A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Digital Hybrid Model Preparation for Virtual Planning of Reconstructive Dentoalveolar Surgical Procedures
In This Article
Summary
A workflow for creating three-dimensional (3D) virtual hybrid models has been designed based on cone-beam computed tomography dataset and intraoral optical scans utilizing radiographic image segmentation methods and free-form surface modeling. Digital models are used for the virtual planning of reconstructive dentoalveolar surgical procedures.
Abstract
Virtual, hybrid three-dimensional (3D) model acquisition is presented in this article, utilizing the sequence of radiographic image segmentation, spatial registration, and free-form surface modeling. Firstly cone-beam computed tomography datasets were reconstructed with a semi-automatic segmentation method. Alveolar bone and teeth are separated into different segments, allowing 3D morphology, and localization of periodontal intrabony defects to be assessed. The severity, extent, and morphology of acute and chronic alveolar ridge defects are validated concerning adjacent teeth. On virtual complex tissue models, positions of dental implants can be planned in 3D. Utilizing spatial registration of IOS and CBCT data and subsequent free-form surface modeling, realistic 3D hybrid models can be acquired, visualizing alveolar bone, teeth, and soft tissues. With the superimposition of IOS and CBCT soft tissue, thickness above the edentulous ridge can be assessed about the underlying bone dimensions; therefore, flap design and surgical flap management can be determined, and occasional complications may be avoided.
Introduction
Technological advancements in dentistry have enabled computer-aided treatment planning and simulation of surgical procedures and prosthetic rehabilitation. Two essential methods for 3D data acquisition in digital dentistry are: (1) cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)1 and (2) intraoral optical scanning (IOS)2. Digital information of all relevant anatomical structures (alveolar bone, teeth, soft tissues) can be acquired using these tools to plan reconstructive dentoalveolar surgical procedures.
Cone-beam technology was first introduced in 1996 by an Italian research group. Delivering significantly lower radiation dose and higher resolution (compared to conventional computed tomography), CBCT has quickly become the most frequently used 3D imaging modality in dentistry and oral surgery3. CBCT is often used to plan different surgical procedures (e.g., periodontal regenerative surgery, alveolar ridge augmentation, dental implant placement, orthognathic surgery)1. CBCT datasets are viewed and can be processed in radiographic imaging software that provides 2D images, and 3D renders-however, most imaging software use threshold-based algorithms for 3D image reconstruction. Thresholding methods set the upper and lower bounds of a voxel grey value interval. Voxels that fall in between these bounds will be rendered in 3D. This method allows speedy model acquisition; however, since the algorithm cannot differentiate anatomical structures from metal artifacts and scattering, the 3D renders are highly inaccurate and have very little diagnostic value4,5. For the reasons mentioned above, many fields within dentistry still rely on conventional 2D radiographs (intraoral radiographs, panoramic X-ray) or the 2D images of CBCT datasets5. Our research group presented a semi-automatic image segmentation method in a recently published article, using open-source radiographic image processing software6 wherein anatomically based 3D reconstruction of CBCT datasets is performed7. With the help of this method, anatomical structures were differentiated from metal artifacts, and, more importantly, alveolar bone and teeth could be separated. Therefore, a realistic virtual model of hard tissues could be acquired. 3D models were used to evaluate intrabony periodontal defects and for treatment planning before regenerative periodontal surgeries.
Intraoral optical surface scanners provide digital information on clinical conditions (clinical crown of the teeth and soft tissues). The original intended purpose of these devices was to directly acquire digital models of patients for the planning and fabrication of dental prostheses with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technologies8. However, due to the wide range of applications, their use was quickly implemented in other fields of dentistry. Maxillo-facial surgeons combine IOS and CBCT into a hybrid setup that can be utilized for virtual osteotomy and digital planning of orthognathic surgeries9,10. Dental implantology is probably the field that uses digital planning and guided execution most commonly. Navigated surgery eliminates most complications related to implant mispositioning. The combination of CBCT datasets and stereolithography (.stl) files of IOS is routinely used to plan the guided implant placement and the fabrication of static implant drilling guides11,12. Intraoral scans superimposed over CBCT datasets have also been used to prepare esthetic crown lengthening13; however, soft tissues were superimposed only over CBCT datasets reconstructed with thresholding algorithms. Yet, to perform accurate 3D virtual planning of regenerative-reconstructive surgical interventions and dental implant placement, realistic 3D hybrid models of patients must be composed of CBCT and IOS data.
Hence, this article aims to present a step-by-step method to acquire realistic hybrid digital models for virtual surgical planning before reconstructive dentoalveolar surgical interventions.
Protocol
This study was conducted in complete accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Before manuscript preparation, written informed consent was provided and signed by the patient. The patient granted permission for data usage for the demonstration of the protocol.
1. Radiographic image processing
- Load DICOM files into the software
- Download the newest version of the medical imaging software and open it.
NOTE: After opening the software, the home screen will appear. - Click Load DICOM Data on the sidebar.
NOTE: The DICOM database will pop up, showing the previously loaded DICOM datasets.- Click Import DICOM files in the DICOM database, select the DICOM dataset in the destination folder and click Import.
NOTE: The newly added DICOM dataset will appear in the list of studies.
- Click Import DICOM files in the DICOM database, select the DICOM dataset in the destination folder and click Import.
- Select the study and click Load at the bottom of the window.
NOTE: The DICOM dataset will be opened, and four views (coronal, axial, sagittal, and 3D) of the loaded data will be visible. Nodes are listed on the left-hand side. Theoretically, the described method can be performed on any CT or CBCT regardless of image quality (voxel size, artifacts). However, the segmentation process of higher-quality CBCT/CT scans is more straightforward, and higher-quality 3D models can be acquired. A shown CBCT scan was taken with the following parameters: voxel size: 150 µm, anode voltage: 84 kV, tube current: 40 mA, Field-of-view: 8 x 5 cm. The process can be stopped at any stage; make sure to save the scene before exiting. To save, click the save icon on the left-hand side of the toolbar and save it as a "medical record bundle" (.mrb) by clicking on the box icon in the "save scene" window.
- Download the newest version of the medical imaging software and open it.
- Volume rendering and cropping volume
- Crop the area of interest (upper or lower jaw) to reduce the file size and rendering time. Click the Modules bar visible on the left-hand side of the toolbar to view a scroll-down window showing frequently used modules.
- Select the Volume Rendering module from the dropdown window. To make volume rendering visible, click the eye icon next to the "Volumes" bar.
- Select the desired preset to view the volume render and move the "Shift" slider until the hard tissues can be viewed clearly.
NOTE: For CBCT scans, the CT-Bone preset is recommended. - Check the box next to "Enable" and click the eye icon next to "Display ROI" in the "Crop" section to make the ROI (Region of interest) visible.
NOTE: A wireframe box around the dataset in all 2D views and the 3D view will appear. By dragging the sides of the box, the volume will be cropped to the desired area. - Access the "Crop Volume" module to finalize cropping. Select the original dataset as the input volume.
NOTE: Input ROI is automatically set to ROI that was previously created. - Select Create new volume from the "Output volume" dropdown bar to create a new output volume. Uncheck Interpolated cropping in the advanced settings section and click Apply.
NOTE: When returning to the "Data module," the new cropped volume will appear as a new node.
- Segmentation of CBCT dataset
- Access the Segment Editor module for segmentation.
NOTE: Segmentation is when 3D reconstructions of anatomical structures are generated based on the CBCT dataset to allow more accessible analysis. - Select the previously created cropped volume as the Master Volume of the active segmentation. Click +Add to add, and -Remove to remove segments. Rename them according to the anatomical structure they will represent.
NOTE: Alveolar bone and all teeth will be separate segments within the segmentation - Start with the segmentation of the alveolar bone. From the list of effects, select Level Tracing, a semi-automatic tool that outlines the region where pixels have the same background value as the selected pixel.
- Drag the mouse to the perimeter of the bone on one of the 2D views for a yellow line to appear around the selected area and press the left mouse button to generate the segment on the selected slice of the dataset.
NOTE: Segmentation can be done in any of the 2D views; however, sagittal and axial orientations work the best. - Use the Paint and Erase hand tools to modify the segment and correct mistakes if the "Level Tracing" tool did not outline the entire section of the bone or if artifacts present on the slice were also included.
- Access the Segment Editor module for segmentation.
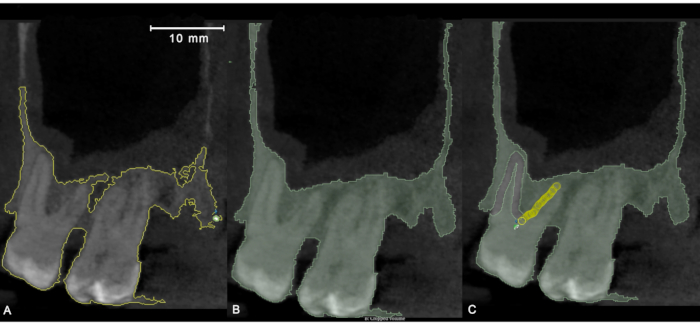
Figure 1: Application of "Level Tracing" semi-automatic segmentation tool in sagittal orientation. (A) Outlining the region of pixels with the same background value with a yellow line. (B) Results of "Level Tracing" and subsequent manual segmentation. (C) Refinement of semi-automatic segmentation with the help of manual tools (paint, erase). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
NOTE: Using number keys to allow fast switching between tools.
- Exclude both teeth and implants from the bone segment. Outline teeth and implants using the Erase tool and delete all highlighted pixels representing them.
- Repeat the same process on every 5th slice of the dataset in the selected orientation.
NOTE: Click Show 3D to view the segmentation in three dimensions. Set the smoothening factor slider to 0.00. - Compute the missing segments upon completion of this phase-select Fill between slices from the effects list.
NOTE: This tool calculates the missing segments based on those created previously using a morphological contour interpolation algorithm. - Click Initialize to activate contour interpolation, and if the results are satisfactory, click Apply. Scroll through the dataset upon completion to check and correct occasional mistakes.
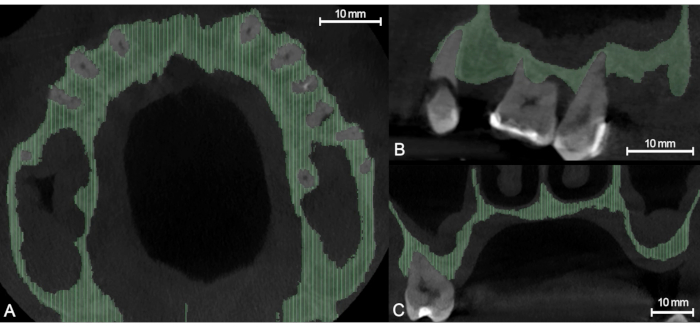
Figure 2: Morphological contour interpolation with "Fill Between Slices," light green areas indicating the automatically reconstructed part of the segment. (A) Axial view. (B) Sagittal view. (C) Coronal view. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
NOTE: Make sure that only the segment is visible on which the interpolation is applied. The visibility of the segments can be toggled in the segments list.
- Make segment boundaries smoother by removing protrusions using the Smoothing effect. Select Median as the smoothing method and set the "Kernel size" to 5 x 5 x 5 pixels by adjusting the mm value in the bracket and clicking Apply.
- Repeat the same steps for the segmentation of teeth once the segmentation of alveolar bone is completed.
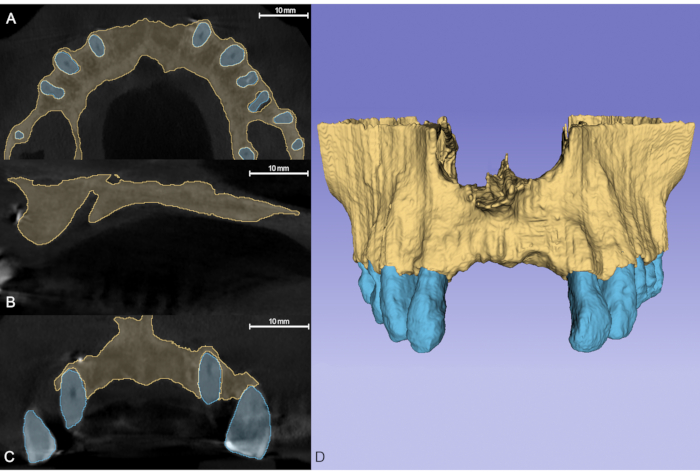
Figure 3: Finished segmentation, the brown segment representing bone and the blue segment representing teeth. (A) Axial view. (B) Sagittal view. (C) Coronal view. (D) The 3D model is generated automatically from the segments created previously. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Set the "Modify other segments" bar to Allow overlap before tooth segmentation so that the newly created segments will not overwrite the previously created ones.
- Spatial registration of CBCT dataset and IOS
NOTE: Spatial registration is necessary because the coordinate systems for the CBCT dataset and the IOS are different.- Select Extension Manager From the "View" menu bar and click Install Extensions. Type IGT into the search bar in the right-hand corner, install the SlicerIGT extension and restart the program.
- Load the previously saved .mrb file of the scene by clicking the Data icon and Choose file(s) to add.
- Import the .stl file of IOS by clicking the Data icon in the upper left corner. In the "Add data into the scene" pop-up window, click Choose file(s) to add, go to the destination folder, select the .stl file of the IOS, and click Open.
- Add the .stl file of the intraoral scan as segmentation by selecting Segmentation from the dropdown bar.
NOTE: The installed "IGT" module will now appear in the "Modules" dropdown menu. - Move the cursor over the module, and in the sidebar that appears, select Fiducial Registration Wizard.
- Select Create new Markups Fiducial from the dropdown bar in both the "From fiducials" and the "To fiducials" sections.
NOTE: The software will automatically name the two lists "From" and "To." The "From" list represents the moving volume, which in this case will be the IOS. The "To" list represents the fixed volume, which will be the CBCT dataset. - Place marker points on well-defined anatomical landmarks on the IOS using the "Place a markup point" icon next to the dropdown bar in the "From" section. Markup points will be numbered in order of placement.
NOTE: Place at least 6 points on the cusps and incisal edges of teeth. - Place markers in the same position to create the "To" list and in the same order on the CBCT dataset. Markup points with the same number must represent the same anatomical landmark.
- Create a transformation by selecting Create new LinearTransform from the dropdown menu in the "Registration result transform" section of the sidebar after the two lists are ready.
- Access the "Transforms" module and select the previously created transformation as the Active transform. In the "Apply transform" section, move the IOS segmentation and the "From" markups list from the "Transformable" box to the "Transformed" box to superimpose the IOS over the CBCT dataset.
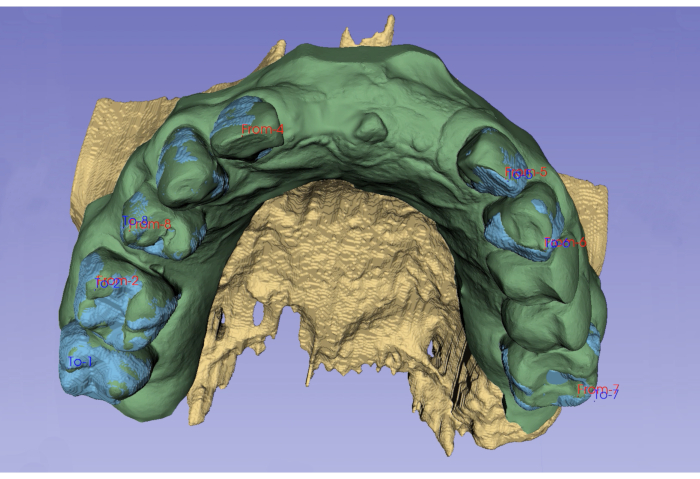
Figure 4: Spatial registration of IOS by placing fiducial markers on well-defined anatomical landmarks. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
NOTE: If necessary, the accuracy of the transformation can be improved by moving the markup points or by adding additional points.
2. Export models as .stl files for free-form surface modeling
- Export the matched hard- and soft-tissue models for further surface modeling after segmentation and spatial registration.
- Go to the Segmentations module and select the segmentation with the alveolar bone and teeth models as the active segmentation. Scroll down to the "Export to files" section, choose the destination folder, and select STL as the file format.
- Uncheck the Merge into single file box, set the Coordinate system to RAS, and click Export.
- Repeat the same process for the IOS, visible as a separate segmentation, save the scene, and close the imaging software.
3. Free-form surface modeling
- Surface smoothing
- Open the CAD software, and on the home screen, click Import. Select the .stl models that were previously exported from the DICOM image processing software.
NOTE: Even though smoothing was performed previously, the surface of the models reconstructed from the CBCT dataset will still appear pixelated, so further surface smoothing is necessary. - Go to Sculpt in the menu bar, and from the brush inventory, select Adaptive reduce.
NOTE: Brush size and strength must be adjusted, depending on the amount of smoothing.
- Open the CAD software, and on the home screen, click Import. Select the .stl models that were previously exported from the DICOM image processing software.
- Separate crown of the teeth from the IOS
NOTE: Crowns of teeth are depicted more accurately on the IOS than on segmented models; therefore, crowns of the segmented teeth models must be replaced with crowns from the IOS.- Click Select in the sidebar and select Brush as the selection tool. Use Unwrap brush brush mode and adjust the size of the brush. Using the brush, select the crown of each tooth until the marginal gingiva on the IOS.
NOTE: Selected surfaces are indicated with an orange color. - Move the cursor to Modify in the sidebar and select Smooth Boundary. Click Apply if the results are satisfactory.
NOTE: Now, the boundary of the selection precisely follows the marginal gingiva. - Go to Edit in the Select sidebar and click Separate to create an individual object from the selected area.
- Repeat the same process for all teeth.
- Go to Analysis in the menu bar and select Inspect.
NOTE: The program will indicate errors in the models. Holes are marked with a blue color. - Select Flat fill as the "Hole fill mode" and click Auto repair all to create closed models from the IOS model and the separated teeth models.Go to Sculpt and smooth the edges of the filled hole using Shrinksmooth brush.
- Repeat the process for all tooth crowns and the rest of the IOS.
- Click Select in the sidebar and select Brush as the selection tool. Use Unwrap brush brush mode and adjust the size of the brush. Using the brush, select the crown of each tooth until the marginal gingiva on the IOS.
- Merge crowns of the teeth with the segmented tooth models.
NOTE: If spatial registration was correctly done, the positions of the crowns of teeth on the IOS and the crowns of segmented teeth should match.- Use the Shrinksmooth brush on the segmented tooth model until they are completely cover by the tooth crowns separated from the IOS.
NOTE: Due to imperfections in both the segmentation and the IOS, the crowns don't always overlap completely. - Select both the separated crown and the segmented model of the same tooth in the Object Browser. In the sidebar that appears, select Boolean union, and click Accept.
NOTE: Now, the crown of the segmented tooth model is replaced by the crown separated from the IOS. - Use Shrinksmooth to smooth the transition.
- Use the Shrinksmooth brush on the segmented tooth model until they are completely cover by the tooth crowns separated from the IOS.
- Subtractions and model composition
- Subtract the bone model from the soft-tissue model to represent the clinical situation realistically.
NOTE: The original IOS without teeth became the model of the soft tissues. - Select both bone and soft-tissue models in the Object Browser and select Boolean Difference.
- Smooth transitions with the Shrinksmooth brush and remove protrusions from the bottom side of the soft-tissue model.
- Subtract teeth from the soft-tissue model using the same process and smooth transitions.
- Subtract the bone model from the soft-tissue model to represent the clinical situation realistically.
- Color models
- Color the surfaces of the models to give a more realistic look since the model is complete now with the teeth, soft tissues, and alveolar bone being separated from one another, representing the clinical situation in 3D.
- Select Sculpt from the sidebar and switch the little slider from Volume to Surface.
- Select PaintVertex from the brush inventory and select the desired color using the color wheel in the Color section of the sidebar. Color the surface of each model (e.g., bone: brown, soft tissue: pink, teeth: white)
Animated Figure 1: Animation of the final, colored model, ready for virtual surgical planning. Please click here to download this Figure.
Results
Virtual allowing three-dimensional (3D) models can be generated using radiographic image segmentation, spatial registration, and free-form modeling. The models digitally depict the clinical situation, making three-dimensional planning of various surgical interventions possible. With separate segmentation of bone and teeth, the boundary between the two anatomical structures is visible, 3D morphology and localization of periodontal intrabony defects are to be assessed. The severity, extent, and morphology of acute and chro...
Discussion
With the presented protocol, periodontal and alveolar defect morphologies can be visualized in three dimensions (3D), providing a more accurate depiction of the clinical situation than can be achieved by 2D diagnostic methods and 3D models generated with thresholding algorithms. The protocol can be divided into three major phases: (1) semi-automatic segmentation of CBCT datasets, (2) spatial registration of CBCT and IOS, and (3) free-form surface modeling. Technically, segmentation can be performed on any three-dimension...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
None
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 3DSlicer | 3DSlicer (The software was first developed at Queen’s University Canada and since it is open source it is constantly developed by it’s community) | 4.13.0-2021-03-19 | Open source radiographic image processing software platform. Software is primarily intended for general medicine, however the wide range of segmentation an modelling tools allow it’s use for dental purposes as well |
| Meshmixer | Autodesk Inc. | 3.5 | Open source free form surface modelling software developed for prototype development and basic 3D sculpting. However, due to the usefulness of tools for dental purpose, not just 3D models, but even static guides for navigated surgery can be designed. |
References
- Jacobs, R., Salmon, B., Codari, M., Hassan, B., Bornstein, M. Cone beam computed tomography in implant dentistry: recommendations for clinical use. BMC Oral Health. 18 (1), 88 (2018).
- Mangano, F., Gandolfi, A., Luongo, G., Logozzo, S. Intraoral scanners in dentistry: a review of the current literature. BMC Oral Health. 17 (1), 149 (2017).
- Pauwels, R., Araki, K., Siewerdsen, J. H., Thongvigitmanee, S. S. Technical aspects of dental CBCT: state of the art. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology. 44 (1), 20140224 (2015).
- Queiroz, P. M., Santaella, G. M., Groppo, F. C., Freitas, D. Q. Metal artifact production and reduction in CBCT with different numbers of basis images. Imaging Science in Dentistry. 48 (1), 41-44 (2018).
- Scarfe, W. C., Azevedo, B., Pinheiro, L. R., Priaminiarti, M., Sales, M. A. O. The emerging role of maxillofacial radiology in the diagnosis and management of patients with complex periodontitis. Periodontology 2000. 74 (1), 116-139 (2017).
- Fedorov, A., et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 30 (9), 1323-1341 (2012).
- Palkovics, D., Mangano, F. G., Nagy, K., Windisch, P. Digital three-dimensional visualization of intrabony periodontal defects for regenerative surgical treatment planning. BMC Oral Health. 20 (1), 351 (2020).
- Papadiochou, S., Pissiotis, A. L. Marginal adaptation and CAD-CAM technology: A systematic review of restorative material and fabrication techniques. Journal of Prosthetic Dentisty. 119 (4), 545-551 (2018).
- Xia, J. J., et al. Algorithm for planning a double-jaw orthognathic surgery using a computer-aided surgical simulation (CASS) protocol. Part 1: planning sequence. International Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery. 44 (12), 1431-1440 (2015).
- Xia, J. J., et al. Algorithm for planning a double-jaw orthognathic surgery using a computer-aided surgical simulation (CASS) protocol. Part 2: three-dimensional cephalometry. International Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery. 44 (12), 1441-1450 (2015).
- Lee, C. Y., Ganz, S. D., Wong, N., Suzuki, J. B. Use of cone beam computed tomography and a laser intraoral scanner in virtual dental implant surgery: part 1. Implant Dentistry. 21 (4), 265-271 (2012).
- Ganz, S. D. Three-dimensional imaging and guided surgery for dental implants. Dental Clinics of North America. 59 (2), 265-290 (2015).
- Güth, J. F., Kauling, A. E. C., Schweiger, J., Kühnisch, J., Stimmelmayr, M. Virtual simulation of periodontal surgery including presurgical CAD/CAM fabrication of tooth-colored removable splints on the basis of CBCT Data: A case report. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry. 37 (6), 310-320 (2017).
- Pauwels, R., et al. Effective radiation dose and eye lens dose in dental cone beam CT: effect of field of view and angle of rotation. The British Journal of Radiology. 87 (1042), 20130654 (2014).
- Li, Q., Chen, K., Han, L., Zhuang, Y., Li, J., Lin, J. Automatic tooth roots segmentation of cone beam computed tomography image sequences using U-net and RNN. Journal of X-ray Science and Technology. 28 (5), 905-922 (2020).
- Lahoud, P., et al. Artificial intelligence for fast and accurate 3D tooth segmentation on CBCT. Journal of Endodontics. 47 (5), 827-835 (2021).
- Blume, O., Donkiewicz, P., Back, M., Born, T. Bilateral maxillary augmentation using CAD/CAM manufactured allogenic bone blocks for restoration of congenitally missing teeth: A case report. Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry. 31 (3), 171-178 (2019).
- Hartmann, A., Seiler, M. Minimizing risk of customized titanium mesh exposures - a retrospective analysis. BMC Oral Health. 20 (1), 36 (2020).
- Varga, E., et al. Guidance means accuracy: A randomized clinical trial on freehand versus guided dental implantation. Clinical Oral Implants Research. 31 (5), 417-430 (2020).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved