Method Article
Optimized Incorporation of Alkynyl Fatty Acid Analogs for the Detection of Fatty Acylated Proteins using Click Chemistry
In This Article
Summary
The study of fatty acylation has important implications in cellular protein interactions and diseases. Presented here is a modified protocol to improve click chemistry detection of fatty acylated proteins, which can be applied in various cell types and combined with other assays, including pulse-chase and mass spectrometry.
Abstract
Fatty acylation, the covalent addition of saturated fatty acids to protein substrates, is important in regulating a myriad of cellular functions in addition to its implications in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Recent developments in fatty acylation detection methods have enabled efficient and non-hazardous detection of fatty acylated proteins, particularly through the use of click chemistry with bio-orthogonal labeling. However, click chemistry detection can be limited by the poor solubility and potential toxic effects of adding long chain fatty acids to cell culture. Described here is a labeling approach with optimized delivery using saponified fatty acids in combination with fatty-acid free BSA, as well as delipidated media, which can improve detection of hard to detect fatty acylated proteins. This effect was most pronounced with the alkynyl-stearate analog, 17-ODYA, which has been the most commonly used fatty acid analog in click chemistry detection of acylated proteins. This modification will improve cellular incorporation and increase sensitivity to acylated protein detection. In addition, this approach can be applied in a variety of cell types and combined with other assays such as pulse-chase analysis, stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture, and mass spectrometry for quantitative profiling of fatty acylated proteins.
Introduction
Fatty acylation involves the covalent addition of fatty acids to proteins and is well known for its importance in promoting protein-membrane interactions but has been also shown to promote protein-protein interactions, conformational changes, and regulate catalytic sites of enzymes1,2,3,4,5,6,7. Fatty acylation has emerged as a potential drug target in a myriad of diseases, including infection, cancer, inflammation, and neurodegeneration, where disruptions in palmitoylation have been documented8,9,10,11,12,13. This has been primarily spurred by the development of new chemical detection methods, which enabled large-scale identification of S-acylated protein targets.
Fatty acylation can include a variety of modifications involving the covalent addition of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, but typically refers to N-myristoylation and S-acylation. N-myristoylation refers to the addition of myristic acid to N-terminal glycines either co-translationally on nascent polypeptides or post-translationally on newly exposed N-terminal glycines following proteolytic cleavage2,14. N-myristoylation occurs through an irreversible amide bond. On the other hand, S-acylation typically refers to the reversible addition of long chain fatty acids to cysteine residues via a thioester bond. The most common form of this modification includes the incorporation of palmitate and, therefore, is commonly referred to as S-palmitoylation, or simply palmitoylation11,15. In many ways, S-palmitoylation is similar to phosphorylation. It is dynamic, enzymatically regulated, and proving to be highly tractable.
Up until the last decade, studying fatty acylation was hindered by limited detection methods, which required radioactively labeled fatty acids. This had several disadvantages, including cost, safety issues and very long detection times. Typically, either tritiated or iodinated palmitate was used for the detection of S-acylation16. Tritiated palmitate required lengthy detection periods with autoradiography film, which can take weeks to months. While [125I] iodo-fatty acid analogs shortened detection times, it presented a much higher safety risk and required close thyroid monitoring of experimenters. In addition, these methods were non-quantitative, therefore, limiting the ability to measure dynamic palmitoylation, and also time consuming to set-up and clean-up due to the extra personal protective equipment and radioactive monitoring. Finally, radioactive labels were not well suited for proteomic studies and typically limited to low throughput detection of specific proteins of interest. As more substrates were detected and, inevitably the enzymes that mediate each modification were identified, it was clear that new detection methods were required17,18,19,20,21. Almost simultaneously, several new methods arose for the detection of fatty acylated proteins. The first exploits the reversibility and reactivity of the thioester bond of S-acylation. The acyl-biotin exchange (ABE) assay chemically replaces palmitate with biotin for subsequent pulldown of S-acylated proteins using avidin agarose beads and direct detection by western blot22,23,24. Next, bio-orthogonal labeling of fatty acids and chemoselective addition to tags or handles were developed that included the use of the Staudinger ligation and click chemistry25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33. Finally, similar to the ABE, acyl-resin assisted capture (RAC) essentially replaces S-acylated sites with thiol-reactive beads for capture and detection of S-acylated proteins34,35. Together, the exchange and click-chemistry-based assays have provided more efficient and sensitive methods of acylation detection and affinity purification for downstream analysis and have subsequently led to the discovery of thousands of S-acylated proteins8,36.
The term click chemistry encompasses a group of chemical reactions, but most commonly refers to the Cu(I)-catalyzed azido-alkyne [3+2] cycloaddition reaction mechanism between an alkynyl group and an azido group27,28,37. Particularly, in the case of fatty acylation, click chemistry involves the detection of S-palmitoylation or N-myristylation by incorporating bio-orthogonal 16-carbon alkynyl-palmitate (15-hexadecynoic acid; 15-HDYA) or the 14-carbon alkynyl-myristate (13-tetradecynoic acid; 13-TDYA), respectively, into cells to label endogenously acylated proteins28. After cell lysis and immunoprecipitation of the protein of interest, a click chemistry reaction (covalent linkage between an alkyne and an azide) is performed to bind an affinity probe, typically biotin, for detection by western blot28,37. Alternatively, click chemistry can be performed on the total cell lysate and fatty acylated proteins can be affinity purified for identification by mass spectrometry. The initial click chemistry reaction with azido-biotin increased the selectivity and sensitivity of detection over a million times compared to radioactivity2. Another advantage of click chemistry is that it can be combined with other classical labeling methods, such as pulse-chase analysis of protein turnover using azido-homoalanine for quantitative analysis38. In addition, fluorescent probes can be used instead of biotin or other biochemical probes, such as FLAG or Myc tags, in order to examine protein localization16,28,39.
Despite the relative ease of use of click chemistry, detection can be limited by the low solubility and potential toxicity of using long chain free fatty acids in cell culture40. In particular, despite the preference of palmitate during S-acylation for the majority of proteins, many studies have used the 18-carbon stearate (17-octadecynoic acid - 17-ODYA) rather than palmitate (15-HDYA) for detecting S-acylated proteins due to its commercial availability and relatively low cost. However, 17-ODYA is very insoluble and requires special attention when being used. In addition, click chemistry can require some nuanced preparation and storage of chemicals. Herein, the protocol describes a labeling approach, which optimizes delivery using saponification of fatty acids, delivery with fatty-acid free BSA, and delipidated fetal bovine serum (FBS) to increase solubility and bypass potential toxic effects of adding free fatty acids to cells28. This method works in a variety of cell types and has even been used in live animals28.
Protocol
1. Cell culture
- To supplement DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium) for cell culture, add 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS), 1x Penicillin-Streptomycin, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 100 mM sodium pyruvate (1% vol/vol).
- Plate approximately 5 x 105 HEK293T cells/well of a 6-well tissue culture dish and grow for 18 h in a 37 °C humidified incubator with 5% CO2 to reach 75%-80% confluency.
- Fatty acid serum deprivation
- To prepare labeling media, prepare DMEM as above (step 1.1) without 10% FBS. Replace FBS with 5% dextran-charcoal coated FBS (DCC-FBS). Pre-warm to 37 °C before use.
- Gently wash the cells with 1x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at room temperature and replace with labeling media.
NOTE: HEK293T cells detach from tissue culture plates easily. Take care when washing cells and replacing media. Minimize agitation during transfer to and from the incubator as much as possible. - Return the cells to the 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2 and incubate approximately 45 min (minimum 15 min is effective), up to 60 min, prior to proceeding with metabolic labeling with fatty acids.
2. Preparation and saponification of fatty acid analogs
- Prepare the stock solutions of alkynyl fatty acids ahead of time by solubilizing in DMSO to achieve the following concentrations and store at -20 °C. Thaw at room temperature as needed. Store the preparations for their best performance under N2 or Ar.
Alkynyl-myristate (13-tetradecynoic acid, 13-TDYA): 25 mM
Alkynyl-palmitate (15-hexadecynoic acid; 15-HDYA): 100 mM
Alkynyl-stearate (17-octadecynoic acid; 17-ODYA): 100 mM - To prepare 20% fatty acid free BSA (FAFBSA), weigh 2 g of FAFBSA in a 50 mL disposable tube.
- Bring up to 10 mL with pre-warmed (37 °C) DMEM.
- Mix by end-over-end rotation or by vortexing, and place in a 37 °C water bath to dissolve FAFBSA completely.
- Use 0.2 µm filter to filter sterilize the medium.
- Aliquot in approximately 1 mL volumes and store at -20 °C. Thaw as needed and warm to 37 °C in a water bath prior to use.
- To enhance the solubility of the fatty acid and fatty acid analogs, saponify by incubating with 20% molar excess of potassium hydroxide (KOH) in 3 mL glass conical reaction vials.
NOTE: These vials allow the salt to remain soluble while ensuring the FAFBSA does not congeal from the high heat. The use of glass also prevents fatty acids from sticking to the plastic.- Pipette out at least 2 µL of alkynyl fatty acid analog directly to the bottom of a 3 mL conical reaction vial. Prepare 2 µL of lipid per well of a 6-well plate used (see Table 1).
NOTE: Due to the hydrophobicity of fatty acids, it is best to coat the tip of the pipette by drawing up the desired volume several times before dispensing it into the reaction vial. - Dilute 1 M KOH to concentrations equal to 20% molar excess of the alkynyl fatty acid label (30 mM for 13-TDYA and 120 mM for 15-HDYA and 17-ODYA).
- Pipette out an equal amount of diluted KOH (1 µL : 1 µL fatty acid : KOH) close to the bottom of the reaction vial on the edge of the glass, such that the dispensed volume of the KOH mixes with the fatty acid.
- Close the lid of the vial and tap gently to mix the solutions.
NOTE: The mixture may solidify quickly, especially with increasing lengths of the hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acid. Be careful not to pipet the solid (i.e., do not mix by pipetting). - Heat the reaction vial at 65 °C for approximately 5 min, or as soon as the fatty acid is incorporated (solution becomes clear).
NOTE: Fatty acids with a higher number of carbons and decreased solubility, such as stearate (17-ODYA), may require longer incubation times to be fully incorporated intothe KOH at 65 °C. Raise the temperature to 70 °C if needed. A water bath is best. Take care that the liquid does not evaporate too much. - Once the fatty acids have gone into solution and no visible solids remain, pipette prewarmed 20% FAFBSA such that the volume ratio of fatty acids: KOH: FAFBSA is 1: 1: 50 to achieve a final concentration of 20x BSA-bound alkynyl fatty acids.
- Mix by pipetting up and down. The solution typically appears clear with no visible solids.
NOTE: Typically, any small solids will go into solution after incubation at 37 °C. - Incubate the fatty acid and FAFBSA for 15 min at 37 °C.
NOTE: The saponified label at this point is stable beyond 15 min.
- Pipette out at least 2 µL of alkynyl fatty acid analog directly to the bottom of a 3 mL conical reaction vial. Prepare 2 µL of lipid per well of a 6-well plate used (see Table 1).
| Total media volume (mL) | Vol. fatty acid or fatty acid analog (µL) | Vol. KOH (µL) | Vol. 20% FAFBSA (µL) | Total vol. of BSA-conjugated saponified label (µL) |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 200 | 208 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 100 | 104 |
Table 1: Saponified fatty acid labeling ratios. Experimental volumes of fatty acid, KOH, and FAFBSA for the saponification of fatty acid label according to the volume of media used.
- As a control, repeat step 2.3. with fatty acids without an alkyne label.
- Label the cells with 1/20 volume of the 20x fatty acid-BSA conjugate directly onto the starvation media (typically, 100 µL in 2 mL media/cells) to achieve a final concentration of 1% BSA and 25 µM for alkynyl-myristate, or 100 µM for alkynyl-palmitate and alkynyl-stearate.
NOTE: To minimize the amount of physical disturbance to the attached cells, form a droplet at the tip of the pipette close to the surface of the media instead of pipetting directly into the media. If using acylation inhibitors, add at least 15 min prior to the labeled fatty acids. Times may vary depending on the cells or inhibitor used. It has been recommended to use the saponification for this step as well28.- For comparison, add non-saponified lipids by pipetting 2 µL (or equivalent to volume saponified) of unlabeled fatty acid directly into the starvation media.
- Place cells back into the incubator and incubate for 3-6 h.
NOTE: Optimal labeling timing may need to be determined for each cell type or experimental condition. Longer incubation times can potentially lead to the breakdown of the fatty acids by β-oxidation and/or incorporation into other lipid groups, such as phospholipids28.
- Gently wash the cells with 1x PBS at room temperature.
- Harvest and lyse the cells with 500 µL ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)-free modified radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (0.1% SDS, 50 mM N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N-ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1% non-denaturing detergent, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 2 mM MgCl2 with freshly added 1 mM phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride (PMSF), and 10 µg/µL Pepstatin A (or EDTA-free complete protease inhibitor cocktail)) by rocking the lysates for 15 min at 4 °C.
- Centrifuge the lysates at 16,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Collect the supernatant in 1.7 mL microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20 °C until ready to proceed with click reaction.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here. Lysates are stable at -20 °C for up to 1 month. However, it is recommended to proceed with the click reaction in a timely manner.
- Quantify the protein concentrations using an appropriate assay as per the manufacturer's protocol, such as a detergent compatible (DC) assay.
3. Click reaction on cell lysates
- Prepare the reagents for click chemistry.
- Dissolve tris-(benzyltriazolylmethyl) amine (TBTA) in DMSO to 2 mM. Store in small aliquots with desiccant at -20 °C for up to 2-3 months. Best stored under N2 or Ar.
- Dissolve CuSO4 in ddH2O water to achieve 50 mM. Store at room temperature for up to 2 months.
- Dissolve tris-carboxyethylphosphine (TCEP) in ddH2O water to 250 mM. Store in darkness at 4 °C and make fresh 50 mM dilutions just prior to the click reaction.
- Prepare 2 mM azide in DMSO. Store in small aliquots with desiccant at -20 °C for up to 6 months. Best stored under N2 or Ar.
NOTE: It was observed that the products with three or more polyethylene glycols groups worked best with biotin.
- Bring 50-100 µg of protein lysates in 1.7 mL microcentrifuge tubes to the same volume using the same lysis buffer as above.
NOTE: Keep the reaction volume as small as possible (20-100 µL).- Add sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) to each sample to attain a final 1% concentration.
- Prepare a master mix of click reagents so that the final concentrations after addition to the lysates are: 100 µM TBTA (2 mM stock), 1 mM CuSO4, (50 mM stock) 1 mM TCEP (50 mM stock), and 100 µM azide probe (2 mM stock). Combine stock solutions accordingly (see Table 2).
NOTE: The order is important. Mix completely after addition of each component. - Add appropriate volumes of the master mix into the lysates. Mix by pipetting up and down.
- Incubate for 30 min in the dark in a 37 °C water bath. Agitate/mix occasionally.
| Total reaction vol (µL) | Vol. protein (µL) | Vol. TBTA (2 mM) (µL) | Vol. CuSO4 (50 mM) (µL) | Vol. TCEP (50 mM) (µL) | Vol. azido probe (2 mM) (µL) |
| 50 | 43 | 2.5 | 1 | 1 | 2.5 |
| 100 | 86 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
Table 2: Click reagent and protein volume ratios. Experimental volumes of the click chemistry reagents and corresponding stock concentrations, in addition to the volumes of protein samples.
4. Click reaction on immunoprecipitated proteins
- Alternatively, it is possible to perform the click reaction on immunoprecipitated (IP) proteins on or off the beads.
NOTE: Typically, performing click off the beads leads to the least background and is best when testing new proteins of interest.- Transfect cells for the protein of interest, in this case, wildtype myristoylated C-terminal huntingtin (HTT) fused to GFP (myr-ctHTT-GFP) and ctHTT-GFP with a G2A substitution, using calcium phosphate DNA coprecipitation, as previously described41.
- Plate 2.5 x 105 cells/well in 6-well tissue culture plates and grow overnight to ~70-80% confluency.
- Prepare the DNA mix by adding 2.5 µg DNA in 10 µL with 99.75 µL molecular grade H2O to a 1.7 mL microcentrifuge tube. Then, add 15.25 µL CaCl2 dropwise to the DNA mix.
- Add DNA/CaCl2 mixture to a separate tube containing 125 µL 2x HEPES buffered saline (HBS, pH 7.0) in a dropwise manner with mixing.
- Slowly add the DNA/CaCl2/HBS mix to cells. After 2-4 h, replace the media and incubate overnight. Proceed with labeling from steps 1.3-2.8.
- Prepare equal volumes of 500 µg protein in lysis buffer.
- Perform IP by incubating with rabbit anti-GFP for ctHTT-GFP rotating overnight at 4 °C.
- Add 15-20 µL protein G beads pre-equilibrated with lysis buffer to each tube and allow it to react end-over-end at 4 °C for 3 h.
- Wash the beads with lysis buffer and resuspend in 45 µL 1% SDS 50 mM HEPES buffer.
- Heat the beads at 80 °C for 15 min and invert the tubes or agitate approximately every 5 min. Briefly spin the tubes and return to 80 °C.
- Collect the supernatant containing the proteins while the samples are still warm.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here and the immunoprecipitated samples can be stored at -20 °C or -80 °C, if not used for click chemistry right away. - Allow 43 µL of the supernatant to react with 7 µL master mix of click reagents.
- Proceed with the reaction as stated in step 3.2.3.
- Transfect cells for the protein of interest, in this case, wildtype myristoylated C-terminal huntingtin (HTT) fused to GFP (myr-ctHTT-GFP) and ctHTT-GFP with a G2A substitution, using calcium phosphate DNA coprecipitation, as previously described41.
5. SDS-PAGE and western blotting
- Stop the reaction and denature by adding 1x sample loading buffer containing 25 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) and heat at 95 °C for 5 min.
NOTE: Up to 100 mM DTT can be used28. Do not use β-mercaptoethanol with S-acylated proteins as it can hydrolyze the thioester bonds and remove the clicked fatty acid analog. - Briefly spin down the samples.
- Separate the proteins with SDS-PAGE on a polyacrylamide gel, in duplicates.
NOTE: Two gels are required for the alkaline treatment with KOH to confirm the presence of thioester bonds. If using a fluorescent azide probe, acylation can be detected in-gel or after transfer using the indicated excitation channel. - Transfer to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (activated in methanol and rinsed in ddH2O - 5 min each) with semi-dry transfer apparatus at 25 V, 1.0 A (constant) for 30 min.
- After briefly rinsing the membranes with ddH2O, soak one replicate membrane in 0.1 M KOH in methanol/water (9:1 v/v) and the other in 0.1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.0 in methanol/water (9:1 v/v) as a non-alkaline control for 60 min at room temperature with gentle rocking.
- Rinse the membranes briefly in ddH2O water, followed by 6 times of 5 min washes in PBS-T (1x PBS, 0.1% Tween 20).
NOTE: Wash thoroughly. - Block the membranes overnight in 5% skim milk blocking buffer (1x PBS, 0.1% Tween20).
6. Perform western blot
- Where indicated, probe with fluorescently tagged Streptavidin (1:5000) and loading control, anti-GAPDH rhodamine (1:5000) in 5% BSA blocking buffer (0.01% SDS, 1x PBS, 0.1% Tween20) at room temperature for 45-60 min with gentle rocking, in darkness.
- Probe the immunoprecipitated protein blot first with primary anti-GFP antibody in 5% skim milk blocking buffer, then with appropriate secondary antibodies in 5% BSA as in step 6.1.
- Wash the membranes for 5 min in PBS-T (1x PBS, 0.1% Tween20) a total of four repeats and rinse with ddH2O water before imaging.
Results
The difference in labeling efficiency between saponified and non-saponified (non-sap) alkynyl fatty acids for click chemistry detection can be visualized and compared by the signal intensity of fatty acylated proteins through western blot (Figure 1). A noticeable effect was observed with increasing length of the acyl chains. In cells labeled with alkynyl-stearate (alk-stear), saponification of the fatty acid and delivery with BSA for metabolic labeling drastically increased the detection of S-acylated protein signal through click chemistry and detection by a fluorescent azido probe (Figure 1, right), suggesting an overall increase in cellular incorporation of the alkynyl fatty acid label. Conversely, no noticeable difference was observed in cells treated with the shortest and most soluble fatty acid, alkynyl-myristate (alk-myr; 13-tetradecynoic acid or 13-TDYA). Cells labeled with alkynyl-palmitate (Figure 1, middle) showed an intermediate increase in label compared to alkynyl-myristate (13-TDYA), but less than alkynyl-stearate.
Importantly, treatment of PVDF membranes with 0.1 M KOH largely removed the fatty acid labels from cells incubated with alkynyl-palmitate and alkynyl-stearate, confirming that the majority of the signal was through an ester or thioester bond (Figure 1, middle and right, bottom panels). As expected, the incorporation of alkynyl-myristate was mostly alkali-resistant (Figure 1, left, bottom panels), due to the attachment of myristate to proteins through an amide bond.
Figure 2 demonstrates the versatility and sensitivity of click chemistry to detect fatty acylation of immunoprecipitated proteins. HEK293T cells were transfected with myristoylated C-terminal huntingtin (HTT) fused to GFP (myr-ctHTT-GFP) and labeled with alkynyl-myristate, as previously described18. Following immunoprecipitation, ctHTT-GFP was released from the beads and subjected to click chemistry alongside the lysates. Not only was myristoylation of wildtype (WT) myr-ctHTT-GFP detected in the immunoprecipitates, but it was strongly detected in the lysates, whereas the G2A mutation completely blocked myristoylation of the ctHTT-GFP (Figure 2).
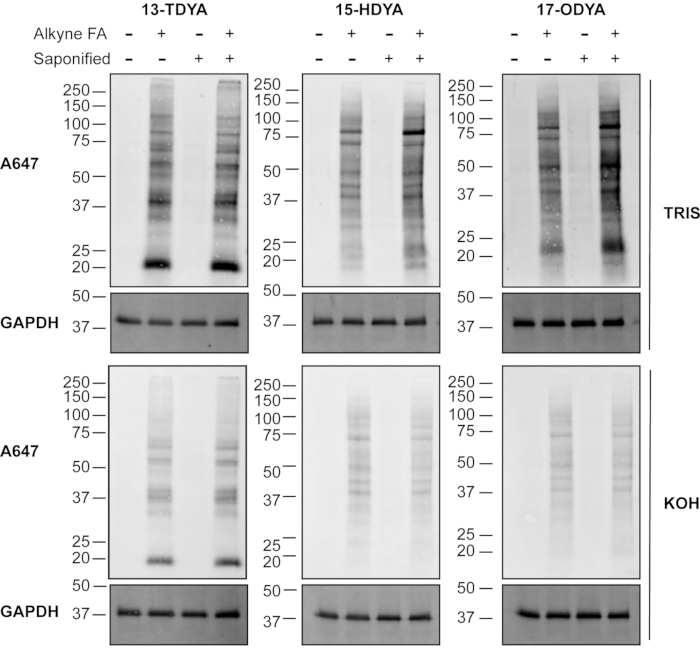
Figure 1: Detection of fatty acylated proteins using click chemistry. HEK293T cells were incubated with the indicated fatty acids directly (non-sap) or following saponification (sap) and incubation with the carrier protein BSA, as described in protocol 2.1-2.7. Alkynyl-fatty acids were linked to fluorescent azide by subjecting 100 µg of protein lysates to click chemistry, separated by SDS-PAGE, and transferred to PVDF membranes. After treatment with 0.1 M Tris pH 7.0 or 0.1 M KOH, to reverse thioester bonds, fatty acylation was detected using a fluorescent azide. GAPDH was used as a loading control; anti-GAPDH rhodamine (1:5,000). Alk-myr = 13-TDYA, alk-pal = 15-HDYA, alk-ste = 17-ODYA. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
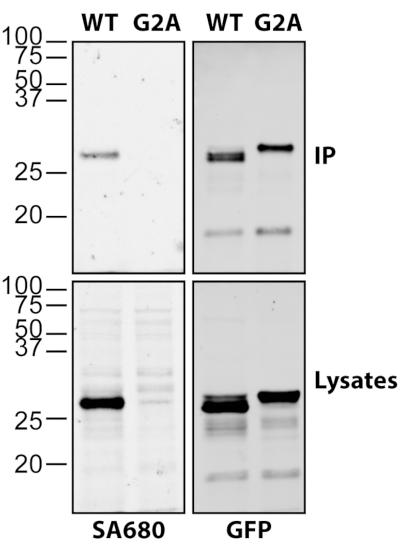
Figure 2: Detection of N-myristoylated ctHTT-GFP using click chemistry. HEK293T cells were transfected with C-terminally truncated (ct) and myristoylatable form of HTT (myr-ctHTT-GFP) and labeled with alkynyl-myristate. A non-myristoylatable form with the essential glycine replaced with an alanine was included (G2A). Following harvesting and lysis, ctHTT-GFP was immunoprecipitated using goat anti-GFP. Lysates were subjected to click chemistry reaction (left) as well as immunoprecipitates following release from the beads. Myristoylation was detected using Streptavidin Alexa 680 (SA680). GFP was detected using rabbit anti-GFP in combination with anti-rabbit Alexa 488. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
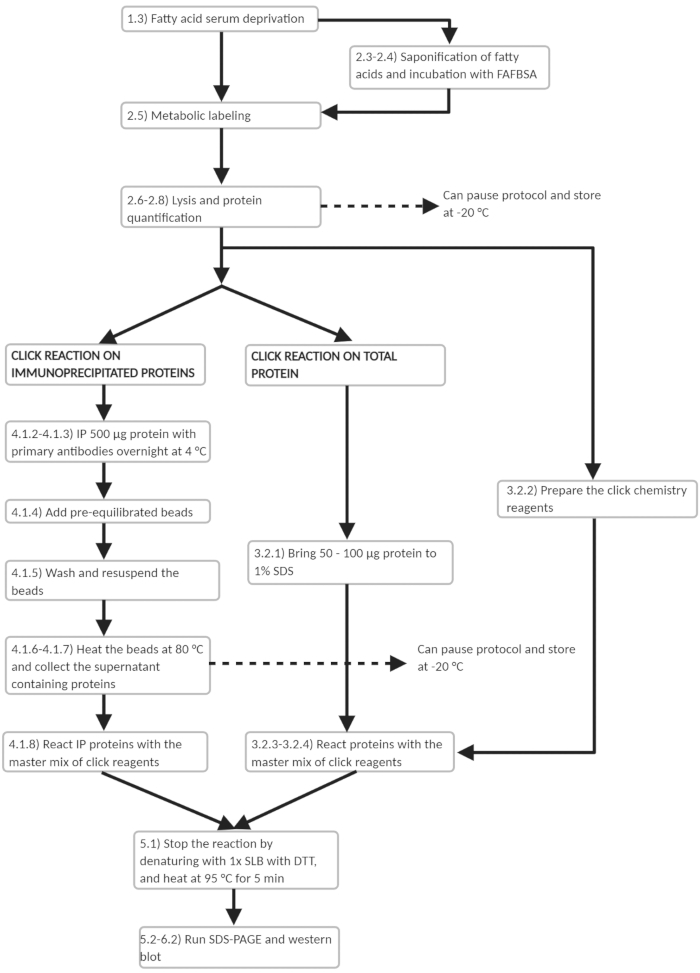
Figure 3: Workflow scheme of experimental protocol. Workflow outline of the main experimental steps in the protocol. Several points are noted where the protocol may be paused. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
Direct addition of fatty acids to cells in culture can result in insolubility, precipitation of lipids, and lipotoxicity40. Consequently, adding fatty acids directly to cells may not only result in poor cellular uptake and low availability of the fatty acid label, but also a decreased number of viable cells for downstream analysis, as well as activation of off-target pathways. However, many metabolic labeling protocols for click chemistry detection involve direct addition of fatty acids and a large number of palmitoyl-proteome studies using click chemistry detection to date seldom saponify the fatty acids labels or incubate them with BSA8,36. It is important to consider the fact that the efficiency and sensitivity of click chemistry detection of fatty-acylated proteins are dependent on sufficient cellular uptake of the fatty acid analogs. Therefore, it is reasonable to speculate that many S-acylated proteins may have escaped detection in proteomic studies due to a low availability of the fatty acid labels from poor incorporation into the cells, especially when the longer chain fatty acid 17-ODYA was used. 17-ODYA, or alkynyl-stearate, has been the widely used label of choice for several studies due to its commercial availability and its early use8,36. However, the results of this protocol demonstrate that saponification of 17-ODYA results in the largest increase in the detection of S-acylated proteins, in comparison to shorter chain fatty acids such as palmitate or myristate. Therefore, repeating these experiments with saponified labels may yield additional substrates of S-acylation that may have been previously overlooked. Further, while most palmitoyl acyltransferases prefer palmitate for S-acylation, some do have preferences for other lengths of fatty acids such as stearate15,38,44. In addition, some proteins or even specific sites within proteins prefer one fatty acid over another15,45. Therefore, studies using 17-ODYA may have a bias towards proteins S-acylated with stearate, not palmitate, while also under-representing those proteins due to lower detection.
The improved metabolic labeling efficiency for click chemistry relies on the saponification of lipids and incubation with FAFBSA steps, as well as the delipidated FBS. All fatty acids must be completely saponified in KOH with no visible solids remaining before proceeding with incubation with FAFBSA. This can be a difficult step and timing is crucial. After the saponified fatty acids have gone into solution at 65 °C, add warm BSA immediately as further heating will cause evaporation of the DMSO from the fatty acids. In addition, the saponified label will begin to re-solidify as soon as it begins to cool. Therefore, the FAFBSA must be warm and added rapidly after the salt has become soluble. The glass reaction vials, and their shape are important for this step. They allow the saponified lipid to be warm enough to remain soluble, while cool enough to ensure that the FAFBSA does not congeal. Sufficient mixing via pipetting is also important at this step to ensure a homogenous solution for labeling.
The reagents for click chemistry need to be properly stored, typically with desiccants or under N2 or Ar gas at -20 °C to -80 °C. Lack of acylation signal or weak signal may be due to unstable reagents, particularly older TBTA and azide stock solutions. Furthermore, care must be taken with fluorescent azide stock solutions, which need to be protected from light as much as possible. In addition, variables such as method of lipid deprivation and labeling time may need to be tested to determine the optimal conditions depending on the type of cell used. For example, neuronal cells may need longer labeling times because media changes and lipid deprivation are difficult (unpublished).
The benefit of this protocol is most dramatic when used for longer-chain fatty acids. For shorter chains, the increase in signal intensity becomes less dramatic, but is still likely protective to the cells. While the suggested modifications will improve protein acylation detection in general, click chemistry is still considered a lipid-centric method1 that is limited to detection of dynamically, not stably S-acylated proteins1. Other limitations to consider include the requirement of fatty acid deprivation to promote labeling, and its relatively limited range of compatible cell types when compared to the acyl-biotin exchange (ABE) detection of S-acylation16. Despite these limitations, click chemistry detection is quicker than most acyl-exchange assays and is better suited for detection of proteins that do not tolerate the repeated protein precipitation steps required for acyl-exchange assays. In addition, this approach can be combined with simultaneous labeling using other click assays such as pulse-chase analysis38.
The use of this modification for metabolic labeling for click chemistry increased overall detection of acylated proteins, particularly S-acylated, with a variety of proteomic techniques that are used in conjunction with click chemistry. As shown, fluorogenic detection can be used as an alternative to biotin (Figure 1)28. This is particularly useful because there are no endogenously fluorescent proteins in the cell lysates. In addition, fluorophores that are only activated after click chemistry can be used46. The saponified and FAFBSA-bound fatty acid for click chemistry labeling can help with difficulties detecting proteins of interest due to an overall increase in the amount of label available in the cell and by limiting toxic effects of adding fatty acids directly to the media. It can also be utilized in conjunction with mass spectrometry27 to increase detection of low abundance proteins, especially when taken together with the recent advancement using machine-learning algorithms preventing redundant measurements to increase sensitivity to low abundance proteins, as opposed to existing data-dependent acquisition that favors detection of the most abundant proteins47. In addition, click chemistry can be combined with stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) and pulse-chase methods to produce quantifiable data on dynamic protein S-acylation27. Finally, the Hannoush group has combined click chemistry with proximity ligation assay (PLA) to allow single-cell visualization and examinations into subcellular distribution of palmitoylated proteins43,48.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC; RGPIN-2019-04617). Lucia Liao was funded by The Ram and Lekha Tumkur Memorial Scholarship through the Department of Biology at the University of Waterloo, and the Lucy Morrison Memorial Bursary through IODE Ontario, in addition to the graduate research funding from the University of Waterloo comprising the Graduate Research Studentship (50503-11072), Science Graduate Award, and Graduate Teaching Assistantship. The authors would like to thank all members of the Martin lab for their support in preparing this manuscript, particularly Stephanie Ryall, Harleen Gill, and Sadia Khan who helped initially set-up the Martin Lab in preparation for these studies. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Luc Berthiaume for the kind gift of the ctHTT-GFP constructs and Dr. Shaun Sanders for critical input in preparing the manuscript. Figure 3 was created with BioRender.com.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 13-tetradecynoic acid (alkynyl myristic acid) (25mM) | Click Chemistry Tools | 1164 | |
| 15-hexadecynoic acid (alkynyl palmitic acid) (100mM) | Click Chemistry Tools | 1165 | |
| 17-octadecynoic acid (alkynyl stearic acid) (100 mM) | Cayman Chemical Company | 90270 | |
| 30% acrylamide/bis solution 29:1 | Biorad | 1610156 | |
| 96-well plate reader | Biorad | N/A | |
| AFDye 647 azide plus | Click Chemistry Tools | 1482 | |
| Ammonium persulfate (APS) | Biorad | 1610700 | |
| Anti-GAPDH hFAB Rhodamine | Biorad | 12004167 | |
| Anti-rabbit Alexa 488 | Invitrogen | A11034 | |
| Anti-Tubulin hFAB Rhodamine | Biorad | 12004166 | |
| Biotin Azide | Click Chemistry Tools | 1265 | |
| Bis-tris, ultrapure | VWR | 715 | |
| Calcium chloride | J.T. Baker | 1332-1 | |
| Centrifuge 16,000xg, 4°C | Thermo Scientific | N/A | |
| Charcoal STRP FBS One Shot (DCC-FBS) | Life Technologies | A3382101 | |
| ChemiDoc Imager | Biorad | N/A | |
| Copper sulfate (1 mM) | VWR | BDH9312 | |
| Deoxycholic acid sodium salt monohydrate | MP Biomedicals | 102906 | |
| Detergent compatible (DC) assay | Biorad | N/A | |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | VWR | 0231-500 mL | |
| DMEM, 1x | Wisent Inc | 319015CL | |
| Ethanol, anhydrous | N/A | N/A | |
| Fatty Acid Free BSA | MP Biomedicals | 219989950 | |
| Fast Blot Turbo Semi-dry transfer | Biorad | N/A | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 12483-020 | |
| FluoroTrans W PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) transfer membrane | Pall Life Sciences | BSP0161 | |
| HEPES (4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-ethanesulfonic) acid | VWR | 5011 | |
| Humidified Incubator at 37°C and 5% CO2 | VWR | N/A | |
| Igepal CA-630 | Alfa Aesar | J61055 | |
| Image Lab Software | Biorad | N/A | |
| L-glutamine supplement solution | Wisent Inc | 609-065-EL | |
| Magnesium chloride | Fisher Scientific | BP214-500 | |
| Methanol | VWR | BDH1135 | |
| Myristic Acid (25 mM) | VWR | M0476-25G | |
| Palmitic acid (100 mM) | VWR | P0002-25G | |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin, 10x | Wisent Inc | 450201EL | |
| Pepstatin A (synthetic) | Enzo Life Sciences | ALX-260-085-M005 | |
| Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride | Enzo Life Sciences | ALX-270-184-G005 | |
| Phosphate buffered saline, 10x, pH 7.4 | VWR | 75801-000 | |
| Polyclonal Goat antibody to GFP (Affinity Purified) | Eusera | EU4 | |
| FluoroTrans W PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) transfer membrane | Pall Life Sciences | BSP0161 | |
| Potassium hydroxide | Ward's Science | 470302-100 | |
| Rabbit polyclonal antibody to GFP | Eusera | EU1 | |
| Sodium chloride | VWR | 0241-1KG | |
| Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) | Fisher Scientific | BP166-500 | |
| Sodium pyruvate | Wisent Inc | 600-110-EL | |
| Streptavidin Alexa Fluor 680 conjugate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | S21378 | |
| Tris-(benzyltriazolylmethyl)amine (TBTA) (100 uM) | Click Chemistry Tools | 1061 | |
| Tris-(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine HCl (TCEP) (1mM) | Soltec Ventures | M115 | |
| Tris Base | Fisher Scientific | BP152-5 | |
| Trypsin/EDTA | Wisent Inc | 325-043-CL | |
| Tween 20 Reagent Grade 1L | VWR | 97062-332 | |
| WHEATON NextGen V Vials 3 mL | VWR | 89085-424 |
References
- Zaballa, M. E., vander Goot, F. G. The molecular era of protein S-acylation: spotlight on structure, mechanisms, and dynamics. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 53 (4), 1-31 (2018).
- Martin, D. D. O., Beauchamp, E., Berthiaume, L. G. Post-translational myristoylation: Fat matters in cellular life and death. Biochimie. 93 (1), 18-31 (2011).
- Hallak, H., et al. Covalent binding of arachidonate to G protein alpha subunits of human platelets. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 269 (7), 4713-4716 (1994).
- O'Brien, P. J., Zatz, M. Acylation of bovine rhodopsin by [3H]palmitic acid. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 259 (8), 5054-5057 (1984).
- Liang, X., et al. Heterogeneous fatty acylation of Src family kinases with polyunsaturated fatty acids regulates raft localization and signal transduction. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (33), 30987-30994 (2001).
- Thinon, E., Percher, A., Hang, H. C. Bioorthogonal chemical reporters for monitoring unsaturated fatty-acylated proteins. ChemBioChem. 17 (19), 1800-1803 (2016).
- Veit, M., Reverey, H., Schmidt, M. F. G. Cytoplasmic tail length influences fatty acid selection for acylation of viral glycoproteins. Biochemical Journal. 318 (1), 163-172 (1996).
- Sanders, S. S., et al. Curation of the mammalian palmitoylome indicates a pivotal role for palmitoylation in diseases and disorders of the nervous system and cancers. PLOS Computational Biology. 11 (8), 1004405 (2015).
- Hannoush, R. N. Synthetic protein lipidation. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 28, 39-46 (2015).
- Martin, D. D. O., Hayden, M. R. Post-translational myristoylation at the cross roads of cell death, autophagy and neurodegeneration. Biochemical Society Transactions. 43 (2), 229-234 (2015).
- Young, F. B., Butland, S. L., Sanders, S. S., Sutton, L. M., Hayden, M. R. Putting proteins in their place: Palmitoylation in Huntington disease and other neuropsychiatric diseases. Progress in Neurobiology. 97 (2), 220-238 (2012).
- Hansen, A. L., Mukai, K., Schopfer, F. J., Taguchi, T., Holm, C. K. Sting palmitoylation as a therapeutic target. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 16 (3), 236-241 (2019).
- Veit, M. Palmitoylation of virus proteins. Biology of the Cell. 104 (9), 493-515 (2012).
- Jiang, H., et al. Protein lipidation: Occurrence, mechanisms, biological functions, and enabling technologies. Chemical Reviews. 118 (3), 919-988 (2018).
- Greaves, J., et al. Molecular basis of fatty acid selectivity in the zDHHC family of S-acyltransferases revealed by click chemistry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 114 (8), 1365-1374 (2017).
- Gao, X., Hannoush, R. N. A decade of click chemistry in protein palmitoylation: Impact on discovery and new biology. Cell Chemical Biology. 25 (3), 236-246 (2018).
- Tsutsumi, R., Fukata, Y., Fukata, M. Discovery of protein-palmitoylating enzymes. Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology. 456 (6), 1199-1206 (2008).
- Roth, A. F., Feng, Y., Chen, L., Davis, N. G. The yeast DHHC cysteine-rich domain protein Akr1p is a palmitoyl transferase. The Journal of Cell Biology. 159 (1), 23-28 (2002).
- Lobo, S., Greentree, W. K., Linder, M. E., Deschenes, R. J. Identification of a Ras Palmitoyltransferase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (43), 41268-41273 (2002).
- Ohno, Y., Kihara, A., Sano, T., Igarashi, Y. Intracellular localization and tissue-specific distribution of human and yeast DHHC cysteine-rich domain-containing proteins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 1761 (4), 474-483 (2006).
- Huang, K., et al. Huntingtin-interacting protein HIP14 Is a palmitoyl transferase involved in palmitoylation and trafficking of multiple neuronal proteins. Neuron. 44 (6), 977-986 (2004).
- Drisdel, R. C., Green, W. N. Labeling and quantifying sites of protein palmitoylation. BioTechniques. 36 (2), 276-285 (2004).
- Roth, A. F., Wan, J., Green, W. N., Yates, J. R., Davis, N. G. Proteomic identification of palmitoylated proteins. Methods. 40 (2), 135-142 (2006).
- Wan, J., Roth, A. F., Bailey, A. O., Davis, N. G. Palmitoylated proteins: purification and identification. Nature Protocols. 2 (7), 1573-1584 (2007).
- Martin, D. D. O., et al. Rapid detection, discovery, and identification of post-translationally myristoylated proteins during apoptosis using a bio-orthogonal azidomyristate analog. The FASEB Journal. 22 (3), 797-806 (2007).
- Kostiuk, M. A., et al. Identification of palmitoylated mitochondrial proteins using a bio-orthogonal azido-palmitate analogue. The FASEB Journal. 22 (3), 721-732 (2008).
- Martin, B. R., Wang, C., Adibekian, A., Tully, S. E., Cravatt, B. F. Global profiling of dynamic protein palmitoylation. Nature Methods. 9 (1), 84-89 (2012).
- Yap, M. C., et al. Rapid and selective detection of fatty acylated proteins using ω-alkynyl-fatty acids and click chemistry. Journal of Lipid Research. 51 (6), 1566-1580 (2010).
- Hang, H. C., Wilson, J. P., Charron, G. Bioorthogonal chemical reporters for analyzing protein lipidation and lipid trafficking. Accounts of Chemical Research. 44 (9), 699-708 (2011).
- Thinon, E., et al. Global profiling of co- and post-translationally N-myristoylated proteomes in human cells. Nature Communications. 5 (1), 4919 (2014).
- Charron, G., Wilson, J., Hang, H. C. Chemical tools for understanding protein lipidation in eukaryotes. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 13 (4), 382-391 (2009).
- Hang, H. C., et al. Chemical probes for the rapid detection of fatty-acylated proteins in mammalian cells. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 129 (10), 2744-2745 (2007).
- Heal, W. P., et al. Site-specific N-terminal labelling of proteins in vitro and in vivo using N-myristoyl transferase and bioorthogonal ligation chemistry. Chemical Communications. (4), 480-482 (2007).
- Forrester, M. T., et al. Site-specific analysis of protein S-acylation by resin-assisted capture. Journal of Lipid Research. 52 (2), 393-398 (2011).
- Brigidi, G. S., Bamji, S. X. Detection of protein palmitoylation in cultured hippocampal neurons by immunoprecipitation and acyl-biotin exchange (ABE). Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (72), e50031 (2013).
- Blanc, M., et al. SwissPalm: Protein palmitoylation database. F1000Research. 4, 261 (2015).
- Heal, W. P., Wickramasinghe, S. R., Leatherbarrow, R. J., Tate, E. W. N -Myristoyl transferase-mediated protein labelling in vivo. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. 6 (13), 2308-2315 (2008).
- Lin, D. T. S., Conibear, E. ABHD17 proteins are novel protein depalmitoylases that regulate N-Ras palmitate turnover and subcellular localization. eLife. 4, 11306 (2015).
- Charron, G., et al. Robust fluorescent detection of protein fatty-acylation with chemical reporters. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (13), 4967-4975 (2009).
- Alsabeeh, N., Chausse, B., Kakimoto, P. A., Kowaltowski, A. J., Shirihai, O. Cell culture models of fatty acid overload: Problems and solutions. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 1863 (2), 143-151 (2018).
- Jordan, M., Schallhorn, A., Wurm, F. M. Transfecting mammalian cells: Optimization of critical parameters affecting calcium-phosphate precipitate formation. Nucleic Acids Research. 24 (4), 596-601 (1996).
- Martin, B. R., Cravatt, B. F. Large-scale profiling of protein palmitoylation in mammalian cells. Nature Methods. 6 (2), 135-138 (2009).
- Gao, X., Hannoush, R. N. Single-cell in situ imaging of palmitoylation in fatty-acylated proteins. Nature Protocols. 9 (11), 2607-2623 (2014).
- Muszbek, L., Haramura, G., Cluette-Brown, J. E., Cott, E. M. V., Laposata, M. The pool of fatty acids covalently bound to platelet proteins by thioester linkages can be altered by exogenously supplied fatty acids. Lipids. 34, 331-337 (1999).
- Brett, K., et al. Site-specific S-Acylation of influenza virus hemagglutinin. The location of the acylation site relative to the membrane border is the decisive factor for attachment of stearate. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 289 (50), 34978-34989 (2014).
- Shieh, P., et al. CalFluors: A universal motif for fluorogenic azide probes across the visible spectrum. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137 (22), 7145-7151 (2015).
- Pelletier, A. R., et al. MealTime-MS: A machine learning-guided real-time mass spectrometry analysis for protein identification and efficient dynamic exclusion. bioRxiv. , 110726 (2020).
- Gao, X., Hannoush, R. N. Method for cellular imaging of palmitoylated proteins with clickable probes and proximity ligation applied to Hedgehog, tubulin, and Ras. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 136 (12), 4544-4550 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved