Method Article
An Enzyme-free Method for Isolation and Expansion of Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
In This Article
Summary
This protocol provides an enzyme-free method for isolating mesenchymal stem cells from abdominoplasty and lipoaspirate samples using an explant method. The absence of harsh enzymes or centrifugation steps provides for clinically relevant stem cells that can be used for studies in vitro or transferred back to the clinic.
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a population of multipotent cells that can be isolated from various adult and fetal tissues, including adipose tissue. As a clinically relevant cell type, optimal methods are needed to isolate and expand these cells in vitro. Most methods to isolate adipose-derived MSCs (ADSCs) rely on harsh enzymes, such as collagenase, to digest the adipose tissue. However, while effective at breaking down the adipose tissue and yielding a high ADSC recovery, these enzymes are expensive and can have detrimental effect on the ADSCs — including the risks of using xenogeneic components in clinical applications. This protocol details a method to isolate ADSCs from fresh lipoaspirate and abdominoplasty samples without enzymes. Briefly, this method relies on mechanical disassociation of any bulk tissue followed by an explant-type culture system. The ADSCs are permitted to migrate out of tissue and onto the tissue culture plate, after which the ADSCs can be cultured and expanded in vitro for any number of research and/or clinical applications.
Introduction
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a class of multipotent adult stem cells that can be isolated from various adult and fetal tissues, including from adipose tissue. These cells are an attractive cell type for both basic research and clinical applications due to their plasticity to differentiate into cells of all germ layers in vitro, cross allogeneic barriers, home to areas of inflammation, and suppress inflammation (reviewed in Sherman, et al.1). Adipose-derived MSCs (ASCs) are particularly appealing due to their ease of obtainment, as adipose tissue is generally considered discard tissue following routine liposuction and abdominoplasty procedures. However, once obtained, the samples are generally subjected to harsh conditions – either enzymatic condition or centrifugation — in order to isolate the ASCs2,3. This method illustrates a simple procedure for isolating ASCs using an explant method, in the absence of harsh enzymatic or centrifugation steps.
The most common method of isolating ASCs consists of washing an adipose sample, enzymatically digesting the sample with collagenase, centrifuging the sample, and finally lysing the red blood cells prior to culturing the ASCs4. While efficient at isolating a high yield of ASCs, the use of xenogeneic components (e.g., enzymatic digestion with collagenase) is considered more than "minimally manipulated" by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and may pose risks such as immune reaction, prohibiting the cells' use in the clinic5,6. To minimize the risks of xenogeneic components, many groups have suggested non-animal derived, manufactured enzymes to digest the adipose tissue. However, these enzymes are still harsh, and can alter the cell phenotype7.
Other methods of isolating ASCs include high-speed centrifugation, using forces as high as 1,200 x g, and vortexing to isolate the ASCs8. Even forces as low as 400 x g were sufficient in isolating viable ASCs9. While these cells do produce a large quantity of viable cells, many protocols failed to proliferate beyond 14 days8. Further, mechanical isolation yields fewer recovered cells than enzymatic digestion, but a higher proportion of isolated cells were ASCs as compared to other cells endogenous to adipose tissue at passage 010.
The isolation of a purer, more viable population of ASCs in less time, coupled with the cost and risks of xenogeneic components, makes enzymatic digestion less and less appealing for translation to the clinic. While mechanical isolation is initially a favorable approach, there is significant disparity in the methods used, and the volume of tissue processed is limited to the size of the specialized centrifugal units, and can be dependent on operator consistency2.
While both enzymatic digestion and centrifugation quickly yield a high volume of ASCs, these isolated cells show phenotypic changes, yielding questions about their behavior when returned to a patient2. An explant-based method of ASC isolation, as described in this protocol, is thus being employed by some groups, whereby the ASCs migrate out of small pieces of solid adipose tissue3,11,12. This migration is likely an effect of the cells being drawn to the nutrient rich media. Like other populations of MSCs, ASCs adhere to plastic, and survive and proliferate in the used tissue culture media (components below), permitting their isolation from the other cell types from the adipose tissue. While fewer cells are initially recovered — often taking > 1 week until cells are visible on the tissue culture plate — these unmanipulated ASCs will proliferate in vitro, permitting expansion of the cells to clinically relevant volumes11,12,13.
Protocol
The use of lipoaspirate and abdominoplasty samples has been approved by The Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Rutgers University — Newark Campus.
1. Preparation of Tissue Culture Media
- Sterilely prepare 500 mL of tissue culture media prior to isolating ASCs. To prepare the culture media, add 10% defined fetal calf serum (FCS) and Penicillin-Streptomycin (10,000 U/100 mL) to Dulbecco's minimal essential media (DMEM) with high glucose and 2 mM L-glutamine. The media can be stored at 4 °C for up to 3 weeks and should always be used warm (between room temperature to 37 °C).
- If a different media is preferred for culture of the stem cells, prepare that media instead.
2. Isolation of ASCs from Adipose Tissue
- Obtain lipoaspirates or abdominoplasty sample(s). Following IRB approval, obtain such samples as discard tissue following various surgical procedures. Transport the lipoaspirates to the laboratory in whichever vessel the surgeon removed the tissue; transport abdominoplasty samples in an operating room specimen bag or container.
- Store the sample(s) at room temperature for up to 6 h or at 4 °C for up to 24 h if not processing immediately. Tissue samples processed beyond the aforementioned times will likely have a diminished cell yield. Keep abdominoplasty samples moist by the addition of 1x sterile phosphate buffered saline.
- From this point onwards, conduct all steps in a laminar flow hood under aseptic conditions. Wear gloves for personal protection. Keep 10% bleach, 70% ethanol, and paper towels nearby to quickly clean up any biological spills. Disposed of any excess tissue as biomedical waste.
- Mince the samples into < 1 mm pieces. If the abdominoplasty block is too large to work with, cut a manageable size of tissue off of the block prior to mincing. Transfer the abdominoplasty tissue to the lid of a sterile 100 mm plate. Use a sterile needle to hold a piece of tissue in place and use a sterile scalpel to mince the pieces off by either cutting or gently shredding off of the bulk tissue.
- This step is generally not needed for lipoaspirates. However, if large tissue chunks are observed in the lipoaspirate, remove such chunks with sterile forceps and process as above.
- Transfer the tissue to a fresh tube and invert or shake the sample 5–6 times to ensure mixing of all layers. Optional: if the lipoaspirate has fully settled, remove and discard the oil layer prior to mixing.
- Transfer 2.5–5 mL of tissue to a 100 mm vacuum-gas plasma treated tissue culture plate (Table of Materials). Measure the volume of the sample by pouring into a fresh centrifuge tube. If necessary, use a sterile spatula to assist with transferring the tissue.
- Add an equivalent volume of tissue culture media to the plate. Gently swirl the plate to mix the contents.
- Incubate the pates at 37 °C in 5% CO2 until a sufficient number of cells are seen on the base of the plate. Over time, the cells will migrate from within the tissue onto the plate surface, at which point they will adhere to the plastic. As they exit the tissue, the cells will appear as small clusters around the tissue pieces.
- Every 24 h, remove as much fluid as possible and replace with a similar amount of media. Leave the pieces of tissue in place, if possible.
- Once a sufficient number of cells are noted on the plate (>10 clusters of > 15–25 cells on the plate) or after 7 days, whichever is sooner, remove all remaining pieces of tissue.
- Culture the ASCs in tissue culture media until they reach 70% confluency or until the clusters become dense (>5 dense clusters of cells on the plate, each with a diameter of approximately > 500 μm), at which point the cells are to be passaged.
3 Culture of ASCs
- Passage the ASCs when the parent plate reaches approximately 70% confluency. Take care to avoid over confluency of the ASC cultures.
- Gently rinse the plate with 1x phosphate buffered saline and trypsinize the adherent cells. To trypsinize the cells, aspirate the phosphate buffered saline and add 1 mL of Trypsin with 0.25% EDTA to each plate and incubate at 37 °C for 5 min. After 5 min, confirm de-adherence by microscopy. If the cells are still adherent, return the cells to the incubator for an additional 5 min.
- Add a small amount of media (approximately 25% of total trypsin volume) to the plate to deactivate the trypsin, and gently wash the base of the plate using the media/trypsin. To wash the plate, hold the plate at a slight angle and gently pipette the media/trypsin from the top of the plate downwards, loosening any weekly attached cells from the plate. The cells can be re-plated at a 1:3 ratio or seeded at a density of 120,000–500,000 cells per plate.
- If seeding based on cell count, transfer the trypsin/media from the plate into a conical centrifuge tube, and pellet the cells by centrifugation at 300 x g for 7 min. Resuspend the cells in tissue culture media (approximately 1 mL per initial plate) and count the cells prior to seeding. To count the cells, transfer 10 μL of the cell suspension into the hemocytometer and count the cells present in the 4 x 4 quadrant at each corner of the grid. Average these values together and multiply the value by 104 to calculate the cell number.
- Add media to the plate prior to seeding the cells. Add the cells in a dropwise manner and then swirl the plate to ensure even distribution across the plate.
NOTE: After 3 passages, the adherent cells should appear asymmetrical and spindle shaped. ASC phenotype and behavior can be confirmed using flow cytometry and differentiation assays.
- Confirmation of ASC phenotype and behavior using flow cytometry and differentiation assays
- Flow cytometry
- Collect and pellet the cells as described above. Wash the pelleted with 1x phosphate buffered saline and label the cells with the manufacturer recommended volumes of antibody. A detailed protocol for flow cytometry, a common laboratory procedure, can be found here12,14,15.
- Select surface marker panels from the following to confirm the ASC phenotype: negative for CD14, CD31, CD34, CD45, and CD106; and positive for CD29, CD36, CD44, CD73, CD90, and CD10516,17,18,19. The presence of CD36 and absence of CD106 discern ASCs from bone marrow-derived MSCs20.
- Differentiation Assays: Confirm multilineage differentiation using an MSC differentiation kit. Kits are available from multiple manufacturers to confirm adipogenic, osteogenic, and chondrogenic differentiation capacity. Change the kit-provided media every 3–4 days as per the manufacturer's protocols for 3 weeks or until morphological differentiation is observed.
- Flow cytometry
- Culture the cells for multiple passages; the number of passages needed will depend on the application(s). At each passage, confirm the MSC cell morphology and phenotype using the aforementioned cell surface markers, and ensure multilineage differentiation capacity has not been lost. While the expansion potential differs among donors, most samples can be expanded for up to 6-9 passages.
- Cryopreserve the cells and store in liquid nitrogen for future use.
4 Cryopreservation of ASCs
- Prepare 10 mL of freezing solutions A and B.
- For freezing solution A, add 20% FCS to DMEM with high glucose.
- For freezing solution B, add 20% FCS and 20% dimethyl sulfide (DMSO) to DMEM with high glucose.
- Pellet the cells by centrifuging at 300 x g for 5 min. Resuspend the cells in a small volume of freezing solution A and count the cells using a hemocytometer as in step 3.3.1.
- Calculate the final volume that the cells will be resuspended in to reach a final cell concentration of 500,000–1,000,000 cells/mL. Use freezing solution A to resuspend the pellet in 50% of that final volume. Slowly add an equal volume of freezing solution B dropwise while agitating the tube to reach the final cell concentration.
- Immediately freeze the cells in 1–2 mL cryovials. Freeze the cryovials in a controlled rate freezer or in a freezing container placed at -80 °C, which decreases the temperature by 1 °C/min. Following the controlled freeze (overnight for a freezing container), transfer the cells to liquid nitrogen for long term storage.
Results
Using the method detailed here, ASCs were successfully isolated from lipoaspirate and abdominoplasty samples (Figure 1). After three passages, the isolated cells were found to have an MSC morphology (asymmetrical, spindle shape) and phenotype, similar to ASCs following enzymatic digestion (Figure 2). Prior studies from our group and others have shown these ASCs to differentiate into adipocytes, osteocytes, and neurons like other MSCs, including ASCs isolated by other means11,21.
In most cases, ASCs migration onto the tissue culture plate can be visualized within 3–5 days by bright field microscopy. However, in some cases, only sparse cells will be visible after 7 days. In rare cases, the cells will not migrate onto the plate and/or will not proliferate up until the third passage. This outcome generally correlates with a delay in processing the tissue sample.
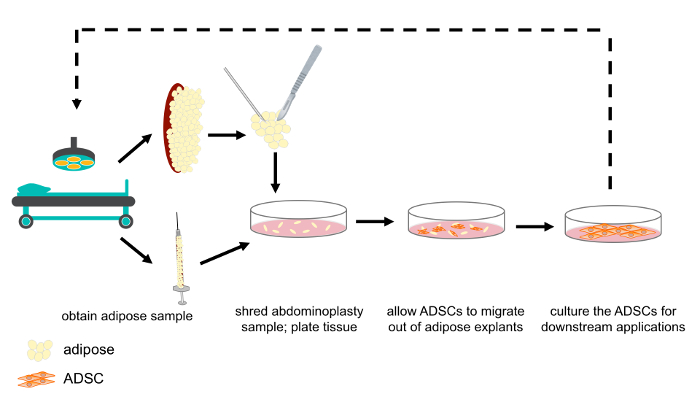
Figure 1: Schematic representation of ASC isolation from abdominoplasty and lipoaspirate samples. Abdominoplasty and lipoaspirate samples were obtained as discard tissue following routine surgical procedures. Abdominoplasty samples were shredded, after which either abdominoplasty or lipoaspirate samples were plated as explants in tissue culture media. The ASCs migrated out of the tissue, towards the nutrient rich media. After 1 week, the explants were removed and ASCs cultured for downstream experimentation and/or clinical application. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
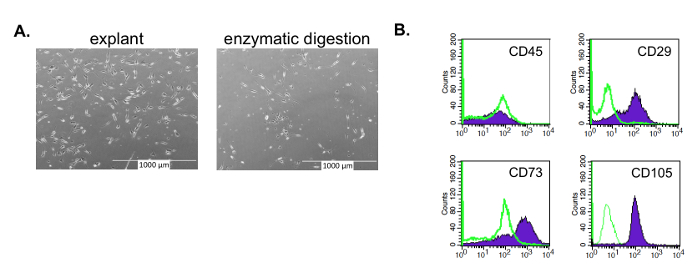
Figure 2: Isolated ASCs with an MSC morphology and phenotype. ASCs isolated by the enzyme-free, explant method have an MSC morphology and phenotype at passage 3. (A) Like other MSCs, these ASCs have an asymmetrical, spindle shape, whether isolated by explant or enzymatic method (e.g., collagenase). The ASCs isolated using the enzyme method yield a longer, narrower morphology as compared to the explant isolated ASCs; the latter closer resemble MSCs derived from other enzyme-free isolation methods, such as bone marrow derived-MSCs. (B) Like other MSCs, the explant isolated ASCs are negative for CD45 and positive for CD73, CD90, and CD105. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
ASCs are an attractive source of MSCs due to the easy access of the tissue. For both clinical and research applications, scientists must bear in mind donor variability when isolating and culturing these cells. For reasons yet to be elucidated, MSCs from different donors show different capacities to proliferate in vitro, which will subsequently affect the ASC's migration out of the adipose explant and proliferation capacity. While variability can be observed in the time it takes for the ASCs isolated from these enzyme-free explants to reach confluency, it was rare for a sample not to proliferate in vitro.
Beyond donor variability, the most likely source of failure of the cells to migrate out of the tissue and/or proliferate in vitro is the length of time that the tissue was stored prior to processing. When the samples were allowed to sit for >12 h prior to processing or were not kept moist between harvesting and processing, poorer migration and proliferation rates were observed. The only samples that frequently failed to proliferate were abdominoplasty samples that were not kept moist with a saline solution: in these cases, the tissue in the center of the tissue block was often moist enough to process, but occasionally needed to be discarded. It is thus critical to keep the tissue moist from time of harvest through processing.
In cases where ASCs are not observed on the plate at the 1 week mark, the adipose explants should still be removed from the tissue culture plates lest tissue necrosis occur. Sometimes there are too few cells to easily identify, but those few cells will be capable of expanding within the culture system. If the cells are still not observed at 3 weeks, the isolation should be considered failed.
In some cases, particularly of abdominoplasty, it is not possible to obtain a truly aseptic sample due to the limitations within the surgical arena. If it is not possible to use a sterile vessel to transport the tissue from the operating room to a laminar flow hood, removing the outer 1 cm of the tissue is generally sufficient to prevent microorganism contamination. If the abdominoplasty sample is attached to skin, the skin can be wiped with 70% ethanol to sterilize that surface prior to mincing the adipose tissue.
During the mincing process, it is critical that the tissue is minced into small, fine pieces. If the explants are too large, there will be insufficient surface area for the ASCs to migrate out of the tissue and onto the plate. Further, it is critical that the tissue does not remain in the plate any longer than necessary lest the tissue become necrotic.
A limitation of this method is the use of an enzyme (in the described protocol, trypsin) to detach the ASCs during the tissue culture process. Other non-animal derived enzymes, such as Accutase, can be replaced to remove the need for animal derived products, however, this will increase the cost of the tissue culture. For this reason, among others, numerous groups are investigating non-two-dimensional tissue culture methods such as bioreactors and scaffold-based systems to increase MSC growth potential while minimizing the need to detach the cells from their substrate22.
When moving ASCs to the clinic, a major limitation of the explant isolation method is the reliance on a good manufacturing practice (GMP) level tissue culture facility, which many medical centers lack. In these cases, any of the self-enclosed commercially available enzyme- or centrifugation-based methods would need to be employed. However, as GMP facilities become more prevalent, this effect is expected to be limited. In the meantime, even such facilities lacking GMP tissue culture facilities can consider using the explant method for studying ASCs in vitro: the less manipulation, the more akin these cells are to their in vivo counterparts11.
This method provides a simple way of isolating ASCs from adipose tissue — both lipoaspirates and abdominoplasties — in the absence of harsh enzymes or centrifugation steps. While the initial yield of ASCs is lower than that of other methods, the ASCs will proliferate in vitro, minimizing the effect of the lower initial yield. The lack of excessive or forceful manipulation makes ASCs isolated in such a manner particularly relevant, since there are fewer questions (i.e., whether the observed effects are due to the cells themselves or to the cells' manipulation during the isolation process).
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose
Acknowledgements
The authors have no acknowledgements
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide | Fisher Bioreagents | BP231 | |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium - high glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | D5671 | |
| Falcon 3003 tissue culture plates | Corning | Corning | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Sigma-Aldrich | F2442 | serum is batch tested to ensure it supports MSC growth |
| L-Glutamine solution | Sigma-Aldrich | G7513 | |
| Mr. Frosty | Nalgene | 5100-0001 | |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | P4333 | |
| Trypsin-EDTA solution | Sigma-Aldrich | T4049 |
References
- Sherman, L. S., Shaker, M., Mariotti, V., Rameshwar, P. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells in drug therapy: New perspective. Cytotherapy. 19 (1), 19-27 (2017).
- Conde-Green, A., et al. Shift toward Mechanical Isolation of Adipose-derived Stromal Vascular Fraction: Review of Upcoming Techniques. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open. 4 (9), 1017(2016).
- Hendijani, F. Explant culture: An advantageous method for isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human tissues. Cell Proliferation. 50 (2), (2017).
- Zuk, P. A., et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Engineering. 7 (2), 211-228 (2001).
- Chang, H., et al. Safety of adipose-derived stem cells and collagenase in fat tissue preparation. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 37 (4), 802-808 (2013).
- Spees, J. L., et al. Internalized antigens must be removed to prepare hypoimmunogenic mesenchymal stem cells for cell and gene therapy. Molecular Therapy. 9 (5), 747-756 (2004).
- Tsuji, K., et al. Effects of Different Cell-Detaching Methods on the Viability and Cell Surface Antigen Expression of Synovial Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Transplantation. 26 (6), 1089-1102 (2017).
- Markarian, C. F., et al. Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: a comparison among different methods. Biotechnology Letters. 36 (4), 693-702 (2014).
- Palumbo, P., et al. In vitro evaluation of different methods of handling human liposuction aspirate and their effect on adipocytes and adipose derived stem cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 230 (8), 1974-1981 (2015).
- Shah, F. S., Wu, X., Dietrich, M., Rood, J., Gimble, J. M. A non-enzymatic method for isolating human adipose tissue-derived stromal stem cells. Cytotherapy. 15 (8), 979-985 (2013).
- Sherman, L. S., Conde-Green, A., Kotamarti, V. S., Lee, E. S., Rameshwar, P. Enzyme-Free Isolation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1842, 203-206 (2018).
- Raposio, E., Caruana, G., Bonomini, S., Libondi, G. A novel and effective strategy for the isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: minimally manipulated adipose-derived stem cells for more rapid and safe stem cell therapy. Plast and Reconstructive Surgery. 133 (6), 1406-1409 (2014).
- Sherman, L. S., Conde-Green, A., Sandiford, O. A., Rameshwar, P. A discussion on adult mesenchymal stem cells for drug delivery: pros and cons. Therapeutic Delivery. 6 (12), 1335-1346 (2015).
- Menon, V., Thomas, R., Ghale, A. R., Reinhard, C., Pruszak, J. Flow cytometry protocols for surface and intracellular antigen analyses of neural cell types. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (94), 52241(2014).
- Barlow, S., et al. Comparison of human placenta- and bone marrow-derived multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells and Development. 17 (6), 1095-1107 (2008).
- Munoz, J. L., et al. Feline bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) show similar phenotype and functions with regards to neuronal differentiation as human MSCs. Differentiation. 84 (2), 214-222 (2012).
- Amati, E., et al. Generation of mesenchymal stromal cells from cord blood: evaluation of in vitro quality parameters prior to clinical use. Stem Cell Research and Therapy. 8 (1), 14(2017).
- Bajek, A., et al. Does the liposuction method influence the phenotypic characteristic of human adipose-derived stem cells. Bioscience Reports. 35 (3), (2015).
- Palumbo, P., et al. Methods of Isolation, Characterization and Expansion of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs): An Overview. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (7), (2018).
- Bourin, P., et al. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy. 15 (6), 641-648 (2013).
- Ghorbani, A., Jalali, S. A., Varedi, M. Isolation of adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells without tissue destruction: a non-enzymatic method. Tissue and Cell. 46 (1), 54-58 (2014).
- Bunpetch, V., Wu, H., Zhang, S., Ouyang, H. From "Bench to Bedside": Current Advancement on Large-Scale Production of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells and Development. 26 (22), 1662-1673 (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved