需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
亲和色谱法表达和纯化人基质金属蛋白酶-3
摘要
His-tag纯化,透析和活化用于提高细菌中可溶性活性基质金属蛋白酶-3催化结构域蛋白表达的产量。蛋白质级分通过SDS-PAGE凝胶进行分析。
摘要
基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)属于麦地金星蛋白酶家族,在细胞外基质(ECM)降解和重塑中起核心作用,以及与几种生长因子和细胞因子的相互作用。特异性 MMP 的过表达是多种疾病的原因,如癌症、神经退行性疾病和心血管疾病。MMPs最近一直是人们关注的焦点,作为开发可以治疗与MMP过表达相关的疾病的治疗方法的目标。
为了研究溶液中的MMP机制,需要更简单和更强大的重组蛋白表达和纯化方法来生产活性,可溶性MMP。然而,由于缺乏翻译后机制,大多数MMPs的催化结构域不能在 大肠 杆菌(大肠杆菌)中以可溶性形式表达,而哺乳动物表达系统通常成本高昂且产量较低。MMP包涵体必须经历繁琐而费力的广泛纯化和重新折叠过程,从而显着降低MPP在天然构象中的产量。本文提出了一种使用Rosetta2(DE3)pLysS(以下简称R2DP)细胞产生基质金属蛋白酶-3催化结构域(MMP-3cd)的方案,该结构域包含N端His-tag,后跟pro-domain(Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd)用于亲和纯化。R2DP细胞通过含有细菌表达系统中通常罕见的密码子的氯霉素耐药质粒增强真核蛋白的表达。与重组蛋白表达的传统细胞系BL21(DE3)相比,使用这种新菌株的纯化提高了纯化的Hixx6-pro-MMP-3cd的产量。在激活和脱盐后,pro结构域与N端His-tag一起被切割,提供活性MMP-3cd,可立即用于无数 体外 应用。该方法不需要昂贵的设备或复杂的融合蛋白,并且描述了细菌中重组人MMP的快速产生。
引言
大多数复杂的真核蛋白在表达后会经历复杂的翻译后修饰,需要高度辅助的蛋白质折叠和辅助因子才能发挥作用1。由于成本高昂且缺乏可靠的表达和纯化方法,即使在小规模的实验室实验中,在细菌宿主中产生大量可溶性人蛋白仍然是一项重大挑战2,3。MMPs,具有大分子量的人内肽酶,当在 大肠杆菌 中表达时,通常表现为不溶性包涵体。提取可溶性人MMP通常会导致费力,耗时的溶解和重新折叠过程4。
MMP在生理和致病过程中都起着关键作用。人MMP是23种锌内肽酶的家族,按结构和底物特异性分类,尽管具有高度保守的催化结构域,但其表达方式不同5,6。MMPs作为无活性酶原分泌,通过翻译后激活及其内源性抑制剂,金属蛋白酶的组织抑制剂(TIMPs)7,8,9,10进行调节。虽然MMP最初因其在ECM周转中的作用而得到认可,但它也与发育,形态发生,组织修复和重塑有关8。MMPs的失调与癌症以及神经退行性疾病,心血管疾病和纤维化疾病以及其他疾病显着相关5,7。
开发强大的大规模MMP生产方法对于确保通过生化和基于细胞的测定对MMP机制的未来研究取得成功至关重要。各种MMP以前已经在细菌中表达11,包括Hisx6标记的MMPs,而不会改变MMP活性12,13,14,15。但是,这些方法包括可能难以复制的繁琐、冗长的步骤。
哺乳动物细胞也可用于表达许多不同的人类蛋白质,同时确保正确的翻译后修饰16。虽然哺乳动物表达系统是生产具有适当翻译后修饰的重组人类蛋白的理想选择,但该方法的主要缺点是初始产量低,生长培养基和试剂昂贵,达到稳定表达系的时间长,以及被真菌或细菌等其他物种污染的风险2,11.此外,哺乳动物细胞系中的MMP产生来自相关细胞蛋白(如TIMPs或纤连蛋白)的杂质11。与在哺乳动物细胞中观察到的缓慢细胞生长不同,细菌表达系统在短时间内提供大规模的蛋白质生产以及更简单的培养基和生长要求。然而,由于细菌表达系统中缺乏其他相关细胞蛋白(即TIMPs),较高浓度的活性MMP通过自体蛋白水解而降解,导致MMP产量低17。
本文描述了使用 大肠杆菌 作为表达宿主的重组Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd的细菌表达,纯化和活化的详细方法,因为它具有可负担性,简单性并且成功产生更高的MMPs产量2,3,18。由于 大肠杆菌 缺乏重组MMP和其他复杂蛋白质所需的蛋白质折叠机制和翻译后处理,许多 大肠杆菌 菌株已被设计以克服这些限制,使 大肠杆菌 成为更适合表达重组人MMP-3cd的宿主,19,20.例如,本研究中使用的R2DP菌株通过提供含有 大肠杆菌中很少使用的密码子的氯霉素耐药质粒来增强真核表达。
如本方案所述,在R2DP细胞中从pET-3a载体中过表达相对纯的包涵体(图1)后,提取Hisx6-pro-MMP-3催化结构域(MMP-3cd)蛋白并变性4。使用亲和标签色谱纯化Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd3,19。在重新折叠和透析后,Pro-MMP-3cd(酶原)被4-氨基苯基乙酸汞(APMA)激活,SDS-PAGE分析用于评估产量和进一步纯化的必要性5,21。该协议以可溶性MMP-3cd的表达、纯化和活化为例。然而,它也可以用作具有相似表达和激活机制的其他MMPs和人蛋白酶表达的指南(图2)。对于MMP-3cd以外的其他蛋白质,建议读者在尝试此方案之前确定其靶蛋白的最佳缓冲液组成和方法。
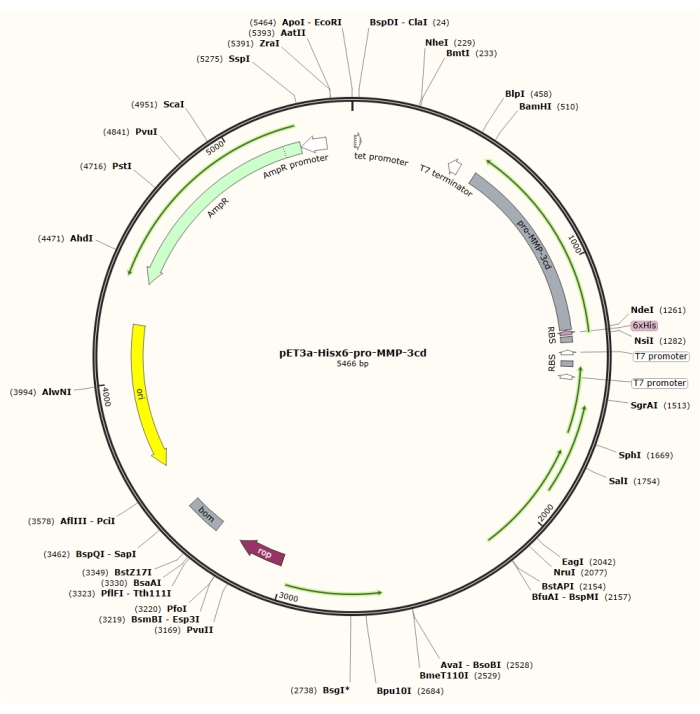
图1:pET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd质粒的质粒图谱。 pET-3a载体包括氨苄西林抗性基因。将N端Hisx6标签序列克隆到基于pET-3a的载体中,包括pro-MMP-3cd,以在BamHI和NdeI限制位点之间的T7启动子的控制下产生pET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd结构。 请点击此处查看此图的放大版本。

图2:Pro-MMP-3cd的细菌表达,纯化,重新折叠和活化。 1.1:pET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd质粒转化为BL21(DE3)或R2DP细胞。1.2:使用IPTG诱导Pro-MMP-3cd蛋白表达。1.3:化学裂解和超声处理用于提取Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd蛋白,这些蛋白主要不溶于包涵体并存在于包涵体中。尿素用于使包涵体中的蛋白质变性和增溶。变性Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd蛋白通过亲和色谱纯化纯化。3.在透析过程中,通过逐渐从缓冲液中除去尿素,将洗脱的Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd缓慢重新折叠。4.最后,通过去除N端前肽结构域,使用APMA激活重新折叠的MMP-3cd蛋白。APMA随后通过脱盐从溶液中除去。这些数字对应于描述这些步骤的协议部分。缩写:MMP-3cd =基质金属蛋白酶-3催化结构域;APMA = 4-氨基苯基汞乙酸酯。 请点击此处查看此图的放大版本。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
研究方案
1. MMP表达式
- pET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd的克隆和转化成R2DP细胞
- 在消化缓冲液中用NdeI和BamHI限制性内切酶消化pET-3a质粒(见材料表)。在40μL的总反应体积中,加入4μL消化缓冲液,33μL100ng / μL质粒和1.5μL每种限制性内切酶,并允许反应进行〜2小时,直到在37°C下完成。
- 对MMP-3cd序列进行PCR反应以插入N端His-tag。使用25μL PCR混合物(见 材料表),2.5μL10μM引物(补充图S1)和1.25μL的100ng / μL插入序列。将无菌水加入50μL的最终反应体积中。
- 在1%琼脂糖凝胶上运行PCR产物和消化的载体。根据制造商的协议,使用凝胶回收试剂盒(参见 材料表)纯化凝胶条带。
- 使用DNA组装混合物将扩增的PCR产物克隆到NdeI和BamHI限制位点之间的消化载体中(见 材料表)。使用在线工具确定总反应体积为15μL的插入物和切割载体的所需体积。
- 在冰上解冻50μL等分试样的高转化效率细胞(见 材料表)直至解冻。将SOC生长培养基(见 材料表)预热至37°C和LB-氨苄西林(LB Amp)板(见 材料表)。
- 将1-2μLpET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd组装反应加入50μL等分试样中。在冰上孵育30分钟。
- 通过在42°C下孵育30s来热冲击细胞。在冰上孵育2分钟。
- 向每种转化剂混合物中加入950μL SOC生长培养基。在250转/分和37°C下摇动1小时。
- 将转化剂的板100μL放在LB Amp板上,并在37°C下孵育过夜。
- 将每个分离的菌落接种在10 mL LB Amp培养基中。在250rpm和37°C下摇匀过夜。
- 根据制造商的miniprep试剂盒方案提取质粒DNA(见 材料表)。使用T7正向和反向引物确认构建的顺序(补充图S1)。
注意:pET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd构建DNA可以储存在-20°C。 准备就绪后,继续转换为R2DP细胞。 - 在冰上解冻一个20μL等分试样的R2DP细胞(见 材料表)2-5分钟。将SOC生长培养基预热至室温,LB Amp CamR 板至37°C(见 材料表)。
- 将1 μL 100 ng/μL序列确认的pET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd加入50 μL等分试样中。轻轻搅拌混合,然后将管子放回冰块。
- 将管子在冰上孵育5分钟。
- 通过在42°C下孵育正好30秒来热休克细胞。不要摇晃。
- 将细胞放在冰上2分钟。
- 向转化剂混合物中加入80μL室温SOC培养基。在250转/分和37°C下摇动1小时。
- 将转化子放在LB Amp CamR 板上,并在37°C下孵育过夜。
- 生长和诱导
- 在37°C下将来自LB Amp CamR 板的单个分离的R2DP pET-3a-Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd转化剂的菌落接种在10 mL的LB Amp CamR 培养基中。 以250转/分摇匀过夜(约16小时)。如果需要,从每种培养物中保存等分试样,并制备40%(v / v)甘油(见 材料表)储备。
- 每次过夜培养,将含有500 mL LB Amp CamR 培养基的1 L烧瓶接种至600nm(OD 600)0.05-0.1的光密度。
注意:这应该使细胞返回对数生长。 - 在多个时间点测量OD600 ,通常为3-4小时,直到它落在0.4和0.6之间。
- 在诱导之前,将一部分培养物等分到1.5mL微量离心管中(见 材料表)并标记其 未诱导馏分。将其储存在-80°C以进行凝胶分析。如果不运行SDS-PAGE凝胶,请跳过此步骤并继续执行步骤1.2.5。
- 使用1M异丙基-ß-D-硫代乳糖吡喃糖苷(IPTG)储备物诱导培养物至终浓度为1mM(见 材料表)。继续在37°C振荡器中孵育3-4小时。
注意:在表达过程中,阅读器应确定诱导时的最佳OD600 和IPTG浓度。如果纯化后产量基本下降,则纯化缓冲液中的咪唑浓度可能需要调整,或者可能需要进一步超声处理细胞沉淀。 - 在离心培养物之前,将一部分培养物等分到第二个1.5mL微量离心管中并标记其 诱导馏分。将其储存在-80°C以进行凝胶分析。如果不运行SDS-PAGE凝胶,请跳过此步骤并继续执行步骤1.2.7。
- 将细胞培养物以最大速度和4°C在250mL锥形瓶(见 材料表)中离心10分钟。
- 重复步骤1.2.7,直到培养物完全沉淀。
注意:暂停:细胞沉淀可以在-80°C下冷冻,稍后解冻以进行进一步处理。否则,请跳过此步骤并继续执行步骤 1.3.1。
- 包涵体提取和增溶
注意:准备新鲜的10M尿素,最好不早于提前一天,彻底搅拌直至完全溶解。不要加热或高压灭菌尿素;将其储存在室温下。- 将沉淀(从步骤1.2.8开始)重悬于裂解缓冲液中(见 材料表)。每克沉淀,加入3mL裂解缓冲液,并通过涡旋或移液重悬。在4°C下摇匀过夜。
- 每1L培养物加入1.25mL的10%(w / v)脱氧胆酸钠(见 材料表)。在室温下以150转/分摇动30分钟。
- 每1升培养物加入10μLDNase I(见 材料表)。在室温下以150转/分摇动30分钟。
- 在13,000× g 和4°C下离心10分钟。
- 留出一小部分 裂解的MMP 用于凝胶分析。储存在-80°C。 如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤1.3.6。
注意:离心后,沉淀可能是串状的,没有紧凑的包装,使得丢弃上清液有风险。如果是这种情况,请跳过步骤 1.3.6 并继续执行步骤 1.3.7。 - 从离心样品中弃去上清液。
注意:此时可以暂停实验方案,并将细胞沉淀在-80°C下冷冻并在稍后解冻。否则,请跳过此步骤并继续执行步骤 1.3.7。 - 通过上下移液将沉淀重悬于100 mL / L包涵体缓冲液培养物(见 材料表)中。
- 在超声处理过程中,将样品放在冰上以防止过热。对每个样品进行超声处理,持续 6 个周期,每次 15 秒,输出 5 个脉冲和 50% 脉冲。在循环之间留出 15 秒的冷却时间。
注意:如有必要,将样品转移到50 mL锥形管中以进行进一步离心(见 材料表)。在13,000× g 和4°C下离心10分钟。 - 留出一小部分 超声MMP 用于凝胶分析。储存在-80°C。 如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤1.3.11。
- 检查颗粒。如果串联,请重复步骤 1.3.8-1.3.10。如果沉淀是紧凑的,则弃去上清液并继续步骤1.3.12。
注意:可以重复包涵体缓冲液中的超声处理,以从裂解的细胞碎片中回收更多的蛋白质。然而,过多的超声处理会导致剪切,从而损害MMP产量。该协议可以在此阶段暂停,细胞沉淀可以在-80°C下冷冻并在以后解冻。 - 通过移液将1 L培养物中的每个沉淀重悬于5mL增溶缓冲液(见 材料表)中。在冰上孵育至少30分钟,以使蛋白质溶解。
- 留出一小部分 可溶的MMP 用于凝胶分析。储存在-80°C。 如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤1.3.14。
- 在13,000× g 和4°C下离心细胞10分钟,不要丢弃上清液。
- 如果沉淀在离心后形成/残留,将上清液倒入单独的50mL锥形管中。通过上下移液将沉淀重悬在另一个5mL增溶缓冲液(每1L培养物)中。
- 在13,000× g 和4°C下离心10分钟。不要丢弃上清液。
- 重复步骤1.3.13和1.3.14,直到离心后形成少量或没有沉淀或仅留下灰色沉淀物。池化上清液。弃置或储存在-80°C下沉淀以进行额外的超声处理。
2. MMP净化和重新折叠
- His-tag (HT) 亲和力纯化
- 根据制造商的协议,用混合良好的Ni-NTA树脂填充重力流柱(见材料表)。让树脂沉降并从储存缓冲液中分离出来,使得两层之间形成一条明显的线。
注意:切勿让树脂干燥,因为空气会穿透树脂并损害蛋白质产量。在两次使用之间,执行第2.2节中描述的树脂再生程序。 - 让储存缓冲液排出。用两个树脂床体积的HT平衡缓冲液填充色谱柱。
- 沥干超线程平衡缓冲液并丢弃。当柱子排空时,将蛋白质提取物以13,000×g离心1分钟,并使用0.22μm过滤器进行过滤灭菌(见 材料表)。
- 将废物容器换成标有 HT流通的50 mL锥形管。将制备的蛋白质提取物加入色谱柱中。
- 重新应用流通以最大化绑定。
- 留出一小部分 流通分数 用于凝胶分析。储存在-80°C。 如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤2.1.7。
- 立即用15 mL HT洗涤缓冲液洗涤树脂(见材料表)。将流经物收集在标有HT Wash的15 mL锥形管(见材料表)中。
注:通过分光光度法获得280nm(A280)处的吸光度值,并与分子量和消光系数(ε)一起用于估计蛋白质浓度。对于变性的Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd,分子量为29.86 kDa,ε为34.38 M-1 cm-1。 - 针对 HT 清洗缓冲器进行消隐,测量并记录 A280。重复步骤2.1.7和2.1.8,并加入额外的洗涤分数。一旦A280接近基线并且杂质最小化,请继续执行步骤2.1.9。
- 留出一小部分 洗涤分数 用于凝胶分析。重复多次洗涤分数。将馏分储存在-80°C。 如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤2.1.10。
- 通过加入5mLHT洗脱缓冲液立即洗脱His标记的蛋白质(见 材料表)。将流经物收集为0.5-1 mL馏分,在标有 HT洗脱的微量离心管中。
- 留出一部分 洗脱馏分 用于凝胶分析。对多个洗脱级分重复上述步骤。将馏分储存在-80°C。 如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤2.1.12。
- 如果A280>0.3 mg / mL,用HT平衡缓冲液稀释馏分(见 材料表)。
注意:洗脱的部分必须稀释至0.3mg / mL或更低的A280,以防止透析期间沉淀。该协议可以在这里暂停,并将混合的馏分在-80°C下冷冻并在稍后解冻。否则,请跳过此步骤并继续执行步骤 2.2.1。
- 根据制造商的协议,用混合良好的Ni-NTA树脂填充重力流柱(见材料表)。让树脂沉降并从储存缓冲液中分离出来,使得两层之间形成一条明显的线。
- 树脂再生
- 用10个树脂床体积的HT再生缓冲液(见 材料表)和10个树脂床体积的无菌水洗涤树脂。
- 将树脂作为50%浆料储存在20%(v / v)乙醇中的水中。
3. 蛋白质再折叠
注:对于体积较小的透析盒,透析盒可以以较低的样品损失风险使用。如果使用较大的体积,则需要透析管(见 材料表)。
- 透析
注意:透析的最佳蛋白质浓度约为0.3 mg / mL。如果在透析过程中发生明显的沉淀,则使用逐步透析方法降低每次透析之间的尿素浓度梯度,并添加更多的中间步骤(例如,从6 M到5 M,然后是5 M到4 M,而不是跳过5 M阶段)。由于冻融循环会破坏细胞和蛋白质结构,因此尽量减少方案中的停顿至关重要。- 根据制造商的协议,根据 洗脱馏分 样品的体积使用适量的透析管。
- 将洗脱的MMP级分浸没在透析管中,浸没在1 L透析缓冲液1中(见 材料表)。在磁力搅拌器上搅拌管子及其内容物在4°C下不少于8小时。
- 转移到1 L透析缓冲液2(见 材料表)。在磁力搅拌器上搅拌管子及其内容物在4°C下不少于8小时。
- 转移到1 L透析缓冲液3(见 材料表)。在磁力搅拌器上搅拌管子及其内容物在4°C下不少于8小时。
- 将样品转移到新的50 mL锥形管中,并将其标记为 透析MMP。
- 检查试管是否有任何沉淀物。如果形成沉淀,请在13,000× g 和4°C下离心样品1分钟。
- 将上清液转移到新的15 mL锥形管中,并将其标记为 Refolded MMP。
- 留出一个馏分用于凝胶分析,并将其标记为 重折叠MMP。储存在-80°C。 如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤3.1.9。
注意:如果产量低,沉淀物可以溶解在HT平衡缓冲液中,并用透析管重复第3.1节中的步骤。如果不进行凝胶分析或必须在此处暂停实验方案,请将样品在-80°C下冷冻并在以后解冻。如果收益率在所需范围内,请继续执行步骤 3.2.1。
- 重新集中
注:重折叠和变性Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd的消光系数预计相同;因此,A280 计算不受影响。- 将样品重新浓缩至0.5 mg / mL。使用400 mL搅拌池(见 材料表)将样品浓缩至15 mL。为防止起泡,如有需要,请使用 50 mL 再浓缩管进一步浓缩。
注意:如果形成沉淀物,可以将其沉淀并溶解在HT平衡缓冲液中。然后,重复第 3.1 节和第 3.2.1 节。否则,请继续执行步骤 3.2.2。 - 留出一个馏分用于凝胶分析,并将其标记为 浓缩MMP。
注意:实验方案可以在这里暂停,样品在-80°C下冷冻并稍后解冻。
- 将样品重新浓缩至0.5 mg / mL。使用400 mL搅拌池(见 材料表)将样品浓缩至15 mL。为防止起泡,如有需要,请使用 50 mL 再浓缩管进一步浓缩。
4. 激活
- 4-氨基苯基乙酸汞(APMA)活化
注:APMA具有剧毒。在激活前制作20 mM APMA的新鲜储备溶液,并在使用APMA时始终在通风橱下工作。将APMA废物丢弃到其容器中。- 每1 mL等分试样MMP(1 mg / mL),加入50μL20 mM APMA(见 材料表)以达到1 mM的最终APMA浓度。在37°C下孵育过夜。
- 如果形成沉淀物,请在4°C下以最大速度离心10分钟。 将上清液储存在标有 活化MMP的1.5 mL微量离心管中。将沉淀物丢弃到标有APMA废物的容器中。
- 留出一个馏分用于凝胶分析,并将其标记为 活化MMP。
注意:实验方案可以在这里暂停,样品在-80°C下冷冻并稍后解冻。如果不执行凝胶分析,请继续执行步骤4.2.1。活化后,MMP-3cd的分子量和消光系数分别为19.40 kDa和28.42 M-1 cm-1。
- 脱盐
- 按照制造商的协议,使用2 mL脱盐柱(见 材料表)从活化的MMP-3cd样品中除去APMA。
- 留出一个馏分用于凝胶分析,并将其标记为 脱盐MMP。储存在-80°C。 如果不进行凝胶分析,请继续使用其余样品进入第4.3节。
注意:实验方案可以在这里暂停,样品在-80°C下冷冻并稍后解冻。
- 运行 SDS-PAGE 凝胶
- 在SDS-PAGE凝胶上运行所有蛋白质级分:未诱导级分,诱导级分,裂解MMP,超声MMP,溶解MMP,流通级分,洗涤级分,洗脱级分,重折叠MMP,浓缩MMP,活化MMP和脱盐MMP。
- MMP-3的长期储存
- 向脱盐的MMP-3cd样品中加入0.05%(v / v)非离子表面活性剂(见 材料表),并将其储存在-80°C。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
结果
在SDS-PAGE上运行样品时,由于蛋白质以不溶性包涵体的形式表达,因此裂解和超声处理的级分应含有很少或没有Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd提取物,因为蛋白质尚未在尿素中再溶解。 图3 比较了来自BL21(DE3)细胞和R2DP细胞的Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd的His-tag纯化洗脱组分。透析前分别对BL21(DE3)和R2DP细胞进行洗脱级分。在蛋白质脱盐后运行每个步骤的馏分(图4)。所有Hisx6-pro-...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
讨论
大规模生产可溶性、人性、重组型MMPs仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。哺乳动物细胞可以以高成本和长等待时间表达功能性MMP,而 大肠杆菌 迅速产生大量MMP包涵体,必须纯化和重新折叠11,16。R2DP细胞显著提高了MMP包涵体的产量,从而实现了更具成本效益和生产力的MMP再折叠过程。然而, 大肠杆菌 缺乏折叠MMP所需的翻译后机制,尽管工程?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
披露声明
作者声明他们没有相互竞争的经济利益。
致谢
作者要感谢佛罗里达州杰克逊维尔梅奥诊所的Evette Radisky博士和Alexandra Hockla博士提供pET-3a-pro-MMP-3cd质粒作为克隆Hisx6pro-MMP-3cd基因的模板,以及他们的评论,以及内华达大学里诺分校内华达基因组学中心的Paul Hartley博士进行DNA测序。作者还要感谢Cassandra Hergenrader对部分蛋白质表达的帮助。M.R.-S.我要感谢NIH-P20 GM103650-COBRE综合神经科学赠款和UNR研发mICRO SEED资助奖。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.22 µm sterile filter | Sigma Aldrich | SLGP033RS | Used to remove some contaminants from the protein extract before purification, and prevent the Ni-NTA column from clogging |
| 1 L Erlenmeyer flasks | Thermo Fisher Scientific | S76106F | n/a |
| 1 L glass bottles | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 06-414-1D | n/a |
| 1.5 mL microfuge tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 02-682-002 | n/a |
| 15 mL conical tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 339650 | n/a |
| 18 G, 1-in. beveled needle | Amazon | B07S7VBHM2 | Used in combination with the dialysis casette |
| 2 mL desalting column | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 89890 | Removes APMA following activation |
| 2-(N-Morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AAA1610422 | n/a |
| 250 mL conical bottle cushions | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 05-538-53A | Stabilize conical bottles during large-volume centrifugation |
| 250 mL conical bottles | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 05-538-53 | n/a |
| 400 mL stirred cell | Sigma Aldrich | UFSC40001 | Re-concentrates a much larger volume than the centrifugal filter unit. Rosetta2(DE3)pLysS cells produce high volumes of protein that may exceed the 15 mL limit of the centrifugal filter unit |
| 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate (APMA) | Sigma Aldrich | A9563-5G | Activates MMP-3 by cleaving the propeptide |
| 5 mL syringe | Thermo Fisher Scientific | NC0829167 | Used in combination with the dialysis casette |
| 50 mL conical tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 339650 | Used for storage in many purification steps |
| 50 mL re-concentration tube | Sigma Aldrich | UFC901024D | Used for re-concentrating protein samples after dialysis or removing contaminants |
| Agar | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BP1423-500 | Buffer ingredient that solidifies autoclaved LB media upon cooling |
| Ampicillin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BP1760-25 | Antibiotic used with pET3a vector; used at 100 µg/mL in LB media |
| BamHI | NEB | R3136S | Restriction enzyme to be used with the pET3a vector |
| Calcium chloride (CaCl2) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 600-30-23 | The calcium ion stabilizes MMP structure |
| Cell spreaders | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 50-189-7544 | Can be used to spread cells across a petri dish after transformation |
| Chloramphenicol | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 22-055-125GM | Antibiotic used with pET3a vector; used at 34 µg/mL in LB media |
| Dialysis Buffer 1 | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM CaCl2, 1 µM ZnCl2, 4 M Urea. |
| Dialysis Buffer 2 | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM CaCl2, 1 µM ZnCl2, 2 M Urea. |
| Dialysis Buffer 3 | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM CaCl2 , 1 µM ZnCl2. |
| Dialysis clips | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 68011 | Used in combination with snakeskin dialysis tubing |
| Dialysis tubing | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 88243 | Alternative dialysis method that holds much larger sample volumes, but with higher risk of sample loss |
| Digest buffer | NEB | B7204S | Buffer used in digesting the pET3a vector |
| Disposable cuvettes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 21-200-257 | Used to measure the bacterial culture OD during growth and expression |
| Dithiothreitol (DTT) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D107125G | Assists with protein denaturation by reducing any disulfide bonds |
| DNA assembly mix | NEB | E2621S | Used to ligate the Hisx6-pro-MMP-3cd PCR product and digested pET3a vector |
| DNase I | NEB | M0303S | Endonuclease for degrading unfavorable DNA contaminants that could later affect protein purification |
| Ethanol | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A995-4 | n/a |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | J15694-AE | Used in denaturation. Prevents oxidation and subsequent formation of disulfide bonds |
| Gel recovery kit | Promega | A9281 | Isolates and purifies DNA from agarose gels |
| Glycerol | Thermo Fisher Scientific | G33-500 | Used for making glycerol stocks, which are frozen at -80 °C |
| Gravity flow column | BioRad | 7321010 | Used for Ni-NTA purification of recombinantly His-tagged proteins |
| High-transformation efficiency cells | NEB | C2987 | High-transformation efficiency cells with greater chance of success for cloning the N-terminal His-tag into the pET3a-pro-MMP-3cd construct |
| HT Elution Buffer | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM NaCl, 6 M urea, 250 mM imidazole. Adjust pH to 7.4 |
| HT Equilibration Buffer | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM NaCl, 6 M urea. Adjust pH to 7.4 |
| HT Regeneration Buffer | n/a | n/a | 20 mM MES, 0.1 M NaCl. Adjust pH to 5.0 |
| HT Wash Buffer | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM NaCl, 6 M urea, 25 mM imidazole. Adjust pH to 7.4 |
| Hydrochloric acid (HCl) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A144C-212 | Used to pH buffers |
| Imidazole | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AAA1022122 | Mimics the histidine side group. Used to separate non-specifically binding proteins from the his-tagged target protein |
| Inclusion Body Buffer | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM EDTA, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM DTT, 2% v/v Triton X 100, 0.5 M Urea. Adjust pH to 8.0 |
| Isopropyl-ß-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | FERR0392 | A reagent that induces target gene expression in pET3a. Make 0.5 mL 1 M aliquots, filter sterilize and store in -20 °C |
| LB Amp CamR media | n/a | n/a | To be poured into a sterible 1 L bottle or 1 L flask. For 1 L, add 25 g LB Broth. Sterilize by autoclaving. Once cooled to below 50 °C, add ampicillin to 100 µg/mL and chloramphenicol to 34 µg/mL |
| LB Amp CamR plates | n/a | n/a | To be poured into sterile petri dishes. Pour until the petri dish lid is completely covered. 1 L of media yields 40-60 plates. For 1 L: 25 g LB Broth, 16 g Agar. Sterilize by autoclaving. Once cooled to below 50 °C, add ampicillin to 100 µg/mL and chloramphenicol to 34 µg/mL |
| LB Broth | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BP1426-2 | Pre-mixed with tryptone, yeast extract, and sodium chloride |
| Lysis Buffer | n/a | n/a | 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM EDTA, 100 mM NaCl, 0.133 g/mL lysozyme, 0.49% v/v Triton X-100. Adjust pH to 8.0 |
| Lysozyme | MP Biomedicals | 195303 | Used in protein extraction. Enzyme that lyses bacterial cell walls |
| Miniprep kit | Promega | A1330 | If successful, extracts the pET3a-pro-MMP-3cd construct from transformants |
| NdeI | NEB | R0111S | Restriction enzyme to be used with the pET3a vector |
| Ni-NTA resin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PI88221 | Used to bind recombinant his-tagged proteins. This strong interaction can be displaced with higher concentrations of imidazole |
| Nonionic surfactant | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PI28316 | Storage detergent for preventing MMP aggregation. Minimizes interactions between hydrophobic residues on the MMP surface and water molecules, without disrupting catalytic activity. |
| PCR mix | NEB | M0492S | A PCR reagent for inserting an N-terminal his-tag into the pET3a-pro-MMP-3cd vector |
| pET plasmid | Addgene | n/a | The pET3a vector offers ampicillin resistance, inducible expression of a target gene, and sequencing with T7 primers |
| Petri dishes | VWR | 25384-342 | Used for plating transformants on LB agar media |
| R2DP cells | Novagen | 714033 | BL21 derivatives with enhanced expression of eukaryotic proteins. Contain tRNAs of codons found to be rare in e. coli |
| SOC growth media | NEB | B9020S | Non-selective growth media for rapid growth during transformation |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BP358-1 | Used in buffers and helps with protein stability |
| Sodium deoxycholate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PI89905 | Detergent used in protein extraction. Lyses cell walls |
| Solubilization Buffer | n/a | n/a | 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM NaCl, 10 mM DTT, 6 M Urea. Adjust pH to 8.0 |
| Tris base | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BP152-1 | Common buffer used in the physiological pH range. Temperature-sensitive |
| Triton X-100 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | M1122980101 | Detergent used for cell lysis |
| Urea | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AAJ75826A7 | First chaotropic agent for disrupting protein secondary structure |
| Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AAA162810E | Stabilizes MMP structure. The zinc ion is found in the catalytic site of MMP-3 |
参考文献
- Portolano, N., et al. Recombinant protein expression for structural biology in HEK 293F suspension cells: A novel and accessible approach. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (92), e51897(2014).
- Subedi, G. P., Johnson, R. W., Moniz, H. A., Moremen, K. W., Barb, A. High yield expression of recombinant human proteins with the transient transfection of HEK293 cells in suspension. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (106), e53568(2015).
- Nilvebrant, J., Alm, T., Hober, S. Orthogonal protein purification facilitated by a small bispecific affinity tag. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (59), e3370(2012).
- Yang, Z., et al. Highly efficient production of soluble proteins from insoluble inclusion bodies by a two-step-denaturing and refolding method. PLoS One. 6 (7), 22981(2011).
- Hu, X., Beeton, C. Detection of functional matrix metalloproteinases by zymography. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (45), e2445(2010).
- Radisky, E. S., Raeeszadeh-Sarmazdeh, M., Radisky, D. C. Therapeutic potential of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition in breast cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 118 (11), 3531-3548 (2017).
- Raeeszadeh-Sarmazdeh, M., Do, L. D., Hritz, B. G. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors: Potential for the development of new therapeutics. Cells. 9 (5), 1313(2020).
- Nagase, H., Visse, R., Murphy, G. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovascular Research. 69 (3), 562-573 (2006).
- Raeeszadeh-Sarmazdeh, M., et al. Directed evolution of the metalloproteinase inhibitor TIMP-1 reveals that its N- and C-terminal domains cooperate in matrix metalloproteinase recognition. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 294 (24), 9476-9488 (2019).
- Batra, J., et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10) interaction with tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases TIMP-1 and TIMP-2. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (19), 15935-15946 (2012).
- Singh, K. K., Jain, R., Ramanan, H., Saini, D. K. Expression and purification of matrix metalloproteinases in Escherichia coli. Matrix Metalloproteases. Galea, C. A. , Humana Press. New York, NY. 3-16 (2017).
- Manka, S. W., et al. Structural insights into triple-helical collagen cleavage by matrix metalloproteinase 1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (31), 12461-12466 (2012).
- Gomis-Ruth, F. X., et al. Mechanism of inhibition of the human matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-1 by TIMP-1. Nature. 389 (6646), 77-81 (1997).
- Shirian, J., et al. Converting a broad matrix metalloproteinase family inhibitor into a specific inhibitor of MMP-9 and MMP-14. FEBS Letters. 592 (7), 1122-1134 (2018).
- Li, C., et al. Purification of recombinant histidine-tagged catalytic domain of MMP-13 in one step using affinity column and renaturation of it with histidine tag. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies. 37 (15), 2118-2130 (2014).
- Aydin, H., Azimi, F. C., Cook, J. D., Lee, J. E. A convenient and general expression platform for the production of secreted proteins from human cells. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (65), e4041(2012).
- McNiff, M. L., Haynes, E. P., Dixit, N., Gao, F. P., Laurence, J. S. Thioredoxin fusion construct enables high-yield production of soluble, active matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) in Escherichia coli. Protein Expression and Purification. 122, 64-71 (2016).
- Maity, R., et al. GST-His purification: A two-step affinity purification protocol yielding full-length purified proteins. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (80), e50320(2013).
- Stefan, A., Ceccarelli, A., Conte, E., Montón Silva, A., Hochkoeppler, A. The multifaceted benefits of protein co-expression in Escherichia coli. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (96), e52431(2015).
- Yadavalli, R., Sam-Yellowe, T. HeLa based cell free expression systems for expression of Plasmodium rhoptry proteins. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (100), e52772(2015).
- Zeytuni, N., Zarivach, R. Purification of the M. magneticum strain AMB-1 magnetosome associated protein MamAΔ41. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (37), e1844(2010).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。