A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
A Cross-Disciplinary and Multi-Modal Experimental Design for Studying Near-Real-Time Authentic Examination Experiences
In This Article
Summary
An experimental design was developed to investigate the real-time influences of an examination experience to assess the emotional realities students experience in higher education settings and tasks. This design is the result of a cross-disciplinary (e.g., educational psychology, biology, physiology, engineering) and multi-modal (e.g., salivary markers, surveys, electrodermal sensor) approach.
Abstract
Over the past ten years, research into students' emotions in educational environments has increased. Although researchers have called for more studies that rely on objective measures of emotional experience, limitations on utilizing multi-modal data sources exist. Studies of emotion and emotional regulation in classrooms traditionally rely on survey instruments, experience-sampling, artifacts, interviews, or observational procedures. These methods, while valuable, are mainly dependent on participant or observer subjectivity and is limited in its authentic measurement of students' real-time performance to a classroom activity or task. The latter, in particular, poses a stumbling block to many scholars seeking to objectively measure emotions and other related measures in the classroom, in real-time.
The purpose of this work is to present a protocol to experimentally study students' real-time responses to exam experiences during an authentic assessment situation. For this, a team of educational psychologists, engineers, and engineering education researchers designed an experimental protocol that retained the limits required for accurate physiological sensor measurement, best-practices of salivary collection, and an authentic testing environment. In particular, existing studies that rely on physiological sensors are conducted in experimental environments that are disconnected from educational settings (e.g., Trier Stress Test), detached in time (e.g., before or after a task), or introduce analysis error (e.g., use of sensors in environments where students are likely to move). This limits our understanding of students' real-time responses to classroom activities and tasks. Furthermore, recent research has called for more considerations to be covered around issues of recruitment, replicability, validity, setups, data cleaning, preliminary analysis, and particular circumstances (e.g., adding a variable in the experimental design) in academic emotions research that relies on multi-modal approaches.
Introduction
Psychologists have long understood the importance of humans' emotions in elucidating their behaviors1. Within the study of education, Academic Achievement Emotions (AEE) has become the focus of emotion research2. Researchers that use AAE argue that the situational contexts students find themselves in are important to consider when examining students' emotions. Students may experience test-related, class-related, or learning-related emotions that involve multi-component processes, including affective, physiological, motivational, and cognitive components. AEE is expressed in two forms: valence (positive/negative) and activation (focused/unfocused energy). Positive activating emotions, such as enjoyment, may increase reflective processes like metacognition, whereas positive deactivating emotions such as pride may result in low levels of cognitive processing. Negative activating emotions such as anger and anxiety may spark engagement, whereas negative deactivating emotions such as hopelessness may dampen motivation3,4,5. Academic emotions contribute to how we learn, perceive, decide, respond, and problem-solve2. To regulate academic emotions, an individual must possess self-efficacy (SE)6,7,8, which is their confidence in their ability to employ control over their motivation, behavior, and social environment6. Self-efficacy and academic emotions are interrelated, where lower self-efficacy is tied to negative deactivating emotions (e.g., anxiety, anger, boredom) and higher self-efficacy is tied to positive activating emotions (e.g., happiness, hope, excitement)6,7,8. SE is also believed to be strongly tied to performance6,7,8.
Research that has examined classroom emotions have relied on self-reports, observations, interviews, and artifacts (e.g., exams, projects)9,10. Although these methods provide rich contextual information about students' classroom experiences, they have significant limitations. For example, interviews, observations, and self-reports rely on individuals' introspections10. Other methods have sought to examine academic emotions more proximally than prior researchers, such as those based on experience-sampling approaches where researchers ask students to report on their emotions during the school day11. Although this research allows us to report students' emotions more accurately, this work relies on self-report methods and does not allow for real-time reporting as students have to pause their work on the exam to address the experience survey.
Recently, researchers have begun to address concerns about self-report measures through the use of biological or physiological measures of emotion9, that combined with other instruments or techniques such as surveys, observations, or interviews, consists of a multi-modal form of data collection for educational and psychological research12. For example, biological techniques, including salivary biomarkers, are being used to understand the role biological processes have on cognition, emotion, learning, and performance13,14,15. For cognitive processes, androgens (e.g., testosterone) have been linked to different spatial recognition patterns in adults and children16,17 whereas hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical hormones (e.g., cortisol) and adrenergic hormones (e.g., salivary α-amylase or sAA) are linked to stress responsiveness amongst individuals18,19,20.
Electrodermal activity (EDA) represents a physiological measure of the activation of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and is linked to increased activation of the system, cognitive load, or intense emotional responses21,22,23. In examination activities, EDA is affected by physical mobility21,22, bodily and ambient temperatures24,25,26,27, and verbalization of thoughts28, as well as sensitivity and degree of connectivity of the analog-digital electrodes to the skin29.
Although these can be limitations to using EDA, this technique can still provide valuable insight into what happens during near-real-time examinations and can serve as a promising tool to explore AEE and by extent, self-efficacy. As a result, an accurate picture of students' AEE can be obtained through a combination of survey methods, to determine the valence of emotion, and physiological and biological data, to measure the activation of that emotion. This paper builds upon a previous publication on examination activities30 and expands the scope of that work to include multi-modal approaches (using experience-sampling surveys, EDA sensors, and salivary biomarkers) in an examination scenario. It is essential to mention that the protocol described below allows for multiple participant data to be collected at the same time within a single experimental setting.
Protocol
Procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) under a general review at Utah State University for studies on human subjects and use of these constructs. The typical results include two semesters of an engineering statics course, each with a slightly different experimental setup, at a western institution of higher education in the United States. Practice exams, whose content paralleled the actual exams, were developed by the course instructor and were used for our study. Please note that the protocol outlined below describes concurrent steps, and some steps may overlap.
1. Considerations for Experimental Designs and Integration of Disciplinary Practices
As researchers consider experimental designs of this nature, disciplinary knowledge and approaches must be integrated in a way that complements and sustains the main research goal. As new instruments and methods are added, additional validation considerations are needed. In this work, we will explore an experimental study where surveys and electrodermal sensors were used for one of the semesters (experimental design A), and salivary biomarker collection (i.e., cortisol and sAA) was added to the subsequent semester (experimental design B). Below are the considerations for the two setups:
- Experimental Design with Surveys and Electrodermal Sensors
- Electrodermal sensors are sensitive. Participants’ startle responses, if unintentionally activated, can create a significant spike in EDA response. This is particularly important when considering multiple participants for data collection, whose actions may enhance these startle responses. As such, be sure to set up the workspace carefully to minimize as many distractions as possible. As shown in Figure 1, include a testing shield if exploring examination experiences for an individual or group of individuals.
NOTE: To increase the ecological validity of the testing environment, plan to provide any material that a student would be using on their actual exam (e.g., workbooks, equation sheets) to allow participants to reflect upon and work out any needed exam problems - Electrodermal sensors provide a signal every 1/4th of a second. To allow an event to be defined and studied, implement a plan to collect a precise measure of the onset of a task. When time synching electrodermal sensors with surveys, make sure that the presentation of the survey question is synchronized to the electrodermal sensor by using the internal clock of the computer to establish a data collection timeframe (see Figure 1). If using any Bluetooth-enabled electrodermal sensors (e.g., see Table of Materials), synch times in Greenwich Meridian Time (GMT) to account for time zone changes and daylight savings time differences during data collection procedures30.
NOTE: If using a web server for the presentation of stimuli (e.g., test question, survey item, etc.), be sure to align the times between the server and the computer internal clock as these are not typically synched. Note that it may be necessary to pre-install a cross-platform web server (e.g., XAMPP or other Apache servers) to each computer used for the study. If intending to sync a web camera for video recording purposes, consider using security software that allows recording of the date, time, hour, minute, second and millisecond (e.g., 01/01/2000 04:01:02:05) of the video. Note that this video must also be synched with the computer’s internal clock and the other devices (e.g., EDA sensor). Set the web cameras to measure the participant’s face at different angles, if needed. We recommend that for a frontal faced web camera; the video is positioned parallel to the workstation surface and for downward facing web cameras to position the video at 30° to 45° from the workstation surface to the participant’s face. - Place the electrodermal sensor on the non-dominant hand of the participant to minimize any noise in the signal due to movement or electrode contact error during data collection, as suggested in a prior protocol30. If researchers would like to minimize artifacts in the EDA due to movement, one alternative is to include a wrist gel pad in a location that is comfortable to the participant and that simultaneously allows them to rest their non-dominant hand on.
NOTE: The placement of the laptop computer, gel pad, sensor, exam sheets, and other elements in the study must be standardized to ensure repeatability across examination conditions and semesters. As shown in Figure 1, painter’s tape was used to center each item (e.g., laptops, exam sheets, cameras) of the experimental setup consistently across participants and semesters of data collection. - For electrodermal sensor readings, establish a period during which participants have achieved a relaxed state to establish baseline EDA data31. For this, either indicate a time at the beginning of the exam for participants to stare at the testing shield (~5–15 minutes) or program this cue into the laptop computer as part of the timestamping program. Upon completing this period, participants can commence with any pertinent surveys and exam questions. In the same vein, assign a relaxation period at the end of the exam experience.
- Electrodermal sensors are sensitive. Participants’ startle responses, if unintentionally activated, can create a significant spike in EDA response. This is particularly important when considering multiple participants for data collection, whose actions may enhance these startle responses. As such, be sure to set up the workspace carefully to minimize as many distractions as possible. As shown in Figure 1, include a testing shield if exploring examination experiences for an individual or group of individuals.
- Experimental Design with Surveys, Electrodermal Sensors, and Salivary Biomarkers
- When integrating electrodermal sensors with surveys and salivary biomarkers, ensure that disruptions are minimized to the best extent possible. As one strategy, create a training video to help participants understand how to provide their salivary samples at set time periods of the exam according to manufacturing specifications (see Table of Materials) to minimize interruptions from the researchers.
NOTE: In this study, the researchers were interested in collecting saliva during four time-points: beginning, middle, end, and post-exam. However, researchers can choose other times they deem appropriate for their study. Also, we used the swab collection method32 instead of its passive drool method33 for ease of use and faster sample collection times. Also, we selected cortisol34 and sAA35 kits (see Table of Materials) and followed manufacturer specifications in its processing. However, if your group does not have a biological lab to conduct these forms of testing, other providers may be able to analyze the samples32,36. - When collecting saliva samples, have a cooler with dry ice with an internal temperature of -20 °C; this will prevent room-temperature degradation of enzymes for the cortisol samples34. If collecting salivary alpha-amylase, its stability is much longer (~five days at room temperature and allowing for 5 freeze-thaw cycles35). If collecting both, as was the case in this study, follow the guidelines needed to store salivary cortisol samples according to manufacturer recommendations34,35.
- If using the swab collection method25, have the swab remain either in the inner cheek or under the tongue of the participant for 60 s. When handling the vials and sample collection caps, follow manufacturer protocols34,35 and convey the information to participants before the commencement of the study.
NOTE: If the experiment is more granular (e.g., question by question data collection), make sure to record the onset and offset times of each salivary sample collection, as these may need to be accounted for in the EDA analysis. The same applies to the onset and offset of survey data collection times. For salivary data collection, our group developed a flagging system to allow participants to notify the researcher/proctor when a salivary sample was ready to be collected. Consider designating multiple proctors to assist with during an experimental session in case multiple salivary samples are ready to be collected and stored.
- When integrating electrodermal sensors with surveys and salivary biomarkers, ensure that disruptions are minimized to the best extent possible. As one strategy, create a training video to help participants understand how to provide their salivary samples at set time periods of the exam according to manufacturing specifications (see Table of Materials) to minimize interruptions from the researchers.
2. Setup and cleaning pre- and post-experiment
- Surveys
- In survey form, organize a scheduling process, designate participant IDs, and collect any demographic information, as needed. Also, establish or pre-label any pertinent survey questions in preparation for data export. This will enable faster and more efficient data cleaning, management, and statistical analyses.
- Sync the survey presentation and exit times throughout the exam protocol. If integrating sensors or video, sync these technologies with the survey software as well.
- As a matter of courtesy and in the interest of contributing to a cordial and welcoming research environment, and if instructors agree, set up an automated follow-up email containing responses to the exam questions to be sent to participants immediately or soon after their participation in the session.
- Electrodermal Sensors
- Plan to pre-schedule participants to an examination session/time, assess any medical information and dietary habits for EDA and saliva collection30 and hand dominance for EDA collection30, and remind participants to avoid consumption of sugary or caffeinated products the day of the experiment. This is important as certain medical conditions (e.g., metabolic disorders) and dietary habits (e.g., caffeine consumption) can influence EDA (and salivary values), as suggested in a prior protocol30.
- Before participants arrive, make sure sensors are correctly calibrated, software updates have been taken care of, and sensors have been cleaned with 70% alcohol wipes30.
- When fitting the EDA sensor on a participant’s wrists, make sure to place it on the participant’s non-dominant hand. To fit the EDA sensor:
- Place the sensor with the button facing down towards the thumb.
- With their palms facing up towards their face, have participants draw an imaginary line from the space between the second and third finger of their non-dominant hand to their mid-wrist area and place the sensor electrodes there.
- Ask participants to fit the sensor straps in a way that is not too tight or too loose.
NOTE: A representative image of this fitting can be found in Figure 2.
- When starting the sensor, be sure to follow manufacturer protocols31 to ensure the sensors are set up to collect data. In this experiment, the protocol is tailored to use with a particular brand of sensors (see Table of Materials), although researchers are welcome to use any physiological sensor of their choosing.
- For devices used here, depress the sensor button for three seconds. A green light will blink intermittently, followed by a red blinking light, and then a fade-out occurs.
- During fade-out, to make sure the sensor is ON, press the button once for less than 1 s. If it blinks red, it is indicating that it is recording data.
- When turning the sensor OFF, press the button for 3 s. The sensor will turn off if the lights on the bottom of the wristband go from green to fade.
- To retrieve the data from the sensor, connect it to the computer, and upload the data in the managing software system according to manufacturer recommendations31.
- Salivary Biomarkers
- As stated before, pre-assess any medical conditions or dietary habits that may influence salivary values during analysis. Also, remind participants not to wear any lip balm, make-up, or products near the lips when they arrive at the session, as this could introduce contaminants that may influence cortisol and salivary alpha-amylase samples. If participants arrive wearing these products, gently guide them to a restroom or provide appropriate wipes that would remove these products without introducing other chemicals (e.g., water on a napkin versus make-up remover towels). Finally, clear experiment rooms of food or drinks that have a strong smell (e.g., pizza, oranges) that may enhance salivary production among participants.
- Upon participants’ arrival to the experimental room, hand participants 1 ounce of water poured into a cup in their presence. Ask them to swish and swallow the water. This is done to clear the mouth of any food residues that may influence the cortisol and salivary alpha-amylase data.
- If collecting EDA data in conjunction with saliva, gently remind participants to minimize hand movement in the hand that has the EDA sensor. As such, participants will need to be informed that any saliva sample collection provided has to be done in their dominant hand. To facilitate this process, it is recommended that the experimental setup includes pre-labeled vials and a stand to minimize any loss of samples (refer to Figure 1).
- When collecting salivary samples, wear fresh nitrile gloves to minimize any dust particulate or any other contaminant from hand oils to be transferred to the salivary sample vial.
- As indicated previously, immediately transfer the samples to a cooler that has an internal temperature of -20 °C.
3. Increasing ecological validity in light of surveys, electrodermal sensors, and salivary biomarkers
- Concerning exam authenticity
- To provide an authentic testing experience, align the exam content with course content. For this, review the course content in conjunction with a group of content experts, including the course instructor.
- Select an evaluation (test or assessment) of the course content that can be replicated in an experimental setting, or that can complement existing course content (e.g., practice exam).
NOTE: Depending on the Institutional Review Board policies of your institution, using real exams may not be allowed due to its potential harm to students’ grades in the course. As such, an equivalent experience (e.g., practice exam) may be considered instead. - Alongside the instructor, develop an answer key and exam problems and its solutions to be used to collect performance data at a granular level (i.e., question by question) and/or macro-level (i.e., entire exam) depending on the goals of the research
- Ask the instructor also to provide any additional materials that are typically used in their exams (e.g., cheat sheets) or any allowable materials (e.g., textbooks, list of references) typically used in their courses. Experimenters should be prepared to provide these tools to the participants.
- Make sure that the testing environment parallels the experimental setup (e.g., exam times, the offering of exam—testing center or classroom, etc.) and its features such as desk space, lighting, the temperature of the room, among others.
- Concerning survey inclusion
- Depending on the number of survey questions, it will be important to account for the approximate times; it might take participants to complete the survey questions while they are taking their exam.
- Allot additional test-taking time to account for interruptions and design the examination program to return students to a particular exam problem if a survey prompt interrupted them. Also, be sure this interruption time is consistent across participants (e.g., beginning, middle, and end of the exam).
- Depending on the type of experimental design, if the granular type of responses is needed (e.g., question by question), plan to present the exam problem first, then prompt participants to respond to the survey question, and then allow participants to enter their response (e.g., open-text, multiple choice, etc.). This will allow participants first to view the problem and respond to the survey question according to the presented problem. If the experimental design is on a macro-level, make sure that participants are allowed to reflect on the exam experience up to that point before responding.
NOTE: Theories and hypotheses are important to consider in this step as the choice of the particular kind of presentation of an item (e.g., survey, exam) will matter. For example, if studying self-efficacy, this is best assessed at the level of the test question, while academic achievement emotions are typically asked pre-, during-, and post-exam.
- Concerning electrodermal activity sensors
- To ensure participants are not being overly stressed due to the experimental protocol, include calibration and relaxation periods throughout the exam experience. One strategy could be to allow participants to refocus their attention between questions. Beginning with a simple-to-respond question (e.g., “what day of the week are we in?”) and allow participants 30 s to rest in between each exam question.
NOTE: Keep in mind that understanding the design of the exam questions itself and predicting what students’ reactions may be important (e.g., increased cognitive loads or neural efficiencies37) as they could influence the salivary marker and EDA data collection. For example, the exam questions should all be in the form of essay entry, which would require hand movement that can influence EDA data24,25 or an exam may be designed by varying levels of difficulty, which could influence students’ cognitive loads or neural efficiencies37. - Ensure that the time stamping program will account for any changes in the examination experience (e.g., calibration periods, onset and offset of in-between calibration questions, survey questions onset and offset, start and finish of the exam). This is an important step as it will allow for data source matching, which will determine the intervals or events to be processed and analyzed.
- To ensure participants are not being overly stressed due to the experimental protocol, include calibration and relaxation periods throughout the exam experience. One strategy could be to allow participants to refocus their attention between questions. Beginning with a simple-to-respond question (e.g., “what day of the week are we in?”) and allow participants 30 s to rest in between each exam question.
- Concerning salivary biomarker use
- Be mindful of when to collect salivary biomarkers.
NOTE: Salivary bio-marker studies typically are explored through a pre-pre-mid-post-post-post design32,33,34,35,36. As cortisol takes 20 minutes to respond to stress14, these time lags are needed to observe cortisol onset and recovery. In the case of students’ preparing for an exam, participants may be worried about taking the exam, and, thus, a before-onset measure may not be possible. It is also important not to interrupt students frequently during the exam. In our study, we opted to collect saliva once before onset, once during, immediately after, and 20 minutes after the exam as quietly as possible to minimize disruptions. A sample testing timeline is provided in Figure 3. - In the examination program, include timed prompts to cue participants when it is time to collect saliva. Include a 60-s timer, so participants are aware of the duration of the salivary collection. Return participants to the problem they were working on in the exam once the 60 s are complete.
- Be mindful of when to collect salivary biomarkers.
4. Considerations for data processing and analysis
- Survey
- Be sure that data outputs are labeled and organized appropriately to allow for effective data management and ensure statistical programs (e.g., SPSS, SAS) can perform any needed analysis.
- Identify any potential outlier data based upon standards for survey outlier detection38 as well as any determined through the demographic data collected previously (e.g., medical conditions).
- Determine the type of statistical analysis and/or modeling to conduct based upon the established research question(s) and/or hypotheses
- Electrodermal Activity
- Note that electrodermal data outputs may vary by company. For the device used in this study31, data outputs are presented as a single column with a starting time measured in GMT, followed by the frequency of data collection and the EDA measured in microSiemens. The EDA data then increments according to the frequency of data collection. Since the data is dependent on the time of onset, convert this time to UNIX time according to manufacturing protocols and previous protocols30. This will allow more seamless synchronization of the EDA data changes throughout the experiment.
- Identify and remove any potential manufacturer sources of outliers, such as sensor malfunction, incomplete data collection, or poor contact of the electrodes in the skin. These will be identified by negative values or constant near-zero continual data segments in the data output sheet.
- Identify and remove any potential user-generated sources of outliers such as erratic movements (e.g., hand hitting desk or nervous tapping), survey or salivary biomarker collection periods, or large changes in body temperatures or blood volume pressure readings.
- To remove noise due to movement, do the following series of steps:
- First, scan through the participants’ accelerometer (ACC) profiles, also provided by the wrist sensor. Note that the data will have X, Y, and Z columns indicating three-dimensional horizontal, vertical, and spatial hand movements, respectively. Calculate the moving average of this accelerometer data according to the Euclidean Distance (L2-Norm)39,53 equation to calculate the total movement:
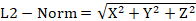
- Calculate the standard deviation of the Euclidean distance values for the entire participant set and rank-order them. Calculate the average values of the Euclidian distance values too.
- Calculate the coefficient of variance of the Euclidean distance values to determine the signal-to-noise ratios40 according to the following equation:
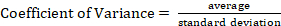
NOTE: Coefficient of variance values that exceed a score of 1 indicates an outlier and must be removed from analysis according to recommendations in handling signaling data33. - Once the noise due to movement is removed, determine the needed threshold to filter the data. For this, calculate the upper and lower limits of the 95% of the standard deviation of the signals. Any data outside these ranges can be either removed from the dataset/analysis or imputed according to the researcher´s goals and objectives. For this study, we opted to average the outside ranges with the determined acceptable data.
- Return to the EDA data and use the time-stamped accelerometer data to identify the corresponding intervals of EDA (which have also been time-stamped).
NOTE: To sync accelerometer and electrodermal data, note that the recording frequencies are different (4 Hz for EDA and 32 Hz for ACC) so they must first be aligned. Since, inherently, there will be more ACC data than EDA data, use the average EDA values to account for this difference.
- First, scan through the participants’ accelerometer (ACC) profiles, also provided by the wrist sensor. Note that the data will have X, Y, and Z columns indicating three-dimensional horizontal, vertical, and spatial hand movements, respectively. Calculate the moving average of this accelerometer data according to the Euclidean Distance (L2-Norm)39,53 equation to calculate the total movement:
- Once EDA data sets have been cleaned41,42 though the filtered accelerometer data, proceed to separate the tonic (baseline) and phasic (immediate, reactive) signals using prescribed tools (e.g.., Ledalab, EDA Explorer)43,44, for statistical analysis, primarily the phasic, filtered EDA data are used and values (e.g., magnitudes, number of peaks, latency times) are calculated based upon the research question/hypothesis and using methods described by Bouscien22,23.
- Salivary Biomarker
- For both cortisol and salivary alpha-amylase assays, follow manufacturer protocols22,23,24,25,26,27,28 and technician recommendations about terms of use, storage, and handling samples.
- Spin thawed samples at 1,500 x g at 4 °C. Be sure to remove the swabs carefully and that the vials have salivary supernatant at the bottom of the vial to ensure mucin separation.
- As good practice, before following the assay protocols, do a buffer rinsing of the wells using a plate washer before processing. This is particularly important for cortisol.
- Ensure that the optical density plate reader has been pre-programmed to the appropriate temperatures (e.g., sAA samples require incubation temperatures of 37 °C whereas cortisol samples require room temperature readings) and wavelengths (i.e., sAA requires 405 nm and cortisol requires 450 nm and 490–492 nm reference filters). For sAA assays, it is recommended that the plate reader used has both a shaker and an incubator inside.
- Follow manufacturer protocols34,35 to calculate the concentration values of each sample and the corresponding intra- and inter-assay percent of the coefficient of variation (%CV) equations to identify outliers from the data set (this is calculated differently compared to the equation provided previously). Please note that, for sAA, keep track of the lot numbers used in the controls as they are not standardized.
- First, average the %CV of the controls by lot number and then average these values to get a grand average %CV score.
- For samples, the manufacturer recommends that the intra-assay of samples should have a %CV under 10% while the controls should have an inter-assay %CV under 15%34,35. However, these %CV values will significantly depend on the laboratory conditions and equipment used to conduct the research. As such, consider alternate methods of immunoassay assay validation as needed45.
- Freeze saliva samples at -80 °C after the assay to allow verification of its validation. Do not freeze thaw more than once to prevent further enzymatic degradation of the samples or controls.
- Data Triangulation
- Depending on the research question or hypothesis, correlate relevant variables. Ensure that all outliers and data are appropriately pre-processed and filtered before use46.
- Determine if the sample size, data collection points, observed statistical power, and research questions or hypothesis necessitate amalgamating data47, or utilizing repeated-measures analytic techniques48,49,50.
- Accounting for inter-individual differences in task time51 and the delay in response of salivary biomarkers to stress14, use timestamps, or determine events to sync datasets together.
- Using statistical models and software, analyze the data set, and interpret findings.
contains the 16 zip files. Each zip file contains all of the EOL quizzes for a given Core chapter. They will want to unzip this file, and then each zip file gets loaded individually into Canvas.
Results
In this study, we were interested in studying the influences of self-efficacy, performance, and physiological (EDA sensors) and biological (sAA and cortisol) responses of undergraduate engineering students as they took a practice exam. The data shown is a representative subset of samples: (a) one that considered surveys and electrodermal sensors (experiment design A) and (b) one that included the same exam along with the salivary biomarker data (experiment design B). While we collected em...
Discussion
Although physiological measures have been used in many authentic learning contexts, it is critical to design a study environment that is mindful of the limits of the current technology. Our design balances the need for an authentic testing environment and accommodates the technology. Comfortably limiting participant movement, reducing unintended interruptions, and timestamping participants' testing responses are all critical steps within the protocol.
The space and expense of the electrode...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF) No. EED-1661100 as well as an NSF GRFP grant given to Darcie Christensen (No. 120214). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material do not necessarily reflect those of NSF or USU. We want to thank Sheree Benson for her kind discussions and recommendations for our statistical analysis.
Author contributions in this paper are as follows: Villanueva (research design, data collection and analysis, writing, editing); Husman (research design, data collection, writing, editing); Christensen (data collection and analysis, writing, editing); Youmans (data collection and analysis, writing, and editing); Khan (data collection and analysis, writing, editing); Vicioso (data collection and analysis, editing); Lampkins (data collection and editing); Graham (data collection and editing)
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1.1 cu ft medical freezer | Compact Compliance | # bci2801863 | They can use any freezer as long as it can go below -20 degrees Celsius; these can be used to store salivary samples for longer periods of time (~4 months) before running salivary assays. |
| Camping Cooler | Amazon | (any size/type) | Can be used to store salivary samples during data collection |
| E4 sensor | Empatica Inc | E4 Wristband Rev2 | You can use any EDA sensor or company as long as it records EDA and accelerometry |
| EDA Explorer | https://eda-explorer.media.mit.edu/ | (open-source) | Can be used to identify potential sources of noise that are not necessarily due to movement |
| Laptops | Dell | Latitude 3480 | They can use any desktop or laptop |
| Ledalab | http://www.ledalab.de/ | (open-source) | Can be used to separate tonic and phasic EDA signals after following filtration steps |
| MATLAB | https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html | (version varies according to updates) | To be used for Ledalab, EDA Explorer, and to create customized time-stamping programs. |
| Salivary Alpha Amylase Enzymatic Kit | Salimetrics | # 1-1902 | For the salivary kits, you should plan to either order the company to analyze your samples and/or go to a molecular biology lab for processing |
| Salivary Cortisol ELISA Kit | Salimetrics | # 1-3002 | For the salivary kits, you should plan to either order the company to analyze your samples and/or go to a molecular biology lab for processing |
| Testing Divider (Privacy Shields) | Amazon | #60005 | They can use any brand of testing shield as long as they cover the workspace |
| Web Camera | Amazon | Logitech c920 | They can use any web camera as long as it is HD and 1080p or greater |
References
- William, J. What is an emotion?. Mind. 9 (34), 188-205 (1884).
- Pekrun, R., Linnenbrink-Garcia, L., Pekrun, R., Linnenbrink-Garcia, L. Emotions in education: Conclusions and future directions. International handbook of emotions in education. , 659-675 (2014).
- Pekrun, R. The control-value theory of achievement emotions: Assumptions, corollaries, and implications for educational research and practice. Educational Psychology Review. 18 (4), 315-341 (2006).
- Pekrun, R., Perry, R. P. Control-value theory of achievement emotions. International Handbook of Emotions in Education. , 120-141 (2014).
- Pekrun, R., Stephens, E. J., Harris, K. R. Academic emotions. APA Educational Psychology Handbook. , 3-31 (2011).
- Bandura, A. . Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. , (1997).
- Bandura, A. . Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. , (1986).
- Bandura, A., Pajares, F., Urdan, T. Guide for constructing self-efficacy scales. Self-efficacy beliefs of adolescents. , 307-337 (2006).
- Jarrell, A., Harley, J. M., Lajoie, S., Naismith, L. Success, failure and emotions: examining the relationship between performance feedback and emotions in diagnostic reasoning. Educational Technology Research and Development. 65 (5), 1263-1284 (2017).
- Pekrun, R., Bühner, M., Pekrun, R., Linnenbrink-Garcia, L. Self-report measures of academic emotions. International Handbook of Emotions in Education. , 561-566 (2014).
- Nett, U. E., Goetz, T., Hall, N. C. Coping with boredom in school: An experience sampling perspective. Contemporary Educational Psychology. 36 (1), 49-59 (2011).
- Azevedo, R. Defining and measuring engagement and learning in science: Conceptual, theoretical, methodological, and analytical issues. Educational Psychologist. 50 (1), 84-94 (2015).
- Spangler, G., Pekrun, R., Kramer, K., Hofman, H. Students’ emotions, physiological reactions, and coping in academic exams. Anxiety, Stress, & Coping. 15 (4), 413-432 (2002).
- Husman, J., Cheng, K. C., Puruhito, K., Fishman, E. J. Understanding engineering students stress and emotions during an introductory engineering course. American Society of Engineering Education. , (2015).
- Vedhara, K., Hyde, J., Gilchrist, I., Tytherleigh, M., Plummer, S. Acute stress, memory, attention and cortisol. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 25 (6), 535-549 (2000).
- Berenbaum, S. A., Moffat, S., Wisniewski, A., Resnick, S., de Haan, M., Johnson, M. H. Neuroendocrinology: Cognitive effects of sex hormones. The Cognitive Neuroscience of Development: Studies in Developmental Psychology. , 207-210 (2003).
- Lundberg, U., Frankenhaeuser, M. Pituitary-adrenal and sympathetic-adrenal correlates of distress and effort. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 24 (3-4), 125-130 (1980).
- Nater, U. M., Rohleder, N. Salivary alpha-amylase as a non-invasive biomarker for the sympathetic nervous system: Current state of research. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 34 (4), 486-496 (2009).
- Denson, T., Spanovic, M., Miller, N., Cooper, H. Cognitive appraisals and emotions predict cortisol and immune responses: A meta-analysis of acute laboratory social stressors and emotion inductions. Psychological Bulletin. 135 (6), 823-853 (2009).
- Van Stegeren, A. H., Wolf, O. T., Kindt, M. Salivary alpha amylase and cortisol responses to different stress tasks: Impact of sex. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 69 (1), 33-40 (2008).
- Benedek, M., Kaernbach, C. A continuous measure of phasic electrodermal activity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 190 (1), 80-91 (2010).
- Boucsein, W., Backs, R. W., Backs, R. W., Boucsein, W. Engineering psychophysiology as a discipline: Historical and theoretical aspects. Engineering psychophysiology. Issues and applications. , 3-30 (2000).
- Boucsein, W., Backs, R. W., Duffy, V. G. The psychophysiology of emotion, arousal, and personality: Methods and models. Handbook of digital human modeling. , 35-38 (2009).
- Turpin, G., Shine, P., Lader, M. H. Ambulatory electrodermal monitoring: effects of ambient temperature, general activity, electrolyte media, and length of recording. Psychophysiology. 20, 219-224 (1983).
- Posada-Quintero, H. F., et al. Timevarying analysis of electrodermal activity during exercise. PLoS ONE. 13 (6), e0198328 (2018).
- Lobstein, T., Cort, J. The relationship between skin temperature and skin conductance activity: Indications of genetic and fitness determinants. Biological Psychology. 7, 139-143 (1978).
- Scholander, T. Some measures of electrodermal activity and their relationships as affected by varied temperatures. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 7, 151-158 (1963).
- Schwerdtfeger, A. Predicting autonomic reactivity to public speaking: don't get fixed on self-report data!. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 52 (3), 217-224 (2004).
- Braithwaite, J. J., Watson, D. G., Jones, R., Rowe, M. A guide for analysing electrodermal activity (EDA) & skin conductance responses (SCRs) for psychological experiments. Psychophysiology. 49 (1), 1017-1034 (2013).
- Villanueva, I., Valladares, M., Goodridge, W. Use of galvanic skin responses, salivary biomarkers, and self-reports to assess undergraduate student performance during a laboratory exam activity. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (108), e53255 (2016).
- Empatica, . E4 wristband from Empatica: User’s manual. Empatica. , 1-32 (2018).
- Salimetrics, . Collection methods: Passive drool using the saliva collection aid. Salimetrics Technical Summary. , 1-2 (2018).
- Salimetrics, . Collection methods: Passive drool using the saliva collection aid. Salimetrics Technical Summary. , 1-2 (2018).
- Salimetrics, . Expanded range high sensitivity salivary cortisol enzyme immunoassay kit. Salimetrics Technical Summary. , 1-21 (2016).
- Salimetrics, . Salivary α-amylase kinetic enzyme assay kit. Salimetrics Technical Summary. , 1-17 (2016).
- . Innovative Hormone Testing: Saliva Test Specifications, ZRT Laboratory Reports Available from: https://www.zrtlab.com/resources/ (2014)
- Call, B., Goodridge, W., Villanueva, I., Wan, N., Jordan, K. Utilizing electroencephalography measurements for comparison of task-specific neural efficiencies: spatial intelligence tasks. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (114), (2016).
- Ruel, E. E., Wagner, W. E., Gillespie, B. J. . The practice of survey research: theory and applications. , (2016).
- Barrett, P. Euclidean distance: raw, normalized, and double-spaced coefficients. The Technical Whitepaper Series. 6, 1-26 (2005).
- Groeneveld, R. A. Influence functions for the coefficient of variation, its inverse, and CV comparisons. Communications in Statistics- Theory and Methods. 40 (23), 4139-4150 (2011).
- Tronstad, C., Staal, O. M., Sælid, S., Martinsen, &. #. 2. 1. 6. ;. G. Model-based filtering for artifact and noise suppression with state estimation for electrodermal activity measurements in real time. 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. , 2750-2753 (2015).
- Routray, A., Pradhan, A. K., Rao, K. P. A novel Kalman filter for frequency estimation of distorted signals in power systems. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. 51 (3), 469-479 (2002).
- Benedek, M., Kaernbach, C. A continuous measure of phasic electrodermal activity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 190, 80-91 (2010).
- Taylor, S., et al. Automatic Identification of Artifacts in Electrodermal Activity Data. 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. , 1934-1937 (2015).
- Andreasson, U., et al. A practical guide to immunoassay method validation. Frontiers in Neurology. 6 (179), 1-8 (2015).
- Adam, E. K., Kumari, M. Assessing salivary cortisol in large-scale, epidemiological research. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 34 (10), 1423-1436 (2009).
- Pruessner, J. C., Kirschbaum, C., Meinlschmid, G., Hellhammer, D. H. Two formulas for computation of the area under the curve represent measures of total hormone concentration versus time-dependent change. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 28 (7), 916-931 (2003).
- Girden, E. R. . ANOVA: Repeated measures. , (1992).
- Raudenbush, S. W., Bryk, A. S. . Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods (Vol. 1). , (2002).
- Duncan, T. E., Duncan, S. C., Strycker, L. A. . An introduction to latent variable growth curve modeling: Concepts, issues, and application. , (2013).
- Mehta, P. D., West, S. G. Putting the individual back into individual growth curves. Psychological Methods. 5 (1), 23-43 (2000).
- Khan, M. T. H., Villanueva, I., Vicioso, P., Husman, J. Exploring relationships between electrodermal activity, skin temperature, and performance during engineering exams. , (Accepted).
- Christensen, D., Khan, M. T. H., Villanueva, I., Husman, J. Stretched Too Much? A Case Study of Engineering Exam-Related Predicted Performance, Electrodermal Activity, and Heart Rate. , (Accepted).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved