10.5 : Relating Angular And Linear Quantities - I
If the rotational definitions are compared with the definitions of linear kinematic variables from motion along a straight line and motion in two and three dimensions, we can observe a mapping of the linear variables to the rotational ones.
When comparing the linear and rotational variables individually, the linear variable of position has physical units of meters, whereas the angular position variable has dimensionless units of radians, as it is the ratio of two lengths. The linear velocity has units of m/s, and its counterpart, the angular velocity, has units of rad/s.
In the case of circular motion, the linear tangential speed of a particle at a radius r from the axis of rotation is related to the angular velocity by the relation
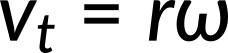
This could also apply to points on a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis. Here, only circular motion is considered. In a circular motion, both uniform and nonuniform, there exists a centripetal acceleration. The centripetal acceleration vector points inward from the particle executing circular motion toward the axis of rotation.
Thus, in a uniform circular motion, when the angular velocity is constant and the angular acceleration is zero, we observe a linear acceleration, that is, centripetal acceleration, since the tangential speed is a constant.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 10.3: Relating Angular and Translational Quantities.
Bölümden 10:

Now Playing
10.5 : Relating Angular And Linear Quantities - I
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
6.5K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.1 : Açısal Hız ve Yer Değiştirme
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
15.0K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.2 : Açısal Hız ve İvme
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
9.0K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.3 : Sabit Açısal İvme ile Dönme - I
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
6.6K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.4 : Sabit Açısal İvme ile Dönme - II
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
5.9K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.6 : Açısal ve Doğrusal Büyüklüklerin İlişkilendirilmesi - II
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
5.4K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.7 : Atalet Momenti
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
11.9K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.8 : Atalet Momenti ve Dönme Kinetik Enerjisi
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
7.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.9 : Atalet momenti: hesaplamalar
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
6.7K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.10 : Bileşik cisimlerin atalet momenti
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
6.1K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.11 : Paralel Eksen Teoremi
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
6.4K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.12 : Dik Eksen Teoremi
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
2.7K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.13 : Dönen Koordinat Sistemlerinde Vektör Dönüşümü
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
1.4K Görüntüleme Sayısı

10.14 : Coriolis Kuvveti
Rotasyon ve Rijit Cisimler
3.1K Görüntüleme Sayısı
JoVE Hakkında
Telif Hakkı © 2020 MyJove Corporation. Tüm hakları saklıdır