A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Advanced Self-Healing Asphalt Reinforced by Graphene Structures: An Atomistic Insight
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Graphene-modified asphalt nanocomposite has shown an advanced self-healing ability compared to pure asphalt. In this protocol, molecular dynamics simulations have been applied in order to understand the role of graphene in the self-healing process and to explore the self-healing mechanism of asphalt components from the atomistic level.
Abstract
Graphene can improve the self-healing properties of asphalt with high durability. However, the self-healing behaviors of graphene-modified asphalt nanocomposite and the role of incorporated graphene are still unclear at this stage. In this study, the self-healing properties of pure asphalt and graphene-modified asphalt are investigated through molecular dynamics simulations. Asphalt bulks with two crack widths and locations for graphene are introduced, and the molecular interactions among asphalt components and the graphene sheet are analyzed. The results show that the location of graphene significantly affects the self-healing behaviors of asphalt. Graphene near the crack surface can greatly accelerate the self-healing process by interacting with the aromatic molecules through π-π stacking, while graphene at the top area of the crack tip has a minor impact on the process. The self-healing process of asphalt goes through the reorientation of asphaltene, polar aromatic, and naphthene aromatic molecules, and the bridging of saturate molecules between crack surfaces. This in-depth understanding of the self-healing mechanism contributes to the knowledge of the enhancement for self-healing properties, which will help to develop durable asphalt pavements.
Introduction
Deterioration under daily vehicle loadings and variant environmental conditions, and the aging of asphalt during service result in degradation or even structural failures, i.e., cracking and raveling, which can further weaken the durability of asphalt pavements. The inherent response of asphalt to repair micro-cracks and voids automatically helps it recover from damages and restore strength1. This self-healing capability can considerably extend the service life of asphalt, save costs on maintenance, and reduce the emission of greenhouse gases2,3. The self-healing behavior of asphalt generally depends on several influencing factors, including its chemical composition, the degree of damage, and environmental conditions4. The improved self-healing capability of asphalt that can fully heal damage within a short period is desired; this has attracted extensive research interest in better mechanical performance and durability for asphalt pavements within civil engineering.
Novel methods to improve the self-healing capability of asphalt mainly include three approaches - inducing heating, encapsulation healing, and incorporating nanomaterials - which can be applied individually or simultaneously5,6. Inducing heating can significantly improve the mobility of asphalt and activate its self-healing for recovery7. The self-healing technology of asphalt by inducing heating can be ascribed to the assisted self-healing technique, which indicates that the self-healing properties of asphalt are improved by external stimuli. The objective of adding the steel wool fibers is to enhance the electrical conductivity so as to increase the healing capacity of the asphalt binder8. The approach to induce heat is to expose these electrically conductive fibers to the high-frequency alternating electromagnetic field, which can induce eddy currents, and the heat energy can diffuse into the asphalt binder by the conductive fibers9. The steel wool fibers enhance not just the electrical conductivity but also the thermal conductivity, both of which can positively affect the self-healing properties of asphalt. However, it is challenging to select the proper mixing time for fibers10. The length of fibers decreases with increased mixing time and influences thermal conductivity, while the decreased mixing time leads to clusters of fibers and impedes the mechanical properties of asphalt9. The encapsulation method can supply light components of aged asphalt such as aromatics and saturates and refresh the self-healing capability of asphalt11,12. However, this is a once-only treatment, and the healing materials cannot be replenished after the release. With the development of nanotechnology, nanomaterials have become promising modifiers for enhancing asphalt-based materials. Asphalt binders incorporated with nanomaterials present better thermal conductivity and mechanical properties13. Graphene with excellent mechanical performance and high thermal performance is regarded as an excellent candidate to improve the self-healing ability of asphalt14,15,16,17. The increased healing properties of graphene-modified asphalt can be attributed to the fact that graphene increases the capacity of the asphalt binder to be heated and produce heat transfer inside the asphalt binder, which means that graphene-modified asphalt can be heated more rapidly and reach up to higher temperature than pure asphalt18. The generated heat can be transferred throughout the graphene-modified asphalt at a faster speed than that through pure asphalt. The crack region of the asphalt binder can be influenced easily and healed faster by the heat flow with higher temperature and higher heating capacity. The self-healing reaction will begin if the energy that is equal to or larger than the healing activation energy exists at the crack surface of the asphalt19. Graphene can improve the thermal activation healing performance and accelerate the healing rate of asphalt19,20. Besides, graphene can save heating energy up to 50% during the healing process, which can benefit energy efficiency and reduce maintenance costs21. As a microwave-absorbent material, graphene is reported to improve the healing ability of asphalt during the rest period of microwave heating22. It is expected that the addition of graphene into asphalt will improve not only the mechanical performance but also the self-healing and energy-saving capacity, which requires in-depth knowledge of the self-healing mechanism.
Self-healing at the nanoscale is mainly due to the wetting and diffusion of asphalt molecules at the fractured faces23. As asphalt consists of various polar and non-polar molecules, its self-healing capability is strongly related to molecular interactions and movements of asphalt molecules of different components1. However, current research mainly relies on experimental techniques to quantify macroscopic mechanical properties, which causes missing information in the change of microstructures and the interactions among asphalt molecules when trying to understand the healing mechanism. The reinforcing mechanism of graphene in the self-healing capability of asphalt is also unclear at this stage. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations play an influential role in investigating molecular interactions and motions of nanocomposite systems, and link microstructural deformation with molecular interactions and movements24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31. MD simulations have become more and more popular for analyzing material behaviors that cannot be accessed easily by experiments32,33. Existing studies have shown the feasibility and availability of MD simulations in asphalt systems; the cohesion, adhesion, aging, and thermomechanical properties of asphalt and asphalt composites can be explored by MD simulations34,35,36,37. The self-healing behaviors of asphalt can also be predicted by MD simulations38,39,40. Therefore, it is believed that the investigation using MD simulations is an effective way to understand both the self-healing and reinforcing mechanisms.
The objectives of this study are to investigate the self-healing behaviors of pure asphalt and graphene-modified asphalt nanocomposites and to understand the role of graphene in improving the healing capacity of asphalt through MD simulations. The self-healing simulations of pure asphalt and graphene-modified asphalt composites are carried out by introducing cracks into the initial structures. The self-healing capabilities are characterized by the contour of atom numbers, the reorientation and entanglement of molecules at the fractured face, and the mobility of asphalt components during the self-healing processes. By investigating the healing efficiency of graphene at different sites, the reinforcing mechanism of graphene contributing to the self-healing abilities of asphalt is unveiled, which can help with the monitoring of nanofillers in an optimal way and thus enable the life extension of asphalt pavements. An investigation of the self-healing capacity at the atomistic scale can provide an efficient way to develop advanced asphalt-based materials for future research.
According to asphalt chemistry, asphalt consists of various types of hydrocarbons and non-hydrocarbons with different polarity and shapes, which can mainly be divided into the four components of asphaltene, polar aromatics, naphthene aromatics, and saturates41,42. Asphaltene molecules are relatively larger and heavier than other molecules in asphalt, with a mean atomic mass of roughly 750 g/mol and a molecular diameter in the range of 10-20 Å. It has been widely accepted that asphaltene is composed of large aromatic cores that contain heteroatoms and are surrounded by different lengths of alkyl groups43. A modified asphaltene molecule is constructed, as shown in Figure 1a. The molecules of polar aromatics and naphthene aromatics are constructed based on the polarity and the element ratio of asphalt molecules, with benzobisbenzothiophene (C18H10S2) representing the polar aromatic molecule and 1,7-dimethylnaphthalene (C12H12) chosen as the representative naphthene aromatic molecule, as shown in Figure 1b-c. N-docosane (n-C22H46) is constructed as shown in Figure 1d. The parameters listed in Table 1 for asphalt molecules are selected and used to meet the desired criteria, including the elemental mass fraction, the atom ratio, and the aromatic/aliphatic ratio, of real asphalt from experiments41. The same mass ratio has been defined in our previous studies, and the other thermomechanical properties like density, glass transition temperature, and viscosity are in good agreement with experimental data of real asphalt36. The molecular structure of graphene applied in this study is shown in Figure 1e. The adopted graphene sheet in this study has no defect and no fold compared to that of the real case, while the real graphene sheet usually has several defects such as atomic vacancies and Stone-Wales defects44, and some of the graphene sheets can be folded during the mixing process in the asphalt matrix45. These imperfect situations are not considered in this study, since we focus on the effect of the site of the graphene sheet on the self-healing properties and choose it as the only variable. The variables of graphene sheets in terms of the defects and folded cases will be the focus of our future studies. The mass ratio of graphene to asphalt in this study is 4.75%, which is the normal situation (<5%) for graphene modified asphalt in the experiment46,47.
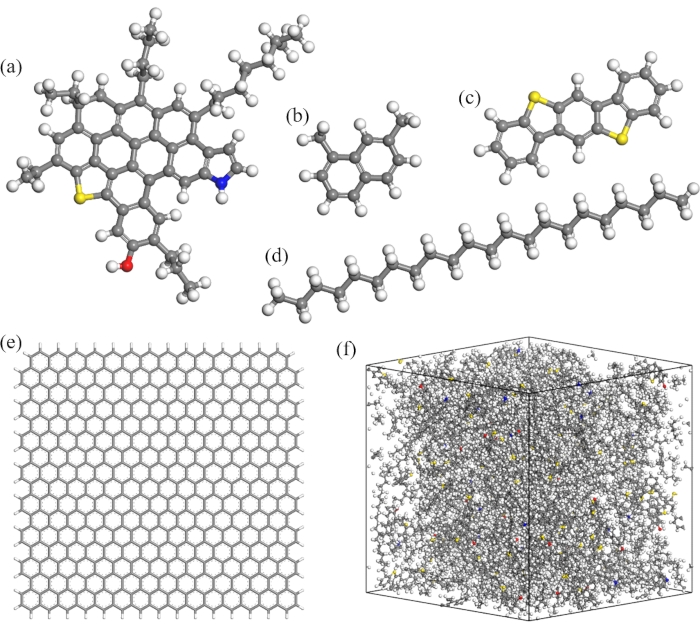
Figure 1: Chemical structure. The atomistic models of (a) asphaltene molecule (C53H55NOS), (b) naphthene aromatic molecule (C12H12), (c) polar aromatic molecule (C18H10S2), (d) saturate molecule (C22H46), (e) graphene, and (f) pure asphalt. For the atomistic asphalt model, the carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and hydrogen atoms are shown in gray, red, blue, yellow, and white, respectively. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Asphalt model | Mass (g/mol) | Chemical formula | Numbers of molecules | Total mass (g/mol) | Mass fraction (%) |
| Asphaltene | 754.04 | C53H55NOS | 43 | 32423.72 | 26 |
| Naphthene aromatic | 156.22 | C12H12 | 65 | 10154.3 | 8 |
| Polar aromatic | 290.38 | C18H10S2 | 74 | 21485.16 | 17 |
| Saturate | 310.59 | C22H46 | 205 | 63670.95 | 49 |
| Asphalt binder | 387 | 127734.13 | 100 | ||
| Graphene | 6369.28 | C525H63 | 1 | 6369.28 |
Table 1: Overall components of pure asphalt model and graphene-modified asphalt model.
With respect to the protocol described below, two types of wedge-like cracks with different sizes are inserted into the middle of the asphalt model with a blunt crack tip and two parallel crack surfaces, while the middle-top area of the asphalt bulk remains intact. Two crack widths are chosen as 15 Å and 35 Å, as shown in Figure 2a-b. The reason for selecting 15 Å is that the crack width should be wider than the cutoff of 12 Å to avoid the early self-healing of asphalt molecules during the equilibrium process while investigating an extreme case for a small crack. The reason for selecting 35 Å is that the crack width should be wider than the length of the saturate molecules of 34 Å in order to prevent the bridging effect. The height of the crack is 35 Å, the same as the box width, and the depth of the crack is 70 Å, the same as the box length. In the real situation, the observed micro-crack sizes can be varied in the range from several micrometers to several millimeters, which is far larger than the length scale we are modeling here. Normally, the length scale in MD simulation is limited to the scale of 100 nm, which is still several orders of magnitude smaller than the real crack size. However, the cracks initiate at the nanoscale and grow into macroscale cracks with continuous deformation48. The understanding of the self-healing mechanism at the nanoscale can help to prevent the growth and further propagation of the crack at the macroscale. Even though the selected crack sizes are in the range of nanometer, the results can still be influential and applicable to explore the self-healing behaviors of asphalt molecules. There are two locations for the graphene sheets in the crack areas: one is on top of the crack tip and the other is perpendicular to the left crack surface. It has been found that these are the most common positions for graphene in graphene-modified nanocomposites with cracks49.
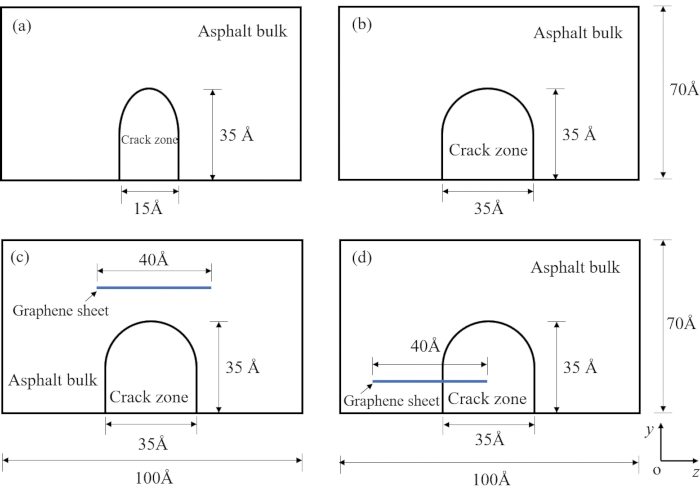
Figure 2: The self-healing schemes for pure asphalt and graphene-modified asphalt. The self-healing model of pure asphalt with a crack width of (a) 15 Å and (b) 35 Å. The self-healing model of graphene-modified asphalt with the graphene sheet is located (c) at the top of the crack tip and (d) perpendicular to the crack surface. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
In MD simulations, the intramolecular and intermolecular interactions in the asphalt nanocomposites are described by the Consistent Valence Forcefield (CVFF)50, which works well with asphalt and graphene-based materials. The functional form of CVFF is expressed as the following expression:
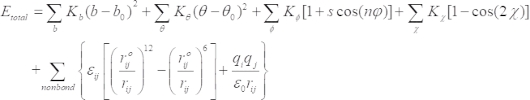 1
1
Here, the total energy Etotal is composed of the bonded energy terms and the non-bonded energy terms. The bonded interactions consist of the covalent bond stretching, the bond angle bending energy, the torsion angle rotation, and the improper energies as expressed in the first four terms. The non-bonded energy includes an LJ-12-6 function for the van der Waals (vdW) term and a Coulombic function for the electrostatic interactions. CVFF has been widely employed in simulating asphalt materials51,52. The simulated physical and mechanical properties such as density, viscosity, and bulk modulus are in good agreement with the experimental data, which demonstrates the reliability of CVFF51. CVFF is not only suitable for inorganic materials, but it has also been successfully employed in structures consisting of organic and inorganic phases such as asphalt-silica52 and the system of epoxy-graphene53. In addition, the interfacial interactions between graphene and asphalt can be characterized by CVFF36,54. Since the major part in selecting forcefield is to determine the asphalt-graphene interface, the non-bonded interactions described by CVFF are more reliable, which is also considered in our previous study36. Overall, the forcefield CVFF is adopted in this study. The partial charges for different kinds of atoms are calculated by the forcefield-assigned method.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Build the atomistic models
- Open the Materials Studio software to create five 3D atomistic documents and rename these documents as graphene, asphaltene, polar aromatics, naphthene aromatics, and saturates, respectively.
- Build the graphene model by creating the unit cell of graphene sheet in the 3D atomistic document using the Sketch Atom option.
- Construct the final structure using the Supercell option in the Build > Symmetry menu. Define the size of the graphene sheet as 40 Å x 40 Å, which is larger than the asphalt chains and the crack width.
- Build and pack the four types of asphalt molecules.
- Use the Sketch Atom option to draw the molecular structures of asphaltene, polar aromatics, naphthene aromatics, and saturates separately.
- Pack the four kinds of asphalt molecules into the simulation box using the Calculation option in the Modules > Amorphous Cell menu.
- Build the asphalt structure with the crack.
- Set the height of the crack zone in the x dimension the same as the height of the box of 70 Å and the depth of the crack zone in the y dimension is half of the height of the box as 35 Å.
- Set two cases of the crack widths in the z dimension of 15 Å and 35 Å. Delete the redundant molecules in the crack zones of the middle-down area of asphalt bulk using the Delete option and keep the asphalt matrix in the middle-up area unchanged.
- Build the graphene-modified asphalt structure with the crack. Incorporate the graphene sheet into the top area of the crack tip and the left crack surface separately before the packing step using the Copy + Paste command.
- Pack the asphalt molecules into the simulation box based on the final compositions listed in Table 1 to construct the graphene-modified asphalt structure.
- Convert the structure file to a data file. Save the structure files as the molecule files with structure information (*.car and *.mdf) from Materials Studio. Convert the molecule files (*.car and *.mdf) to data files using the msi2lmp tool in large-scale atomic/molecular massively parallel simulator (LAMMPS)55 package. Read the data file by the read_data command in LAMMPS.
2. Perform the simulations
- Define the parameters of the simulations.
- Set the timestep as 1 fs in the input file considering the balance of accuracy and efficiency of the carried simulations.
- Set the cutoff distance of non-bonded interactions as 12 Å, which is less than half the length of the simulation box in consideration of the periodic boundary condition and the calculational efficiency.
- Employ the particle-particle particle-mesh (PPPM) algorithm to describe the long-range Coulombic interactions and set the relative error in per-atom forces calculated by the long-range solver as 10-5 for high accuracy.
- Fix the profile of crack. Select the asphalt molecules on the profile by the Group Molecules command in LAMMPS. Apply the constraints on the asphalt molecules using the Fix Spring/Self command in LAMMPS to avoid the movements of asphalt molecules.
- Achieve the equilibrium
- Keep the whole simulation box fully relaxed after 500 ps under the isothermal-isobaric (NPT) ensemble with a temperature of 300 K and pressure of 1 atm.
- Make the asphalt bulk equilibrated to the desired density value of the experimental measurements41 of 0.95-1.05 g/cm3 by continuously examining the temperature, pressure, density, and energy values using the Thermal command.
- Check the convergence of potential energy and the mean-squared displacement (MSD) in the whole system for achieving the fully relaxed state.
- Perform the self-healing process.
- Set the whole simulation box under the NPT ensemble with a temperature of 300 K and pressure of 1 atm.
- Remove the constraint of the asphalt molecules on the contour of the crack zone.
- Track and record the size of the simulation box and the coordinates of atoms and use the Dump command for postprocessing.
- Average the simulation results during the self-healing process over three independent configurations with three different initial velocity seeds in order to decrease the random errors.
3. Postprocessing
- Visualize the self-healing behaviors. Open the Open Visualization Tool OVITO56 to visualize the simulation progress, and then open the trajectory files in the lammpstrj format generated by LAMMPS55. Record the snapshots of the self-healing process and track the paths of asphalt molecules using the Render command.
- Analyze the contour of the atom number. Export the coordinates of the atoms to data analysis and graphing software from the trajectory files outputted from LAMMPS. Project the coordinates of atoms in the whole system onto the yz plane. Record atom numbers at different areas of the yz plane and plot the contour with different colors.
- Analyze the atom mobility and relative position.
- Analyze the atom mobility of different asphalt components by the mean-squared displacement (MSD) using the Compute msd command.
- Calculate the relative positions between graphene and asphalt molecules by the radial distribution functions (RDF) curves for the system of graphene-modified asphalt systems with the 15 Å and 35 Å crack widths using the Compute rdf command in LAMMPS.
- Draw the RDF curves to check how the density of asphalt varies as a function of distance from the graphene sheet.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
The contour of atom number
The contours of the atom number of pure asphalt and graphene-modified asphalt models in the yz plane are shown in Figure 3, where the color bar from blue to red exhibits atom numbers varying from 0 to 28. Figure 3a-c illustrates the contour of the atom number of the structures with 15 Å crack width in pure asphalt and asphalt nanocomposites modified by graphene at the crack ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The critical steps within the Protocol part are as follows: step 1.4 - Build and pack the four types of asphalt molecules; step 1.5 - Build the asphalt structure with the crack; step 2.3 - Achieve the equilibrium; step 2.4 - Perform the self-healing process. These steps indicate the most cohesive and important contents of the protocol. To create the desired shapes of the inserted crack, the packing process is modified compared to the normal packing in Materials Studio. The crack shape is created and filled inside the sim...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the support from City University of Hong Kong Strategic Research Grant with the Project No. 7005547, the support from the Research Grants Council (RGC) of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China, with the Project No. R5007-18, and the support from Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee under the grant JCYJ20170818103206501.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Atomistic models of asphalt and graphene/Materials Studio | BIOVIA | Materials Studio 8.0 | The atomistic models are built for molecular dynamics simulations. |
| Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator Package | Sandia National Laboratories | lammps-stable20 | The equilibrium is achieved under NPT ensemble, and the atomistic models get self-healed. |
| OVITO | Materials Science Department of Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany | ovito-basic-3.1.0-win64 | The self-healing behaviors of the atomistic models are visualized. |
| Origin | OriginLab | Origin 2018 64Bit | The contours of the atom numbers of the trajectory are drawn and analyzed. |
References
- Sun, D., et al. A comprehensive review on self-healing of asphalt materials: Mechanism, model, characterization and enhancement. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 256, 65-93 (2018).
- Hung, A. M., Mousavi, M., Fini, E. H. Implication of wax on hindering self-healing processes in bitumen. Applied Surface Science. 523, 146449(2020).
- Lv, Q., et al. Investigating the asphalt binder/mastic bonding healing behavior using bitumen bonding strength test and X-ray Computed Tomography scan. Construction and Building Materials. 257, 119504(2020).
- Liang, B., et al. Review on the self-healing of asphalt materials: Mechanism, affecting factors, assessments and improvements. Construction and Building Materials. 266, 120453(2021).
- Xu, S., et al. Self-healing asphalt review: From idea to practice. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 5, 1800536(2018).
- Tabaković, A., Schlangen, E. Self-healing Materials, Advances in Polymer Science. , Chapter 335 285-306 (2015).
- García, Á Self-healing of open cracks in asphalt mastic. Fuel. 93, 264-272 (2012).
- Karimi, M. M., Amani, S., Jahanbakhsh, H., Jahangiri, B., Alavi, A. H. Induced heating-healing of conductive asphalt concrete as a sustainable repairing technique: A review. Cleaner Engineering and Technology. 4, (2021).
- Gulisano, F., Gallego, J. Microwave heating of asphalt paving materials: Principles, current status and next steps. Construction and Building Materials. 278, 121993(2021).
- García, Á, Schlangen, E., Ven, M. vd, Bochove, G. v Optimization of composition and mixing process of a self-healing porous asphalt. Construction and Building Materials. 30, 59-65 (2012).
- Aguirre, M. A., Hassan, M. M., Shirzad, S., Daly, W. H., Mohammad, L. N. Micro-encapsulation of asphalt rejuvenators using melamine-formaldehyde. Construction and Building Materials. 114, 29-39 (2016).
- Su, J. -F., Qiu, J., Schlangen, E., Wang, Y. -Y. Experimental investigation of self-healing behavior of bitumen/microcapsule composites by a modified beam on elastic foundation method. Materials and Structures. 48 (12), 4067-4076 (2014).
- Yoo, D. Y., Kim, S., Kim, M. J., Kim, D., Shin, H. O. Self-healing capability of asphalt concrete with carbon-based materials. Journal of Materials Research and Technology-Jmr&T. 8 (1), 827-839 (2019).
- Qin, Z., Jung, G. S., Kang, M. J., Min Jeong, M. J. The mechanics and design of a lightweight three-dimensional graphene assembly. Science Advances. 3 (1), 1601536(2017).
- Jung, G. S., Yeo, J., Tian, Z., Qin, Z., Buehler, M. J. Unusually low and density-insensitive thermal conductivity of three-dimensional gyroid graphene. Nanoscale. 9 (36), 13477-13484 (2017).
- Campbell, P. G., Worsley, M. A., Hiszpanski, A. M., Baumann, T. F., Biener, J. Synthesis and functionalization of 3D nano-graphene materials: Graphene aerogels and graphene macro assemblies. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (105), e53235(2015).
- Li, H., et al. Induction heating and healing behaviors of asphalt concretes doped with different conductive additives. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering. 2019, 1-10 (2019).
- Moreno-Navarro, F., Sol-Sánchez, M., Gámiz, F., Rubio-Gámez, M. C. Mechanical and thermal properties of graphene modified asphalt binders. Construction and Building Materials. 180, 265-274 (2018).
- Liu, J., Hao, P., Dou, Z., Wang, J., Ma, L. Rheological, healing and microstructural properties of unmodified and crumb rubber modified asphalt incorporated with graphene/carbon black composite. Construction and Building Materials. 305, 124512(2021).
- Wang, R., Qi, Z., Li, R., Yue, J. Investigation of the effect of aging on the thermodynamic parameters and the intrinsic healing capability of graphene oxide modified asphalt binders. Construction and Building Materials. 230, 116984(2020).
- Gulisano, F., Crucho, J., Gallego, J., Picado-Santos, L. Microwave healing performance of asphalt mixture containing Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) slag and Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNPs). Applied Sciences. 10 (4), 1428(2020).
- Li, C., Wu, S., Chen, Z., Tao, G., Xiao, Y. Improved microwave heating and healing properties of bitumen by using nanometer microwave-absorbers. Construction and Building Materials. 189, 757-767 (2018).
- Varma, R., Balieu, R., Kringos, N. A state-of-the-art review on self-healing in asphalt materials: Mechanical testing and analysis approaches. Construction and Building Materials. 310, 125197(2021).
- Lau, D., Jian, W., Yu, Z., Hui, D. Nano-engineering of construction materials using molecular dynamics simulations: Prospects and challenges. Composites Part B: Engineering. 143, 282-291 (2018).
- Jian, W., Lau, D. Creep performance of CNT-based nanocomposites: A parametric study. Carbon. 153, 745-756 (2019).
- Wang, X. Q., Jian, W., Buyukozturk, O., Leung, C. K. Y., Lau, D. Degradation of epoxy/glass interface in hygrothermal environment: An atomistic investigation. Composites Part B: Engineering. 206, 108534(2021).
- Jian, W., Lau, D. Understanding the effect of functionalization in CNT-epoxy nanocomposite from molecular level. Composites Science and Technology. 191, 108076(2020).
- Hao, H., Tam, L. -h, Lu, Y., Lau, D. An atomistic study on the mechanical behavior of bamboo cell wall constituents. Composites Part B: Engineering. 151, 222-231 (2018).
- Qin, R., Zhou, A., Yu, Z., Wang, Q., Lau, D. Role of carbon nanotube in reinforcing cementitious materials: An experimental and coarse-grained molecular dynamics study. Cement and Concrete Research. 147, 106517(2021).
- Jian, W., Wang, X., Lu, H., Lau, D. Molecular dynamics simulations of thermodynamics and shape memory effect in CNT-epoxy nanocomposites. Composites Science and Technology. 211, 108849(2021).
- Jing, C., et al. Regenerated and rotation-induced cellulose-wrapped oriented CNT fibers for wearable multifunctional sensors. Nanoscale. 12 (30), 16305-16314 (2020).
- Yazdandoost, F., Mirzaeifar, R., Qin, Z., Buehler, M. J. Multiscale mechanics of the lateral pressure effect on enhancing the load transfer between polymer coated CNTs. Nanoscale. 9 (17), 5565-5576 (2017).
- Doblack, B. N., Allis, T., Davila, L. P. Novel 3D/VR interactive environment for MD simulations, visualization and analysis. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (94), (2014).
- Xu, M., et al. Improved chemical system for molecular simulations of asphalt. Energy & Fuels. 33 (4), 3187-3198 (2019).
- Xu, G., Wang, H. Molecular dynamics study of oxidative aging effect on asphalt binder properties. Fuel. 188, 1-10 (2017).
- Nie, F., Jian, W., Lau, D. An atomistic study on the thermomechanical properties of graphene and functionalized graphene sheets modified asphalt. Carbon. 182, 615-627 (2021).
- Cui, B., Gu, X., Hu, D., Dong, Q. A multiphysics evaluation of the rejuvenator effects on aged asphalt using molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Cleaner Production. 259, (2020).
- Sun, W., Wang, H. Self-healing of asphalt binder with cohesive failure: Insights from molecular dynamics simulation. Construction and Building Materials. 262, 120538(2020).
- He, L., et al. Self-healing behavior of asphalt system based on molecular dynamics simulation. Construction and Building Materials. 254, 119225(2020).
- Sun, D., Lin, T., Zhu, X., Tian, Y., Liu, F. Indices for self-healing performance assessments based on molecular dynamics simulation of asphalt binders. Computational Materials Science. 114, 86-93 (2016).
- Li, D. D., Greenfield, M. L. Chemical compositions of improved model asphalt systems for molecular simulations. Fuel. 115, 347-356 (2014).
- Redelius, P., Soenen, H. Relation between bitumen chemistry and performance. Fuel. 140, 34-43 (2015).
- Schulze, M., Lechner, M. P., Stryker, J. M., Tykwinski, R. R. Aggregation of asphaltene model compounds using a porphyrin tethered to a carboxylic acid. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. 13 (25), 6984-6991 (2015).
- Robertson, A. W., Warner, J. H. Atomic resolution imaging of graphene by transmission electron microscopy. Nanoscale. 5 (10), 4079-4093 (2013).
- Yang, L., Zhou, D., Kang, Y. Rheological properties of graphene modified asphalt binders. Nanomaterials (Basel). 10 (11), 2197(2020).
- Zeng, W. B., Wu, S. P., Pang, L., Sun, Y. H., Chen, Z. W. The utilization of graphene oxide in traditional construction materials: Asphalt. Materials. 10 (1), 48(2017).
- Li, R., Xiao, F., Amirkhanian, S., You, Z., Huang, J. Developments of nano materials and technologies on asphalt materials - A review. Construction and Building Materials. 143, 633-648 (2017).
- Yu, T., Zhang, H., Wang, Y. Multi-gradient analysis of temperature self-healing of asphalt nano-cracks based on molecular simulation. Construction and Building Materials. 250, 118859(2020).
- Gao, C., Liu, T., Shuai, C., Peng, S. Enhancement mechanisms of graphene in nano-58S bioactive glass scaffold: mechanical and biological performance. Scientific Reports. 4, 4712(2014).
- Maple, J. R., Dinur, U., Hagler, A. T. Derivation of force fields for molecular mechanics and dynamics from ab initio energy surfaces. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 85 (15), 5350-5354 (1988).
- Xu, M., Yi, J., Feng, D., Huang, Y. Diffusion characteristics of asphalt rejuvenators based on molecular dynamics simulation. International Journal of Pavement Engineering. 20 (5), 615-627 (2019).
- Wang, H., Lin, E., Xu, G. Molecular dynamics simulation of asphalt-aggregate interface adhesion strength with moisture effect. International Journal of Pavement Engineering. 18 (5), 414-423 (2017).
- Yu, J., et al. Insights on the capillary transport mechanism in the sustainable cement hydrate impregnated with graphene oxide and epoxy composite. Composites Part B: Engineering. 173, (2019).
- Zhou, X., et al. Evaluation of thermo-mechanical properties of graphene/carbon-nanotubes modified asphalt with molecular simulation. Molecular Simulation. 43 (4), 312-319 (2017).
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular-dynamics. Journal of Computational Physics. 117 (1), 1-19 (1995).
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO-the Open Visualization Tool. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering. 18 (1), 015012(2010).
- Chen, Z., Pei, J., Li, R., Xiao, F. Performance characteristics of asphalt materials based on molecular dynamics simulation-A review. Construction and Building Materials. 189, 695-710 (2018).
- Sun, D., Sun, G., Zhu, X., Ye, F., Xu, J. Intrinsic temperature sensitive self-healing character of asphalt binders based on molecular dynamics simulations. Fuel. 211, 609-620 (2018).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved