccator. Leave it for about 12 h.
- Put the tweezers into the bottom side of the lowest layer PVDF flm1 and peel off bonded 3 layers PVDF flm1, SU-8 mesh structure, and PVDF flm2 simultaneously from the substrate, as shown in Figure 3k.
Results
We fabricated a bimorph-type VEH composed of two layers of PVDF films and an intermediate layer composed of an SU-8 mesh structure, as shown in Figure 4. The electrodes of the upper and lower PVDF are connected in series to obtain output voltage. The optical image and the two SEM images are elastic layers with a mesh structure. According to the images, the elastic layer processed by the backside inclined exposure appears to have fine 3D mesh patterns without development failure.
Figure 5 shows the results of vibration tests. In the vibration tests, two VEHs—one with a meshed core and the other with a solid-core structure—as the elastic layer are evaluated to verify the validity of meshed-core-type VEH. The VEHs are set on a vibration shaker and excited with a vibration acceleration of 1.96 m/s2 (0.2 G). Both the meshed-core-type and solid-core-type VEHs showed sinusoidal output synchronized with a sinusoidal input. The meshed-core-type VEH exhibited a 42.6% higher output voltage than the solid-core type VEH. Figure 5b shows the frequency response of the maximum output power. The meshed-core-type VEH exhibited a resonance frequency of 18.7 Hz, which is 15.8% lower than the solid-core-type VEH, and an output power of 24.6 μW, which is 68.5% higher than the solid-core-type VEH.
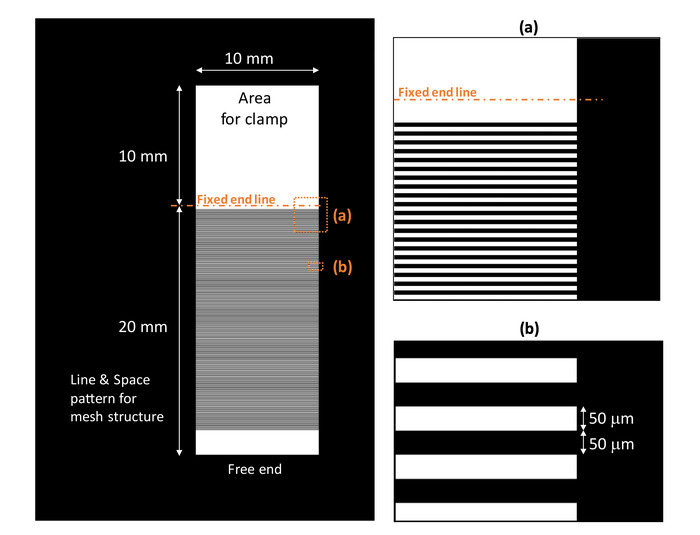
Figure 1: Photomask layout for photolithography to fabricate elastic layer with a 3D meshed-core structure. The photomask has two parts. One is the area for clamping, and the other contains the line and space patterns for mesh-structure patterning. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
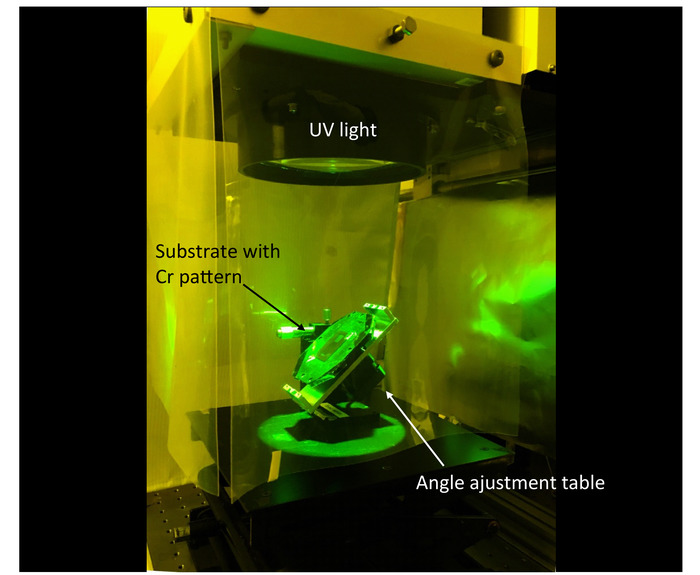
Figure 2: Set-up for inclined exposure. UV light is exposed vertically to the inclined substrate with a Cr pattern placed on angle adjustment table. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
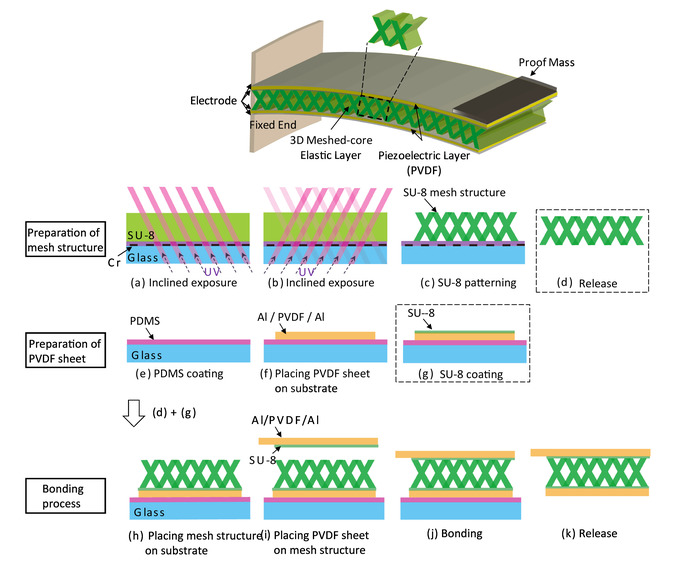
Figure 3: Schematic of a proposed piezoelectric vibration energy harvester with a 3D meshed-core structure and the fabrication process of the harvester. The fabrication process can be divided into 3 sections: (a)-(d) represent the fabrication process of the 3D mesh structure, (e)-(g) represent the preparation of the PVDF film on a glass substrate, and (h)-(j) represent the bonding process to form a bimorph cantilever. (These figures are published under gold Open Access, Creative Commons license and have been modified from [21].) Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
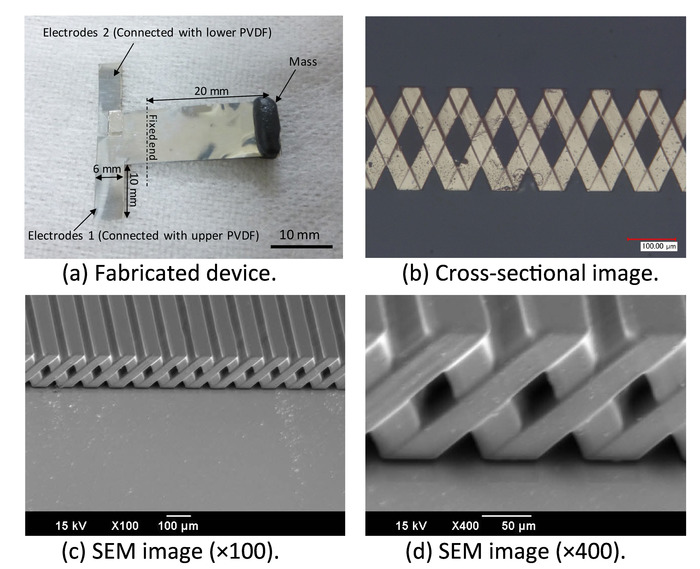
Figure 4: (a) Photograph of the fabricated bimorph meshed-core vibration energy harvester, (b) cross-sectional optical image of the 3D meshed-core structure, (c) and (d) SEM images of SU-8 meshed-core elastic layer. (These figures are published under gold Open Access, Creative Commons license and have been modified from [21].) Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
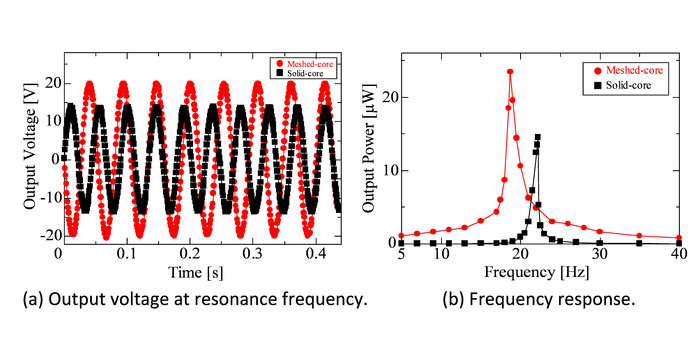
Figure 5: (a) Sinusoidal output voltage of load resistance under each resonance condition (meshed-core 18.7 Hz, solid-core 22.2 Hz) and (b) Maximum output power as a function of vibration frequency under optimum load resistance (meshed-core 17 MΩ, solid-core 13 MΩ) and 0.2 G acceleration. (These figures are published under gold Open Access, Creative Commons license and have been modified from [21].) Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
The successful fabrication of the 3D mesh structure and the proposed bimorph VEH described above is based on four critical and distinctive steps.
The first critical step is processing using backside inclined exposure. In principle, it is possible to fabricate a mesh structure by inclined exposure from the upper surface using the contact lithography technique. However, backside exposure presents a more accurate processing precision than contact lithography, and defects during development are less likely to occur28,29. This is because the gap between the photomask and the photoresist could arise due to the waviness of the photoresist surface. Hence, light diffraction occurs and processing precision is lowered because of the gap. Therefore, in this study, we fabricated a mesh structure using the backside inclined exposure method. In addition, the measured value of the structural angle of the fabricated mesh structure is about 65°, with just a 1% error as compared with the designed value of 64°. From the result, we conclude that it is appropriate to apply the backside inclined exposure method to fabricate the mesh structure.
The second critical step is the development process of SU-8. If a developing defect occurs, the mesh structure loses inherent flexibility. To develop the thick SU-8 film, typically 10-15 min is used. However, this developing time is insufficient for the development of a 3D mesh structure. The 3D mesh structure differs from the 2D pattern fabricated by photolithography because it has many internal voids inside the membrane. If the developing time is short, development does not progress to the interior of the mesh structure, causing patterning failure. That is why, it is necessary to apply a relatively long development time, 20-30 min32. If finer patterns are required, even longer developing time may be necessary. However, at that time, we have to consider the swelling caused by long development time33.
Next, the method to exploit a PDMS-formed substrate in the bonding process of PVDF film and SU-8 mesh structure is unique. It makes spin coating possible and, as a result, PVDF and SU-8 can be easily adhered using a spin-coated SU-8 thin adhesive layer. PVDF and SU-8 can be bonded, even by using a commercially available instant glue. However, the adhesive material hardens after the adhesive is solidified. Moreover, it is difficult to form a thin film with the instant glue. If the thickness of the instant glue is larger, it will increase the rigidity of the entire device. An increase in rigidity leads to an increase in the resonance frequency (i.e., it prevents lowering the resonance frequency, which is the main purpose of this study). On the other hand, using the SU-8 thin film formed by spin coating as an adhesion layer does not greatly affect the increase in rigidity because the formed SU-8 film is thin. In addition, as the mesh structure is made of SU-8, it is possible to increase the adhesive strength by using the same material for the adhesion layer. That is why the SU-8 adhesion has enough adhesive strength to bond an SU-8 mesh structure and PVDF films. Furthermore, from the aspect of reproducibility of the device, it would be useful to use the SU-8 thin film as an adhesion layer, as a constant film thickness can be realized by spin coating film formation.
Fourth, the coating method of SU-8 is distinctive. We have selected a spray multilayer coating method for the SU-8 thick film. Although it is possible to form a thick film by spin coating, large surface waviness occurs, and it is difficult to coat the film uniformly34. On the other hand, using the spray multi-coating method reduces the waviness and suppresses the error of film thickness in the substrate34. Particularly, attention needs to be given to large waviness because when the thickness of the 3D mesh structure becomes nonuniform, the vibration characteristics and rigidity of the device is changed by the partially increased or decreased thickness.
In principle, as photolithography uses UV light, the fabricable shapes are limited. It is true that we can fabricate complex structures such as a 3D mesh structure by using inclined exposure. However, arbitrary shapes such as a three-dimensional structure with a curved shape in the film thickness direction are difficult to form35,36. The 3D printing can produce arbitrary three-dimensional shapes, and the design is flexible. However, the throughput of the fabrication is low, and the processing precision and mass production are inferior to photolithography. Thus, it is not suitable for fabricating structures with fine patterns in a short time. In addition, processing 3D CAD data is necessary, and it takes time to create the 3D model. On the other hand, in the case of photolithography, especially in the inclined exposure method, the CAD data necessary for the photomask is two-dimensional, and the design is relatively easy. For example, the oriented design for a 3D mesh structure is just the 2D line and space patterns, as shown in Figure 3. Considering these facts, in this research, we exploited the 3D lithography technique to develop a flexible 3D mesh structure.
In this study, we fabricated a flexible 3D mesh structure and applied it to the elastic layer of a bimorph cantilever type VEH for the purpose of lowering resonance frequency and increasing output power. Since the proposed method is useful in lowering resonance frequency, it will be useful for vibration energy harvester targeted for low-frequency application such as wearable devices, monitoring sensors for public buildings and bridge, house appliances, etc. Further improvement of output power would be expected by combining the trapezoidal shape, triangle shape, and thickness optimization which is previously proposed in other papers37,38,39.
Disclosures
We have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by JSPS Science Research Grant JP17H03196, JST PRESTO Grant Number JPMJPR15R3. The support from MEXT Nanotechnology Platform Project (The University of Tokyo Microfabrication Platform) to the fabrication of photomask is greatly appreciated.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| SU-8 3005 | Nihon Kayaku | Negative photoresist | |
| KF Piezo Film | Kureha | Piezoelectric PVDF film, 40 mm | |
| Vibration Shaker | IMV CORPORATION | m030/MA1 | Vibration Shaker |
| Spray coater | Nanometric Technology Inc. | DC110-EX | |
| Sputtering equipment | Canon Anelva Corporation | E-200S | |
| PDMS | Dow Corning Toray Co. Ltd | SILPOT 184 W/C | Dimethylpolysiloxane |
| Spin coater | MIKASA Co. Ltd | 1H-DX2 | |
| Digital oscilloscope | Teledyne LeCroy Japan Corporation | WaveRunner 44Xi-A | |
| SEM | JEOL Ltd. | JCM-5700LV | |
| Digital microscope | Keyence Corporation | VHX-1000 |
References
- Karim, F., Zeadally, S. Energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks A comprehensive review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 55, 1041-1054 (2016).
- Wei, C., Jing, X. A comprehensive review on vibration energy harvesting: Modelling and realization. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 74, 1-18 (2017).
- Priya, S., et al. A Review on Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting: Materials, Methods, and Circuits. Energy Harvesting and Systems. 4 (1), 3-39 (2017).
- Arroyo, E., Badel, A., Formosa, F., Wu, Y., Qiu, J. Comparison of electromagnetic and piezoelectric vibration energy harvesters: Model and experiments. Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical. 183, 148-156 (2012).
- Inoue, S., et al. A Fluidic Vibrational Energy Harvester for Implantable Medical Device Applications. IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines. 137 (6), 152-158 (2017).
- Sano, C., Mitsuya, H., Ono, S., Miwa, K., Toshiyoshi, H., Fujita, H. Triboelectric energy harvesting with surface-charge-fixed polymer based on ionic liquid. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials. 19 (1), 317-323 (2018).
- Tsutsumino, T., Suzuki, Y., Kasagi, N., Sakane, Y. Seismic Power Generator Using High-Performance Polymer Electret. Int. Conf. MEMS'06. 06, 98-101 (2006).
- Arakawa, Y., Suzuki, Y., Kasagi, N. Micro Seismic Power Generator Using Electret Polymer Film. The Fourth International Workshop on Micro and Nanotechnology for Power Generation and Energy Conversion Applications Power MEMS 2004. , 37-38 (2004).
- Kim, S. G., Priya, S., Kanno, I. Piezoelectric MEMS for energy harvesting. MRS Bulletin. 37 (11), 1039-1050 (2012).
- Rocha, J. G., Gonçalves, L. M., Rocha, P. F., Silva, M. P., Lanceros-Méndez, S. Energy harvesting from piezoelectric materials fully integrated in footwear. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 57 (3), 813-819 (2010).
- Chen, D., Chen, K., Brown, K., Hang, A., Zhang, J. X. J. Liquid-phase tuning of porous PVDF-TrFE film on flexible substrate for energy harvesting. Applied Physics Letters. 110, 153902(2017).
- Kim, H. S., Kim, J. H., Kim, J. A review of piezoelectric energy harvesting based on vibration. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing. 12 (6), 1129-1141 (2011).
- Aktakka, E. E., Peterson, R. L., Najafi, K. Thinned-PZT on SOI process and design optimization for piezoelectric inertial energy harvesting. Transducers'11. , 1649-1652 (2011).
- Xu, R., et al. Screen printed PZT/PZT thick film bimorph MEMS cantilever device for vibration energy harvesting. Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical. 188, 383-388 (2012).
- Shen, D., et al. Micromachined PZT cantilever based on SOI structure for low frequency vibration energy harvesting. Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical. 154 (1), 103-108 (2009).
- Bin Fang, H., et al. Fabrication and performance of MEMS-based piezoelectric power generator for vibration energy harvesting. Microelectronics Journal. 37 (11), 1280-1284 (2006).
- Lefeuvre, E., Badel, A., Richard, C., Petit, L., Guyomar, D. A comparison between several vibration-powered piezoelectric generators for standalone systems. Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical. 126 (2), 405-416 (2006).
- Ishida, K., et al. Insole pedometer with piezoelectric energy harvester and 2 v organic circuits. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits. 48 (1), 255-264 (2013).
- Qi, Y., Kim, J., Nguyen, T. D., Lisko, B., Purohit, P. K., Mcalpine, M. C. Enhanced Piezoelectricity and Stretchability in Energy Harvesting Devices Fabricated from Buckled PZT Ribbons. Nano Letters. 11 (3), 1331-1336 (2011).
- Dagdeviren, C., et al. Conformal piezoelectric systems for clinical and experimental characterization of soft tissue biomechanics. Nature Materials. 14 (7), 728-736 (2015).
- Tsukamoto, T., Umino, Y., Shiomi, S., Yamada, K., Suzuki, T. Bimorph piezoelectric vibration energy harvester with flexible 3D meshed-core structure for low frequency vibration. Science and Technology of Advanced Material. 19 (1), 660-668 (2018).
- Bayrashev, A., Parker, A., Robbins, W. P., Ziaie, B. Low frequency wireless powering of microsystems using piezoelectric-magnetostrictive laminate composites. TRANSDUCERS 2003 - 12th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Digest of Technical Papers. 2, 1707-1710 (2003).
- Yildirim, T., Ghayesh, M. H., Li, W., Alici, G. A review on performance enhancement techniques for ambient vibration energy harvesters. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 71, 435-449 (2017).
- Karami, M. A., Inman, D. J. Electromechanical modeling of the low-frequency zigzag micro-energy harvester. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures. 22 (3), 271-282 (2011).
- Liu, H., Lee, C., Kobayashi, T., Tay, C. J., Quan, C. Piezoelectric MEMS-based wideband energy harvesting systems using a frequency-up-conversion cantilever stopper. Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical. 186, 242-248 (2012).
- Ramadan, K. S., Sameoto, D., Evoy, S. A review of piezoelectric polymers as functional materials for electromechanical transducers. Smart Materials and Structures. 23 (3), 033001(2014).
- Sharma, T., Je, S. S., Gill, B., Zhang, J. X. J. Patterning piezoelectric thin film PVDF-TrFE based pressure sensor for catheter application. Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical. 177, 87-92 (2012).
- Lee, J. B., Choi, K. H., Yoo, K. Innovative SU-8 lithography techniques and their applications. Micromachines. 6 (1), 1-18 (2015).
- Kim, K., et al. A tapered hollow metallic microneedle array using backside exposure of SU-8. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering. 14 (4), 597-603 (2004).
- Vaezi, M., Seitz, H., Yang, S. A review on 3D micro-additive manufacturing technologies. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 67 (5-8), 1721-1754 (2013).
- Gates, B. D., Xu, Q., Stewart, M., Ryan, D., Willson, C. G., Whitesides, G. M. New approaches to nanofabrication: Molding, printing, and other techniques. Chemical Reviews. 105 (4), 1171-1196 (2005).
- Zhang, J., Tan, K. L., Gong, H. Q. Characterization of the polymerization of SU-8 photoresist and its applications in micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS). Polymer Testing. 20 (6), 693-701 (2001).
- Chuang, Y. J., Tseng, F. G., Lin, W. K. Reduction of diffraction effect of UV exposure on SU-8 negative thick photoresist by air gap elimination. Microsystem Technologies. 8 (4-5), 308-313 (2002).
- Akamatsu, M., Terao, K., Takao, H., Shimokawa, F., Oohira, F., Suzuki, T. Improvement of coating uniformity for thick photoresist using a partial spray coat. The 7th Annual IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (IEEE-NEMS2012). , W3P-33 (2012).
- Ingrole, A., Hao, A., Liang, R. Design and modeling of auxetic and hybrid honeycomb structures for in-plane property enhancement. Materials and Design. 117, 72-83 (2017).
- Schubert, C., Van Langeveld, M. C., Donoso, L. A. Innovations in 3D printing: A 3D overview from optics to organs. British Journal of Ophthalmology. 98 (2), 159-161 (2014).
- Muthalif, A. G. A., Nordin, N. H. D. Optimal piezoelectric beam shape for single and broadband vibration energy harvesting: Modeling, simulation and experimental results. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. 54, 417-426 (2015).
- Tai, W. C., Zuo, L. On optimization of energy harvesting from base-excited vibration. Journal of Sound and Vibration. 411, 47-59 (2017).
- Song, J., Zhao, G., Li, B., Wang, J. Design optimization of PVDF-based piezoelectric energy harvesters. Heliyon. 3 (9), e00377(2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved