A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Plasma-Assisted Molecular Beam Epitaxy Growth of Mg3N2 and Zn3N2 Thin Films
In This Article
Summary
This article describes the growth of epitaxial films of Mg3N2 and Zn3N2 on MgO substrates by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy with N2 gas as the nitrogen source and optical growth monitoring.
Abstract
This article describes a procedure for growing Mg3N2 and Zn3N2 films by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy (MBE). The films are grown on 100 oriented MgO substrates with N2 gas as the nitrogen source. The method for preparing the substrates and the MBE growth process are described. The orientation and crystalline order of the substrate and film surface are monitored by the reflection high energy electron diffraction (RHEED) before and during growth. The specular reflectivity of the sample surface is measured during growth with an Ar-ion laser with a wavelength of 488 nm. By fitting the time dependence of the reflectivity to a mathematical model, the refractive index, optical extinction coefficient, and growth rate of the film are determined. The metal fluxes are measured independently as a function of the effusion cell temperatures using a quartz crystal monitor. Typical growth rates are 0.028 nm/s at growth temperatures of 150 °C and 330 °C for Mg3N2 and Zn3N2 films, respectively.
Introduction
The II3-V2 materials are a class of semiconductors that have received relatively little attention from the semiconductor research community compared to III-V and II-VI semiconductors1. The Mg and Zn nitrides, Mg3N2 and Zn3N2, are attractive for consumer applications because they are composed of abundant and non-toxic elements, making them inexpensive and easy to recycle unlike most III-V and II-VI compound semiconductors. They display an anti-bixbyite crystal structure similar to the CaF2 structure, with one of the interpenetrating fcc F-sublattices being half-occupied2,3,4,5. They are both direct band gap materials6, making them suitable for optical applications7,8,9. The band gap of Mg3N2 is in the visible spectrum (2.5 eV)10, and the band gap of Zn3N2 is in the near-infrared (1.25 eV)11. To explore the physical properties of these materials and their potential for electronic and optical device applications, it is critical to obtain high quality, single crystal films. Most work on these materials to date has been carried out on powders or polycrystalline films made by reactive sputtering12,13,14,15,16,17.
Molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) is a well-developed and versatile method for growing single-crystal compound semiconductor films18 that has the potential to yield high quality materials using a clean environment and high-purity elemental sources. Meanwhile, MBE rapid shutter action enables changes to a film at the atomic layer scale and allows for precise thickness control. This paper reports on the growth of Mg3N2 and Zn3N2 epitaxial films on MgO substrates by plasma-assisted MBE, using high purity Zn and Mg as vapor sources and N2 gas as the nitrogen source.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. MgO substrate preparation
NOTE: Commercial one-side epi-polished (100) oriented single crystal MgO square substrates (1 cm x 1 cm) were employed for the X3N2 (X = Zn and Mg) thin film growth.
- High temperature annealing
- Place the MgO on a clean sapphire wafer sample carrier with the polished side facing upwards in a furnace and anneal for 9 h at 1,000 °C. Raise the temperature to 1000 °C over a 10 min period.
NOTE: High temperature annealing removes carbon from the surface and reconstructs the surface crystal structure of the MgO single crystal substrates. - Cool the MgO substrates to the room temperature (RT).
- Place the MgO on a clean sapphire wafer sample carrier with the polished side facing upwards in a furnace and anneal for 9 h at 1,000 °C. Raise the temperature to 1000 °C over a 10 min period.
- Substrate cleaning
- Collect the annealed MgO substrates and rinse in deionized water in a clean borosilicate glass beaker.
- Boil the MgO substrates in 100 mL of acetone in a 250 mL borosilicate glass beaker for 30 min to remove inorganic carbon contamination from handling.
NOTE: Cover the beaker and do not allow the acetone to boil dry. - Drain the acetone and rinse the MgO substrates in 50 mL of methanol.
- Blow-dry the substrates with nitrogen gas, then store the dry, clean substrates in the clean chip tray.
2. Operation of VG V80 MBE
- Open the cooling water for the preparation chamber, cryoshroud on the growth chamber (see Figure 1), effusion cells, and quartz crystal microbalance sensor.
- Turn on the Ar-ion laser with a wavelength of 488 nm. The laser light is brought to the MBE chamber with an optical fiber from the laser, which is located in another room.
- Turn on the reflection high energy electron diffraction gun (RHEED), 13.56 Mhz radio frequency (rf) plasma generator, and quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) system.
3. Substrate loading
- Fast entry lock
- Mount a clean MgO substrate on the molybdenum sample holder (Figure 2A) using tungsten spring clips.
- Turn off the turbo pump on the fast entry lock (FEL) and vent the FEL chamber with nitrogen. Open the FEL when the chamber pressure reaches atmospheric pressure.
- Remove the sampler holder cassette out of the FEL and load the sample holder with the substrate into the cassette.
- Load the cassette back into the FEL and turn the turbo pump back on.
- Wait for the pressure in the FEL to drop to 10-6 Torr.
- Increase the temperature of the fast entry lock to 100 °C over a period of 5 min and degas the substrates with the holders for 30 min in the fast entry lock.
- Make sure the pressure in the fast entry lock is below 10-7 Torr before opening the vacuum valve to the preparation chamber. Transfer the holder using the wobble stick transfer mechanism to the preparation chamber, then ramp up the degassing station to 400 °C and allow it to degas for 5 h.
- Transfer the degassed holder by the trolley transfer mechanism to the sample manipulator in the growth chamber. Increase the substrate temperature up to 750 °C over a period of 30 min and allow the sample to outgas in the manipulator for another 30 min. Make sure the cooling water is turned on in the cryoshroud to avoid overheating the cryoshroud.
- Drop the temperature of the substrate to 150 °C for Zn3N2 film growth and 330°C for Mg3N2 film growth using the thermocouple in the sample manipulator to measure the sample temperature.
- In-situ RHEED
- Set the voltage on the electron gun to 15 kV and filament current to 1.5 A once the growth chamber pressure is below 1 x 10-7 Torr.
- Rotate the substrate holder until 1) the electron gun is aligned along a principle crystallographic axis of the substrate and 2) a clear single crystal electron diffraction pattern is visible.
- Take a picture of the RHEED pattern and save the picture.
- Close the shutter on the effusion cell and stop the flow of nitrogen. Measure the RHEED pattern for the deposited film when the chamber pressure is below 10-7 Torr.
4. Metal flux measurements
- Use standard group III type effusion cells or low temperature effusion cells for Mg and Zn.
- Load the crucibles with 15 g and 25 g of high purity Mg and Zn shot, respectively.
- When the growth chamber has achieved a vacuum of 10-8 Torr or better, and before loading the substrate holder, outgas the Zn or Mg source effusion cells up to 250 °C at a ramp rate of ~20 °C/min and allow it to outgas for 1 h with the shutters closed.
- After the substrate has been loaded into the sample manipulator, heat the Zn and/or Mg effusion cells to 350 °C or 390 °C respectively, at a ramp rate of ~10 °C/min, and wait 10 min for them to stabilize with the shutters closed.
- Use the retractable quartz crystal monitor to measure the metal flux. Position the quartz crystal sensor in front of the substrate inside the chamber. Make sure the substrate is fully covered by the detector so that no metal is deposited on the substrate.
- Input the density of the metal of interest (ρZn = 7.14 g/cm3, ρMg = 1.74 g/cm3) into the quartz crystal monitor (QCM) controller.
- To calibrate the flux, open the shutter for one of the metal sources and allow the effusion cell to deposit on the sensor. The QCM system converts its internal measurement of mass to thickness.
- Calculate the elemental flux from the slope of the increasing thickness as a function of time shown on the QCM. The rate of increase of the thickness over a few minutes is proportional to the elemental flux. In two example cases, a Zn flux of 0.45 nm/s and a Mg flux of 1.0 nm/s are obtained.
- Change the temperature of the effusion cells and repeat step 4.8 if the temperature dependence of the flux is required. The measured temperature dependence of the Mg and Zn flux is shown in Figure 3 for this specific growth system.
- When the flux measurements are complete, close the shutters on the effusion cells and retract the quartz crystal sensor.
5. Nitrogen plasma
- Turn off the filament current and high voltage on the RHEED gun to prevent damage in the presence of a high N2 gas pressure in the growth chamber.
- Open the gas valve on the high pressure N2 cylinder.
- Slowly open the leak valve slowly until the nitrogen pressure in the growth chamber reaches 3 x 10-5-4 x 10-5 Torr.
- Set the power of the plasma generator to 300 W.
- Ignite the plasma with the ignitor on the plasma source. A bright purple glow will be visible from the viewport when the plasma ignites, as shown in Figure 2B.
- Adjust the control on the rf matching box to minimize the reflected power as much as possible. A reflected power of less than 15 W is good; in this case, the reflected power is reduced to 12 W.
6. In situ laser light scattering
- Focus the chopped 488 nm Argon laser light reflected from the substrate in the growth chamber onto the Si photodiode so that an electrical signal can be detected by the lock-in amplifier. This is accomplished by adjusting the angle of the substrate by rotating the substrate holder around two axes and adjusting the position of the Si detector, then focusing the lens that collects the reflected light as shown in Figure 4.
- Open the shutter of one of the metal sources.
- Record the time-dependent reflectivity with a computer-controlled data logger. The growth of an epitaxial film will produce an oscillatory reflected signal with time associated with thin film optical interference between the front and back surfaces of the film.
- To protect the film from oxidation in air, deposit an encapsulation layer to protect the film from oxidation in air. This is especially important for Mg3N2 which oxidizes rapidly in air.
- In order to deposit a MgO encapsulation layer, close the nitrogen gas, switch to oxygen gas, repeat step 5.3, and increase the oxygen pressure to 1 x 10-5 Torr.
- Set the power of the plasma generator to 250 W and repeat step 5.5. The plasma starts at lower rf power with oxygen gas than with nitrogen gas.
- Open the shutter on the Mg source, and repeat step 6.4 for 5-10 min.
NOTE: This will produce a MgO film that is about 10 nm thick. The uncapped Mg3N2 films are yellow but fade quickly to a whitish color within 20 s upon exposure to air. Consequently, an encapsulation layer is required to allow time for measurements on the films before they oxidize after removal from the vacuum chamber. - Close the gas valves, turn off the laser, and ramp down the substrate and cell temperatures to ~25 °C in 30 min. Turn off the cooling water and the rf power to the plasma source.
- After several growth runs, the optical windows become covered with metal. Remove the metal by wrapping the window in aluminum foil and heating it with heating tape to 400 °C and a temperature ramp rate of ~15 °C/min or slower over the course of a weekend.
7. Growth rate determination
- Use Equation 1 below to describe the optical reflectivity of the sample11,19.
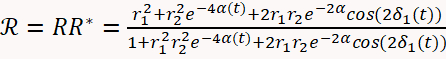 (1)
(1)
Where:
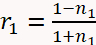 (1 - a)
(1 - a)
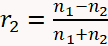 (1 - b)
(1 - b)
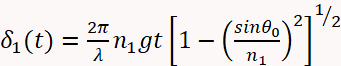 (1 - c)
(1 - c)
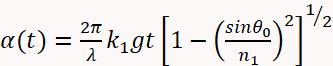 (1 - d)
(1 - d) - And where: n2 = 1.747 is the refractive index of the MgO substrate at a wavelength of 488 nm; θ0 is the angle of the incident beam measured with respect to the substrate surface normal; and t is time. The optical constants of the film (n1 and k1) and growth rate are obtained by fitting the reflectivity as a function of time in Equation 1.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
The black object in the inset in Figure 5B is a photograph of an as-grown 200 nm Zn3N2 thin film. Similarly, the yellow object in the inset in Figure 5C is an as-grown 220 nm Mg3N2 thin film. The yellow film is transparent to the extent that it is easy-to-read text placed behind the film10.
The surface ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
A variety of considerations is involved in the choice of substrates and establishing the growth conditions that optimize the structural and electronic properties of the films. The MgO substrates are heated at high temperature in air (1000 °C) to remove carbon contamination from the surface and improve the crystalline order in the substrate surface. Ultrasonic cleaning in acetone is a good alternative method to clean the MgO substrates.
The (400) X-ray diffraction peak for the Zn3
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| (100) MgO | University Wafer | 214018 | one side epi-polished |
| Acetone | Fisher Chemical | 170239 | 99.8% |
| Argon laser | Lexel Laser | 00-137-124 | 488 nm visible wavelength, 350 mW output power |
| Chopper | Stanford Research system | SR540 | Max. Frequency: 3.7 kHz |
| Lock-in amplifier | Stanford Research system | 37909 | DSP SR810, Max. Frequency: 100 kHz |
| Magnesium | UMC | MG6P5 | 99.9999% |
| MBE system | VG Semicon | V80H0016-2 SHT 1 | V80H-10 |
| Methanol | Alfa Aesar | L30U027 | Semi-grade 99.9% |
| Nitrogen | Praxair | 402219501 | 99.998% |
| Oxygen | Linde Gas | 200-14-00067 | > 99.9999% |
| Plasma source | SVT Associates | SVTA-RF-4.5PBN | PBN, 0.11" Aperture, Specify Length: 12" – 20" |
| Si photodiode | Newport | 2718 | 818-UV Enhanced, 200 - 1100 nm |
| Zinc | Alfa Aesar | 7440-66-6 | 99.9999% |
References
- Suda, T., Kakishita, K. Band-gap energy and electron effective mass of polycrystalline Zn3N2. Journal of Applied Physics. 99 (7), 076101.1-076101.3 (2006).
- Hu, J., Bando, Y., Zhan, J., Zhi, C., Golberg, D. Carbon nanotubes as nanoreactors for fabrication of single-crystalline Mg3N2 nanowires. Nano Letters. 6 (6), 1136-1140 (2006).
- Fang, C. M., Groot, R. A., Bruls, R. J., Hintzen, H. T., With, G. Ab initio band structure calculations of Mg3N2 and MgSiN2. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 11 (25), 4833-4842 (1999).
- Yoo, S. H., Walsh, A., Scanlonc, D. O., Soon, A. Electronic structure and band alignment of zinc nitride, Zn3N2. RSC Advances. 4 (7), 3306-3311 (2014).
- Partin, D. E., Williams, D. J., O'Keeffe, M. The crystal structures of Mg3N2 and Zn3N2. Journal of Solid-State Chemistry. 132 (1), 56-59 (1997).
- Ullah, M., Murtaza, G., Ramay, S. M., Mahmood, A. Structural, electronic, optical and thermoelectric properties of Mg3X2 (X = N, P, As, Sb, Bi) compounds. Materials Research Bulletin. 91, 22-30 (2017).
- Li, C. T. Electrocatalytic zinc composites as the efficient counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells: study on the electrochemical performance and density functional theory Calculations. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 7 (51), 28254-28263 (2015).
- Sinha, S., Choudhury, D., Rajaraman, G., Sarkar, S. Atomic layer deposition of Zn3N2 thin films: growth mechanism and application in thin film transistor. RSC Advances. 5 (29), 22712-22717 (2015).
- Bhattacharyya, S. R., Ayouchi, R., Pinnisch, M., Schwarz, R. Transfer characteristic of zinc nitride based thin film transistors. Physica Status Solidi C. 9 (3-4), 469-472 (2012).
- Wu, P., Tiedje, T. Molecular beam epitaxy growth and optical properties of Mg3N2 films. Applied Physics Letters. 113 (8), 082101.1-082101.4 (2018).
- Wu, P., et al. Molecular beam epitaxy growth and optical properties of single crystal Zn3N2 films. Semiconductor Science and Technology. 31 (10), 10LT01.1-10LT01.4 (2016).
- Jiang, N., Georgiev, D. G., Jayatissa, A. H. The effects of the pressure and the oxygen content of the sputtering gas on the structure and the properties of zinc oxy-nitride thin films deposited by reactive sputtering of zinc. Semiconductor Science and Technology. 28 (2), 025009(2013).
- Nakano, Y., Morikawa, T., Ohwaki, T., Taga, Y. Electrical characterization of p-type N-doped ZnO films prepared by thermal oxidation of sputtered Zn3N2 films. Applied Physics Letters. 88 (17), 172103.1-172103.3 (2006).
- Cao, X., Yamaguchi, Y., Ninomiya, Y., Yamada, N. Comparative study of electron transport mechanisms in epitaxial and polycrystalline zinc nitride films. Journal of Applied Physics. 119 (2), 025104.1-025104.10 (2016).
- Jia, J., Kamijo, H., Nakamura, S., Shigesato, Y. How the sputtering process influence structural, optical, and electrical properties of Zn3N2 films. MRS Communications. 8 (2), 314-321 (2018).
- Trapalis, A., Hefferman, J., Farrer, I., Sherman, J., Kean, A. Structural, electrical and optical characterization of as-grown and oxidized zinc nitride films. Journal of Applied Physics. 120 (20), 205102.1-205102.9 (2016).
- Núñez, C. G., et al. On the zinc nitride properties and the unintentional incorporation of oxygen. Thin Solid Films. 520 (6), 1924-1929 (2012).
- Oshima, T., Fujita, S. (111)-oriented Zn3N2 growth on a-plane sapphire substrates by molecular beam epitaxy. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics. 45 (111), 8653-8655 (2006).
- Heavens, O. S. Optical properties of thin solid films. , Butterworth, London. 46-48 (1955).
- Heyns, A. H., Prinsloo, L. C., Range, K. J., Stassen, M. The vibrational spectra and decomposition of α-calcium nitride (α-Ca3N2) and magnesium nitride (Mg3N2). Journal of Solid-State Chemistry. 137, 33-41 (1998).
- Lewis, R. B., Bahrami-Yekta, V., Patel, M. J., Tiedje, T., Masnadi-Shirazi, M. Closed-cycle cooling of cryopanels in molecular beam epitaxy. Journal of Vacuum Science Technology B. 32 (2), 02C102.1-02C102.7 (2014).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved